论文笔记(one-shot object detection)
论文题目:A training-Free, one-shot detection framework for Geospatial Objects in Remote Sensing Images
提出一种新的目标检测思路,用来解决小样本情况下的目标检测问题.
来源:cvpr 2019
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/pdf/1904.02302.pdf
深度学习目标检测的现状(需要大量的数据,而且非常耗时,难以满足小样本条件下的):现有的监督学习方法are data-hungry and time-comsuming.
This restriction makes them unsuitable for limited data and urgent tasks, especially in the applications of remote sensing.
本文提出的研究方法:受启发于人类可以从小样本中快速学习的能力,propose a training-free, one-shot geospatial object detection framework for remote sensing images.
主要由以下几部分组成:
(1) a feature extractor with remote sensing domain knowledge;
(2) a multi-level feature fusion method
(3) a novel similarity metric method
(4) a 2-stage object detection pipeline.
实验结果:在污水处理厂和机场检测上测试了本文提出的方法.
论文特点:可以作为training-free, one-shot地理空间目标检测的baseline.
1. 介绍
启发:人类可以只看目标一次,就可以达到对目标的快速识别能力,但是机器目前无法达到这样的水平. 也就是在小样本情况下的深度学习目标检测仍然存在很大的困难.
在遥感图像领域,相比自然图像而言,数据相对要少很多,同时由于遥感图像覆盖范围广,背景比较复杂,目标的大小尺寸则相对更小,导致现有的监督学习方法性能受限,特别是检测新的目标的时候,模型的灵活性较差,通常需要再次对新数据进行训练.
因此, 如何解决遥感图像领域的小样本快速目标检测和识别问题,是当前急需解决的问题.
本文的思路:提出一种training-free, one-shot地理空间目标检测框架. We train the model on image classification task and test it on object detection task. As a result, it does not require any labelled data for the object detection task. 具体来说,我们在遥感图像分类数据集上训练一个特征提取器, 这样特征提取器可以学习一些遥感领域的知识. 当特征提取器训练好后,本文的方法就不需要再训练了,也就是说training-free. 与之前在目标检测任务中训练模型不同,通过设计一个更好的处理方式来赋予模型检测新类别的能力.
思路的实现过程:给定一个小的查询图像和一个大的目标图像,特征提取器可以提取特征,然后通过计算他们之间的相似性来在target image中寻找相似的区域.
本文方法的特点:
(1) training-free for the object detection;
(2)类别不可知的方法,也就是说可以检测任何类别的目标.
(3) 可以摆脱目标样本标注耗时,工作量大的问题;
(4)灵活性强,可以扩展到few-shot learning领域.
主要贡献:
(1) 提出了一个什么方-we propose a training-free, one-shot object detection framework, which consists of a feature extractor, a multi-level feature fusion method and a novel similarity metric method.
(2) 设计了一个检测流-we design a 2-stage detection pipeline to improve the detection performance, and proves its effectiveness by the experiment.
(3) 获得了非常好的性能-the proposed method has achieved a promising result for the sewage treatment plant and airport detections in remote sensing images.
2. 方法
目的:to detect geospatial objects on a large target image with only a single query image of a geospatial object. 通过一个查询的地理空间目标图像来检测目标.
需要考虑的三个问题?
(1) How to extract the image features?
(2) How to find the similar regions?
(3) How to get the objects bounding boxes?
方法的总体流程如下:
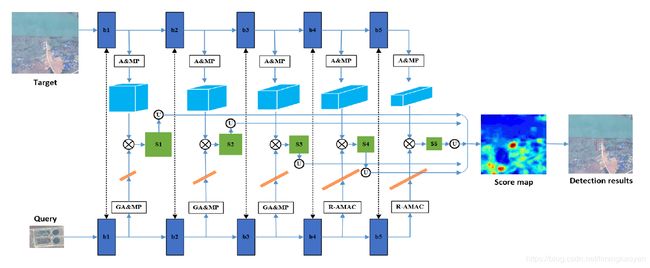
2.1 特征提取
采用VGG16在NWPU-RESISC45数据集上进行训练后,作为特征提取器.
NWPU-RESISC45数据集包含31500幅图像,包含45种不同场景,每个类别700张图片。
用训练后的VGG16模型作为特征提取器提取查询图像和target图像的特征.
2.2 多级特征融合方法
R-MAC (Regional Maximum Activation of Convolutions) is a feature encoding method, which encodes a set of regions into short vectors over the feature maps of size WxHxC, 如下图所示.
 更具体些,R-MAX samples a lot of square regions uniformly at L different scales. When scale l is 1, the width and height of a region are both equal to min (W, H), and the number of regions is m.
更具体些,R-MAX samples a lot of square regions uniformly at L different scales. When scale l is 1, the width and height of a region are both equal to min (W, H), and the number of regions is m.
…
2.3 相似度量
Similarity can be measured by the convolution of the query feature vector and the target features for each convolution block. 因此,可以得到5个score map, 将他们上采样输入图像的大小. 然后, 最终的score map是这5个上采样score map的平均.
2.4 两阶段检测流程
最后相似区域的阈值设置的公式为:
threshold = (meanscore + maxscore) / 2
如果target images中得分高于first threshold=0.7, 则将其裁剪下来,并输入到特征提取器中,得到更优的目标特征. 然后,通过对query feature和target feature进行点积运算,得到similarity score. 最后,那些得分高于second threshold=0.9的区域保留下来作为最终的检测结果.
3. 实验
3.1 污水处理厂检测
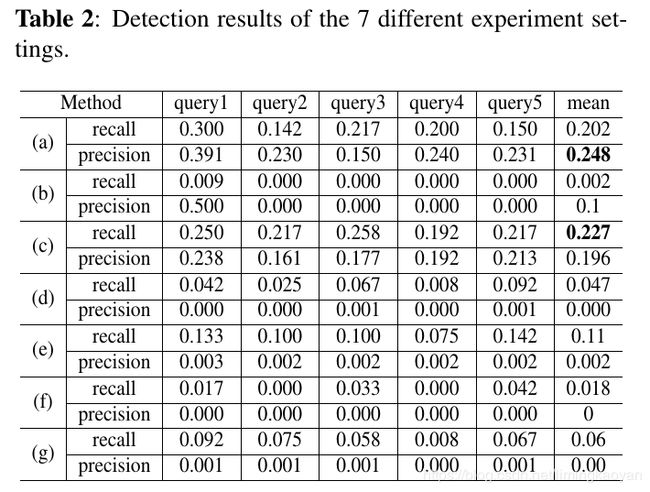
随机选取了5个查询图像,评估了不同情况下的性能.

3.1.1 特征融合方法分析
这部分,比较了7种不同的特征融合方法.

A&MP表示平均池化和最大池化特征的级联.
GA&MP表示全局平均池化和全局最大池化特征的级联.
(a) multi-level特征融合方法:Similarity are computed with the query and target features of all blocks.
对于query特征,采用global- and max-pooling for block 1-3 and R-AMAC for block 4-5.
对于target特征,we execute global average- and max-pooling for all blocks.
(b) Block 5 特征:
© 平均和最大池化特征:
(d) 平均池化特征:
(e) 最大池化特征:
(f) 平均池化特征 + R-AAC (Regional Average Activation of Convolutions)特征:
(g) 最大池化特征 + R-MAC特征:
3.1.2 与一阶段和二阶段方法比较

3.2 飞机场检测
4. 结论
提出了:
方法特点:
实验结果:
