状态机模式接受命令解析指令(modbus、AT指令)
状态机模式接受命令解析指令(modbus、AT指令)
- 状态机模式接受命令解析指令(modbus、AT指令)
- 状态机介绍
- 串口介绍
- 接收数据核心模块详解
- 代码实现
- 实际应用
- 状态机介绍
- 串口介绍
- 接收数据核心模块详解
- 代码实现
- 实际应用
状态机介绍
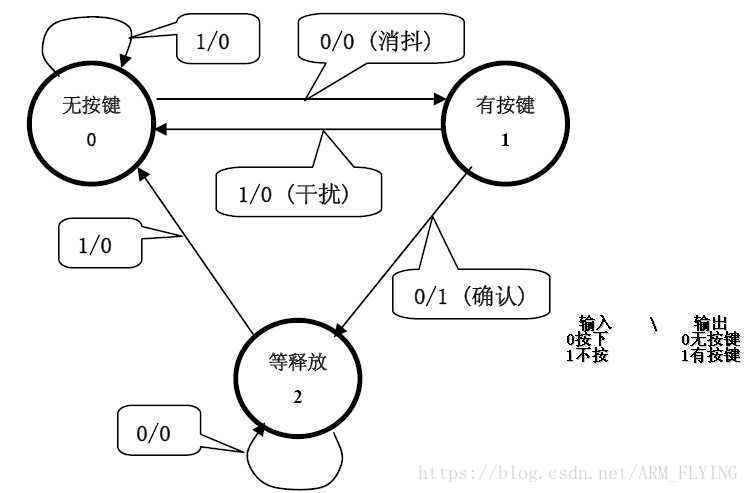
所谓的状态机,重点在状态两字。一个LED灯有两种状态:亮S0或灭S1;如果是一个按键的话根据不同的定义可能会有很多状态:初始状态就是啥也没动未按下S0,确认有键按下S1,键稳定按下状态S2,键释放状态S3,当然在S2和S3之间可以加入很多不同时间的状态来区分长按和短按也可以简单的抽象为三个状态S0、S1、S3。
下图的按键状态机就是抽象了三个状态,无按键按下、有按键、等待释放。状态的切换使用箭头表示。如何成功读取到一次按键呢,我们都知道机械按键是存在抖动的情况的,因此我们需要加入消抖的动作。程序中每次读取按键相应的引脚,根据上一次状态的值和当前引脚高低电平的值确定状态将如何切换。一次完整的扫描按键为:每0ms扫描一次按键状态,假如有按键按下了那么从S0->S1;一次检测按键还是按下的状态10ms消抖成功了则从S1->S2状态否则为误按切回到S0没有按下状态;下一次10ms后检测发现按键是弹起状态则一次按键读取成功否则维持状态S2表示按键并没有释放继续等待释放,在这个状态下可以添加不同时长的设置。
串口介绍
串口是通用异步收发传输器(Universal Asynchronous Receiver Transmitter)UART
最精简的连接方法只有3根线:TXD RXD GND
TxD:发送数据
RxD:接收数据
Gnd:给双方提供参考电平
在串口发送数据时,CPU将并行数据写入UART,UART按照一定的格式在一根电线上串行发出
接收数据时,UART检测另一根电线上的信号,将串行收集放在缓冲区中,CPU即可读取UART获取这些数据
UART以全双工方式传输数据,最精简的连接方法只有3根线:
串口的时序如下图:由于是异步传输器,时钟信号是事先规定好的(9600 115200 baud rate),协议一般包括一个起始位0 数据位8bit 停止位1 ,有的时候还有校验位但是使用一位校验位不准所以一般不用。

接收数据核心模块详解
我们知道串口的波特率一般不会太低或者太高,我们就以9600 和 115200 2中常见的为例做说明。为什么我们能使用状态机的方式来接收指令呢?我们先来提出需要解决的几个问题:
1.我们怎么判断串口是否接收数据完成了?
2.我们如何知道发送的指令长度会是多少呢?
3.怎么样才能快速的响应指令呢?
上面说到串口传输数据的时候是以一定的时钟传输的,当波特率是9600bit/s的时候按照每个字节传输10bit的情况下计算传输一个字节数据需要1000/960 ms ≈ 1ms。程序设计时我们肯定需要保存串口接收的数据和接收到的字节数,每2ms查询一次串口接收的字节数:字节数和上一次的不一样则表示串口还在继续接收,否则表示接收是完成的。
代码实现
串口初始化代码 usart.c
[USART_RX_BUF 为串口接收缓冲区,uint8_t USART_RX_BUF[USART_REV_LEN]][6]
[USART_REV_LEN 为串口接收的最大个数,#define USART_REV_LEN 100][6]
/**
******************************************************************************
* @file USART/USART_Printf/main.c
* @author MCD Application Team
* @version V1.4.0
* @date 24-July-2014
* @brief Main program body
******************************************************************************
* @attention
*
* © COPYRIGHT 2014 STMicroelectronics
*
* Licensed under MCD-ST Liberty SW License Agreement V2, (the "License");
* You may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at:
*
* http://www.st.com/software_license_agreement_liberty_v2
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*
******************************************************************************
*/
/* Includes ------------------------------------------------------------------*/
#include "usart.h"
#include "stm32f0xx.h"
#include "sysclk.h"
uint16_t USART_RX_STA;
//uint8_t USART_TX_BUF[USART_REV_LEN]; // usart1 semd data buf
uint8_t USART_RX_BUF[USART_REV_LEN]; // usart1 recv data buf
uint8_t Usart_Delaytime;
/**
* @brief Configure the USART Device
* @param None
* @retval None
*/
void USART_init(int bound)
{
GPIO_InitTypeDef GPIO_InitStructure;
USART_InitTypeDef USART_InitStructure;
// COLCK init
/* Enable GPIO clock */
RCC_AHBPeriphClockCmd(RCC_AHBPeriph_GPIOA, ENABLE);
/* Enable USARTs Clock */
RCC_APB2PeriphClockCmd(RCC_APB2Periph_USART1, ENABLE);
// GPIO init
GPIO_PinAFConfig(GPIOA,GPIO_PinSource9,GPIO_AF_1);
GPIO_PinAFConfig(GPIOA,GPIO_PinSource10,GPIO_AF_1);
/*
* USART1_TX -> PA9 , USART1_RX -> PA10
*/
GPIO_InitStructure.GPIO_Pin = GPIO_Pin_9|GPIO_Pin_10;
GPIO_InitStructure.GPIO_Mode = GPIO_Mode_AF;
GPIO_InitStructure.GPIO_OType = GPIO_OType_PP;
GPIO_InitStructure.GPIO_PuPd = GPIO_PuPd_UP;
GPIO_InitStructure.GPIO_Speed = GPIO_Speed_50MHz;
GPIO_Init(GPIOA, &GPIO_InitStructure);
USART_InitStructure.USART_BaudRate = bound;//???????
USART_InitStructure.USART_WordLength = USART_WordLength_8b;//?????
USART_InitStructure.USART_StopBits = USART_StopBits_1;//?????
USART_InitStructure.USART_Parity = USART_Parity_No;//?????
USART_InitStructure.USART_HardwareFlowControl = USART_HardwareFlowControl_None;//?????
USART_InitStructure.USART_Mode = USART_Mode_Rx | USART_Mode_Tx;//??????
USART_Init(USART1, &USART_InitStructure); //??????
USART_ITConfig(USART1, USART_IT_RXNE, ENABLE);//??????
NVIC_Config();
/* Enable Usart */
USART_Cmd(USART1, ENABLE);
}
/**
* @brief Configures the nested vectored interrupt controller.
* @param None
* @retval None
*/
void NVIC_Config(void)
{
NVIC_InitTypeDef NVIC_InitStructure;
/* Enable the USART Interrupt */
NVIC_InitStructure.NVIC_IRQChannel = USART1_IRQn;
NVIC_InitStructure.NVIC_IRQChannelPriority = 0;
NVIC_InitStructure.NVIC_IRQChannelCmd = ENABLE;
NVIC_Init(&NVIC_InitStructure);
}
/**
* @brief Retargets the C library printf function to the USART.
* @param None
* @retval None
*/
void Put_char(uint8_t ch){
/* Place your implementation of fputc here */
/* e.g. write a character to the USART */
USART_SendData(USART1, (uint8_t) ch);
/* Loop until transmit data register is empty */
while (USART_GetFlagStatus(USART1, USART_FLAG_TXE) == RESET);
}
/**
* @brief Retargets the C library printf function to the USART.
* @param _cData is send data
* @retval None
*/
void USART1_SendByte(uint8_t _cData)
{
// while(!((USART1->ISR)&(1<<7)));
// USART1->TDR=_cData;
USART_SendData(USART1, _cData);
while(USART_GetFlagStatus(USART1,USART_FLAG_TC) == RESET);
/* e.g. write a character to the USART */
}
void USART1_SendString(uint8_t *_sDat,uint16_t _iLen)
{
uint16_t i=0;
for(i=0 ;i<_iLen ;i++ ){
USART1_SendByte(_sDat[i]);
}
}
/**
* @brief Retargets the C library printf function to the USART.
* @param None
* @retval return read data from usart1
*/
uint8_t USART1_ReceiveByte(void)
{
while(!(USART1->ISR & (1<<5)));//???????
return(USART1->RDR); //????
}
#pragma import(__use_no_semihosting)
struct __FILE
{
int handle;
/* Whatever you require here. If the only file you are using is */
/* standard output using printf() for debugging, no file handling */
/* is required. */
};
/* FILE is typedef’ d in stdio.h. */
FILE __stdout;
//??_sys_exit()??????????
void _sys_exit(int x)
{
x = x;
}
//???fputc??
int fputc(int ch, FILE *f)
{
/* Place your implementation of fputc here */
USART_SendData(USART1, ch);
/* e.g. write a character to the USART */
while(USART_GetFlagStatus(USART1,USART_FLAG_TC) == RESET);
return ch;
}
// USART1_IRQHandler interrupt
void USART1_IRQHandler(void)
{
uint8_t Recv_Dat;
if(USART_GetITStatus(USART1, USART_IT_RXNE) != RESET) {
Recv_Dat = USART_ReceiveData(USART1);
USART_RX_BUF[USART_RX_STA&0XFF]=Recv_Dat ;
USART_RX_STA++;
}
if( (USART_RX_STA&0xFF) > 100) {
USART_RX_STA = 0;
}
} [main.c 中的代码片段][6]
[在main函数中,有一个2ms的计时器每2ms扫描一次串口接收的字节数并保存,新的字节数和老字节数作对比:不一样则表示串口正在接收数据此时立马跳出处理其他事情,一样则对应着串口此时没有接收数据判断接收的字节数是否为0,是0则没有接收到任何数据。判断接收到指令之后直接对指令进行解析,还可以多条指令连发接收的时候会存在一个缓冲区,在程序中对数据处理不断循环解析直到解析完所有指令。][6]
while (1)
{
if( syscolck.t2ms ) { // 2ms
static uint8_t Usart_LastLen ;
uint8_t Usart_NewLen = (USART_RX_STA&0xFF);
if( (Usart_LastLen == Usart_NewLen) && (Usart_NewLen > 0)) {
// recv data and end
int iRet = 0;
uint8_t iCount = 0;
uint8_t Temp_buf[64] = {0};
Usart_NewLen=USART_RX_STA&0xFF;
// Parse the data stream
// Analysis data, and according to the instruction postback different data
for(iCount =0 ;iCountwhile( (iRet!= -1) && (iRet!= 0) ) {
if( Usart_NewLen >= iRet ) {
Usart_NewLen -= iRet;
}else {
break;
}
for(iCount =0 ;iCount0;
}
Usart_LastLen = (USART_RX_STA&0xFF);
syscolck.t2ms = 0;
}
} 实际应用
实际使用中使用此状态机模式接收解析命令,能够很稳定的接收指令并做相应的解析响应的速度也能够满足要求。
具体的代码片段:
/**
******************************************************************************
* @file USART/USART_Printf/main.c
* @author MCD Application Team
* @version V1.4.0
* @date 24-July-2014
* @brief Main program body
******************************************************************************
* @attention
*
* © COPYRIGHT 2014 STMicroelectronics
*
* Licensed under MCD-ST Liberty SW License Agreement V2, (the "License");
* You may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at:
*
* http://www.st.com/software_license_agreement_liberty_v2
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*
******************************************************************************
*/
/* Includes ------------------------------------------------------------------*/
#include "usart.h"
#include "hchoadc.h"
#include "sysclk.h"
#include "protocol.h"
#include "flash.h"
#include "stdlib.h"
#ifdef __GNUC__
/* With GCC/RAISONANCE, small printf (option LD Linker->Libraries->Small printf
set to 'Yes') calls __io_putchar() */
#define PUTCHAR_PROTOTYPE int __io_putchar(int ch)
#else
#define PUTCHAR_PROTOTYPE int fputc(int ch, FILE *f)
#endif /* __GNUC__ */
/* Private functions ---------------------------------------------------------*/
// This is a sensor-related structure that stores sensor-related data and setting variables
g_StructTrait2P g_sGasTrait2P;
g_StructCoef g_sGasSaveCoef;
/**
* @brief Main program
* @param None
* @retval Nonef
*/
int main(void)
{
/* USART configuration */
// USART :9600, DataBits: 8, StopBits: 1, Parity: No
USART_init(9600);
// Using DMA Collect AD value
ADC_DMAInit();
if(1) {
Flash_ReadData(FLASH_USER_START_ADDR,(uint32_t *)&g_sGasSaveCoef,sizeof(g_sGasSaveCoef));
}else {
g_sGasSaveCoef.dEquationA = 1;
}
if (SysTick_Config(SystemCoreClock / 1000))
{
/* Capture error */
while (1);
}
g_sGasTrait2P.ucCalculationFlag |= 0x10; // Preheating starts
while (1)
{
if( syscolck.t2ms ) { // 2ms
static uint8_t Usart_LastLen ;
uint8_t Usart_NewLen = (USART_RX_STA&0xFF);
if( (Usart_LastLen == Usart_NewLen) && (Usart_NewLen > 0)) {
// recv data and end
int iRet = 0;
uint8_t iCount = 0;
uint8_t Temp_buf[64] = {0};
Usart_NewLen=USART_RX_STA&0xFF;
// Parse the data stream
// Analysis data, and according to the instruction postback different data
for(iCount =0 ;iCountwhile( (iRet!= -1) && (iRet!= 0) ) {
if( Usart_NewLen >= iRet ) {
Usart_NewLen -= iRet;
}else {
break;
}
for(iCount =0 ;iCount0;
}
Usart_LastLen = (USART_RX_STA&0xFF);
syscolck.t2ms = 0;
}
if( syscolck.t100ms && (syscolck.t2ms == 0)){
// Get the filter ad and Formaldehyde concentration value , HCHO and VOC
ADC_GetFilterVoltage();
syscolck.t100ms = 0;
}
if( (syscolck.t2ms == 0) && (g_sGasTrait2P.ucCalculationFlag & 0x01) ) {
//if( (syscolck.t2s) ) {
// Calculate the quadratic coefficient
double fA[3][4]={{0,0,0},{0,0,0},{0,0,0}};
float fX[3]={0};
float fY[3]={0};
float p,aik;
int i,j,k;
Flash_ReadData(FLASH_USER_START_ADDR,(uint32_t *)&g_sGasSaveCoef,sizeof(g_sGasSaveCoef));
/********************************************************/
fX[0] = g_sGasSaveCoef.uiCalibrationHchoAd[0];
fX[1] = g_sGasSaveCoef.uiCalibrationHchoAd[2];
fX[2] = g_sGasSaveCoef.uiCalibrationHchoAd[1];
// fX[0] = 785;
// fX[1] = 1015;
// fX[2] = 1270;
fY[0] = g_sGasSaveCoef.uiCalibrationHchoConcentration[0];
fY[1] = g_sGasSaveCoef.uiCalibrationHchoConcentration[2];
fY[2] = g_sGasSaveCoef.uiCalibrationHchoConcentration[1];
//
// fX[0] = 785;
// fX[1] = 1015;
// fX[2] = 1270;
//
// fY[0] = 19;
// fY[1] = 50;
// fY[2] = 111;
/******************************************************/
for(i=0;i<3;i++)//n
{
fA[0][0]=fA[0][0]+fX[i]*fX[i];
fA[0][1]=fA[0][1]+fX[i];
fA[0][2]=3;
fA[0][3]=fA[0][3]+fY[i];
fA[1][0]=fA[1][0]+fX[i]*fX[i]*fX[i];
fA[1][1]=fA[1][1]+fX[i]*fX[i];
fA[1][2]=fA[1][2]+fX[i];
fA[1][3]=fA[1][3]+fX[i]*fY[i];
fA[2][0]=fA[2][0]+fX[i]*fX[i]*fX[i]*fX[i];
fA[2][1]=fA[2][1]+fX[i]*fX[i]*fX[i];
fA[2][2]=fA[2][2]+fX[i]*fX[i];
fA[2][3]=fA[2][3]+fX[i]*fX[i]*fY[i];
}
for(k=0;k<3;k++)//???
{
p=fA[k][k];
for(j=k;j<4;j++)
fA[k][j]/=p;
for(i=0;i<3;i++)
if(i!=k)
{
aik=fA[i][k];
for(j=k;j<4;j++)
fA[i][j]=fA[i][j]-aik*fA[k][j];
}
}
//printf("x1=%18.9f \n x2=%18.9f \n x3=%18.9f\n",fA[0][3],fA[1][3],fA[2][3]);
g_sGasSaveCoef.dEquationA = fA[0][3];
g_sGasSaveCoef.dEquationB = fA[1][3];
g_sGasSaveCoef.dEquationC = fA[2][3];
Flash_WriteData(FLASH_USER_START_ADDR,(uint32_t *)&g_sGasSaveCoef,sizeof(g_sGasSaveCoef));
g_sGasTrait2P.ucCalculationFlag &= ~(0x01);
}
if( syscolck.t800ms && (syscolck.t2ms == 0)) {
ADC_GetFilterResult();
syscolck.t800ms = 0;
}
if( syscolck.t2s && (syscolck.t2ms == 0)) {
// Can read the s
// Flash_ReadData(FLASH_USER_START_ADDR,(uint32_t *)&g_sGasSaveCoef,sizeof(g_sGasSaveCoef));
if(g_sGasTrait2P.ucPrintDebugFlag){
printf("HchoAd0 = %d , HchoCal0 = %d , HchoAd1 %d, HchoCal1 = %d , HchoAd2 %d, HchoCal2 = %d , HchoA = %f , ,HchoB = %f ,HchoC = %f ",g_sGasSaveCoef.uiCalibrationHchoAd[0] ,
g_sGasSaveCoef.uiCalibrationHchoConcentration[0], g_sGasSaveCoef.uiCalibrationHchoAd[1], g_sGasSaveCoef.uiCalibrationHchoConcentration[1],
g_sGasSaveCoef.uiCalibrationHchoAd[2], g_sGasSaveCoef.uiCalibrationHchoConcentration[2],
g_sGasSaveCoef.dEquationA ,g_sGasSaveCoef.dEquationB , g_sGasSaveCoef.dEquationC );
}
if(g_sGasTrait2P.ucPrintCalFlag){
printf("HchoFlip5 = %d , HchoAvg = %d , HchoFinal = %f , HchoiResult %d, uiHchoLife = %d ", (g_sGasTrait2P.usOriginalSensorOriginalFlip[3]*3000/0xFFF),
(uint32_t)g_sGasTrait2P.uiOriginalHchoVoltageAvg, g_sGasTrait2P.fFinalResult , g_sGasTrait2P.uiHchoResult,
g_sGasSaveCoef.uiHchoLife );
}
syscolck.t2s = 0;
}
}
}