Thermal框架分析
文章目录
- Thermal概况
- Thermal框架结构
- 1.Thermal zone device
- 2.Thermal cooling device
- 3.Thermal governor
- 4.Thermal core
Thermal概况
Thermal是Linux内核中的温度控制模块,主要用于控制在系统运行过程中芯片产生的热量,通过传感器设备实时监控设备温度,在温度发生变化时候通过一定的cooling机制促使芯片和外设工作环境温度能够稳定在安全的范围内。因此,不管是在Linux或者Andriod系统中,Thermal都将对产品的热设计、功耗及CPU频率进行动态平衡性管理。
Thermal Design重要性有:过热导致CPU/GPU性能下降、影响用户体验以及会影响器件的使用寿命。
本文将以目前(2019-10-24)最新的Llinux kernel4.4版本的Thermal模块源码进行相应的框架分析,逐行分析kernel模块代码,旨在理解Thermal模块的整体框架功能及实现方式,为了方便在源码中查阅,相应位置会备注内核源码所在位置。
Thermal框架结构
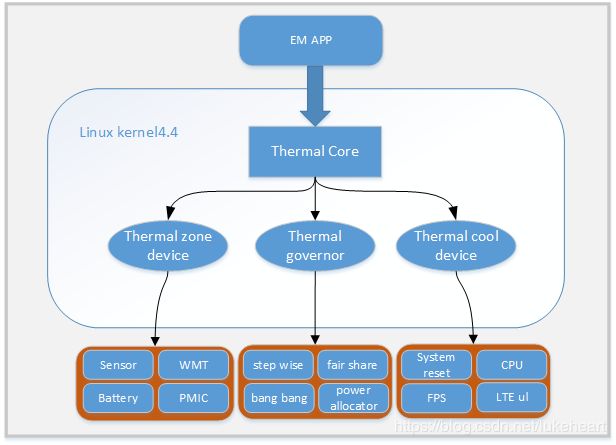
1.Thermal zone device:获取温度的设备。作为框架读取温度的输入,同时从设备树中读取参数注册设备,一般一个Driver对应一个thermal zone。
2.Thermal cooling device:控制温度的设备。CPU/GPU一是可以加快散热,二是可以降低产热量。
3.Thermal governor:控制温度的策略(方法)。通过不同的算法实现不同的降温手段,如:set_ wise,fair_share等等。
4.Thermal core:Thermal框架的中枢核心,同时作为User space和kernel的接口。
1.Thermal zone device
//源码位置:kernel/include/linux/thermal.h
/*定义thermal_zone_device结构体*/
struct thermal_zone_device {
int id; //每个设备对应的唯一设备ID
char type[THERMAL_NAME_LENGTH];//设备类型
struct device device;
struct thermal_attr *trip_temp_attrs;//sysfs的触发点属性:触发温度
struct thermal_attr *trip_type_attrs;//sysfs的触发点类型
struct thermal_attr *trip_hyst_attrs;
void *devdata;//设备数据指针
int trips;//thermal模块支持的触发点数量
int passive_delay;//执行设备cooling时,两次轮询之间要等待的毫秒数
int polling_delay;//检查触发点是否通过,两次轮询之间等待的毫秒数
int temperature;//当前温度。This is only for core code,drivers should use thermal_zone_get_temp() to get the current temperature
int last_temperature;//先前的温度读取
int emul_temperature;
int passive;//如果约过了触发点,置1,否则为0.
unsigned int forced_passive;
struct thermal_zone_device_ops *ops;//设备的操作函数(核心!!!)
struct thermal_zone_params *tzp;//thermal zone 参数
struct thermal_governor *governor;//定义降温策略结构体governor
void *governor_data;//governor指针
struct list_head thermal_instances;
struct idr idr;
struct mutex lock;//给Thermal_instances列表加锁保护
struct list_head node;//thermal_tz_list中的节点(在thermal_core.c中)
struct delayed_work poll_queue;//利用poll轮询机制来处理延迟工作
};Thermal zone device源码位置:kernel/include/linux/thermal.h。thermal_zone_device结构体的代码各个参数的分析如上图所示,thermal_zone_device结构中的struct thermal_zone_device_ops 函数将对device进行相应的操作,相对而言比较重要,见下图分析。
//源码位置:kernel/include/linux/thermal.h
/*thermal_zone_device_ops设备的操作函数*/
struct thermal_zone_device_ops {
/*绑定函数*/
int (*bind) (struct thermal_zone_device *,
struct thermal_cooling_device *);
/*解除绑定函数*/
int (*unbind) (struct thermal_zone_device *,
struct thermal_cooling_device *);
/*温度获取函数*/
int (*get_temp) (struct thermal_zone_device *, int *);
int (*get_mode) (struct thermal_zone_device *,
enum thermal_device_mode *);
int (*set_mode) (struct thermal_zone_device *,
enum thermal_device_mode);
int (*get_trip_type) (struct thermal_zone_device *, int,
enum thermal_trip_type *);
/*获取触发点函数*/
int (*get_trip_temp) (struct thermal_zone_device *, int, int *);
/*设置触发点函数函数*/
int (*set_trip_temp) (struct thermal_zone_device *, int, int);
int (*get_trip_hyst) (struct thermal_zone_device *, int, int *);
int (*set_trip_hyst) (struct thermal_zone_device *, int, int);
int (*get_crit_temp) (struct thermal_zone_device *, int *);
int (*set_emul_temp) (struct thermal_zone_device *, int);
int (*get_trend) (struct thermal_zone_device *, int,
enum thermal_trend *);
int (*notify) (struct thermal_zone_device *, int,
enum thermal_trip_type);
};RTFSC发现,设备的操作函数主要有三个比较重要的功能:
1.bind函数:绑定函数主要在LTF(Liunx Thermal Framework)中实现,zone_device和cooling_device会分别向LTF注册,并在LTF中实现绑定功能。
2.温度获取函数:温度的获取主要通过各个传感器的数据采集,经ADC后将模拟信号转变为数字信号,在device的驱动中实现数据的上报(向上封装),每个zone可以看做是一个温度控制区域,管理着一个特定的传感器数据,温度获取函数会去读取相应的zone的温度值。
3.触发点获取函数:set_trip_temp会先自设置trip的初始值,get_trip_temp可以获取触发温度值,通过和获取的温度值比较,governor将会执行相应的策略来实现设备的温度控制。
2.Thermal cooling device
Thermal cooling device/源码位置:kernel/include/linux/thermal.h,cooling device即控制温度的设备。cooling device 维护一个cooling等级,即state,一般state越高即系统的冷却需求越高。cooling device根据不同等级的冷却需求进行冷却行为。 cooling device只根据state进行冷却操作,是实施者,而state的计算由thermal governor完成。【Linux电源管理(五)thermal】
//源码位置:kernel/include/linux/thermal.h
struct thermal_cooling_device {
int id;
char type[THERMAL_NAME_LENGTH];
struct device device;
struct device_node *np;
void *devdata;
/* thermal_cooling_device_ops温控操作函数 */
const struct thermal_cooling_device_ops *ops;
bool updated; /* true if the cooling device does not need update */
struct mutex lock; /* protect thermal_instances list加锁进行保护 */
struct list_head thermal_instances;
struct list_head node;
```c
//源码位置:kernel/include/linux/thermal.h
struct thermal_cooling_device_ops {
/* 获取最大cooling等级 */
int (*get_max_state) (struct thermal_cooling_device *, unsigned long *);
/* 获取当前的cooling等级 */
int (*get_cur_state) (struct thermal_cooling_device *, unsigned long *);
/* 设置当前的cooling等级 */
int (*set_cur_state) (struct thermal_cooling_device *, unsigned long);
int (*state2power)(struct thermal_cooling_device *,
/*获取当前当前CPU的功耗值,包括dynamic功耗和static功耗。*/
int (*get_requested_power)(struct thermal_cooling_device *,
struct thermal_zone_device *, u32 *);
/*将CPU cooling状态转换成需要消耗的功耗值*/
int (*state2power)(struct thermal_cooling_device *,
struct thermal_zone_device *, unsigned long, u32 *);
/*将CPU所能获取的最大功耗值转换成cooling状态 */
int (*power2state)(struct thermal_cooling_device *,
struct thermal_zone_device *, u32, unsigned long *);
};thermal_cooling_device_ops操作函数的具体实现主要是根据governor提供的策略,进行相关的降温具体操作,既可以是降频从而降低热量的产生,也可以是增大降温操作的幅度,比如使用散热片或者风扇进行物理降温。
3.Thermal governor
//源码位置:kernel/include/linux/thermal.h
/**
* struct thermal_governor - structure that holds thermal governor information
* @name: name of the governor
* @bind_to_tz: callback called when binding to a thermal zone. If it
* returns 0, the governor is bound to the thermal zone,
* otherwise it fails.
* @unbind_from_tz: callback called when a governor is unbound from a
* thermal zone.
* @throttle: callback called for every trip point even if temperature is
* below the trip point temperature
* @governor_list: node in thermal_governor_list (in thermal_core.c)
*/
struct thermal_governor {
char name[THERMAL_NAME_LENGTH];
/*绑定到thermal zone时的回调函数*/
int (*bind_to_tz)(struct thermal_zone_device *tz);
/*解除绑定函数*/
void (*unbind_from_tz)(struct thermal_zone_device *tz);
/*throttle函数是governor的核心回调程序,*/
int (*throttle)(struct thermal_zone_device *tz, int trip);
struct list_head governor_list;
};int (*bind_to_tz)(struct thermal_zone_device *tz)是绑定到thermal zone时的回调函数,如果它返回0,governor绑定到thermal zone,否则失败。
int (*throttle)(struct thermal_zone_device tz, int trip)函数是governor的核心回调程序,所有的策略(如下/ Default Thermal Governor */)都将通过这个回调函数实现。
//源码位置:kernel/include/linux/thermal.h
/* Default Thermal Governor */
#if defined(CONFIG_THERMAL_DEFAULT_GOV_STEP_WISE)
#define DEFAULT_THERMAL_GOVERNOR "step_wise"
#elif defined(CONFIG_THERMAL_DEFAULT_GOV_FAIR_SHARE)
#define DEFAULT_THERMAL_GOVERNOR "fair_share"
#elif defined(CONFIG_THERMAL_DEFAULT_GOV_USER_SPACE)
#define DEFAULT_THERMAL_GOVERNOR "user_space"
#elif defined(CONFIG_THERMAL_DEFAULT_GOV_POWER_ALLOCATOR)
#define DEFAULT_THERMAL_GOVERNOR "power_allocator"
#endif上图代码是thermal的 governor默认的一些调整策略:
1.step_wise:开环控制。基于温度阈值和趋势,逐步浏览每个cooling设备的cooling等级。
2.fair_share:基于权重。 根据分配的权重划分确定cooling设备等级。
3.user_space:将热区的控制权移交给用户空间,用户可以客制化相关的热功耗参数。
4.power_allocator:闭环控制。功率基于每个相关设备的功率,温度和当前功耗。
4.Thermal core
thermar core作为中枢注册governor,注册Thermal类,并且基于Device Tree注册Thermal Zone;提供Thermal zone注册函数,Cooling Device注册函数,提供将Cooling设备绑定到Zone的函数,一个Thermal Zone可以有多个Cooling设备;同时还提供一个核心函数Thermal_zone_deviceupdate作为Thermal中断处理函数和轮询函数,轮询时间会根据不同Trip Delay调节。
Thermal core驱动源码位置:kernel/drivers/thermal/thermal_core.c
1.Thermal core驱动的入口函数
//源码位置:kernel/drivers/thermal/thermal_core.c
static int __init thermal_init(void)
{
int result;
/* thermal_register_governors()注册了默认的调整策略函数*/
result = thermal_register_governors();
if (result)
goto error;
/*创建一个class 型的类*/
result = class_register(&thermal_class);
if (result)
goto unregister_governors;
result = genetlink_init();
if (result)
goto unregister_class;
result = of_parse_thermal_zones();
if (result)
goto exit_netlink;
return 0;thermal_register_governors()注册了以下默认的调整策略:
thermal_gov_step_wise_unregister();
thermal_gov_fair_share_unregister();
thermal_gov_bang_bang_unregister();
thermal_gov_user_space_unregister();
thermal_gov_power_allocator_unregister();
2.Thermal core驱动的注册函数
//源码位置:kernel/drivers/thermal/thermal_core.c
struct thermal_zone_device *thermal_zone_device_register(const char *type,
int trips, int mask, void *devdata,
struct thermal_zone_device_ops *ops,
struct thermal_zone_params *tzp,
int passive_delay, int polling_delay)
{
struct thermal_zone_device *tz;
enum thermal_trip_type trip_type;
int result;
int count;
int passive = 0;
struct thermal_governor *governor;
······//代码过长,省略
}thermal_zone_device_register():注册一个新的thermal_zone驱动设备,返回值是指向创建thermal_zone_device的指针。
const char *type:设备类型。
int trips:thermal_zone支持的触发点数。
int mask:指示触发点的可写的字符位。
void *devdata:设备的私有数据指针。
struct thermal_zone_device_ops *ops:thermal_zone_device的标准回调函数。
struct thermal_zone_params *tzp:thermal zone平台参数
passive_delay:两次轮询之间等待的毫秒数
polling_delay:检查时两次轮询之间要等待的毫秒数
3.Thermal zone/cooling device 注册过程中thermal core会调用绑定函数,绑定的过程最主要是一个cooling device 绑定到一个thermal_zone的触发点上。【Linux Thermal】
//源码位置:kernel/drivers/thermal/thermal_core.c
/**
* thermal_zone_bind_cooling_device() - bind a cooling device to a thermal zone
* @tz: pointer to struct thermal_zone_device
* @trip: indicates which trip point the cooling devices is
* associated with in this thermal zone.
* @cdev: pointer to struct thermal_cooling_device
* @upper: the Maximum cooling state for this trip point.
* THERMAL_NO_LIMIT means no upper limit,
* and the cooling device can be in max_state.
* @lower: the Minimum cooling state can be used for this trip point.
* THERMAL_NO_LIMIT means no lower limit,
* and the cooling device can be in cooling state 0.
* @weight: The weight of the cooling device to be bound to the
* thermal zone. Use THERMAL_WEIGHT_DEFAULT for the
* default value
*
* This interface function bind a thermal cooling device to the certain trip
* point of a thermal zone device.
* This function is usually called in the thermal zone device .bind callback.
*
* Return: 0 on success, the proper error value otherwise.
*/
int thermal_zone_bind_cooling_device(struct thermal_zone_device *tz,
int trip,
struct thermal_cooling_device *cdev,
unsigned long upper, unsigned long lower,
unsigned int weight)
{
struct thermal_instance *dev;//用来描述zone和cooling设备在某个trip 上的关系
struct thermal_instance *pos;
struct thermal_zone_device *pos1;
struct thermal_cooling_device *pos2;
unsigned long max_state;
int result, ret;
if (trip >= tz->trips || (trip < 0 && trip != THERMAL_TRIPS_NONE))
return -EINVAL;
/*使得pos1指向tz设备*/
list_for_each_entry(pos1, &thermal_tz_list, node) {
if (pos1 == tz)
break;
}
/*pos2指向cooling设备*/
list_for_each_entry(pos2, &thermal_cdev_list, node) {
if (pos2 == cdev)
break;
}
if (tz != pos1 || cdev != pos2)
return -EINVAL;
/*使用cooling设备的get_max_state函数,得到最大等级状态*/
ret = cdev->ops->get_max_state(cdev, &max_state);
if (ret)
return ret;
/* lower default 0, upper default max_state */
lower = lower == THERMAL_NO_LIMIT ? 0 : lower;
upper = upper == THERMAL_NO_LIMIT ? max_state : upper;
if (lower > upper || upper > max_state)
return -EINVAL;
dev =
kzalloc(sizeof(struct thermal_instance), GFP_KERNEL);//开辟内核内存空间
if (!dev)//判断是否开辟成功
return -ENOMEM;
dev->tz = tz;//dev得到zone设备
dev->cdev = cdev; //dev得到cooling设备
dev->trip = trip; //dev得到温度触发的那个点
dev->upper = upper; //dev得到上限
dev->lower = lower; //dev得到下限
dev->target = THERMAL_NO_TARGET;
dev->weight = weight;
/*调用idr_alloc,动态分配一个id号,并将该id号做为dev的id号*/
result = get_idr(&tz->idr, &tz->lock, &dev->id);
if (result)
goto free_mem;
//用id号做成dev的name
sprintf(dev->name, "cdev%d", dev->id);
//一个kobject对象就对应sys目录中的一个设备,代表这些驱动的结构
//在tz->device.kobj目录下创建指向cdev->device.kobj目录的软链接,name为软链接文件名称。
result =
sysfs_create_link(&tz->device.kobj, &cdev->device.kobj, dev->name);
if (result)
goto release_idr;
sprintf(dev->attr_name, "cdev%d_trip_point", dev->id);
sysfs_attr_init(&dev->attr.attr);
//对属性进行赋值
dev->attr.attr.name = dev->attr_name;
dev->attr.attr.mode = 0444;
dev->attr.show = thermal_cooling_device_trip_point_show; //属性中show函数,具象为一个文件节点cat的调用
result = device_create_file(&tz->device, &dev->attr); //调用sysfs_create_file()在kobj对应的目录下创建attr对应的属性文件
if (result)
goto remove_symbol_link;
sprintf(dev->weight_attr_name, "cdev%d_weight", dev->id);
sysfs_attr_init(&dev->weight_attr.attr);
dev->weight_attr.attr.name = dev->weight_attr_name;
dev->weight_attr.attr.mode = S_IWUSR | S_IRUGO;
dev->weight_attr.show = thermal_cooling_device_weight_show;
dev->weight_attr.store = thermal_cooling_device_weight_store;
result = device_create_file(&tz->device, &dev->weight_attr);
if (result)
goto remove_trip_file;
mutex_lock(&tz->lock); //对zone列表上锁
mutex_lock(&cdev->lock); //对cooling列表上锁
//遍历zone下的thermal_instances列表,看看有没有跟这个准备加入的instances一样的
list_for_each_entry(pos, &tz->thermal_instances, tz_node)
if (pos->tz == tz && pos->trip == trip && pos->cdev == cdev) {
result = -EEXIST;//有就break
break;
}
if (!result) { //没有的话,就分别在zone和cooling的设备的instances列表中加入
list_add_tail(&dev->tz_node, &tz->thermal_instances);//把这个instances加入到zone的instances列表中
list_add_tail(&dev->cdev_node, &cdev->thermal_instances);//把这个instances加入到cooling的instances列表中
}
mutex_unlock(&cdev->lock);//对cooling列表解锁
mutex_unlock(&tz->lock); //对zone列表解锁
if (!result)
return 0;
device_remove_file(&tz->device, &dev->weight_attr);
remove_trip_file:
device_remove_file(&tz->device, &dev->attr);
remove_symbol_link:
sysfs_remove_link(&tz->device.kobj, dev->name);
release_idr:
release_idr(&tz->idr, &tz->lock, dev->id);
free_mem:
kfree(dev);
return result;
}本文旨在通过Liunx内核4.4分析Thermal框架,由于不同的平台在HAL层或者Framework层做了不同的客制化,所以需要根据不同的平台来设计相应的热功耗需求,linux内核层的thermal框架一般而言是不需要修改的,也是为了保证下层的统一性。客制化的需求在上层实现,如高通采用的thermal-engine,首先上层设置trip point,包括恢复温度与临界温度,thermal engine主要有algo_monitor运作sensor monitor起辅助作用够成。
作为从事功耗/性能优化方向工作者来讲,掌握thermal框架的机制原理对于在上层的功耗设计与实现有很大的帮助,从而定制出性能更稳定、功耗更低的Linux/Andriod系统。
PS:2019年10月24日,程序员节快乐,刚好在今天这个特殊的时间节点写了第一篇博客,虽然是看了好多大佬的参考文档,还是希望以后能坚持下去,早日成为一个优秀的程序员,加油。
参考文档:
Linux Thermal 框架解析
Thermal 框架梳理
Linux电源管理(五)thermal
Linux Thermal