SDWebImage-解码、压缩图像
一、简单介绍
研究了下SDWebImage的源码,借鉴了别人的一些资料,感觉逐渐的明白的一些原理,现在就来记录下。
在我们使用 UIImage 的时候,创建的图片通常不会直接加载到内存,而是在渲染的时候默认在主线程上再进行解码并加载到内存。这就会导致 UIImage 在渲染的时候效率上不是那么高效。为了提高效率所以在SDWebImage中就采取在子线程中进行解码图片。
这里再介绍下为什么创建图像的时候是需要解码的因为一般下载的图片或者是我们手动拖进工程的图片都是PNG 或者JPEG或者是其他格式的图片,这些图片都是经过编码压缩后的图片数据,并不是我们的控件可以直接显示的位图,如果我们直接使用加载渲染图片到手机上的时候,系统默认会在主线程立即进行图片的解码工作,这个过程就是把图片数据解码成可以供给控件直接显示的位图数据,由于这个解码操作比较耗时,并且默认是在主线程进行,所以如果加载过多的图片的话肯定是会发生卡顿现象的。
二、源码分析
首先介绍的是根据data来解码成一个UIImage对象的方法
- (UIImage *)decodedImageWithData:(NSData *)data {
if (!data) {
return nil;
}
UIImage *image = [[UIImage alloc] initWithData:data];
//如果是MAC端就直接返回image
#if SD_MAC
return image;
#else
if (!image) {
return nil;
}
//不然的话就要去获取数据中图片的方向
UIImageOrientation orientation = [[self class] sd_imageOrientationFromImageData:data];
//如果图片的方向不是默认向上的话就要去根据其图片信息的方向来重新创建图片
if (orientation != UIImageOrientationUp) {
image = [[UIImage alloc] initWithCGImage:image.CGImage scale:image.scale orientation:orientation];
}
return image;
#endif
}这里再介绍下关于获取图片方向的sd_imageOrientationFromImageData方法,这里面其实就是根据imageData去创建CGImageSourceRef然后去读取其图像的属性
+ (UIImageOrientation)sd_imageOrientationFromImageData:(nonnull NSData *)imageData {
UIImageOrientation result = UIImageOrientationUp;
//创建从Core Foundation 数据对象中读取的图像源
/**
参数1:
参数2:指定额外创建option字典。我们可以在options字典中包含的键来创建图像源。
比如说
kCGImageSourceTypeIdentifierHint
kCGImageSourceShouldAllowFloat
kCGImageSourceShouldCache
kCGImageSourceCreateThumbnailFromImageIfAbsent
kCGImageSourceCreateThumbnailFromImageAlways
kCGImageSourceThumbnailMaxPixelSize
kCGImageSourceCreateThumbnailWithTransform
*/
CGImageSourceRef imageSource = CGImageSourceCreateWithData((__bridge CFDataRef)imageData, NULL);
if (imageSource) {
//调用CGImageSourceCopyPropertiesAtIndex的时候会才去读取图像元数据
//返回图像源中指定位置的图像的属性。
/**
参数1:一个图像的来源
参数2:你想要获得的属性的索引。该指数是从零开始的。index参数设置获取第几张图像
参数3:可以用来请求其他选项的字典。
返回包含与图像相关联的属性的字典。请参见CGImageProperties,以获得可以在字典中使用的属性列表。
CGImageProperties引用定义了代表图像I/O框架使用的图像特征的常量。
*/
CFDictionaryRef properties = CGImageSourceCopyPropertiesAtIndex(imageSource, 0, NULL);
//判断属性存不存在,如果不存在就用默认的UIImageOrientationUp方向
if (properties) {
//typedef const void *CFTypeRef;
CFTypeRef val;
NSInteger exifOrientation;
//返回与给定键关联的值,这里就是返回方向键值所对应的内容
val = CFDictionaryGetValue(properties, kCGImagePropertyOrientation);
//如果其存在的话,就去获取
if (val) {
//将CFNumber对象转换为指定类型的值
/**
参数1:要检查的CFNumber对象。
参数2:指定要返回的数据类型的常量。请参阅CFNumberType以获得可能的值列表。
参数3:返回的时候包含数字的值
*/
CFNumberGetValue(val, kCFNumberNSIntegerType, &exifOrientation);
//转换exif中信息的方向到iOS里面的方向
result = [SDWebImageCoderHelper imageOrientationFromEXIFOrientation:exifOrientation];
} // else - if it's not set it remains at up
CFRelease((CFTypeRef) properties);
} else {
//NSLog(@"NO PROPERTIES, FAIL");
}
//释放这个图像源
CFRelease(imageSource);
}
//返回结果
return result;
}这里再介绍的介绍下imageOrientationFromEXIFOrientation的方法,这个方法就是转换一个EXIF信息中图像方向到iOS中的方向说白了就是从NSInteger转换为UIImageOrientationUp这样的枚举值。
// Convert an EXIF image orientation to an iOS one.
+ (UIImageOrientation)imageOrientationFromEXIFOrientation:(NSInteger)exifOrientation {
// CGImagePropertyOrientation is available on iOS 8 above. Currently kept for compatibility
UIImageOrientation imageOrientation = UIImageOrientationUp;
switch (exifOrientation) {
case 1:
imageOrientation = UIImageOrientationUp;
break;
case 3:
imageOrientation = UIImageOrientationDown;
break;
case 8:
imageOrientation = UIImageOrientationLeft;
break;
case 6:
imageOrientation = UIImageOrientationRight;
break;
case 2:
imageOrientation = UIImageOrientationUpMirrored;
break;
case 4:
imageOrientation = UIImageOrientationDownMirrored;
break;
case 5:
imageOrientation = UIImageOrientationLeftMirrored;
break;
case 7:
imageOrientation = UIImageOrientationRightMirrored;
break;
default:
break;
}
return imageOrientation;
}接下来开始讲下解码图像,在这里面其实刚开始先判断能不能解码图片,这个方法是这样的
+ (BOOL)shouldDecodeImage:(nullable UIImage *)image {
// Prevent "CGBitmapContextCreateImage: invalid context 0x0" error
//如果图片都为空,那肯定返回的是NO
if (image == nil) {
return NO;
}
//不能编码动画图片
// do not decode animated images
if (image.images != nil) {
return NO;
}
CGImageRef imageRef = image.CGImage;
BOOL hasAlpha = SDCGImageRefContainsAlpha(imageRef);
//不支持解码含有透明度的图片
// do not decode images with alpha
if (hasAlpha) {
return NO;
}
return YES;
}
回到这个方法,其实主要的过程就是CGBitmapContextCreate创建一个位图上下文→CGContextDrawImage绘制原始位图到上下文→CGBitmapContextCreateImage创建解码后的新位图。
- (nullable UIImage *)sd_decompressedImageWithImage:(nullable UIImage *)image {
if (![[self class] shouldDecodeImage:image]) {
return image;
}
// autorelease the bitmap context and all vars to help system to free memory when there are memory warning.
// on iOS7, do not forget to call [[SDImageCache sharedImageCache] clearMemory];
//新建自动释放池,将bitmap context和临时变量都添加到池中在方法末尾自动释放以防止内存警告
@autoreleasepool{
//获取传入的UIImage对应的CGImageRef(位图)
CGImageRef imageRef = image.CGImage;
//获取彩色空间
CGColorSpaceRef colorspaceRef = [[self class] colorSpaceForImageRef:imageRef];
//获取高和宽
size_t width = CGImageGetWidth(imageRef);
size_t height = CGImageGetHeight(imageRef);
// kCGImageAlphaNone is not supported in CGBitmapContextCreate.
// Since the original image here has no alpha info, use kCGImageAlphaNoneSkipLast
// to create bitmap graphics contexts without alpha info.
//初始化bitmap graphics context 上下文
/*
参数1:指向要呈现绘图的内存中目标的指针。这个内存块的大小至少应该是(bytesPerRow*height)字节。
如果希望此函数为位图分配内存,则传递NULL。这将使您不必管理自己的内存,从而减少内存泄漏问题。
参数2:所需宽度,以像素为单位
参数3:所需高度
参数4:用于内存中一个像素的每个组件的比特数
参数5:位图中每一行使用的内存字节数。如果数据参数为NULL,传递值为0,则会自动计算值。
参数6:颜色空间
参数7:指定位图是否应该包含一个alpha通道、alpha通道在一个像素中的相对位置,以及关于像素组件是浮点数还是整数值的信息。
指定alpha通道信息的常量使用CGImageAlphaInfo类型声明,可以安全地传递给该参数。
您还可以传递与CGBitmapInfo类型相关联的其他常量。
例如,如何指定颜色空间、每个像素的位元、每个像素的位元以及位图信息,请参阅图形上下文。
*/
//kCGBitmapByteOrderDefault 是默认模式,对于iPhone 来说,采用的是小端模式
CGContextRef context = CGBitmapContextCreate(NULL,
width,
height,
kBitsPerComponent,
0,
colorspaceRef,
kCGBitmapByteOrderDefault|kCGImageAlphaNoneSkipLast);
//如果上下文为NULL,就返回image
if (context == NULL) {
return image;
}
// Draw the image into the context and retrieve the new bitmap image without alpha
/**
这里创建的contexts是没有透明因素的。在UI渲染的时候,实际上是把多个图层按像素叠加计算的过程,需要对每一个像素进行 RGBA 的叠加计算。
当某个 layer 的是不透明的,也就是 opaque 为 YES 时,GPU 可以直接忽略掉其下方的图层,这就减少了很多工作量。
这也是调用 CGBitmapContextCreate 时 bitmapInfo 参数设置为忽略掉 alpha 通道的原因。而且这里主要针对的就是解码图片成位图
*/
//将CGImageRef对象画到上面生成的上下文中,且将alpha通道移除
CGContextDrawImage(context, CGRectMake(0, 0, width, height), imageRef);
//使用上下文创建位图
CGImageRef imageRefWithoutAlpha = CGBitmapContextCreateImage(context);
//从位图创建UIImage对象,返回含有指定的方向和scale的图片
UIImage *imageWithoutAlpha = [[UIImage alloc] initWithCGImage:imageRefWithoutAlpha scale:image.scale orientation:image.imageOrientation];
//释放CG对象
CGContextRelease(context);
CGImageRelease(imageRefWithoutAlpha);
return imageWithoutAlpha;
}
}下面再介绍下关于SDWebImage中的图片压缩的算法,其实简单来说就是将图像矩阵按照规则分割成小型子矩阵进行压缩,然后插值拼接,而且这个算法也是借鉴苹果的,官方Demo链接:https://developer.apple.com/library/content/samplecode/LargeImageDownsizing/Introduction/Intro.html 关于这个算法,苹果的定义就是此代码示例演示了一种支持在有限的内存环境中显示超大图像的方法,方法是将磁盘上的大图像转换为内存中较小的图像。这在原始图像太大而无法按照要显示的要求放入内存的情况下很有用 我目前也只能理解个大概,还有些细节方面还没想到,它是怎么进行优化的,代码都有注释。现在先简单的介绍下回用到的宏吧。
// 每个像素占4个字节大小 共32位
static const size_t kBytesPerPixel = 4;
//每个通道由8位组成
static const size_t kBitsPerComponent = 8;
/*
* Defines the maximum size in MB of the decoded image when the flag `SDWebImageScaleDownLargeImages` is set
* Suggested value for iPad1 and iPhone 3GS: 60.
* Suggested value for iPad2 and iPhone 4: 120.
* Suggested value for iPhone 3G and iPod 2 and earlier devices: 30.
该参数用于设置内存占用的最大字节数。默认为60MB,下面给出了一些旧设备的参考数值。如果图片大小大于该值,则将图片以该数值为目标进行压缩。
*/
static const CGFloat kDestImageSizeMB = 60.0f;
/*
* Defines the maximum size in MB of a tile used to decode image when the flag `SDWebImageScaleDownLargeImages` is set
* Suggested value for iPad1 and iPhone 3GS: 20.
* Suggested value for iPad2 and iPhone 4: 40.
* Suggested value for iPhone 3G and iPod 2 and earlier devices: 10.
设置压缩时对于源图像使用到的*块*的最大字节数。原图方块的大小,这个方块将会被用来分割原图,默认设置为20M。
*/
static const CGFloat kSourceImageTileSizeMB = 20.0f;
//1M有多少字节
static const CGFloat kBytesPerMB = 1024.0f * 1024.0f;
//1M有多少像素 262144个像素
static const CGFloat kPixelsPerMB = kBytesPerMB / kBytesPerPixel;
//目标总像素kDestImageSizeMB为60MB
static const CGFloat kDestTotalPixels = kDestImageSizeMB * kPixelsPerMB;
//目标图像的像素点个数
static const CGFloat kTileTotalPixels = kSourceImageTileSizeMB * kPixelsPerMB;
//目标重叠像素大小
static const CGFloat kDestSeemOverlap = 2.0f; // the numbers of pixels to overlap the seems where tiles meet.关于算法的描述,位图其实简单可以描述为是由像素组成的矩阵,所以下面其实就是把图像当做一个矩阵(或多个矩阵的组合)来进行处理的。
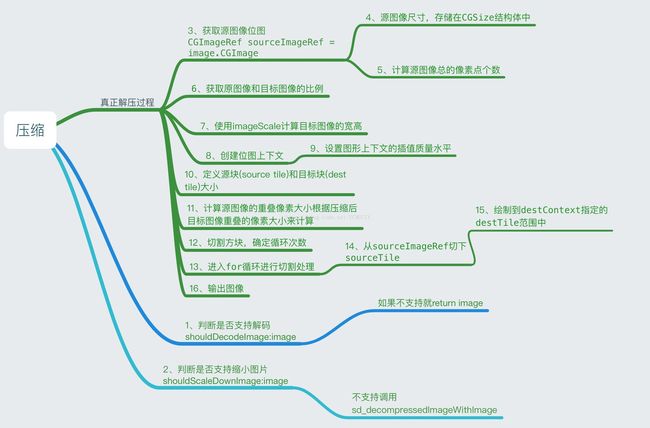
- (nullable UIImage *)sd_decompressedAndScaledDownImageWithImage:(nullable UIImage *)image {
//1、判断图片是否支持解码
if (![[self class] shouldDecodeImage:image]) {
return image;
}
//2、判断图片是否支持缩小也就是压缩,总像素要大于15728640才能压缩,也就是kDestTotalPixels的大小
if (![[self class] shouldScaleDownImage:image]) {
return [self sd_decompressedImageWithImage:image];
}
//声明压缩目标用的上下文
CGContextRef destContext;
// autorelease the bitmap context and all vars to help system to free memory when there are memory warning.
// on iOS7, do not forget to call [[SDImageCache sharedImageCache] clearMemory];
@autoreleasepool {
//3. 获取源图像位图
CGImageRef sourceImageRef = image.CGImage;
//4. 源图像尺寸,存储在CGSize结构体中
CGSize sourceResolution = CGSizeZero;
sourceResolution.width = CGImageGetWidth(sourceImageRef);
sourceResolution.height = CGImageGetHeight(sourceImageRef);
//5. 计算源图像总的像素点个数
float sourceTotalPixels = sourceResolution.width * sourceResolution.height;
// Determine the scale ratio to apply to the input image
// that results in an output image of the defined size.
// see kDestImageSizeMB, and how it relates to destTotalPixels.
//6. 获取原图像和目标图像的比例(以像素点个数为基准),这里是以60MB的像素点为标准了 60MB的总像素要除以原文件的总像素小于1的
float imageScale = kDestTotalPixels / sourceTotalPixels;
//7. 使用imagescale计算目标图像的宽高,所以我目标图像的目标就是到60MB
CGSize destResolution = CGSizeZero;
destResolution.width = (int)(sourceResolution.width*imageScale);
destResolution.height = (int)(sourceResolution.height*imageScale);
//8. 进行图像绘制前的准备工作
// current color space
CGColorSpaceRef colorspaceRef = [[self class] colorSpaceForImageRef:sourceImageRef];
// kCGImageAlphaNone is not supported in CGBitmapContextCreate.
// Since the original image here has no alpha info, use kCGImageAlphaNoneSkipLast
// to create bitmap graphics contexts without alpha info.
//创建位图上下文
destContext = CGBitmapContextCreate(NULL,
destResolution.width,
destResolution.height,
kBitsPerComponent,
0,
colorspaceRef,
kCGBitmapByteOrderDefault|kCGImageAlphaNoneSkipLast);
if (destContext == NULL) {
return image;
}
/*9. 设置图像插值的质量为高,设置图形上下文的插值质量水平CGContextSetInterpolationQuality允许上下文以各种保真度水平内插像素。
在这种情况下,kCGInterpolationHigh通过最佳结果*/
CGContextSetInterpolationQuality(destContext, kCGInterpolationHigh);
//现在定义矩形的大小,用于增量位块从输入图像到输出图像。
// Now define the size of the rectangle to be used for the
// incremental blits from the input image to the output image.
//由于iOS从磁盘检索图像数据的方式,我们使用源图像宽度与源图像的宽度相等
// we use a source tile width equal to the width of the source
// image due to the way that iOS retrieves image data from disk.
/*iOS必须在全宽度的“波段”中从磁盘上解码图像,即使当前的图形上下文被剪切到band内的一个subrect中。因此,我们充分利用了所有的像素数据,
这些数据是由解码操作产生的,通过将我们的平铺大小与输入图像的宽度匹配。
*/
// iOS must decode an image from disk in full width 'bands', even
// if current graphics context is clipped to a subrect within that
// band. Therefore we fully utilize all of the pixel data that results
// from a decoding opertion by achnoring our tile size to the full
// width of the input image.
//10. 定义一个称为*块*的增量矩形(incremental blits,即矩形大小在每一次迭代后都不断增长/减小)用于计算从源图像到目标图像的输出。
CGRect sourceTile = CGRectZero;
//源块的宽度等于源图像的宽度,宽度要保持一定
sourceTile.size.width = sourceResolution.width;
// 块的高度是动态的,我们前面指定了源tile的值,也就是kTileTotalPixels目标图像的像素点个数 根据宽度计算动态的高度
// The source tile height is dynamic. Since we specified the size
// of the source tile in MB, see how many rows of pixels high it
// can be given the input image width.
sourceTile.size.height = (int)(kTileTotalPixels / sourceTile.size.width );
// *块*的起始x值总是为0
sourceTile.origin.x = 0.0f;
//输出的tile与输入的tile比例相同,但图像按比例缩放。图像按比例缩放就要用到插值运算了
// The output tile is the same proportions as the input tile, but
// scaled to image scale.
//同样的方式初始化目标图像的块
CGRect destTile;
//宽度 = 目标图像的宽度
destTile.size.width = destResolution.width;
//高度 = 源图像块的高度 * 缩放比例
destTile.size.height = sourceTile.size.height * imageScale;
destTile.origin.x = 0.0f;
// The source seem overlap is proportionate to the destination seem overlap.
// this is the amount of pixels to overlap each tile as we assemble the ouput image.
//11、计算源图像与压缩后目标图像重叠的像素大小。这里就是按照sourceResolution.height和destResolution.height进行相比
float sourceSeemOverlap = (int)((kDestSeemOverlap/destResolution.height)*sourceResolution.height);
CGImageRef sourceTileImageRef;
//计算组装输出图像所需的读/写操作数
// calculate the number of read/write operations required to assemble the
// output image.
//源图像的高度除以分割源图像的方块的高度得出源图像被分割成多少个方块并赋值给 iterations,再做取余运算取得分割的最大的整数
int iterations = (int)( sourceResolution.height / sourceTile.size.height );
//12、如果tile height不均匀地分割图像高度,则添加另一个迭代来解释剩余的像素。
// If tile height doesn't divide the image height evenly, add another iteration
// to account for the remaining pixels.
int remainder = (int)sourceResolution.height % (int)sourceTile.size.height;
if(remainder) {
iterations++;
}
// Add seem overlaps to the tiles, but save the original tile height for y coordinate calculations.
//定义一个 float 变量 sourceTitleHeightMinusOverlap 存放那个用来分割源图像,大小为 20 MB 的方块的高度。
float sourceTileHeightMinusOverlap = sourceTile.size.height;
//用于切割源图像大小为 20 MB 的方块的高度加上源图像与源图像分割方块的像素重叠数
sourceTile.size.height += sourceSeemOverlap;
//destTile.size.height = sourceTile.size.height * imageScale;
//目标图像的分割方块的高度加上 kDestSeemOverlap(像素重叠数赋值为 2)
destTile.size.height += kDestSeemOverlap;
//13、进行for 循环,y 从0开始,到小于源图像被分割的块数
for( int y = 0; y < iterations; ++y ) {
@autoreleasepool {
//sourceTile 和 destTile 都是宽度和高度固定的,x 值为 0,只有 y 值随着循环的 y 值在变化,sourceTile 的 y 值在递增,destTile 的 y 值在递减,只有最最后一次循环中,如果有余数那么size就会发生变化,这是因为最后一次中去取源图像的高度其实
//sourceTileHeightMinusOverlap = sourceTile.size.height;
sourceTile.origin.y = y * sourceTileHeightMinusOverlap + sourceSeemOverlap;
destTile.origin.y = destResolution.height - (( y + 1 ) * sourceTileHeightMinusOverlap * imageScale + kDestSeemOverlap);
/*14、在用到在一张图片中截取某一部分图片中,用到CGImageRef类中的CGImageCreateWithImageInRect函数
然后循环的从源图像的 sourceImageRef 根据大小为 20 MB 的分割块的不同 CGRect 的矩形区域内获取 sourceTileImageRef,这里sourceTile的高度是根据kTileTotalPixels / sourceTile.size.width
*/
sourceTileImageRef = CGImageCreateWithImageInRect(sourceImageRef, sourceTile);
//计算剩余的像素,所采用的方法
if( y == iterations - 1 && remainder ) {
//destTile.size.height = sourceTile.size.height * imageScale;
float dify = destTile.size.height;
destTile.size.height = CGImageGetHeight( sourceTileImageRef ) * imageScale;
dify -= destTile.size.height;
destTile.origin.y += dify;
}
//15、绘制图像到图形上下文指定的destTile范围中
CGContextDrawImage( destContext, destTile, sourceTileImageRef );
CGImageRelease( sourceTileImageRef );
}
}
CGImageRef destImageRef = CGBitmapContextCreateImage(destContext);
CGContextRelease(destContext);
if (destImageRef == NULL) {
return image;
}
//16、输出图像
UIImage *destImage = [[UIImage alloc] initWithCGImage:destImageRef scale:image.scale orientation:image.imageOrientation];
CGImageRelease(destImageRef);
if (destImage == nil) {
return image;
}
return destImage;
}
}压缩过程简单流程
参考文章:SDWebImage源码解读_之SDWebImageDecoder
SDWebImage源码解析之编解码
SDWebImage源码解析(三)——SDWebImage图片解码/压缩模块