使用STM32编写一个简单的RTOS:5.内核同步(二、互斥锁)
文章目录
- 互斥量
- 源码分析
- 测试
参考资料: RTT官网文档
关键字:分析RT-Thread源码、stm32、RTOS、互斥量。
互斥量
在其他书籍中的名称:
mutex :互斥锁,互斥量,互斥体。
从信号量中我们知道了互斥锁是特殊的二值信号量,只有0和1两种状态。
死锁
由于互斥锁只有两种状态,开锁或者关锁,假如函数A关了锁后,调用了函数B,函数B也要关锁,这时就会导致死锁。
优先级翻转
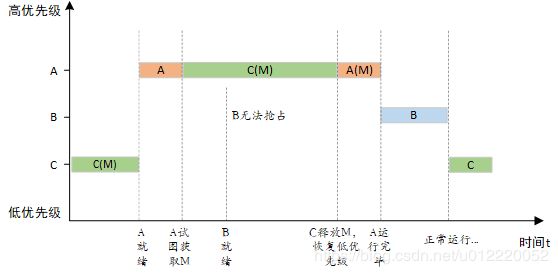
使用信号量会导致的另一个潜在问题是线程优先级翻转问题。所谓优先级翻转,即当一个高优先级线程试图通过信号量机制访问共享资源时,如果该信号量已被一低优先级线程持有,而这个低优先级线程在运行过程中可能又被其它一些中等优先级的线程抢占,因此造成高优先级线程被许多具有较低优先级的线程阻塞,实时性难以得到保证。如下图所示:有优先级为 A、B 和 C 的三个线程,优先级 A> B > C。线程 A,B 处于挂起状态,等待某一事件触发,线程 C 正在运行,此时线程 C 开始使用某一共享资源 M。在使用过程中,线程 A 等待的事件到来,线程 A 转为就绪态,因为它比线程 C 优先级高,所以立即执行。但是当线程 A 要使用共享资源 M 时,由于其正在被线程 C 使用,因此线程 A 被挂起切换到线程 C 运行。如果此时线程 B 等待的事件到来,则线程 B 转为就绪态。由于线程 B 的优先级比线程 C 高,因此线程 B 开始运行,直到其运行完毕,线程 C 才开始运行。只有当线程 C 释放共享资源 M 后,线程 A 才得以执行。在这种情况下,优先级发生了翻转:线程 B 先于线程 A 运行。这样便不能保证高优先级线程的响应时间。
在 RT-Thread 操作系统中,互斥量可以解决优先级翻转问题,实现的是优先级继承算法。优先级继承是通过在线程 A 尝试获取共享资源而被挂起的期间内,将线程 C 的优先级提升到线程 A 的优先级别,从而解决优先级翻转引起的问题。这样能够防止 C(间接地防止 A)被 B 抢占,如下图所示。优先级继承是指,提高某个占有某种资源的低优先级线程的优先级,使之与所有等待该资源的线程中优先级最高的那个线程的优先级相等,然后执行,而当这个低优先级线程释放该资源时,优先级重新回到初始设定。因此,继承优先级的线程避免了系统资源被任何中间优先级的线程抢占。
源码分析
下面看互斥锁在RTT中的实现:
struct rt_mutex
{
struct rt_ipc_object parent; /* 继承自 ipc_object 类 */
rt_uint16_t value; /* 互斥量的值 */
rt_uint8_t original_priority; /* 持有线程的原始优先级 */
rt_uint8_t hold; /* 持有线程的持有次数 */
struct rt_thread *owner; /* 当前拥有互斥量的线程 */
};
还是以分析静态的初始化为例。
rt_err_t rt_mutex_init(rt_mutex_t mutex, const char *name, rt_uint8_t flag)
{
RT_ASSERT(mutex != RT_NULL);
/* init object */
rt_object_init(&(mutex->parent.parent), RT_Object_Class_Mutex, name);
/* init ipc object */
rt_ipc_object_init(&(mutex->parent));
mutex->value = 1;
mutex->owner = RT_NULL;
mutex->original_priority = 0xFF;
mutex->hold = 0;
/* set flag */
mutex->parent.parent.flag = flag;
return RT_EOK;
}
首先将互斥锁加入RT_Object_Class_Mutex类的对象队列链表中,在rt_ipc_object_init中初始化互斥锁的suspend_thread挂载线程。之后是一些变量的初始化,value初始设置为了1,即默认处于开锁状态。
静态对应的脱离函数是rt_mutex_detach:
rt_err_t rt_mutex_detach(rt_mutex_t mutex)
{
RT_ASSERT(mutex != RT_NULL);
/* wakeup all suspend threads */
rt_ipc_list_resume_all(&(mutex->parent.suspend_thread));
/* detach semaphore object */
rt_object_detach(&(mutex->parent.parent));
return RT_EOK;
}
先将等待该互斥锁线程全部唤醒,接着从对象链表中移除。
RTT的关锁函数是rt_mutex_take:
rt_err_t rt_mutex_take(rt_mutex_t mutex, rt_int32_t time)
{
......
/* get current thread */
thread = rt_thread_self();
/* disable interrupt */
temp = rt_hw_interrupt_disable();
/* reset thread error */
thread->error = RT_EOK;
if (mutex->owner == thread)
{
/* it's the same thread */
mutex->hold ++;
}
else
{
__again:
/* The value of mutex is 1 in initial status. Therefore, if the
* value is great than 0, it indicates the mutex is avaible.
*/
if (mutex->value > 0)
{
/* mutex is available */
mutex->value --;
/* set mutex owner and original priority */
mutex->owner = thread;
mutex->original_priority = thread->current_priority;
mutex->hold ++;
}
else
{
/* no waiting, return with timeout */
if (time == 0)
{
/* set error as timeout */
thread->error = -RT_ETIMEOUT;
/* enable interrupt */
rt_hw_interrupt_enable(temp);
return -RT_ETIMEOUT;
}
else
{
/* mutex is unavailable, push to suspend list */
RT_DEBUG_LOG(RT_DEBUG_IPC, ("mutex_take: suspend thread: %s\n",
thread->name));
/* change the owner thread priority of mutex */
if (thread->current_priority < mutex->owner->current_priority)
{
/* change the owner thread priority */
rt_thread_control(mutex->owner,
RT_THREAD_CTRL_CHANGE_PRIORITY,
&thread->current_priority);
}
/* suspend current thread */
rt_ipc_list_suspend(&(mutex->parent.suspend_thread),
thread,
mutex->parent.parent.flag);
/* has waiting time, start thread timer */
if (time > 0)
{
RT_DEBUG_LOG(RT_DEBUG_IPC,
("mutex_take: start the timer of thread:%s\n",
thread->name));
/* reset the timeout of thread timer and start it */
rt_timer_control(&(thread->thread_timer),
RT_TIMER_CTRL_SET_TIME,
&time);
rt_timer_start(&(thread->thread_timer));
}
/* enable interrupt */
rt_hw_interrupt_enable(temp);
/* do schedule */
rt_schedule();
if (thread->error != RT_EOK)
{
/* interrupt by signal, try it again */
if (thread->error == -RT_EINTR) goto __again;
/* return error */
return thread->error;
}
else
{
/* the mutex is taken successfully. */
/* disable interrupt */
temp = rt_hw_interrupt_disable();
}
}
}
}
......
}
参数time的作用和信号量中的作用一样,设置等待时间,为0时表示不等待,为-1时永远等待。
首先判断了当前持有该互斥锁的线程是不是当前线程,是的话hold加1并退出,这样就不会导致在该函数中重复调用关锁操作导致死锁。
如果当前的线程不是互斥锁的持有者,再判断互斥锁是否上锁,如果没有上锁,则将互斥锁上锁,即value–,以及互斥锁的持有者,优先级改为当前线程及其优先级。
如果互斥锁已经被其他线程上锁了,这时判断如果是不等待则直接退出。如果是等待状态,则判断当前的优先级是否比互斥锁持有者的优先级高,高则将持有线程的优先级设置为当前的优先级,防止出现优先级翻转现象。之后将当前线程挂起,并插入互斥锁的等待链表中。接着,如果是永远等待状态则不调用定时器,不是则启动定时器。接着使用调度器调度。
互斥锁的关锁和信号量的获取基本一致,只是多了一步设置锁持有者的优先级,用来防止优先级翻转。
接着看开锁函数rt_mutex_release:
rt_err_t rt_mutex_release(rt_mutex_t mutex)
{
......
need_schedule = RT_FALSE;
/* get current thread */
thread = rt_thread_self();
/* disable interrupt */
temp = rt_hw_interrupt_disable();
/* mutex only can be released by owner */
if (thread != mutex->owner)
{
thread->error = -RT_ERROR;
/* enable interrupt */
rt_hw_interrupt_enable(temp);
return -RT_ERROR;
}
/* decrease hold */
mutex->hold --;
/* if no hold */
if (mutex->hold == 0)
{
/* change the owner thread to original priority */
if (mutex->original_priority != mutex->owner->current_priority)
{
rt_thread_control(mutex->owner,
RT_THREAD_CTRL_CHANGE_PRIORITY,
&(mutex->original_priority));
}
/* wakeup suspended thread */
if (!rt_list_isempty(&mutex->parent.suspend_thread))
{
/* get suspended thread */
thread = rt_list_entry(mutex->parent.suspend_thread.next,
struct rt_thread,
tlist);
RT_DEBUG_LOG(RT_DEBUG_IPC, ("mutex_release: resume thread: %s\n",
thread->name));
/* set new owner and priority */
mutex->owner = thread;
mutex->original_priority = thread->current_priority;
mutex->hold ++;
/* resume thread */
rt_ipc_list_resume(&(mutex->parent.suspend_thread));
need_schedule = RT_TRUE;
}
else
{
/* increase value */
mutex->value ++;
/* clear owner */
mutex->owner = RT_NULL;
mutex->original_priority = 0xff;
}
}
/* enable interrupt */
rt_hw_interrupt_enable(temp);
/* perform a schedule */
if (need_schedule == RT_TRUE)
rt_schedule();
return RT_EOK;
}
首先判断当前线程是否是互斥锁的持有者,如果不是,则直接退出。也就是互斥锁只能是持有者才可以开锁。如果是,则把关锁次数hold–,如果hold为0,即开锁。接着将线程的优先级恢复原来的优先级。然后判断是否还有其他线程在等待该互斥锁,如果没有,则将value++,设置为开锁状态,owner,original_prioriry设置为缺省值。如果有等待线程,则唤醒第一个线程,这里不能唤醒所有线程。接着使用调度器调度。
互斥锁的代码和信号量的基本一致,只是多了一步设置锁持有者的优先级,用来防止优先级翻转。
RTT的互斥锁就介绍到这里。
测试
RTT-MINI中的互斥锁没有优先级之分,也不能使用递归功能。可以看到打印th2之后并没有直接打印th2 mutex lock,而是打印了th1 mutex unlock。


测试源码:https://download.csdn.net/download/u012220052/11236211