图像处理之三种常见双立方插值算法
图像处理之三种常见双立方插值算法
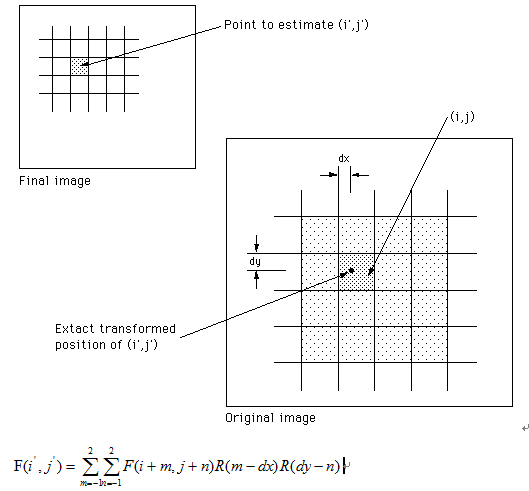
双立方插值计算涉及到16个像素点,其中(i’, j’)表示待计算像素点在源图像中的包含
小数部分的像素坐标,dx表示X方向的小数坐标,dy表示Y方向的小数坐标。具体
可以看下图:
根据上述图示与双立方插值的数学表达式可以看出,双立方插值本质上图像16个像素点
权重卷积之和作为新的像素值。
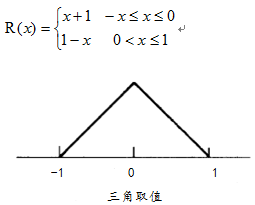
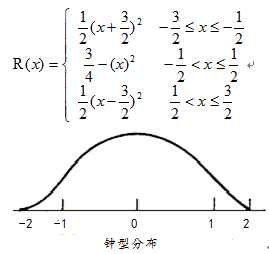
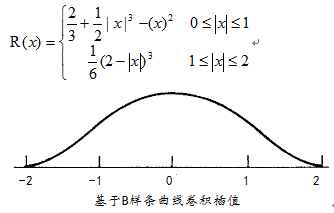
其中R(x)表示插值表达式,可以根据需要选择的表达式不同。常见有基于三角取值、Bell
分布表达、B样条曲线表达式。
1. 基于三角形采样数学公式为
最简单的线性分布,代码实现如下:
private double triangleInterpolation( double f )
{
f = f / 2.0;
if( f < 0.0 )
{
return ( f + 1.0 );
}
else
{
return ( 1.0 - f );
}
}Bell分布采样数学公式基于三次卷积计算实现。代码实现如下:
private double bellInterpolation( double x )
{
double f = ( x / 2.0 ) * 1.5;
if( f > -1.5 && f < -0.5 )
{
return( 0.5 * Math.pow(f + 1.5, 2.0));
}
else if( f > -0.5 && f < 0.5 )
{
return 3.0 / 4.0 - ( f * f );
}
else if( ( f > 0.5 && f < 1.5 ) )
{
return( 0.5 * Math.pow(f - 1.5, 2.0));
}
return 0.0;
}是一种基于多项式的四次卷积的采样计算,代码如下:
private double bspLineInterpolation( double f )
{
if( f < 0.0 )
{
f = -f;
}
if( f >= 0.0 && f <= 1.0 )
{
return ( 2.0 / 3.0 ) + ( 0.5 ) * ( f* f * f ) - (f*f);
}
else if( f > 1.0 && f <= 2.0 )
{
return 1.0 / 6.0 * Math.pow( ( 2.0 - f ), 3.0 );
}
return 1.0;
}package com.gloomyfish.zoom.study;
import java.awt.image.BufferedImage;
import java.awt.image.ColorModel;
import com.gloomyfish.filter.study.AbstractBufferedImageOp;
public class BicubicInterpolationFilter extends AbstractBufferedImageOp {
public final static int TRIANGLE__INTERPOLATION = 1;
public final static int BELL__INTERPOLATION = 2;
public final static int BSPLINE__INTERPOLATION = 4;
public final static int CATMULLROOM__INTERPOLATION = 8;
public final static double B = 0.0;
public final static double C = 0.5; // constant
private int destH; // zoom height
private int destW; // zoom width
private int type;
public BicubicInterpolationFilter()
{
this.type = BSPLINE__INTERPOLATION;
}
public void setType(int type) {
this.type = type;
}
public void setDestHeight(int destH) {
this.destH = destH;
}
public void setDestWidth(int destW) {
this.destW = destW;
}
private double bellInterpolation( double x )
{
double f = ( x / 2.0 ) * 1.5;
if( f > -1.5 && f < -0.5 )
{
return( 0.5 * Math.pow(f + 1.5, 2.0));
}
else if( f > -0.5 && f < 0.5 )
{
return 3.0 / 4.0 - ( f * f );
}
else if( ( f > 0.5 && f < 1.5 ) )
{
return( 0.5 * Math.pow(f - 1.5, 2.0));
}
return 0.0;
}
private double bspLineInterpolation( double f )
{
if( f < 0.0 )
{
f = -f;
}
if( f >= 0.0 && f <= 1.0 )
{
return ( 2.0 / 3.0 ) + ( 0.5 ) * ( f* f * f ) - (f*f);
}
else if( f > 1.0 && f <= 2.0 )
{
return 1.0 / 6.0 * Math.pow( ( 2.0 - f ), 3.0 );
}
return 1.0;
}
private double triangleInterpolation( double f )
{
f = f / 2.0;
if( f < 0.0 )
{
return ( f + 1.0 );
}
else
{
return ( 1.0 - f );
}
}
private double CatMullRomInterpolation( double f )
{
if( f < 0.0 )
{
f = Math.abs(f);
}
if( f < 1.0 )
{
return ( ( 12 - 9 * B - 6 * C ) * ( f * f * f ) +
( -18 + 12 * B + 6 *C ) * ( f * f ) +
( 6 - 2 * B ) ) / 6.0;
}
else if( f >= 1.0 && f < 2.0 )
{
return ( ( -B - 6 * C ) * ( f * f * f )
+ ( 6 * B + 30 * C ) * ( f *f ) +
( - ( 12 * B ) - 48 * C ) * f +
8 * B + 24 * C)/ 6.0;
}
else
{
return 0.0;
}
}
@Override
public BufferedImage filter(BufferedImage src, BufferedImage dest) {
int width = src.getWidth();
int height = src.getHeight();
if (dest == null)
dest = createCompatibleDestImage(src, null);
int[] inPixels = new int[width * height];
int[] outPixels = new int[destH * destW];
getRGB(src, 0, 0, width, height, inPixels);
float rowRatio = ((float) height) / ((float) destH);
float colRatio = ((float) width) / ((float) destW);
int index = 0;
for (int row = 0; row < destH; row++) {
int ta = 0, tr = 0, tg = 0, tb = 0;
double srcRow = ((float) row) * rowRatio;
// 获取整数部分坐标 row Index
double j = Math.floor(srcRow);
// 获取行的小数部分坐标
double t = srcRow - j;
for (int col = 0; col < destW; col++) {
double srcCol = ((float) col) * colRatio;
// 获取整数部分坐标 column Index
double k = Math.floor(srcCol);
// 获取列的小数部分坐标
double u = srcCol - k;
double[] rgbData = new double[3];
double rgbCoffeData = 0.0;
for(int m=-1; m<3; m++)
{
for(int n=-1; n<3; n++)
{
int[] rgb = getPixel(j+m, k+n, width, height, inPixels);
double f1 = 0.0d;
double f2 = 0.0d;
if(type == TRIANGLE__INTERPOLATION)
{
f1 = triangleInterpolation( ((double) m ) - t );
f2 = triangleInterpolation ( -(( (double) n ) - u ) );
}
else if(type == BELL__INTERPOLATION)
{
f1 = bellInterpolation( ((double) m ) - t );
f2 = bellInterpolation ( -(( (double) n ) - u ) );
}
else if(type == BSPLINE__INTERPOLATION)
{
f1 = bspLineInterpolation( ((double) m ) - t );
f2 = bspLineInterpolation ( -(( (double) n ) - u ) );
}
else
{
f1 = CatMullRomInterpolation( ((double) m ) - t );
f2 = CatMullRomInterpolation ( -(( (double) n ) - u ) );
}
// sum of weight
rgbCoffeData += f2*f1;
// sum of the RGB values
rgbData[0] += rgb[0] * f2 * f1;
rgbData[1] += rgb[1] * f2 * f1;
rgbData[2] += rgb[2] * f2 * f1;
}
}
ta = 255;
// get Red/green/blue value for sample pixel
tr = (int) (rgbData[0]/rgbCoffeData);
tg = (int) (rgbData[1]/rgbCoffeData);
tb = (int) (rgbData[2]/rgbCoffeData);
index = row * destW + col;
outPixels[index] = (ta << 24) | (clamp(tr) << 16)
| (clamp(tg) << 8) | clamp(tb);
}
}
setRGB(dest, 0, 0, destW, destH, outPixels);
return dest;
}
public int clamp(int value) {
return value > 255 ? 255 :
(value < 0 ? 0 : value);
}
private int[] getPixel(double j, double k, int width, int height,
int[] inPixels) {
int row = (int) j;
int col = (int) k;
if (row >= height) {
row = height - 1;
}
if (row < 0) {
row = 0;
}
if (col < 0) {
col = 0;
}
if (col >= width) {
col = width - 1;
}
int index = row * width + col;
int[] rgb = new int[3];
rgb[0] = (inPixels[index] >> 16) & 0xff;
rgb[1] = (inPixels[index] >> 8) & 0xff;
rgb[2] = inPixels[index] & 0xff;
return rgb;
}
public BufferedImage createCompatibleDestImage(
BufferedImage src, ColorModel dstCM) {
if ( dstCM == null )
dstCM = src.getColorModel();
return new BufferedImage(dstCM,
dstCM.createCompatibleWritableRaster(destW, destH),
dstCM.isAlphaPremultiplied(), null);
}
}
双立方插值放大以后:
基于这里三种方法实现的双立方插值以后图片跟原图像相比,都有一定模糊
这里时候可以通过后续处理实现图像锐化与对比度提升即可得到Sharpen版本
当然也可以通过寻找更加合适的R(x)函数来实现双立方卷积插值过程时保留
图像边缘与对比度。
转载请务必注明