fastText代码实战篇——手把手教你使用fastText实现文本分类
目录
前言
fastText文本分类代码实战
安装
本文中使用的数据集
fastText文本分类技术流程图
代码
前言
上一篇文章中,我们对fastText的原理进行了介绍,fastText原理篇,接下来我们进行代码实战,本文中使用fastText对新闻文本数据进行文本分类。
fasttext是facebook开源的一个词向量与文本分类工具,在学术上没有太多创新点,好处是模型简单,训练速度非常快。简单尝试可以发现,用起来还是非常顺手的,做出来的结果也不错,可以达到上线使用的标准。
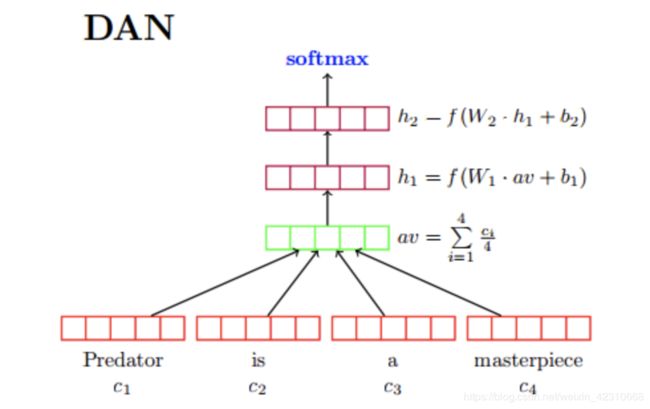
简单说来,fastText做的事情,就是把文档中所有词通过lookup table变成向量,取平均之后直接用线性分类器得到分类结果。fastText和ACL-15上的deep averaging network(DAN,如下图)比较相似,是一个简化的版本,去掉了中间的隐层。论文指出了对一些简单的分类任务,没有必要使用太复杂的网络结构就可以取得差不多的结果。如左图DAN网络结构,右图fastText:
fastText论文中提到的两个tricks
- hierarchical softmax
- 类别数较多时,通过构建一个霍夫曼编码树来加速softmax layer的计算,和之前word2vec中的trick相同
- N-gram features
- 只用unigram的话会丢掉word order信息,fastTex考虑了语序信息即上下文信息,通过加入N-gram features进行补充并用hashing来减少N-gram的存储
fastText文本分类代码实战
安装
pip install fasttext
本文中使用的数据集
数据集:链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/16rvw_F4mSZXVsTZ8vCduAw 密码:ivyt
- 5分类中文新闻文本数据,分别是:technology、car、entertainment、military、sports
- 每类数据取20000条,共计100000条数据作为训练集
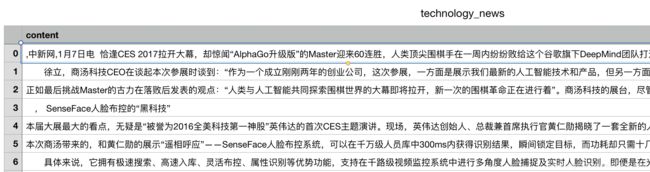
原始数据示例:原始数据需要处理为fasttext要求的数据格式
fastText文本分类要求的数据存储格式:
__label__1 我 爱 中国
- __label__: 类别前缀,__label__后面接类别
- 1: 类别id,用来区分不同类,可自定义
- “我 爱 中国”: 分词后文本
- 代码:
"__label__"+str(label)+"\t"+" ".join(segs)
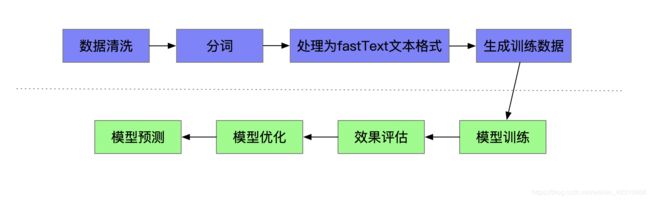
fastText文本分类技术流程图
代码
- 数据读取
import jieba
import pandas as pd
import random
cate_dic = {'technology':1, 'car':2, 'entertainment':3, 'military':4, 'sports':5}
df_technology = pd.read_csv("./origin_data/technology_news.csv", encoding='utf-8')
df_technology = df_technology.dropna()
df_car = pd.read_csv("./origin_data/car_news.csv", encoding='utf-8')
df_car = df_car.dropna()
df_entertainment = pd.read_csv("./origin_data/entertainment_news.csv", encoding='utf-8')
df_entertainment = df_entertainment.dropna()
df_military = pd.read_csv("./origin_data/military_news.csv", encoding='utf-8')
df_military = df_military.dropna()
df_sports = pd.read_csv("./origin_data/sports_news.csv", encoding='utf-8')
df_sports = df_sports.dropna()
technology = df_technology.content.values.tolist()[1000:21000]
car = df_car.content.values.tolist()[1000:21000]
entertainment = df_entertainment.content.values.tolist()[:20000]
military = df_military.content.values.tolist()[:20000]
sports = df_sports.content.values.tolist()[:20000]- 数据清洗、分词、去停用词、整理为fastText要求的文本格式,并生成训练数据
stopwords=pd.read_csv("origin_data/stopwords.txt",index_col=False,quoting=3,sep="\t",names=['stopword'], encoding='utf-8')
stopwords=stopwords['stopword'].values
#分词去停用词,并整理为fasttext要求的文本格式
def preprocess_text(content_lines, sentences, category):
for line in content_lines:
try:
segs=jieba.lcut(line)
segs = list(filter(lambda x:len(x)>1, segs))
segs = list(filter(lambda x:x not in stopwords, segs))
sentences.append("__label__"+str(category)+"\t"+" ".join(segs))
except Exception as e:
print(line)
continue
#生成训练数据
sentences = []
preprocess_text(technology, sentences, cate_dic['technology'])
preprocess_text(car, sentences, cate_dic['car'])
preprocess_text(entertainment, sentences, cate_dic['entertainment'])
preprocess_text(military, sentences, cate_dic['military'])
preprocess_text(sports, sentences, cate_dic['sports'])
#数据打乱
random.shuffle(sentences)- 训练数据写入文档
# 写入数据-fasttext格式
def generate_model_data(sentences):
train_num=int(len(sentences)*0.8)
train_set=sentences[0:train_num]
test_set=sentences[train_num:-1]
print("writing data to fasttext format...")
with open('./data/train_data.txt', 'w') as out:
for sentence in train_set:
out.write(sentence+"\n")
print("done!")
with open('./data/test_data.txt','w') as f:
for sentence in test_set:
f.write(sentence+'\n')
print('done!')
generate_model_data(sentences)- 训练模型
import fasttext
classifier = fasttext.train_supervised('./data/train_data.txt',label='__label__', wordNgrams=2,epoch=20,lr=0.1,dim=100)
#参数说明
'''
train_supervised(input, lr=0.1, dim=100,
ws=5, epoch=5, minCount=1,
minCountLabel=0, minn=0,
maxn=0, neg=5, wordNgrams=1,
loss="softmax", bucket=2000000,
thread=12, lrUpdateRate=100,
t=1e-4, label="__label__",
verbose=2, pretrainedVectors="")
'''
"""
训练一个监督模型, 返回一个模型对象
@param input: 训练数据文件路径
@param lr: 学习率
@param dim: 向量维度
@param ws: cbow模型时使用
@param epoch: 次数
@param minCount: 词频阈值, 小于该值在初始化时会过滤掉
@param minCountLabel: 类别阈值,类别小于该值初始化时会过滤掉
@param minn: 构造subword时最小char个数
@param maxn: 构造subword时最大char个数
@param neg: 负采样
@param wordNgrams: n-gram个数
@param loss: 损失函数类型, softmax, ns: 负采样, hs: 分层softmax
@param bucket: 词扩充大小, [A, B]: A语料中包含的词向量, B不在语料中的词向量
@param thread: 线程个数, 每个线程处理输入数据的一段, 0号线程负责loss输出
@param lrUpdateRate: 学习率更新
@param t: 负采样阈值
@param label: 类别前缀
@param verbose: ??
@param pretrainedVectors: 预训练的词向量文件路径, 如果word出现在文件夹中初始化不再随机
@return model object
"""
- 保存模型
classifier.save_model('./model/fasttext.bin')- 模型批量预测,以及效果评估
’‘’
@return [样本个数, 准确率, 召回率]
‘’‘
train_result=classifier.test('./data/train_data.txt')
print('train_precision:', train_result[1])
print('train_recall:', train_result[2])
print('Number of train examples:', train_result[0])
test_result=classifier.test('./data/test_data.txt')
print('test_precision:', test_result[1])
print('test_recall:', test_result[2])
print('Number of test examples:', test_result[0])
打印结果:
train_precision: 0.9906387350876191
train_recall: 0.9906387350876191
Number of train examples: 70076
test_precision: 0.9036990524032423
test_recall: 0.9036990524032423
Number of test examples: 17518- 模型单例预测
label_to_cate = {1:'technology', 2:'car', 3:'entertainment', 4:'military', 5:'sports'}
texts = '中新网 日电 2018 预赛 亚洲区 强赛 中国队 韩国队 较量 比赛 上半场 分钟 主场 作战 中国队 率先 打破 场上 僵局 利用 角球 机会 大宝 前点 攻门 得手 中国队 领先'
# texts = '这 是 中国 第 一 次 军舰 演习'
labels = classifier.predict(texts)
print(labels)
print(label_to_cate[int(labels[0][0].strip('__label__'))])
打印结果:
(('__label__5',), array([0.9999727]))
sports- 模型加载
model = fasttext.load_model(path)- 模型优化方向
- 上面仅是代码示例,你可以把它封装成一个类
- 进行数据预处理,比如减少不必要字符、优化停用词、过滤出现次数较少的词组等
- 更改样本训练次数epochs(使用参数 –epoch,标准范围[5, 50])
- 更改学习率learning rate(使用参数 –lr,标准范围[0.1-1])
- 使用word n-grams(使用参数 –wordNgrams,标准范围[1-5])