【matplotlib】绘制简单二维、三维图像
学习,matplotlib模块的绘图功能。
主要参考于博客:http://blog.csdn.net/ali197294332/article/details/51694141
具体模块导入在最后第7部分汇总代码中给出。
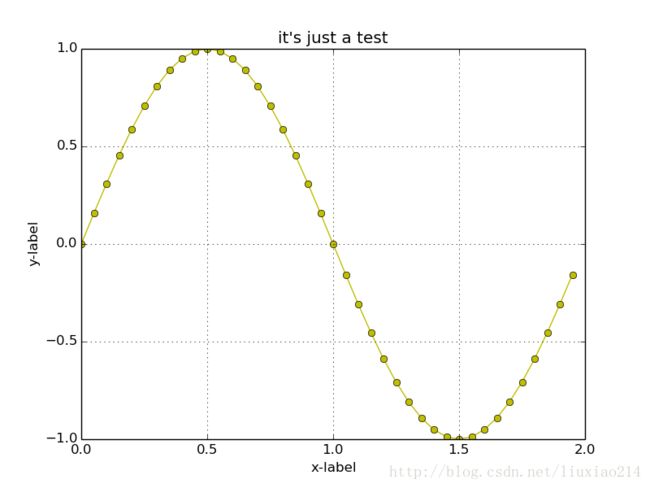
1、绘制基本图像
def initial_image():
# define x\y
x = np.arange(0.0, 2.0, 0.05)
s = np.sin(np.pi * x)
# set color and linestyle
plt.plot(x, s, "yo-")
# set tilte and x\y labels
plt.title("it's just a test")
plt.xlabel("x-label")
plt.ylabel("y-label")
plt.grid() # set gridding
plt.savefig("initial_img.png") # save image
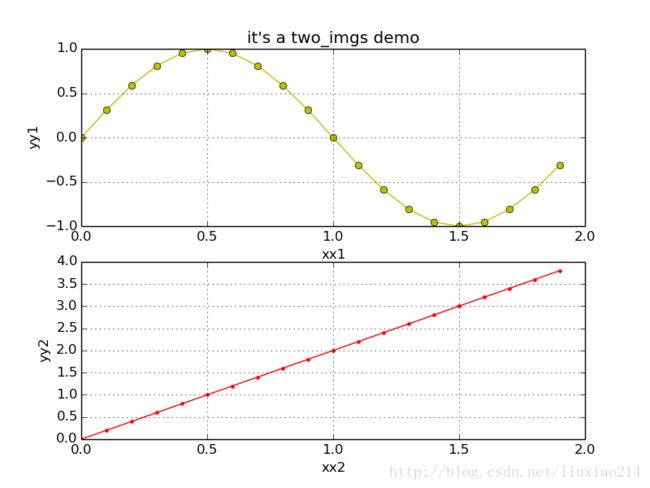
plt.show() # show the image2、一张图中绘制多张图像
def two_images():
x = np.arange(0.0, 2.0, 0.1)
s1 = np.sin(np.pi * x)
s2 = x * 2
plt.subplot(2, 1, 1) # devide 2 rows and 1 cols and get first row
plt.plot(x, s1, "yo-")
plt.title("it's a two_imgs demo")
plt.xlabel("xx1")
plt.ylabel("yy1")
plt.grid()
plt.subplot(2, 1, 2)
plt.plot(x, s2, "r.-")
plt.xlabel("xx2")
plt.ylabel("yy2")
plt.grid()
plt.savefig("two_images.png")
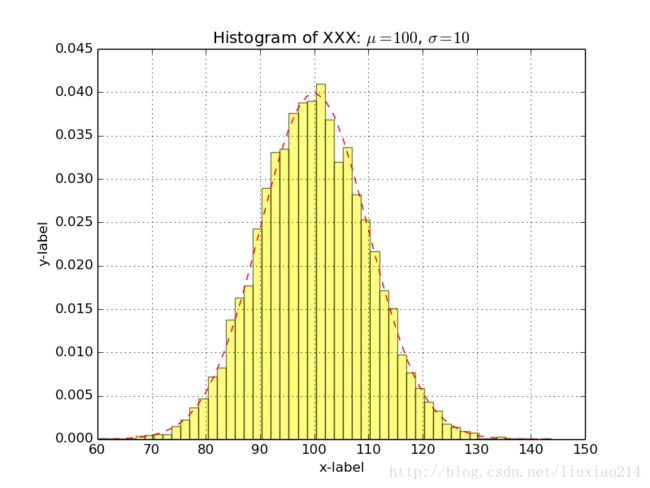
plt.show()3、绘制直方图
def Histogram_demo():
# set u and &
mean = 100
sigma = 10
# produce normal distribution , 10000个数
x = mean + sigma * np.random.randn(10000)
num_bins = 50 # 共50个格子
# 直方图函数, normed=1即和为1,
# 返回50个概率、直方块左边线的x值、各个方块对象
n, bins, patches = plt.hist(x, num_bins, normed=1, facecolor='yellow', alpha=0.5)
y = mlab.normpdf(bins, mean, sigma) # 一条逼近的曲线
plt.plot(bins, y, "r--")
plt.title("Histogram of XXX: $\mu=100$, $\sigma=10$")
plt.xlabel("x-label")
plt.ylabel("y-label")
plt.grid()
plt.subplots_adjust(left=0.15)
plt.savefig("Histogram_demo.png")
plt.show()4、绘制三维空间坐标点
def d3_points():
x_list = [[3,3,2],[4,3,1],[1,2,3],[1,1,2],[2,1,2]]
fig = plt.figure() # 得到画面
ax = fig.gca(projection='3d') # 得到3d坐标的图
# 画点
for x in x_list:
ax.scatter(x[0],x[1],x[2],c='r')
plt.savefig("d3_image.png")
plt.show()5、绘制三维空间平面
def d3_plane():
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(1,1,1,projection='3d') # 一行一列第一个
X = np.arange(1, 10, 1)
Y = np.arange(1, 10, 1)
X,Y = np.meshgrid(X, Y) # 将坐标向量变为坐标矩阵,列为x的长度,行为y的长度
Z = 3*X + 2*Y + 30
# 构建平面
surf = ax.plot_surface(X, Y, Z, rstride=1, cstride=1, cmap=cm.jet, linewidth=0, antialiased=True)
ax.set_xlabel("x-label", color='r')
ax.set_ylabel("y-label", color='g')
ax.set_zlabel("z-label", color='b')
ax.set_zlim3d(0, 100) # 设置z坐标轴
fig.colorbar(surf, shrink=0.5, aspect=5) # 图例
plt.savefig("d3_plane.png")
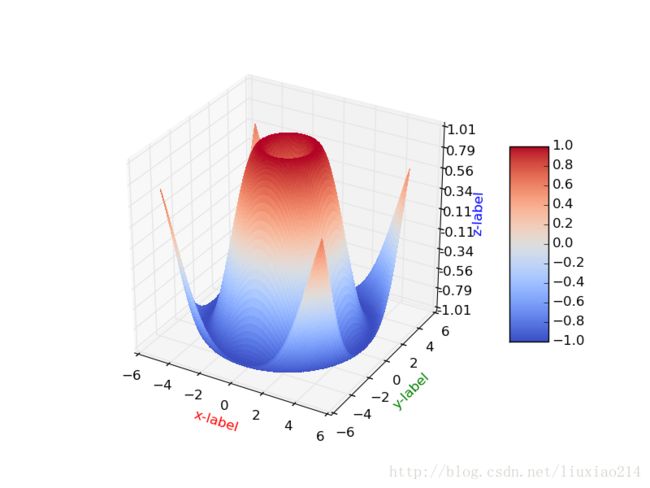
plt.show()6、绘制三维空间曲面
def d3_hookface():
fig = plt.figure() # 得到画面
ax = fig.gca(projection='3d') # 得到3d坐标的图
X = np.arange(-5, 5, 0.1)
Y = np.arange(-5, 5, 0.1)
X,Y = np.meshgrid(X, Y) # 将坐标向量变为坐标矩阵,列为x的长度,行为y的长度
R = np.sqrt(X**2 + Y**2)
Z = np.sin(R)
# 曲面,x,y,z坐标,横向步长,纵向步长,颜色,线宽,是否渐变
surf = ax.plot_surface(X, Y, Z, rstride=1, cstride=1, cmap=cm.coolwarm, linewidth=0, antialiased=False)
ax.set_zlim(-1.01, 1.01)
ax.set_xlabel("x-label", color='r')
ax.set_ylabel("y-label", color='g')
ax.set_zlabel("z-label", color='b')
ax.zaxis.set_major_locator(LinearLocator(10)) # 设置z轴标度
ax.zaxis.set_major_formatter(FormatStrFormatter('%0.02f')) # 设置z轴精度
# shrink颜色条伸缩比例0-1, aspect颜色条宽度(反比例,数值越大宽度越窄)
fig.colorbar(surf, shrink=0.5, aspect=5)
plt.savefig("d3_hookface.png")
plt.show()
7、汇总代码
# -- coding: utf-8 --
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.mlab as mlab
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import cm
from matplotlib.ticker import LinearLocator, FormatStrFormatter
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D
def initial_image():
# define x\y
x = np.arange(0.0, 2.0, 0.05)
s = np.sin(np.pi * x)
# set color and linestyle
plt.plot(x, s, "yo-")
# set tilte and x\y labels
plt.title("it's just a test")
plt.xlabel("x-label")
plt.ylabel("y-label")
plt.grid() # set gridding
plt.savefig("initial_img.png") # save image
plt.show() # show the image
def two_images():
x = np.arange(0.0, 2.0, 0.1)
s1 = np.sin(np.pi * x)
s2 = x * 2
plt.subplot(2, 1, 1) # devide 2 rows and 1 cols and get first row
plt.plot(x, s1, "yo-")
plt.title("it's a two_imgs demo")
plt.xlabel("xx1")
plt.ylabel("yy1")
plt.grid()
plt.subplot(2, 1, 2)
plt.plot(x, s2, "r.-")
plt.xlabel("xx2")
plt.ylabel("yy2")
plt.grid()
plt.savefig("two_images.png")
plt.show()
def Histogram_demo():
# set u and &
mean = 100
sigma = 10
# produce normal distribution , 10000个数
x = mean + sigma * np.random.randn(10000)
num_bins = 50 # 共50个格子
# 直方图函数, normed=1即和为1,
# 返回50个概率、直方块左边线的x值、各个方块对象
n, bins, patches = plt.hist(x, num_bins, normed=1, facecolor='yellow', alpha=0.5)
y = mlab.normpdf(bins, mean, sigma) # 一条逼近的曲线
plt.plot(bins, y, "r--")
plt.title("Histogram of XXX: $\mu=100$, $\sigma=10$")
plt.xlabel("x-label")
plt.ylabel("y-label")
plt.grid()
plt.subplots_adjust(left=0.15)
plt.savefig("Histogram_demo.png")
plt.show()
def d3_points():
x_list = [[3,3,2],[4,3,1],[1,2,3],[1,1,2],[2,1,2]]
fig = plt.figure() # 得到画面
ax = fig.gca(projection='3d') # 得到3d坐标的图
# 画点
for x in x_list:
ax.scatter(x[0],x[1],x[2],c='r')
plt.savefig("d3_image.png")
plt.show()
def d3_plane():
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(1,1,1,projection='3d') # 一行一列第一个
X = np.arange(1, 10, 1)
Y = np.arange(1, 10, 1)
X,Y = np.meshgrid(X, Y) # 将坐标向量变为坐标矩阵,列为x的长度,行为y的长度
Z = 3*X + 2*Y + 30
# 构建平面
surf = ax.plot_surface(X, Y, Z, rstride=1, cstride=1, cmap=cm.jet, linewidth=0, antialiased=True)
ax.set_xlabel("x-label", color='r')
ax.set_ylabel("y-label", color='g')
ax.set_zlabel("z-label", color='b')
ax.set_zlim3d(0, 100) # 设置z坐标轴
fig.colorbar(surf, shrink=0.5, aspect=5) # 图例
plt.savefig("d3_plane.png")
plt.show()
def d3_hookface():
fig = plt.figure() # 得到画面
ax = fig.gca(projection='3d') # 得到3d坐标的图
X = np.arange(-5, 5, 0.1)
Y = np.arange(-5, 5, 0.1)
X,Y = np.meshgrid(X, Y) # 将坐标向量变为坐标矩阵,列为x的长度,行为y的长度
R = np.sqrt(X**2 + Y**2)
Z = np.sin(R)
# 曲面,x,y,z坐标,横向步长,纵向步长,颜色,线宽,是否渐变
surf = ax.plot_surface(X, Y, Z, rstride=1, cstride=1, cmap=cm.coolwarm, linewidth=0, antialiased=False)
ax.set_zlim(-1.01, 1.01)
ax.set_xlabel("x-label", color='r')
ax.set_ylabel("y-label", color='g')
ax.set_zlabel("z-label", color='b')
ax.zaxis.set_major_locator(LinearLocator(10)) # 设置z轴标度
ax.zaxis.set_major_formatter(FormatStrFormatter('%0.02f')) # 设置z轴精度
# shrink颜色条伸缩比例0-1, aspect颜色条宽度(反比例,数值越大宽度越窄)
fig.colorbar(surf, shrink=0.5, aspect=5)
plt.savefig("d3_hookface.png")
plt.show()
def main():
initial_image()
two_images()
Histogram_demo()
d3_points()
d3_plane()
d3_hookface()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()