C++标准输入与输出,cin 标准输入,cout 格式输出【C++标准输入与输出】(3)
- 标准输入与输出(Input&Output)
- cin 标准输入
- 输入中的空白字符
- 字符串输入
- cout 格式输出
- 进制输出
- 域宽/对齐/填充
- 域宽
- 对齐
- 左对齐
- 右对齐
- 填充
- 设置浮点数精度和有效数字
- 注意
标准输入与输出(Input&Output)
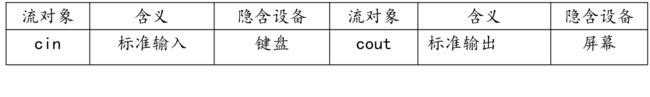
cin 和 cout 是 C++的标准输入和输出流对象。他们在头文件 iostream 中定义,其意义和作用类似于 C 语言中的 scanf 和 printf。
但是scanf 和 printf 与 cin 和 cout 有本质上的区别,scanf 和 printf是函数,cin和cout是类对象,目前我们不需要关心,就当作是同等低位。
#include cin 标准输入
cin代表键盘,>>运算符在C语言中是右移运算符,在这里表示流输入运算符。但是我们说C++是完全兼容C语言的,那么会不会由冲突呢?当然是不会的,这就是一个运算符有多种表达语义,这种现象叫做运算符重载。重载之后会根据运算符具体位置而定语义,例如跟在 cin 之后就是流输入运算符。如果写成a>>b 那就表示右移运算符。
cin >> a >> b >> c;
和
cin >> a;
cin >> b;
cin >> c;
写法是等价的。
输入中的空白字符
C++标准输入解决了C语言中输入存在的一些我们使用过程中非常容易出错的细节问题。
我们接下来看第一种情况:
在C语言中:
#include 执行结果为:

读者这里的输入12a之间是没有空格的,上面代码中scanf中的%d和%c之间是没有空格的。
我们再换另一种输入:

如果在输入的时候中间加上了空格那么a就读取不到了,读取到的就是空格符号。
我们对于代码进行修改:
#include 上面代码中scanf中的%d和%c之间是有空格的。
那么我们再进行输入:
这个时候不管输入换行,空格,制表符都是没有问题的。
在C++里面我们进行查看:
#include 执行结果为:
我们可以看到,在输入的时候这里不管加上空格,换行,还是制表符,或者什么都不加都是没有问题的。
字符串输入
在C语言中:
#include 读取到的是123456789\0
那如果换到C++里面我们进行输入和输出:
#include 所以 cin 这种输入也是不安全的。
我们使用cin类对象的成员函数进行解决:
#include 我们可以看到正确读取到了前9个字符并且加上\0。
我们再换一种写法:
#include 以上的字符串输入是不会出现安全问题的。但是大小不是无穷大的。
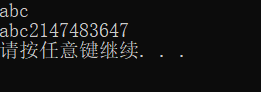
我们可以输出str大小:
#include 执行结果为:
输出的abc后面的就是str的最大值。
最大值是有符号int类型最大值。
cout 格式输出
C 语言中 printf 拥有强大的格式化控制。C++中 cout 对象也可以实现,但略显复杂。多数 C++程序员会在格式输出的时候选择 C语言 的方式, 格式输出中C++是完全兼容 C 语言。
进制输出
cout 中引用了流算子(dec/hex/oct)的概念,后续博客会有详细的说明。现在,读者将其当成一种常规来识记即可。
#include 执行结果为:
但是我们可以看到同样的:
cout << data << endl;
在开始和最后的输出结果时不一样的。因为在最后的 :
cout << data << endl;
前面输出的是8进制。
那么如果在最后一行还要输出十进制就要进行修改输出为10进制:
#include 执行结果为:
域宽/对齐/填充
#include 如果我们没有设置,那么默认就是原来数据。
域宽
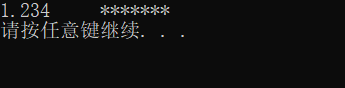
接下来我们进行域宽设置:
#include 执行结果为:
对齐
左对齐
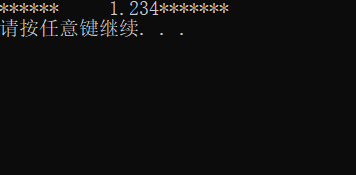
接下来我们进行左对齐设置:
#include 右对齐
#include 以上打印结果表示域宽为10并且右对齐。
填充
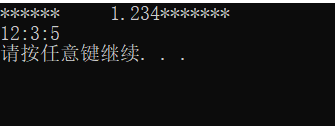
接下来如果我们要输出12:3:5
#include 执行结果为:
我们可以看到这里的域宽设置有问题,3和5域宽为1。
在这设置域宽的时候要每一个输出的变量都要设置,我们进行代码修改:
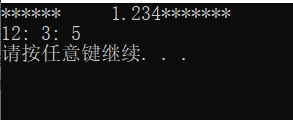
#include 那么接下来我们进行填充:
#include 执行结果为:
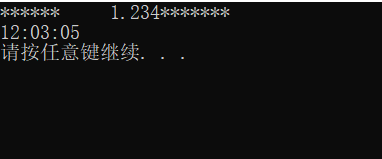
setfill(‘0’) 用于在右对齐左边剩余部分补 0。
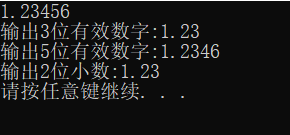
设置浮点数精度和有效数字
#include 注意
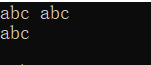
C++在使用cin输入字符串时遇到空格会直接结束。
代码演示:
#include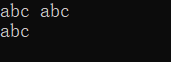
在C语言中使用scanf函数输入字符串也会遇到同样的问题:
代码演示:
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include