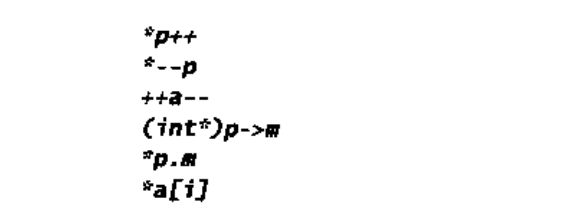1.读入一系列由空白分割的(名字,值)对,其中每个名字是由空白分开的一个单词,值是一个整数或者一个浮点值,计算并打印出对应于每个名字的所有值之和与平均值,以及所有的名字的和与平均值。
#include "stdafx.h"
#include
#include 【相关文档】
1. C++ map的基本操作和使用
2. C++迭代器 iterator
2.找出5中不同结构的器意义无定义的c++结构。找出5中不同的其意义由实现确定的c++结构。
【无定义行为】:
1.超出数组边界的访问
int a[10];
int *p = &a[10]; //a[0]~a[9]可以,a[10]不行
2.使用已经销毁的对象:
int &r = * new int;
delete &r;
r = r+1;//引用不合法
3.企图重新解释变量:
int i ;
*(float*)&i = 1.0;//通过非声明的类型访问
4.强制目标的类型不是元对象的实际类型:
struct B{int i;};
struct D:B{};
B * bp =new B;
D * dp = static_cast(bp); //非法强制
5.强制去掉某个原定义为const对象的const属性
void f(int const &r){const_cast(r) =2;}
int const i = 3;
f(i); //非法的const_cast
【C++标准转换运算符const_cast】
找出具有实现定义的结构也很容易:
1.某个类型的大小:
sizeof(int);
2.type_info::name()的输出:
std::cout<3.按位运算符的作用:
int mistery = ~0;
4.基本类型的最大最小值:
int mx = numeric_limits::max();
5.历史副本的个数:
struct S {
S(S const&)
{std::cout<<"copy\n"}
};
S f(){S a;return a;}
int main(){
f();
return 0;
}
【C++中的"未定义的行为"】
3.找出10个不可移植的c++ 代码的例子
4.给下面不等式加上括号
5.写出下面函数:strlen().他返回的C风格字符串的长度;strcpy(),他将一个c风格字符串复制到另一个;strcmp(),他比较两个c风格字符串。
#include "stdafx.h"
#include
#include
#include //为了使用std::size_t
using namespace std;
size_t Mystrlen(char const *s){
assert(s);
size_t len = 0;
while (s[len]){
++len;
}
return len;
}
void Mystrcpy(char * dest, char const * src){
assert(src && dest);
/*while (*src)
{
*dest++ = *src++;
}
*/
do {
*dest++ = *src;
} while (*src++);
}
enum CStringOrder {
FirstBeforeSecond = -1, Same = 0,
SecondBeforeFirst = 1
};
CStringOrder Mystrcmp(char const * first, const char* second){
assert(first&&second);
unsigned char const * f = (unsigned char const *)(first);
unsigned char const *s = (unsigned char const *)(second);
do {
if ((*f)<(*s))
return FirstBeforeSecond;
else
if ((*s)<(*f))
return SecondBeforeFirst;
else
{
return Same;
}
} while (*(s++) && *(f++));
}
int main(){
char a[] = "abcde";
char b[10];
char *c = "bcdef";
size_t len = Mystrlen(a);
cout << "len: " << len << endl;
Mystrcpy(b,a );
cout << "str:" << b << endl;
CStringOrder res = Mystrcmp(a, b);
cout << "a and :" << res << endl;
}
【相关文档】
0.【C++ 学习笔记】 size_t 和 int
1.size_t
2. C++ assert.h头文件
3.C语言中char*和char[]用法区别分析
6.下一个函数cat(),.他取两个c风格字符串为参数,返回一个字符串,该字符串是两个字符串Dee拼接。利用new为这个结果取得存储。
#include "stdafx.h"
#include
#include
# include
using namespace std;
//第一种方法
char * cat(char const * a, char const*b){
size_t len_a= strlen(a);
size_t len_b = strlen(b);
char* s = new char[len_a+len_b + 1];
//加一是因为拷贝的时候连‘\0’都要拷贝,所以第二个参数是缓冲区要设置成第三个长度加一
strcpy_s(s,len_a+1, a);
strcpy_s(s + len_a,len_b+1, b);
return s;
}
//第二种方法
void concatenate(char const *a, char const * b, char * dest){
while (*a != '\0')*dest++ = *a++;
while (*b != '\0')*dest++ = *b++;
*dest = '\0';
}
int main(){
char * result = cat("c++", "programming");
cout << "method 1: " << result <<" len:" < 【相关文档】
1.strcpy_s与strcpy的比较
2.C语言-L Buffer is too small && 0 解决方法
7写一个函数atoi(const char*).它是以一个c语言风格字符串为参数,返回与之对应的int值,例如:atoi("123")应该是123,使他能够处理简单的十进制之外,还能处理c++的八进制和十六进制形式。修改atoi()以处理c++的字符常量记法。
#include "stdafx.h"
#include
#include
#include //异常处理
#include
using namespace std;
namespace Myatoi_space {
inline int digit(char c, int base) {
int value;
switch (c) {
case '0': value = 0; break;
case '1': value = 1; break;
case '2': value = 2; break;
case '3': value = 3; break;
case '4': value = 4; break;
case '5': value = 5; break;
case '6': value = 6; break;
case '7': value = 7; break;
case '8': value = 8; break;
case '9': value = 9; break;
case 'a': case 'A': value = 10; break;
case 'b': case 'B': value = 11; break;
case 'c': case 'C': value = 12; break;
case 'd': case 'D': value = 13; break;
case 'e': case 'E': value = 14; break;
case 'f': case 'F': value = 15; break;
default:
throw domain_error(string("invalid digit"));
}
if (value >= base)
throw domain_error(string("invalid digit"));
return value;
}
inline char next_char(char const *&p) {
if (*p != '\\') // \ is special; hence '\\'
return *p++;
else { // 3 octal digits:
int char_value = digit(p[1], 8) * 64
+ digit(p[2], 8) * 8
+ digit(p[3], 8);
if (char_value>std::numeric_limits::max()
|| char_value::min())
throw domain_error(string("not a char"));
p += 4; // backslash and 3 octal digits
return char_value;
}
}
void load_first_digit(char const *&s, int &value,
bool &is_negative, int &base) {
char c1 = next_char(s);
is_negative = c1 == '-';
if (c1 == '-' || c1 == '+')
c1 = next_char(s);
if (c1 == '\0') { // "", "-" and "+" are illegal
throw domain_error(string("invalid input"));
}
else if (c1 != '0') {
base = 10;
}
else {
char const *p = s;
char c2 = next_char(p);
if (c2 == 'x' || c2 == 'X') { // "0x..."?
base = 16;
s = p;
c1 = next_char(s);
}
else { // c2!='x' and c2!='X'
base = 8; // I.e., even "0" is treated as octal
}
}
value = digit(c1, base);
}
}
using namespace Myatoi_space;
int Myatoi(char const *s) {
int value, base;
bool is_negative;
load_first_digit(s, value, is_negative, base);
while (char c = next_char(s)) {
if (value>std::numeric_limits::max() / base)
throw range_error(string("out-of-range"));
value *= base;
int d = digit(c, base);
if (value>std::numeric_limits::max() - d)
throw range_error(string("out-of-range"));
value += d;
}
return is_negative ? -value : value;
}
int main() {
printf("atoi(\"123\") = %d\n", Myatoi("123"));
printf("atoi(\"0123\") = %d\n", Myatoi("0123"));
printf("atoi(\"0x123\") = %d\n", Myatoi("0x123"));
}
【相关文档】
1.C++ limits头文件的用法(numeric_limits)
2.c++中exception和stdexcept
3.C++中的namespace
8.写一个函数itoa(int i , char b[]).,,他在b中建立器车的字符串并且返回b
#include "stdafx.h"
#include
using namespace std;
char const digit[] = "123456789";
char * Myitoa(int i, char b[]){
char *p = b;
if (i < 0){
*p++ = '-';
i = -i;
}
int shifter = i;
do{
++p;
shifter = shifter / 10;
} while (shifter);
*p = '\0';
do{
*--p = digit[i % 10];
i = i / 10;
} while (i);
return b;
}