Redis实战(1)-SpringBoot2.0整合Redis自定义注入模板操作Bean组件
概述:本系列博文所涉及的相关内容来源于debug亲自录制的实战课程:缓存中间件Redis技术入门与应用场景实战(SpringBoot2.x + 抢红包系统设计与实战),感兴趣的小伙伴可以点击自行前往学习(毕竟以视频的形式来掌握技术 会更快!) 原文链接:Redis实战(1)-SpringBoot2.0整合Redis自定义注入模板操作Bean组件 ,文章所属技术专栏:缓存中间件Redis技术入门与实战
视频介绍:可以观看以下课程的第1、第2节的视频介绍哦~
1-1课程整体介绍
1-2核心技术列表与课程收益
摘要:对于Redis,相信很多小伙伴早已有所耳闻,更有甚者,已经将其应用到许许多多的项目当中了!没错,它就是目前业界应用相当广泛的其中一种缓存中间件,也可以算是其中的佼佼者吧,从本篇文章开始,我们将基于SpringBoot2.0整合搭建的微服务项目为奠基,开启中间件Redis的实战之路!
内容:本篇文章我们将首先基于SpringBoot2.0搭建的项目整合缓存中间件Redis,在项目中加入跟Redis相关的、常见的配置信息,并自定义注入Redis的模板操作组件StringRedisTemplate和RedisTemplate,最终给大伙撸个简单的Demo并由此开启Redis的实战之旅!
(1)第一步当然是先加入中间件Redis的依赖Jar,如下所示:
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-redis
1.3.3.RELEASE
然后是在配置文件application.properties中加入Redis常见的相关配置信息,包括host、port等基本信息,在这里我们提供了两种配置方式,即“单机模式”和“集群模式”的配置,如下所示:
#redis 单机配置
spring.redis.host=127.0.0.1
spring.redis.port=6379
spring.redis.password=
spring.redis.jedis.pool.min-idle=100
spring.redis.jedis.pool.max-idle=300
spring.redis.jedis.pool.max-active=500
#集群配置
#spring.redis.cluster.nodes=127.0.0.1:6379,127.0.0.1:6380,127.0.0.1:6381,127.0.0.1:6382在该配置文件中,我们还加入了“链接池”的概念,其中,链接池里最小可用的链接数为100个,最大可用的连接数为300个,如果还不够而需要动态扩增时,我们将最终将活跃的链接数增加到500个!(如果500个还不够,那就得堵塞等待了,等待期间,如果时间超过了默认配置的超时时间,那将报出类似于connection reset或者connection error的错误)
(2)接下来,我们将基于整合搭建好的项目自定义注入Redis的操作模板组件,即主要是StringRedisTemplate和RedisTemplate。
值得一提的是,在传统的Java Web项目中,如Spring+SpringMVC+Mybatis整合的项目,一般是直接采用基于Jedis封装出一个JedisUtil工具类,这种方式跟以前使用JDBCUtil操作DB数据库时有点类似,其缺陷还是比较明显的(如需要手动创建链接、关闭链接资源等操作)
而SpringBoot的问世,带来了“约定优先于配置”、“起步依赖”等优点,省去了许多以往需要手动创建、关闭链接等有可能消耗资源的操作,即直接就内置在了SpringBoot Redis的起步依赖中了,而对于如何更加便捷的操作Redis,SpringBoot更是直接封装、提供了两大模板操作组件StringRedisTemplate和RedisTemplate,如下所示我们自定义注入了这两个模板操作组件,即主要指定其序列化的相关策略:
/**
* @EnableCaching:开启缓存(注解生效的)
* redis的操作组件自定义注入配置
* @Author:debug (SteadyJack)
* @Link: wx-> debug0868 qq-> 1948831260
* @Date: 2019/10/29 16:59
**/
@Configuration
@EnableCaching
public class RedisConfig {
@Autowired
private RedisConnectionFactory connectionFactory;
@Bean
public RedisTemplate redisTemplate(){
RedisTemplate redisTemplate=new RedisTemplate<>();
redisTemplate.setConnectionFactory(connectionFactory);
//设置序列化策略
redisTemplate.setKeySerializer(new StringRedisSerializer());
redisTemplate.setValueSerializer(new GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer());
redisTemplate.setHashKeySerializer(new StringRedisSerializer());
redisTemplate.afterPropertiesSet();
return redisTemplate;
}
@Bean
public StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate(){
StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate=new StringRedisTemplate();
stringRedisTemplate.setConnectionFactory(connectionFactory);
return stringRedisTemplate;
}
} (3)至此,我们已经做好了相关的前奏准备,接下来我们写个简单的Demo,意思意思一下“开启Redis的实战之路”:
/**
* @Author:debug (SteadyJack)
* @Link: weixin-> debug0868 qq-> 1948831260
* @Date: 2019/10/29 15:47
**/
@RestController
@RequestMapping("base")
public class BaseController {
private static final Logger log= LoggerFactory.getLogger(BaseController.class);
@Autowired
private StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate;
private static final String RedisHelloWorldKey="SpringBootRedis:HelloWorld";
@RequestMapping(value = "/hello/world/put",method = RequestMethod.POST)
@ResponseBody
public BaseResponse helloWorldPut(@RequestParam String helloName){
BaseResponse response=new BaseResponse(StatusCode.Success);
try {
stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().set(RedisHelloWorldKey,helloName);
response.setData("hello world!");
}catch (Exception e){
log.info("--hello world get异常信息: ",e.fillInStackTrace());
response=new BaseResponse(StatusCode.Fail.getCode(),e.getMessage());
}
return response;
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/hello/world/get",method = RequestMethod.GET)
@ResponseBody
public BaseResponse helloWorldGet(){
BaseResponse response=new BaseResponse(StatusCode.Success);
try {
String result=stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().get(RedisHelloWorldKey);
response.setData(result);
}catch (Exception e){
log.info("--hello world get异常信息: ",e.fillInStackTrace());
response=new BaseResponse(StatusCode.Fail.getCode(),e.getMessage());
}
return response;
}
}上述代码就是简单的基于Redis的String数据类型存储特定的一串信息(在这里指的是一串字符串常量值,由前端传递过来!)
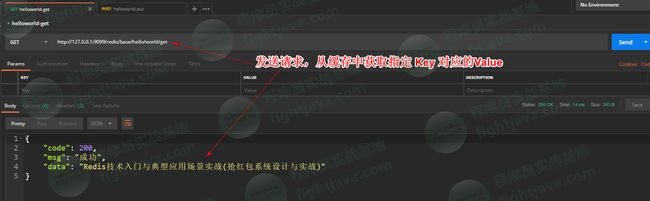
(4)最后,我们基于Postman进行自测(学会自测是一个Java攻城狮必备的技能以及良好的习惯),两张图加以概括吧:
好了,本篇文章我们就介绍到这里了,建议各位小伙伴一定要照着文章提供的样例代码撸一撸,只有撸过才能知道这玩意是咋用的,否则就成了“空谈者”!对Redis相关技术栈以及实际应用场景实战感兴趣的小伙伴可以前往debug搭建的技术社区的课程中心进行学习观看:http://www.fightjava.com/web/index/course/detail/12 !
其他相关的技术,感兴趣的小伙伴可以关注底部Debug的技术公众号,或者加Debug的微信,拉你进“微信版”的真正技术交流群!一起学习、共同成长!
补充:
1、本文涉及到的相关的源代码可以到此地址,check出来进行查看学习:https://gitee.com/steadyjack/SpringBootRedis
2、目前debug已将本文所涉及的内容整理录制成视频教程,感兴趣的小伙伴可以前往观看学习:http://www.fightjava.com/web/index/course/detail/12
3、关注一下debug的技术微信公众号,最新的技术文章、课程以及技术专栏将会第一时间在公众号发布哦
(debug的微信:debug0868 可以加好友交流技术!)
![]()