ActivityManagerService之深入理解Activity启动流程(二)
一、Activity启动方式
activity的启动方式大体可以分三种:
1.通过桌面点击app图标方式启动
2.通过代码的方式启动startActivity
3.adb 的方式 adb shell am start -n 包名/类名 。
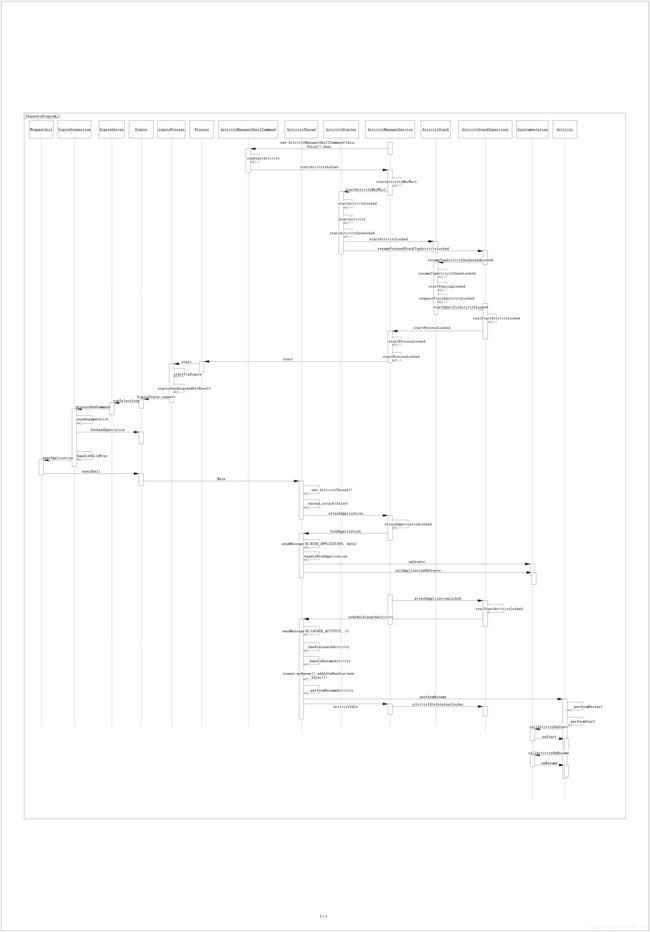
以上三种方式看去不同,其实在进入ActivityManagerService(AMS)都是相同的。第一种和第二种其实是相同的,区别是launcher帮忙我们填写要启动的intent值,这种方式的启动流程网上会有很多,大家可以参考其他博主的文章。第三种adb的方式是本博文需要讲的。先来一张Activity的启动流程图,如果觉得看不清楚的话,可以下载对应的pdf文档:https://download.csdn.net/download/Bill_xiao/12570703
对于上面的流程图我们对Activity的启动流程分三部分:1、应用进程创建前的task的寻找。2、应用进程创建。3、应用进程创建后activity的启动
二、Activity的启动流程
一、应用进程创建前的task的寻找
1.1.1
在输入adb shell am start -n 包名/类名 这个命令的时候,首先会调用Command这个bin程序,之后会调用AMS的onShellCommand的方法。
public void onShellCommand(FileDescriptor in, FileDescriptor out,
FileDescriptor err, String[] args, ShellCallback callback,
ResultReceiver resultReceiver) {
(new ActivityManagerShellCommand(this, false)).exec(
this, in, out, err, args, callback, resultReceiver);
}onShellCommand 方法直接new一个ActivityManagerShellCommand,执行exec。这个架构跟我们之前讲的PackageManagerService类似。
public int exec(Binder target, FileDescriptor in, FileDescriptor out, FileDescriptor err,
String[] args, ShellCallback callback, ResultReceiver resultReceiver) {
String cmd;
int start;
if (args != null && args.length > 0) {
cmd = args[0];
start = 1;
} else {
cmd = null;
start = 0;
}
init(target, in, out, err, args, callback, start);
// Log.i(" PackageManagerService-xiao", "ShellCommand exec cmd:"+cmd);
mCmd = cmd;
mResultReceiver = resultReceiver;
if (DEBUG) Log.i(TAG, "Starting command " + mCmd + " on " + mTarget);
int res = -1;
try {
res = onCommand(mCmd);
.............
} @Override
public int onCommand(String cmd) {
if (cmd == null) {
return handleDefaultCommands(cmd);
}
PrintWriter pw = getOutPrintWriter();
try {
switch (cmd) {
case "start":
case "start-activity":
return runStartActivity(pw);
case "startservice":
case "start-service":
return runStartService(pw, false);
case "startforegroundservice":
case "startfgservice":
case "start-foreground-service":
case "start-fg-service":
return runStartService(pw, true);
case "stopservice":
case "stop-service":
return runStopService(pw);
case "broadcast":
return runSendBroadcast(pw);
case "instrument":
getOutPrintWriter().println("Error: must be invoked through 'am instrument'.");
return -1;
case "trace-ipc":
return runTraceIpc(pw);
case "profile":
return runProfile(pw);
case "dumpheap":
return runDumpHeap(pw);
case "set-debug-app":
return runSetDebugApp(pw);
case "clear-debug-app":
return runClearDebugApp(pw);
case "set-watch-heap":
return runSetWatchHeap(pw);
case "clear-watch-heap":
return runClearWatchHeap(pw);
case "bug-report":
return runBugReport(pw);
case "force-stop":
return runForceStop(pw);
case "crash":
return runCrash(pw);
case "kill":
return runKill(pw);
case "kill-all":
return runKillAll(pw);
case "make-uid-idle":
return runMakeIdle(pw);
case "monitor":
return runMonitor(pw);
case "watch-uids":
return runWatchUids(pw);
case "hang":
return runHang(pw);
case "restart":
return runRestart(pw);
case "idle-maintenance":
return runIdleMaintenance(pw);
case "screen-compat":
return runScreenCompat(pw);
case "package-importance":
return runPackageImportance(pw);
case "to-uri":
return runToUri(pw, 0);
case "to-intent-uri":
return runToUri(pw, Intent.URI_INTENT_SCHEME);
case "to-app-uri":
return runToUri(pw, Intent.URI_ANDROID_APP_SCHEME);
case "switch-user":
return runSwitchUser(pw);
case "get-current-user":
return runGetCurrentUser(pw);
case "start-user":
return runStartUser(pw);
case "unlock-user":
return runUnlockUser(pw);
case "stop-user":
return runStopUser(pw);
case "is-user-stopped":
return runIsUserStopped(pw);
case "get-started-user-state":
return runGetStartedUserState(pw);
case "track-associations":
return runTrackAssociations(pw);
case "untrack-associations":
return runUntrackAssociations(pw);
case "get-uid-state":
return getUidState(pw);
case "get-config":
return runGetConfig(pw);
case "suppress-resize-config-changes":
return runSuppressResizeConfigChanges(pw);
case "set-inactive":
return runSetInactive(pw);
case "get-inactive":
return runGetInactive(pw);
case "send-trim-memory":
return runSendTrimMemory(pw);
case "display":
return runDisplay(pw);
case "stack":
return runStack(pw);
case "task":
return runTask(pw);
case "write":
return runWrite(pw);
case "attach-agent":
return runAttachAgent(pw);
case "supports-multiwindow":
return runSupportsMultiwindow(pw);
case "supports-split-screen-multi-window":
return runSupportsSplitScreenMultiwindow(pw);
case "update-appinfo":
return runUpdateApplicationInfo(pw);
case "no-home-screen":
return runNoHomeScreen(pw);
case "wait-for-broadcast-idle":
return runWaitForBroadcastIdle(pw);
default:
return handleDefaultCommands(cmd);
}
} catch (RemoteException e) {
pw.println("Remote exception: " + e);
}
return -1;
}看了onCommand的方法,不知道读者们有没有跟我一样的恍然大悟,之前adb am执行的命令在这里都能找到。我们也可以自己制定很多的客制化am 命令。既然原理想通了,后面无非就是找与AMS通信的代码函数。
int runStartActivity(PrintWriter pw) throws RemoteException {
Intent intent;
try {
intent = makeIntent(UserHandle.USER_CURRENT);
} catch (URISyntaxException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e.getMessage(), e);
}
if (mUserId == UserHandle.USER_ALL) {
getErrPrintWriter().println("Error: Can't start service with user 'all'");
return 1;
}
String mimeType = intent.getType();
if (mimeType == null && intent.getData() != null
&& "content".equals(intent.getData().getScheme())) {
mimeType = mInterface.getProviderMimeType(intent.getData(), mUserId);
}
do {
if (mStopOption) {
String packageName;
if (intent.getComponent() != null) {
packageName = intent.getComponent().getPackageName();
} else {
List activities = mPm.queryIntentActivities(intent, mimeType, 0,
mUserId).getList();
if (activities == null || activities.size() <= 0) {
getErrPrintWriter().println("Error: Intent does not match any activities: "
+ intent);
return 1;
} else if (activities.size() > 1) {
getErrPrintWriter().println(
"Error: Intent matches multiple activities; can't stop: "
+ intent);
return 1;
}
packageName = activities.get(0).activityInfo.packageName;
}
pw.println("Stopping: " + packageName);
pw.flush();
mInterface.forceStopPackage(packageName, mUserId);//停止进程
try {
Thread.sleep(250);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
}
ProfilerInfo profilerInfo = null;
if (mProfileFile != null || mAgent != null) {
ParcelFileDescriptor fd = null;
if (mProfileFile != null) {
fd = openOutputFileForSystem(mProfileFile);
if (fd == null) {
return 1;
}
}
profilerInfo = new ProfilerInfo(mProfileFile, fd, mSamplingInterval, mAutoStop,
mStreaming, mAgent);
}
pw.println("Starting: " + intent);
pw.flush();
intent.addFlags(Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK);
WaitResult result = null;
int res;
final long startTime = SystemClock.uptimeMillis();
ActivityOptions options = null;
if (mDisplayId != INVALID_DISPLAY) {
options = ActivityOptions.makeBasic();
options.setLaunchDisplayId(mDisplayId);
}
if (mStackId != INVALID_STACK_ID) {
options = ActivityOptions.makeBasic();
options.setLaunchStackId(mStackId);
}
if (mTaskId != INVALID_TASK_ID) {
options = ActivityOptions.makeBasic();
options.setLaunchTaskId(mTaskId);
if (mIsTaskOverlay) {
options.setTaskOverlay(true, true /* canResume */);
}
}
if (mWaitOption) {
result = mInterface.startActivityAndWait(null, null, intent, mimeType,
null, null, 0, mStartFlags, profilerInfo,
options != null ? options.toBundle() : null, mUserId);
res = result.result;
} else {
res = mInterface.startActivityAsUser(null, null, intent, mimeType,
null, null, 0, mStartFlags, profilerInfo,
options != null ? options.toBundle() : null, mUserId);
}
final long endTime = SystemClock.uptimeMillis();
PrintWriter out = mWaitOption ? pw : getErrPrintWriter();
boolean launched = false;
switch (res) {
case ActivityManager.START_SUCCESS:
launched = true;
break;
case ActivityManager.START_SWITCHES_CANCELED:
launched = true;
out.println(
"Warning: Activity not started because the "
+ " current activity is being kept for the user.");
break;
case ActivityManager.START_DELIVERED_TO_TOP:
launched = true;
out.println(
"Warning: Activity not started, intent has "
+ "been delivered to currently running "
+ "top-most instance.");
break;
case ActivityManager.START_RETURN_INTENT_TO_CALLER:
launched = true;
out.println(
"Warning: Activity not started because intent "
+ "should be handled by the caller");
break;
case ActivityManager.START_TASK_TO_FRONT:
launched = true;
out.println(
"Warning: Activity not started, its current "
+ "task has been brought to the front");
break;
case ActivityManager.START_INTENT_NOT_RESOLVED:
out.println(
"Error: Activity not started, unable to "
+ "resolve " + intent.toString());
break;
case ActivityManager.START_CLASS_NOT_FOUND:
out.println(NO_CLASS_ERROR_CODE);
out.println("Error: Activity class " +
intent.getComponent().toShortString()
+ " does not exist.");
break;
case ActivityManager.START_FORWARD_AND_REQUEST_CONFLICT:
out.println(
"Error: Activity not started, you requested to "
+ "both forward and receive its result");
break;
case ActivityManager.START_PERMISSION_DENIED:
out.println(
"Error: Activity not started, you do not "
+ "have permission to access it.");
break;
case ActivityManager.START_NOT_VOICE_COMPATIBLE:
out.println(
"Error: Activity not started, voice control not allowed for: "
+ intent);
break;
case ActivityManager.START_NOT_CURRENT_USER_ACTIVITY:
out.println(
"Error: Not allowed to start background user activity"
+ " that shouldn't be displayed for all users.");
break;
default:
out.println(
"Error: Activity not started, unknown error code " + res);
break;
}
out.flush();
if (mWaitOption && launched) {
if (result == null) {
result = new WaitResult();
result.who = intent.getComponent();
}
pw.println("Status: " + (result.timeout ? "timeout" : "ok"));
if (result.who != null) {
pw.println("Activity: " + result.who.flattenToShortString());
}
if (result.thisTime >= 0) {
pw.println("ThisTime: " + result.thisTime);
}
if (result.totalTime >= 0) {
pw.println("TotalTime: " + result.totalTime);
}
pw.println("WaitTime: " + (endTime-startTime));
pw.println("Complete");
pw.flush();
}
mRepeat--;
if (mRepeat > 0) {
mInterface.unhandledBack();
}
} while (mRepeat > 0);
return 0;
} 上面的代码很长,无非就一些信息合法性的检测以及启动后的返回结果。我们直接看关键代码
res = mInterface.startActivityAsUser(null, null, intent, mimeType,
null, null, 0, mStartFlags, profilerInfo,
options != null ? options.toBundle() : null, mUserId);
startActivityAsUser跟平时在代码中启动startActivity相似,那么mInterface是什么呢?mInterface是IActivityManager,也就是AMS的客户端。mInterface是什么时候创建的呢? 在AMS中onShellCommand方法中创建的(new ActivityManagerShellCommand(this, false))。
1.1.2 startActivityAsUser 和startActivityMayWait
public final int startActivityAsUser(IApplicationThread caller, String callingPackage,
Intent intent, String resolvedType, IBinder resultTo, String resultWho, int requestCode,
int startFlags, ProfilerInfo profilerInfo, Bundle bOptions, int userId) {
enforceNotIsolatedCaller("startActivity");
userId = mUserController.handleIncomingUser(Binder.getCallingPid(), Binder.getCallingUid(),
userId, false, ALLOW_FULL_ONLY, "startActivity", null);
// TODO: Switch to user app stacks here.
return mActivityStarter.startActivityMayWait(caller, -1, callingPackage, intent,
resolvedType, null, null, resultTo, resultWho, requestCode, startFlags,
profilerInfo, null, null, bOptions, false, userId, null, "startActivityAsUser");
} /*
在绝大多数情况下,一个Acitivity的启动是由一个应用进程发起的,IApplicationThread是
应用进程和AMS交互的通道,也可算是调用进程的标示,在本例中,AM并非一个应用进程,所以
传递的caller为null
*/
final int startActivityMayWait(IApplicationThread caller, int callingUid,
String callingPackage, Intent intent, String resolvedType,
IVoiceInteractionSession voiceSession, IVoiceInteractor voiceInteractor,
IBinder resultTo, String resultWho, int requestCode, int startFlags,
ProfilerInfo profilerInfo, WaitResult outResult,
Configuration globalConfig, Bundle bOptions, boolean ignoreTargetSecurity, int userId,
TaskRecord inTask, String reason) {
// Refuse possible leaked file descriptors
//hasFileDescriptors是true代码intent已经绑定了一个activity,这就说明此activity已经启动了
if (intent != null && intent.hasFileDescriptors()) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("File descriptors passed in Intent");
}
//activity开始启动日志
mSupervisor.mActivityMetricsLogger.notifyActivityLaunching();
//区分隐式启动和显示启动,如果是隐式启动的话intent.getComponent()=null
boolean componentSpecified = intent.getComponent() != null;
// Save a copy in case ephemeral needs it
final Intent ephemeralIntent = new Intent(intent);
// Don't modify the client's object!
//创建一个新的Intent,防止客户传入的Intent被修改
intent = new Intent(intent);
//启动某个系统view ,比如照相功能,这个就算是隐式启动
if (componentSpecified
&& intent.getData() != null
&& Intent.ACTION_VIEW.equals(intent.getAction())
&& mService.getPackageManagerInternalLocked()
.isInstantAppInstallerComponent(intent.getComponent())) {
// intercept intents targeted directly to the ephemeral installer the
// ephemeral installer should never be started with a raw URL; instead
// adjust the intent so it looks like a "normal" instant app launch
intent.setComponent(null /*component*/);
componentSpecified = false;
}
//处理intent信息,当存在多个activity时,弹出resolverAcitvity
ResolveInfo rInfo = mSupervisor.resolveIntent(intent, resolvedType, userId);
if (rInfo == null) {
UserInfo userInfo = mSupervisor.getUserInfo(userId);
if (userInfo != null && userInfo.isManagedProfile()) {
// Special case for managed profiles, if attempting to launch non-cryto aware
// app in a locked managed profile from an unlocked parent allow it to resolve
// as user will be sent via confirm credentials to unlock the profile.
UserManager userManager = UserManager.get(mService.mContext);
boolean profileLockedAndParentUnlockingOrUnlocked = false;
long token = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
try {
UserInfo parent = userManager.getProfileParent(userId);
profileLockedAndParentUnlockingOrUnlocked = (parent != null)
&& userManager.isUserUnlockingOrUnlocked(parent.id)
&& !userManager.isUserUnlockingOrUnlocked(userId);
} finally {
Binder.restoreCallingIdentity(token);
}
if (profileLockedAndParentUnlockingOrUnlocked) {
rInfo = mSupervisor.resolveIntent(intent, resolvedType, userId,
PackageManager.MATCH_DIRECT_BOOT_AWARE
| PackageManager.MATCH_DIRECT_BOOT_UNAWARE);
}
}
}
// Collect information about the target of the Intent.
//收集intent所指向的activity信息
ActivityInfo aInfo = mSupervisor.resolveActivity(intent, rInfo, startFlags, profilerInfo);
ActivityOptions options = ActivityOptions.fromBundle(bOptions);
synchronized (mService) {
final int realCallingPid = Binder.getCallingPid();
final int realCallingUid = Binder.getCallingUid();
int callingPid;
if (callingUid >= 0) {
callingPid = -1;
} else if (caller == null) {
callingPid = realCallingPid;
callingUid = realCallingUid;
} else {
callingPid = callingUid = -1;
}
final ActivityStack stack = mSupervisor.mFocusedStack;
stack.mConfigWillChange = globalConfig != null
&& mService.getGlobalConfiguration().diff(globalConfig) != 0;
if (DEBUG_CONFIGURATION) Slog.v(TAG_CONFIGURATION,
"Starting activity when config will change = " + stack.mConfigWillChange);
final long origId = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
/*
AndroidManifest.xml中的Application标签可以声明一个cantSaveState
属性,设置了该属性的Application将不享受系统提供的状态保存/恢复功能。
当一个Application退到后台时,系统会为它保存状态,当调度其到前台运行时, 将恢复它之前的状态,以保证用户体验的连续性。声明了该属性的Application被称为
“heavy weight process”。可惜系统目前不支持该属性,因为PackageParser
将不解析该属性。详情请见PackageParser.java parseApplication函数
*/
if (aInfo != null &&
(aInfo.applicationInfo.privateFlags
& ApplicationInfo.PRIVATE_FLAG_CANT_SAVE_STATE) != 0) {
// This may be a heavy-weight process! Check to see if we already
// have another, different heavy-weight process running.
//heavy-weight进程处理流程
//一般进程名等于包名,有些情况进程名不等于包名,比如shareduid
if (aInfo.processName.equals(aInfo.applicationInfo.packageName)) {
final ProcessRecord heavy = mService.mHeavyWeightProcess;
if(DEBUG_ACTIVITY_START)Log.i("ActivityManagerService-xiao", "ActivityStarter startActivityMayWait aInfo.processName:"+aInfo.processName+",aInfo.applicationInfo.packageName:"+aInfo.applicationInfo.packageName);
if (heavy != null && (heavy.info.uid != aInfo.applicationInfo.uid
|| !heavy.processName.equals(aInfo.processName))) {
int appCallingUid = callingUid;
if (caller != null) {
ProcessRecord callerApp = mService.getRecordForAppLocked(caller);
if (callerApp != null) {
appCallingUid = callerApp.info.uid;
} else {
Slog.w(TAG, "Unable to find app for caller " + caller
+ " (pid=" + callingPid + ") when starting: "
+ intent.toString());
ActivityOptions.abort(options);
return ActivityManager.START_PERMISSION_DENIED;
}
}
IIntentSender target = mService.getIntentSenderLocked(
ActivityManager.INTENT_SENDER_ACTIVITY, "android",
appCallingUid, userId, null, null, 0, new Intent[] { intent },
new String[] { resolvedType }, PendingIntent.FLAG_CANCEL_CURRENT
| PendingIntent.FLAG_ONE_SHOT, null);
Intent newIntent = new Intent();
if (requestCode >= 0) {
// Caller is requesting a result.
newIntent.putExtra(HeavyWeightSwitcherActivity.KEY_HAS_RESULT, true);
}
newIntent.putExtra(HeavyWeightSwitcherActivity.KEY_INTENT,
new IntentSender(target));
if (heavy.activities.size() > 0) {
ActivityRecord hist = heavy.activities.get(0);
newIntent.putExtra(HeavyWeightSwitcherActivity.KEY_CUR_APP,
hist.packageName);
newIntent.putExtra(HeavyWeightSwitcherActivity.KEY_CUR_TASK,
hist.getTask().taskId);
}
newIntent.putExtra(HeavyWeightSwitcherActivity.KEY_NEW_APP,
aInfo.packageName);
newIntent.setFlags(intent.getFlags());
newIntent.setClassName("android",
HeavyWeightSwitcherActivity.class.getName());
intent = newIntent;
resolvedType = null;
caller = null;
callingUid = Binder.getCallingUid();
callingPid = Binder.getCallingPid();
componentSpecified = true;
rInfo = mSupervisor.resolveIntent(intent, null /*resolvedType*/, userId);
aInfo = rInfo != null ? rInfo.activityInfo : null;
if (aInfo != null) {
aInfo = mService.getActivityInfoForUser(aInfo, userId);
}
}
}
}
final ActivityRecord[] outRecord = new ActivityRecord[1];
int res = startActivityLocked(caller, intent, ephemeralIntent, resolvedType,
aInfo, rInfo, voiceSession, voiceInteractor,
resultTo, resultWho, requestCode, callingPid,
callingUid, callingPackage, realCallingPid, realCallingUid, startFlags,
options, ignoreTargetSecurity, componentSpecified, outRecord, inTask,
reason);
Binder.restoreCallingIdentity(origId);
if (stack.mConfigWillChange) {
// If the caller also wants to switch to a new configuration,
// do so now. This allows a clean switch, as we are waiting
// for the current activity to pause (so we will not destroy
// it), and have not yet started the next activity.
mService.enforceCallingPermission(android.Manifest.permission.CHANGE_CONFIGURATION,
"updateConfiguration()");
stack.mConfigWillChange = false;
if (DEBUG_CONFIGURATION) Slog.v(TAG_CONFIGURATION,
"Updating to new configuration after starting activity.");
mService.updateConfigurationLocked(globalConfig, null, false);
}
//就是根据返回值做一些处理,那么res返回成功(即res== IActivityManager.START_SUCCESS的时候)后为何还需要等待呢?
//这是因为目标Activity要运行在一个新的应用进程中,就必须等待那个应用进程正常启动并处理相关请求。注意,只有am设置了-W选项,才会进入wait这一状态。
if (outResult != null) {//设置启动结果
outResult.result = res;
if (res == ActivityManager.START_SUCCESS) {
mSupervisor.mWaitingActivityLaunched.add(outResult); //将该结果加到mWaitingActivityLaunched中保存
do {
try {
mService.wait();//等待启动结果
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
} while (outResult.result != START_TASK_TO_FRONT
&& !outResult.timeout && outResult.who == null);
if (outResult.result == START_TASK_TO_FRONT) {
res = START_TASK_TO_FRONT;
}
}
if (res == START_TASK_TO_FRONT) {
final ActivityRecord r = outRecord[0];
// ActivityRecord may represent a different activity, but it should not be in
// the resumed state.
if (r.nowVisible && r.state == RESUMED) {
outResult.timeout = false;
outResult.who = r.realActivity;
outResult.totalTime = 0;
outResult.thisTime = 0;
} else {
outResult.thisTime = SystemClock.uptimeMillis();
mSupervisor.waitActivityVisible(r.realActivity, outResult);
// Note: the timeout variable is not currently not ever set.
do {
try {
mService.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
} while (!outResult.timeout && outResult.who == null);
}
}
}
mSupervisor.mActivityMetricsLogger.notifyActivityLaunched(res, outRecord[0]);
return res;
}
}以上代码很长大概做了以下几件事:1.复制一个intent,目的是为了防止后续使用篡改了原intent。2. heavy-weight进程处理 3.acitivity启动完成后的返回值处理。在讲startActivityLocked函数之前,先引用邓凡平的深入理解android系统关于栈的相关文章
1.1.3 Task、Back Stack、ActivityStack、ActivityStackSupervisor 及Launch mode
(1) 关于Task及Back Stack的介绍
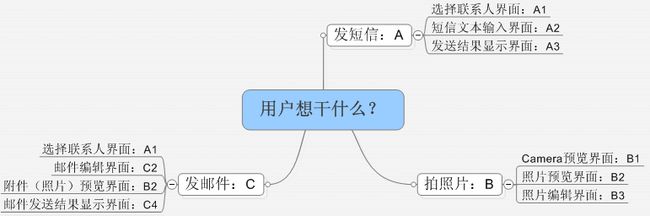
先来看图6-10。
图6-10 用户想干什么
图6-10列出了用户在Android系统上想干的三件事情,分别用A、B、C表示,将每一件事情称为一个Task。一个Task还可细分为多个子步骤,即Activity。
提示为什么叫Activity?读者可参考Merrian-Webster词典对Activity的解释[③]:“an organizational unit forperforming a specific function”,也就是说,它是一个有组织的单元,用于完成某项指定功能。
由图6-10可知,A、B两个Task使用了不同的Activity来完成相应的任务。注意,A、B这两个Task的Activity之间没有复用。
再来看C这个Task,它可细分为4个Activity,其中有两个Activity分别使用了A Task的A1、B Task的B2。C Task为什么不新建自己的Activity,反而要用其他Task的呢?这是因为用户想做的事情(即Task)可以完全不同,但是当细分Task为Activity时,就可能出现Activity功能类似的情况。既然A1、B2已能满足要求,为何还要重复“发明轮子”呢?另外,通过重用Activity,也可为用户提供一致的界面和体验。
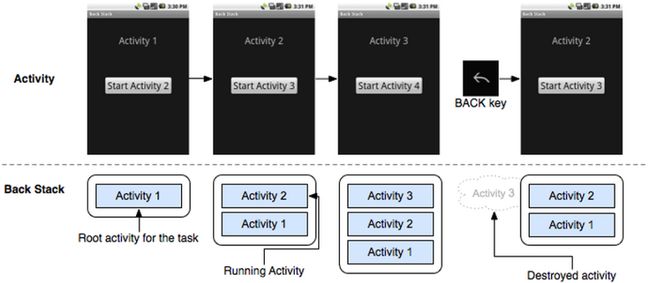
了解Android设计理念后,我们来看看Android是如何组织Task及它所包含的Activity的。此处有一个简单的例子,如图6-11所示。
图6-11 Task及Back Stack示例
由图6-11可知:
· 本例中的Task包含4个Activity。用户可单击按钮跳转到下一个Activity。同时,通过返回键可回到上一个Activity。
· 虚线下方是这些Activity的组织方式。Android采用了Stack的方法管理这3个Activity。例如在A1启动A2后,A2入栈成为栈顶成员,A1成为栈底成员,而界面显示的是栈顶成员的内容。当按返回键时,A3出栈,这时候A2成为栈顶,界面显示也相应变成了A2。
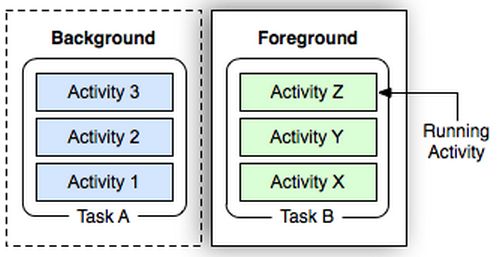
以上是一个Task的情况。那么,多个Task又会是何种情况呢?如图6-12所示。
图6-12 多个Task的情况
由图6-12可知:对多Task的情况来说,系统只支持一个处于前台的Task,即用户当前看到的Activity所属的Task,其余的Task均处于后台,这些后台Task内部的Activity保持顺序不变。用户可以一次将整个Task挪到后台或者置为前台。
提示用过Android手机的读者应该知道,长按Home键,系统会弹出近期Task列表,使用户能快速在多个Task间切换。
以上内容从抽象角度介绍了什么是Task,以及Android如何分解Task和管理Activity,那么在实际代码中,是如何考虑并设计的呢?
(2) 关于ActivityStack的介绍
通过上述分析,我们对Android的设计有了一定了解,那么如何用代码来实现这一设计呢?此处有两点需要考虑:
· Task内部Activity的组织方式。由图6-11可知,Android通过先入后出的方式来组织Activity。数据结构中的Stack即以这种方式工作。
· 多个Task的组织及管理方式。
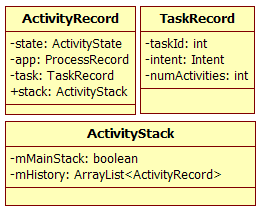
Android设计了一个ActivityStack类来负责上述工作,它的组成如图6-13所示。
图6-13 ActivityStack及相关成员
由图6-13可知:
· Activity由ActivityRecord表示,Task由TaskRecord表示。ActivityRecord的task成员指向该Activity所在的Task。state变量用于表示该Activity所处的状态(包括INITIALIZING、RESUMED、PAUSED等状态)。
· ActivityStack用mTaskHistory这个ArrayList保存ActivityRecord。令人大跌眼镜的是,该mHistory保存了系统中所有Task的ActivityRecord,而不是针对某个Task进行保存。
保持了当前启动的Activity mResumedActivity ,mLastPausedActivity(最近暂停),mPausingActivity(暂停)
final ArrayList
private final RecentTasks mRecentTasks;近期任务栈
查询Activity的方法
private ActivityRecord topRunningActivityLocked(boolean focusableOnly) {
for (int taskNdx = mTaskHistory.size() - 1; taskNdx >= 0; --taskNdx) {
ActivityRecord r = mTaskHistory.get(taskNdx).topRunningActivityLocked();
if (r != null && (!focusableOnly || r.isFocusable())) {
return r;
}
}
return null;
}(3)ActivityStackSupervisor 是栈的大管家,管理ActivityStack和task结构TaskRecord,而且还维护在AMS与WMS的联系。
//当前或者计划启动的activity
ActivityStack mFocusedStack;
private ActivityStack mLastFocusedStack;//在stack切换的过程中记录旧的stack
//等待可见的activity,在startActivityMayWait函数中,可能一些activity启动的线程正等在那里等待可见。当可见后调用notify, START_TASK_TO_FRONT的情况
private final ArrayList
//等待启动一个activity 真正启动activity
/** List of processes waiting to find out about the next launched activity. */
final ArrayList
//正在关闭的
final ArrayList
final ArrayList
final ArrayList
final ArrayList
private final SparseArray
SparseArray
(4) 关于Launch Mode的介绍
Launch Mode用于描述Activity的启动模式,目前一共有4种模式,分别是standard、singleTop、singleTask和singleInstance。初看它们,较难理解,实际上不过是Android玩的一个“小把戏“而已。启动模式就是用于控制Activity和Task关系的。
· standard:一个Task中可以有多个相同类型的Activity。注意,此处是相同类型的Activity,而不是同一个Activity对象。例如在Task中有A、B、C、D4个Activity,如果再启动A类Activity, Task就会变成A、B、C、D、A。最后一个A和第一个A是同一类型,却并非同一对象。另外,多个Task中也可以有同类型的Activity。
· singleTop:当某Task中有A、B、C、D4个Activity时,如果D想再启动一个D类型的Activity,那么Task将是什么样子呢?在singleTop模式下,Task中仍然是A、B、C、D,只不过D的onNewIntent函数将被调用以处理这个新Intent,而在standard模式下,则Task将变成A、B、C、D、D,最后的D为新创建的D类型Activity对象。在singleTop这种模式下,只有目标Acitivity当前正好在栈顶时才有效,例如只有处于栈顶的D启动时才有用,如果D启动不处于栈顶的A、B、C等,则无效。
· singleTask:在这种启动模式下,该Activity只存在一个实例,并且将和一个Task绑定。当需要此Activity时,系统会以onNewIntent方式启动它,而不会新建Task和Activity。注意,该Activity虽只有一个实例,但是在Task中除了它之外,还可以有其他的Activity。
· singleInstance:它是singleTask的加强版,即一个Task只能有这么一个设置了singleInstance的Activity,不能再有别的Activity。而在singleTask模式中,Task还可以有其他的Activity。
注意,Android建议一般的应用开发者不要轻易使用最后两种启动模式。因为这些模式虽然名意上为Launch Mode,但是它们也会影响Activity出栈的顺序,导致用户按返回键返回时导致不一致的用户体验。
除了启动模式外,Android还有其他一些标志用于控制Activity及Task之间的关系。这里只列举一二,详细信息请参阅SDK文档中Intent的相关说明。
· FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK:将目标Activity放到一个新的Task中。
· FLAG_ACTIVITY_CLEAR_TASK:当启动一个Activity时,先把和目标Activity有关联的Task“干掉“,然后启动一个新的Task,并把目标Activity放到新的Task中。该标志必须和FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK标志一起使用。
· FLAG_ACTIVITY_CLEAR_TOP:当启动一个不处于栈顶的Activity时候,先把排在它前面的Activity“干掉”。例如Task有A、B、C、D4个Activity,要要启动B,直接把C、D“干掉”,而不是新建一个B。
1.1.4 通过上面的知识介绍对task和Launcher Mode 有一定的了解,现在我们开始分析startActivityLocked
if (TextUtils.isEmpty(reason)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Need to specify a reason.");
}
mLastStartReason = reason;
mLastStartActivityTimeMs = System.currentTimeMillis();
mLastStartActivityRecord[0] = null;
mLastStartActivityResult = startActivity(caller, intent, ephemeralIntent, resolvedType,
aInfo, rInfo, voiceSession, voiceInteractor, resultTo, resultWho, requestCode,
callingPid, callingUid, callingPackage, realCallingPid, realCallingUid, startFlags,
options, ignoreTargetSecurity, componentSpecified, mLastStartActivityRecord,
inTask);
if (outActivity != null) {
// mLastStartActivityRecord[0] is set in the call to startActivity above.
outActivity[0] = mLastStartActivityRecord[0];
}
// Aborted results are treated as successes externally, but we must track them internally.
return mLastStartActivityResult != START_ABORTED ? mLastStartActivityResult : START_SUCCESS;
}1.1.5 startActivity
private int startActivity(IApplicationThread caller, Intent intent, Intent ephemeralIntent,
String resolvedType, ActivityInfo aInfo, ResolveInfo rInfo,
IVoiceInteractionSession voiceSession, IVoiceInteractor voiceInteractor,
IBinder resultTo, String resultWho, int requestCode, int callingPid, int callingUid,
String callingPackage, int realCallingPid, int realCallingUid, int startFlags,
ActivityOptions options, boolean ignoreTargetSecurity, boolean componentSpecified,
ActivityRecord[] outActivity, TaskRecord inTask) {
int err = ActivityManager.START_SUCCESS;
// Pull the optional Ephemeral Installer-only bundle out of the options early.
final Bundle verificationBundle
= options != null ? options.popAppVerificationBundle() : null;
ProcessRecord callerApp = null;
//如果caller不为空,则需要从AMS中找到它的ProcessRecord以及pid和uid。如果是第一次启动caller=null
//为什么需要记录pid和uid呢?
//因为第一启动app系统会为这个app创建对应的进程和uid和pid。这样就避免了系统重新创建新的进程
if (caller != null) {
callerApp = mService.getRecordForAppLocked(caller);
if (callerApp != null) {
callingPid = callerApp.pid;
callingUid = callerApp.info.uid;
} else {//如调用进程没有在AMS中注册,则认为其是非法的
Slog.w(TAG, "Unable to find app for caller " + caller
+ " (pid=" + callingPid + ") when starting: "
+ intent.toString());
err = ActivityManager.START_PERMISSION_DENIED;
}
}
final int userId = aInfo != null ? UserHandle.getUserId(aInfo.applicationInfo.uid) : 0;
if (err == ActivityManager.START_SUCCESS) {
Slog.i(TAG, "START u" + userId + " {" + intent.toShortString(true, true, true, false)
+ "} from uid " + callingUid);
}
//下面两个变量意义很重要。sourceRecord用于描述启动目标Activity的那个Activity,即startActivity
//resultRecord用于描述接收启动结果的Activity,即该Activity的onActivityResult
//这两个进程一般情况是同一个进程,所以下面的代码也验证了这个猜想
//下面函数isInAnyStackLocked中会调用mActivityDisplays,集合非常重要,里面保持了系统曾经显示的activity和对应的栈
ActivityRecord sourceRecord = null;
ActivityRecord resultRecord = null;
if (resultTo != null) {
sourceRecord = mSupervisor.isInAnyStackLocked(resultTo);
if (DEBUG_RESULTS) Slog.v(TAG_RESULTS,
"Will send result to " + resultTo + " " + sourceRecord);
if (sourceRecord != null) {
if (requestCode >= 0 && !sourceRecord.finishing) {
resultRecord = sourceRecord;
}
}
}
//获取Intent设置的启动标志,它们是和Launch Mode相类似的“小把戏”,
final int launchFlags = intent.getFlags();
//使用这个标签有个前提,即A必须先存在,正如if中sourceRecord
// 不为null的判断所示
if ((launchFlags & Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_FORWARD_RESULT) != 0 && sourceRecord != null) {
// Transfer the result target from the source activity to the new
// one being started, including any failures.
if (requestCode >= 0) {
ActivityOptions.abort(options);
return ActivityManager.START_FORWARD_AND_REQUEST_CONFLICT;
}
resultRecord = sourceRecord.resultTo;
if (resultRecord != null && !resultRecord.isInStackLocked()) {
resultRecord = null;
}
resultWho = sourceRecord.resultWho;
requestCode = sourceRecord.requestCode;
sourceRecord.resultTo = null;
if (resultRecord != null) {
resultRecord.removeResultsLocked(sourceRecord, resultWho, requestCode);
}
if (sourceRecord.launchedFromUid == callingUid) {
// The new activity is being launched from the same uid as the previous
// activity in the flow, and asking to forward its result back to the
// previous. In this case the activity is serving as a trampoline between
// the two, so we also want to update its launchedFromPackage to be the
// same as the previous activity. Note that this is safe, since we know
// these two packages come from the same uid; the caller could just as
// well have supplied that same package name itself. This specifially
// deals with the case of an intent picker/chooser being launched in the app
// flow to redirect to an activity picked by the user, where we want the final
// activity to consider it to have been launched by the previous app activity.
callingPackage = sourceRecord.launchedFromPackage;
}
}
if (err == ActivityManager.START_SUCCESS && intent.getComponent() == null) {
// We couldn't find a class that can handle the given Intent.
// That's the end of that!
err = ActivityManager.START_INTENT_NOT_RESOLVED;
}
if (err == ActivityManager.START_SUCCESS && aInfo == null) {
// We couldn't find the specific class specified in the Intent.
// Also the end of the line.
err = ActivityManager.START_CLASS_NOT_FOUND;
}
if (err == ActivityManager.START_SUCCESS && sourceRecord != null
&& sourceRecord.getTask().voiceSession != null) {
// If this activity is being launched as part of a voice session, we need
// to ensure that it is safe to do so. If the upcoming activity will also
// be part of the voice session, we can only launch it if it has explicitly
// said it supports the VOICE category, or it is a part of the calling app.
if ((launchFlags & FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK) == 0
&& sourceRecord.info.applicationInfo.uid != aInfo.applicationInfo.uid) {
try {
intent.addCategory(Intent.CATEGORY_VOICE);
if (!AppGlobals.getPackageManager().activitySupportsIntent(
intent.getComponent(), intent, resolvedType)) {
Slog.w(TAG,
"Activity being started in current voice task does not support voice: "
+ intent);
err = ActivityManager.START_NOT_VOICE_COMPATIBLE;
}
} catch (RemoteException e) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Failure checking voice capabilities", e);
err = ActivityManager.START_NOT_VOICE_COMPATIBLE;
}
}
}
if (err == ActivityManager.START_SUCCESS && voiceSession != null) {
// If the caller is starting a new voice session, just make sure the target
// is actually allowing it to run this way.
try {
if (!AppGlobals.getPackageManager().activitySupportsIntent(intent.getComponent(),
intent, resolvedType)) {
Slog.w(TAG,
"Activity being started in new voice task does not support: "
+ intent);
err = ActivityManager.START_NOT_VOICE_COMPATIBLE;
}
} catch (RemoteException e) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Failure checking voice capabilities", e);
err = ActivityManager.START_NOT_VOICE_COMPATIBLE;
}
}
final ActivityStack resultStack = resultRecord == null ? null : resultRecord.getStack();
if (err != START_SUCCESS) {
if (resultRecord != null) {
resultStack.sendActivityResultLocked(
-1, resultRecord, resultWho, requestCode, RESULT_CANCELED, null);
}
ActivityOptions.abort(options);
return err;
}
//权限检查失败的处理
boolean abort = !mSupervisor.checkStartAnyActivityPermission(intent, aInfo, resultWho,
requestCode, callingPid, callingUid, callingPackage, ignoreTargetSecurity, callerApp,
resultRecord, resultStack, options);
abort |= !mService.mIntentFirewall.checkStartActivity(intent, callingUid,
callingPid, resolvedType, aInfo.applicationInfo);
//可为AMS设置一个IActivityController类型的监听者,AMS有任何动静都会回调该
//监听者。不过谁又有如此本领去监听AMS呢?在进行Monkey测试的时候,Monkey会
//设置该回调对象。这样,Monkey就能根据AMS放映的情况进行相应处理了
if (mService.mController != null) {//交给回调对象处理,由它判断是否能继续后面的行程
try {
// The Intent we give to the watcher has the extra data
// stripped off, since it can contain private information.
Intent watchIntent = intent.cloneFilter();
abort |= !mService.mController.activityStarting(watchIntent,
aInfo.applicationInfo.packageName);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
mService.mController = null;
}
}
mInterceptor.setStates(userId, realCallingPid, realCallingUid, startFlags, callingPackage);
mInterceptor.intercept(intent, rInfo, aInfo, resolvedType, inTask, callingPid, callingUid,
options);
intent = mInterceptor.mIntent;
rInfo = mInterceptor.mRInfo;
aInfo = mInterceptor.mAInfo;
resolvedType = mInterceptor.mResolvedType;
inTask = mInterceptor.mInTask;
callingPid = mInterceptor.mCallingPid;
callingUid = mInterceptor.mCallingUid;
options = mInterceptor.mActivityOptions;
if (abort) {
if (resultRecord != null) {
resultStack.sendActivityResultLocked(-1, resultRecord, resultWho, requestCode,
RESULT_CANCELED, null);
}
// We pretend to the caller that it was really started, but
// they will just get a cancel result.
ActivityOptions.abort(options);
return START_ABORTED;
}
// If permissions need a review before any of the app components can run, we
// launch the review activity and pass a pending intent to start the activity
// we are to launching now after the review is completed.
//如果需要再检查权限,则启动检查activity
if (mService.mPermissionReviewRequired && aInfo != null) {
if (mService.getPackageManagerInternalLocked().isPermissionsReviewRequired(
aInfo.packageName, userId)) {
IIntentSender target = mService.getIntentSenderLocked(
ActivityManager.INTENT_SENDER_ACTIVITY, callingPackage,
callingUid, userId, null, null, 0, new Intent[]{intent},
new String[]{resolvedType}, PendingIntent.FLAG_CANCEL_CURRENT
| PendingIntent.FLAG_ONE_SHOT, null);
final int flags = intent.getFlags();
Intent newIntent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_REVIEW_PERMISSIONS);
newIntent.setFlags(flags
| Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_EXCLUDE_FROM_RECENTS);
newIntent.putExtra(Intent.EXTRA_PACKAGE_NAME, aInfo.packageName);
newIntent.putExtra(Intent.EXTRA_INTENT, new IntentSender(target));
if (resultRecord != null) {
newIntent.putExtra(Intent.EXTRA_RESULT_NEEDED, true);
}
intent = newIntent;
resolvedType = null;
callingUid = realCallingUid;
callingPid = realCallingPid;
rInfo = mSupervisor.resolveIntent(intent, resolvedType, userId);
aInfo = mSupervisor.resolveActivity(intent, rInfo, startFlags,
null /*profilerInfo*/);
if (DEBUG_PERMISSIONS_REVIEW) {
Slog.i(TAG, "START u" + userId + " {" + intent.toShortString(true, true,
true, false) + "} from uid " + callingUid + " on display "
+ (mSupervisor.mFocusedStack == null
? DEFAULT_DISPLAY : mSupervisor.mFocusedStack.mDisplayId));
}
}
}
// If we have an ephemeral app, abort the process of launching the resolved intent.
// Instead, launch the ephemeral installer. Once the installer is finished, it
// starts either the intent we resolved here [on install error] or the ephemeral
// app [on install success].
if (rInfo != null && rInfo.auxiliaryInfo != null) {
intent = createLaunchIntent(rInfo.auxiliaryInfo, ephemeralIntent,
callingPackage, verificationBundle, resolvedType, userId);
resolvedType = null;
callingUid = realCallingUid;
callingPid = realCallingPid;
aInfo = mSupervisor.resolveActivity(intent, rInfo, startFlags, null /*profilerInfo*/);
}
//创建activity记录对象
ActivityRecord r = new ActivityRecord(mService, callerApp, callingPid, callingUid,
callingPackage, intent, resolvedType, aInfo, mService.getGlobalConfiguration(),
resultRecord, resultWho, requestCode, componentSpecified, voiceSession != null,
mSupervisor, options, sourceRecord);
if (outActivity != null) {//保存到输入参数outActivity数组中
outActivity[0] = r;
}
if (r.appTimeTracker == null && sourceRecord != null) {
// If the caller didn't specify an explicit time tracker, we want to continue
// tracking under any it has.
r.appTimeTracker = sourceRecord.appTimeTracker;
}
final ActivityStack stack = mSupervisor.mFocusedStack;
//如果不是前台activity启动新的activity,需要判断它是否具有权限启动其他app进程
if (voiceSession == null && (stack.mResumedActivity == null
|| stack.mResumedActivity.info.applicationInfo.uid != callingUid)) {
//检查调用进程是否有权限切换Application
if (!mService.checkAppSwitchAllowedLocked(callingPid, callingUid,
realCallingPid, realCallingUid, "Activity start")) {
PendingActivityLaunch pal = new PendingActivityLaunch(r,
sourceRecord, startFlags, stack, callerApp);
//如果调用进程没有权限切换Activity,则只能把这次Activity启动请求保存起来,
//后续有机会时再启动它
mPendingActivityLaunches.add(pal);
ActivityOptions.abort(options);
return ActivityManager.START_SWITCHES_CANCELED;
}
}
//如果前面的权限检查是true的情况
if (mService.mDidAppSwitch) {
// This is the second allowed switch since we stopped switches,
// so now just generally allow switches. Use case: user presses
// home (switches disabled, switch to home, mDidAppSwitch now true);
// user taps a home icon (coming from home so allowed, we hit here
// and now allow anyone to switch again).
mService.mAppSwitchesAllowedTime = 0;
} else {
mService.mDidAppSwitch = true;
}
//启动处于Pending状态的Activity,比如前面因为权限而暂停的activity并且保存在 mPendingActivityLaunches.add
doPendingActivityLaunchesLocked(false);
return startActivity(r, sourceRecord, voiceSession, voiceInteractor, startFlags, true,
options, inTask, outActivity);
}上面代码很长但是其实主要就做两件事:找到适合的launchFlags和安全权限检查。
1.1.6 startActivityUnchecked
private int startActivityUnchecked(final ActivityRecord r, ActivityRecord sourceRecord,
IVoiceInteractionSession voiceSession, IVoiceInteractor voiceInteractor,
int startFlags, boolean doResume, ActivityOptions options, TaskRecord inTask,
ActivityRecord[] outActivity) {
//初始化mStartActivity mIntent等值,确认启动模式 mLaunchFlags的值
setInitialState(r, options, inTask, doResume, startFlags, sourceRecord, voiceSession,
voiceInteractor);
//计算适合的启动flag ,mLaunchFlags值
computeLaunchingTaskFlags();
//计算启动此apk所在的任务栈的信息
computeSourceStack();
mIntent.setFlags(mLaunchFlags);//设置启动模式flag
//得到重复利用的ActivityRecord
ActivityRecord reusedActivity = getReusableIntentActivity();
final int preferredLaunchStackId =
(mOptions != null) ? mOptions.getLaunchStackId() : INVALID_STACK_ID;
final int preferredLaunchDisplayId =
(mOptions != null) ? mOptions.getLaunchDisplayId() : DEFAULT_DISPLAY;
if(DEBUG_ACTIVITY_START)Log.i("ActivityManagerService-xiao", "ActivityStarter startActivityUnchecked reusedActivity:"+reusedActivity);
if (reusedActivity != null) {
// When the flags NEW_TASK and CLEAR_TASK are set, then the task gets reused but
// still needs to be a lock task mode violation since the task gets cleared out and
// the device would otherwise leave the locked task.
if (mSupervisor.isLockTaskModeViolation(reusedActivity.getTask(),
(mLaunchFlags & (FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK | FLAG_ACTIVITY_CLEAR_TASK))
== (FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK | FLAG_ACTIVITY_CLEAR_TASK))) {
mSupervisor.showLockTaskToast();
Slog.e(TAG, "startActivityUnchecked: Attempt to violate Lock Task Mode");
return START_RETURN_LOCK_TASK_MODE_VIOLATION;
}
//如果启动的activity没有管理task,则用存在activity的task
if (mStartActivity.getTask() == null) {
mStartActivity.setTask(reusedActivity.getTask());
}
//如果启动的activity没有管理intent,则用存在activity的intent
if (reusedActivity.getTask().intent == null) {
// This task was started because of movement of the activity based on affinity...
// Now that we are actually launching it, we can assign the base intent.
//设置mStartActivity
reusedActivity.getTask().setIntent(mStartActivity);
}
// This code path leads to delivering a new intent, we want to make sure we schedule it
// as the first operation, in case the activity will be resumed as a result of later
// operations.
if ((mLaunchFlags & FLAG_ACTIVITY_CLEAR_TOP) != 0
|| isDocumentLaunchesIntoExisting(mLaunchFlags)
|| mLaunchSingleInstance || mLaunchSingleTask) {
//FLAG_ACTIVITY_CLEAR_TOP模式下,栈移除所有的activity
final TaskRecord task = reusedActivity.getTask();
// In this situation we want to remove all activities from the task up to the one
// being started. In most cases this means we are resetting the task to its initial
// state.
//清楚task值保留栈顶的activity
final ActivityRecord top = task.performClearTaskForReuseLocked(mStartActivity,
mLaunchFlags);
// The above code can remove {@code reusedActivity} from the task, leading to the
// the {@code ActivityRecord} removing its reference to the {@code TaskRecord}. The
// task reference is needed in the call below to
// {@link setTargetStackAndMoveToFrontIfNeeded}.
if (reusedActivity.getTask() == null) {
reusedActivity.setTask(task);
}
//在前台
if (top != null) {
if (top.frontOfTask) {
// Activity aliases may mean we use different intents for the top activity,
// so make sure the task now has the identity of the new intent.
top.getTask().setIntent(mStartActivity);
}
deliverNewIntent(top);//在调用onNewIntent方法时候传入top的intent值
}
}
sendPowerHintForLaunchStartIfNeeded(false /* forceSend */, reusedActivity);
reusedActivity = setTargetStackAndMoveToFrontIfNeeded(reusedActivity);//判断是否需要移动栈
final ActivityRecord outResult =
outActivity != null && outActivity.length > 0 ? outActivity[0] : null;
// When there is a reused activity and the current result is a trampoline activity,
// set the reused activity as the result.
if (outResult != null && (outResult.finishing || outResult.noDisplay)) {
outActivity[0] = reusedActivity;
}
if ((mStartFlags & START_FLAG_ONLY_IF_NEEDED) != 0) {
// We don't need to start a new activity, and the client said not to do anything
// if that is the case, so this is it! And for paranoia, make sure we have
// correctly resumed the top activity.
resumeTargetStackIfNeeded();
return START_RETURN_INTENT_TO_CALLER;
}
setTaskFromIntentActivity(reusedActivity);
if (!mAddingToTask && mReuseTask == null) {
// We didn't do anything... but it was needed (a.k.a., client don't use that
// intent!) And for paranoia, make sure we have correctly resumed the top activity.
resumeTargetStackIfNeeded();
if (outActivity != null && outActivity.length > 0) {
outActivity[0] = reusedActivity;
}
return START_TASK_TO_FRONT;
}
}
//启动的activity没有包名,直接返回
if (mStartActivity.packageName == null) {
final ActivityStack sourceStack = mStartActivity.resultTo != null
? mStartActivity.resultTo.getStack() : null;
if (sourceStack != null) {
sourceStack.sendActivityResultLocked(-1 /* callingUid */, mStartActivity.resultTo,
mStartActivity.resultWho, mStartActivity.requestCode, RESULT_CANCELED,
null /* data */);
}
ActivityOptions.abort(mOptions);
return START_CLASS_NOT_FOUND;
}
// If the activity being launched is the same as the one currently at the top, then
// we need to check if it should only be launched once.
//启动的activity已经在栈顶了,确认是否还有必要再启动
final ActivityStack topStack = mSupervisor.mFocusedStack;
final ActivityRecord topFocused = topStack.topActivity();
final ActivityRecord top = topStack.topRunningNonDelayedActivityLocked(mNotTop);
final boolean dontStart = top != null && mStartActivity.resultTo == null
&& top.realActivity.equals(mStartActivity.realActivity)
&& top.userId == mStartActivity.userId
&& top.app != null && top.app.thread != null
&& ((mLaunchFlags & FLAG_ACTIVITY_SINGLE_TOP) != 0
|| mLaunchSingleTop || mLaunchSingleTask);
if(DEBUG_ACTIVITY_START)Log.i("ActivityManagerService-xiao", "ActivityStarter startActivityUnchecked dontStart:"+dontStart+",mDoResume:"+mDoResume);
if (dontStart) {
// For paranoia, make sure we have correctly resumed the top activity.
topStack.mLastPausedActivity = null;
if (mDoResume) {
mSupervisor.resumeFocusedStackTopActivityLocked();
}
ActivityOptions.abort(mOptions);
if ((mStartFlags & START_FLAG_ONLY_IF_NEEDED) != 0) {
// We don't need to start a new activity, and the client said not to do
// anything if that is the case, so this is it!
return START_RETURN_INTENT_TO_CALLER;
}
deliverNewIntent(top); //触发onNewIntent
// Don't use mStartActivity.task to show the toast. We're not starting a new activity
// but reusing 'top'. Fields in mStartActivity may not be fully initialized.
mSupervisor.handleNonResizableTaskIfNeeded(top.getTask(), preferredLaunchStackId,
preferredLaunchDisplayId, topStack.mStackId);
return START_DELIVERED_TO_TOP;
}
boolean newTask = false;
final TaskRecord taskToAffiliate = (mLaunchTaskBehind && mSourceRecord != null)
? mSourceRecord.getTask() : null;
// Should this be considered a new task?
int result = START_SUCCESS;
if (mStartActivity.resultTo == null && mInTask == null && !mAddingToTask
&& (mLaunchFlags & FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK) != 0) {
newTask = true;
result = setTaskFromReuseOrCreateNewTask(
taskToAffiliate, preferredLaunchStackId, topStack);
} else if (mSourceRecord != null) {
result = setTaskFromSourceRecord();
} else if (mInTask != null) {
result = setTaskFromInTask();
} else {
// This not being started from an existing activity, and not part of a new task...
// just put it in the top task, though these days this case should never happen.
setTaskToCurrentTopOrCreateNewTask();
}
if (result != START_SUCCESS) {
return result;
}
//授权控制。在SDK中启动Activity的函数没有授权设置方面的参数
mService.grantUriPermissionFromIntentLocked(mCallingUid, mStartActivity.packageName,
mIntent, mStartActivity.getUriPermissionsLocked(), mStartActivity.userId);
mService.grantEphemeralAccessLocked(mStartActivity.userId, mIntent,
mStartActivity.appInfo.uid, UserHandle.getAppId(mCallingUid));
if (mSourceRecord != null) {
mStartActivity.getTask().setTaskToReturnTo(mSourceRecord);
}
if (newTask) {
EventLog.writeEvent(
EventLogTags.AM_CREATE_TASK, mStartActivity.userId,
mStartActivity.getTask().taskId);
}
ActivityStack.logStartActivity(
EventLogTags.AM_CREATE_ACTIVITY, mStartActivity, mStartActivity.getTask());
mTargetStack.mLastPausedActivity = null;
sendPowerHintForLaunchStartIfNeeded(false /* forceSend */, mStartActivity);
//1.创建createWindowContainer ,2.activity切换的时候是否需要动画
mTargetStack.startActivityLocked(mStartActivity, topFocused, newTask, mKeepCurTransition,
mOptions);
if (mDoResume) {
final ActivityRecord topTaskActivity =
mStartActivity.getTask().topRunningActivityLocked();
if (!mTargetStack.isFocusable()
|| (topTaskActivity != null && topTaskActivity.mTaskOverlay
&& mStartActivity != topTaskActivity)) {// 没有获取焦点,不能resume
// If the activity is not focusable, we can't resume it, but still would like to
// make sure it becomes visible as it starts (this will also trigger entry
// animation). An example of this are PIP activities.
// Also, we don't want to resume activities in a task that currently has an overlay
// as the starting activity just needs to be in the visible paused state until the
// over is removed.
mTargetStack.ensureActivitiesVisibleLocked(null, 0, !PRESERVE_WINDOWS);
// Go ahead and tell window manager to execute app transition for this activity
// since the app transition will not be triggered through the resume channel.
mWindowManager.executeAppTransition();
} else {
// If the target stack was not previously focusable (previous top running activity
// on that stack was not visible) then any prior calls to move the stack to the
// will not update the focused stack. If starting the new activity now allows the
// task stack to be focusable, then ensure that we now update the focused stack
// accordingly.
if (mTargetStack.isFocusable() && !mSupervisor.isFocusedStack(mTargetStack)) {
mTargetStack.moveToFront("startActivityUnchecked");
}
mSupervisor.resumeFocusedStackTopActivityLocked(mTargetStack, mStartActivity,
mOptions);
}
} else {
mTargetStack.addRecentActivityLocked(mStartActivity);
}
mSupervisor.updateUserStackLocked(mStartActivity.userId, mTargetStack);
mSupervisor.handleNonResizableTaskIfNeeded(mStartActivity.getTask(), preferredLaunchStackId,
preferredLaunchDisplayId, mTargetStack.mStackId);
return START_SUCCESS;
}这段代码算是Activity启动流程中比较重要的函数,其主要是:1.为新的Activity寻找适合的task和mLaunchFlags的值
2.如果启动的Activity已经在别的task中存在,那就判断是否需要移动task或者新创建一个Activity。如果没有存在(第一次启动Activity的情况下)就可能需要创建新的task来或者创建新的进程。
1.1.7 ActivityStack startActivityLocked
final void startActivityLocked(ActivityRecord r, ActivityRecord focusedTopActivity,
boolean newTask, boolean keepCurTransition, ActivityOptions options) {
TaskRecord rTask = r.getTask();
final int taskId = rTask.taskId;
// mLaunchTaskBehind tasks get placed at the back of the task stack.
if (!r.mLaunchTaskBehind && (taskForIdLocked(taskId) == null || newTask)) {
// Last activity in task had been removed or ActivityManagerService is reusing task.
// Insert or replace.
// Might not even be in.
//task中上一个activity被移除,或者ams重用task,则将该task移到顶部
insertTaskAtTop(rTask, r);
}
TaskRecord task = null;
//启动已经存在的task
if (!newTask) {
// If starting in an existing task, find where that is...
//如果不是新Task,则从mTaskHistory中找到对应的ActivityRecord的位置
boolean startIt = true;
for (int taskNdx = mTaskHistory.size() - 1; taskNdx >= 0; --taskNdx) {
task = mTaskHistory.get(taskNdx);
if (task.getTopActivity() == null) {
// All activities in task are finishing.
//该task所有activity都finishing
continue;
}
if (task == rTask) {
// Here it is! Now, if this is not yet visible to the
// user, then just add it without starting; it will
// get started when the user navigates back to it.
if (!startIt) {
if (DEBUG_ADD_REMOVE) Slog.i(TAG, "Adding activity " + r + " to task "
+ task, new RuntimeException("here").fillInStackTrace());
r.createWindowContainer();
ActivityOptions.abort(options);
return;
}
break;
} else if (task.numFullscreen > 0) {
startIt = false;
}
}
}
// Place a new activity at top of stack, so it is next to interact with the user.
// If we are not placing the new activity frontmost, we do not want to deliver the
// onUserLeaving callback to the actual frontmost activity
final TaskRecord activityTask = r.getTask();
if (task == activityTask && mTaskHistory.indexOf(task) != (mTaskHistory.size() - 1)) {
mStackSupervisor.mUserLeaving = false;
if (DEBUG_USER_LEAVING) Slog.v(TAG_USER_LEAVING,
"startActivity() behind front, mUserLeaving=false");
}
task = activityTask;
// Slot the activity into the history stack and proceed
if (DEBUG_ADD_REMOVE) Slog.i(TAG, "Adding activity " + r + " to stack to task " + task,
new RuntimeException("here").fillInStackTrace());
// TODO: Need to investigate if it is okay for the controller to already be created by the
// time we get to this point. I think it is, but need to double check.
// Use test in b/34179495 to trace the call path.
//创建AppWindowContainerController,保持AMS与WMS(windowmanagerservice)的交互
if (r.getWindowContainerController() == null) {
r.createWindowContainer();
}
task.setFrontOfTask();
//当切换到新的task:不是桌面task也不是近期stack。意思就是没有启动的task。并且保证这个task里面包含了activity
if (!isHomeOrRecentsStack() || numActivities() > 0) {
if (DEBUG_TRANSITION) Slog.v(TAG_TRANSITION,
"Prepare open transition: starting " + r);
if ((r.intent.getFlags() & Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_NO_ANIMATION) != 0) {
//判断是否显示Activity切换动画之类的事情,需要与WindowManagerService交互
mWindowManager.prepareAppTransition(TRANSIT_NONE, keepCurTransition);
mNoAnimActivities.add(r);
} else {//需要动画切换
int transit = TRANSIT_ACTIVITY_OPEN;
if (newTask) {
if (r.mLaunchTaskBehind) {
transit = TRANSIT_TASK_OPEN_BEHIND;
} else {
// If a new task is being launched, then mark the existing top activity as
// supporting picture-in-picture while pausing only if the starting activity
// would not be considered an overlay on top of the current activity
// (eg. not fullscreen, or the assistant)
if (canEnterPipOnTaskSwitch(focusedTopActivity,
null /* toFrontTask */, r, options)) {
focusedTopActivity.supportsEnterPipOnTaskSwitch = true;
}
transit = TRANSIT_TASK_OPEN;
}
}
mWindowManager.prepareAppTransition(transit, keepCurTransition);
mNoAnimActivities.remove(r);
}
boolean doShow = true;
if (newTask) {
// Even though this activity is starting fresh, we still need
// to reset it to make sure we apply affinities to move any
// existing activities from other tasks in to it.
// If the caller has requested that the target task be
// reset, then do so.
if ((r.intent.getFlags() & Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_RESET_TASK_IF_NEEDED) != 0) {
resetTaskIfNeededLocked(r, r);
doShow = topRunningNonDelayedActivityLocked(null) == r;
}
} else if (options != null && options.getAnimationType()
== ActivityOptions.ANIM_SCENE_TRANSITION) {
doShow = false;
}
if (r.mLaunchTaskBehind) {
// Don't do a starting window for mLaunchTaskBehind. More importantly make sure we
// tell WindowManager that r is visible even though it is at the back of the stack.
r.setVisibility(true);
ensureActivitiesVisibleLocked(null, 0, !PRESERVE_WINDOWS);
} else if (SHOW_APP_STARTING_PREVIEW && doShow) {
// Figure out if we are transitioning from another activity that is
// "has the same starting icon" as the next one. This allows the
// window manager to keep the previous window it had previously
// created, if it still had one.
TaskRecord prevTask = r.getTask();
ActivityRecord prev = prevTask.topRunningActivityWithStartingWindowLocked();
if (prev != null) {
// We don't want to reuse the previous starting preview if:
// (1) The current activity is in a different task.
if (prev.getTask() != prevTask) {
prev = null;
}
// (2) The current activity is already displayed.
else if (prev.nowVisible) {
prev = null;
}
}
r.showStartingWindow(prev, newTask, isTaskSwitch(r, focusedTopActivity));
}
} else {
// If this is the first activity, don't do any fancy animations,
// because there is nothing for it to animate on top of.
ActivityOptions.abort(options);
}
}1.1.8 ActivityStackSuppervisor resumeFocusedStackTopActivityLocked
boolean resumeFocusedStackTopActivityLocked(
ActivityStack targetStack, ActivityRecord target, ActivityOptions targetOptions) {
if (!readyToResume()) {
return false;
}
if (targetStack != null && isFocusedStack(targetStack)) {
return targetStack.resumeTopActivityUncheckedLocked(target, targetOptions);
}
final ActivityRecord r = mFocusedStack.topRunningActivityLocked();
if (r == null || r.state != RESUMED) {
mFocusedStack.resumeTopActivityUncheckedLocked(null, null);
} else if (r.state == RESUMED) {
// Kick off any lingering app transitions form the MoveTaskToFront operation.
mFocusedStack.executeAppTransition(targetOptions);
}
return false;
}1.1.9 ActivityStack resumeTopActivityUncheckedLocked
boolean resumeTopActivityUncheckedLocked(ActivityRecord prev, ActivityOptions options) {
if (mStackSupervisor.inResumeTopActivity) {
// Don't even start recursing.
return false;
}
boolean result = false;
try {
// Protect against recursion.
mStackSupervisor.inResumeTopActivity = true;
result = resumeTopActivityInnerLocked(prev, options);
} finally {
mStackSupervisor.inResumeTopActivity = false;
}
// When resuming the top activity, it may be necessary to pause the top activity (for
// example, returning to the lock screen. We suppress the normal pause logic in
// {@link #resumeTopActivityUncheckedLocked}, since the top activity is resumed at the end.
// We call the {@link ActivityStackSupervisor#checkReadyForSleepLocked} again here to ensure
// any necessary pause logic occurs. In the case where the Activity will be shown regardless
// of the lock screen, the call to {@link ActivityStackSupervisor#checkReadyForSleepLocked}
// is skipped.
//暂停现在在栈顶的activity
final ActivityRecord next = topRunningActivityLocked(true /* focusableOnly */);
if (next == null || !next.canTurnScreenOn()) {
checkReadyForSleep();
}
return result;
}1.2.0 ActivityStack resumeTopActivityUncheckedLocked
//当找不到resume的activity时,则直接回到桌面
//当resume状态activity不为空,则执行startPausingLocked,暂停该Activity
//当Activity之前启动过,则直接resume,否则执行startSpecificActivityLocked
private boolean resumeTopActivityInnerLocked(ActivityRecord prev, ActivityOptions options) {
//系统没有进入booting或者booted状态被,则不允许启动Activity
//系统没有启动完成不启动activity
if (!mService.mBooting && !mService.mBooted) {
// Not ready yet!
return false;
}
// Find the next top-most activity to resume in this stack that is not finishing and is
// focusable. If it is not focusable, we will fall into the case below to resume the
// top activity in the next focusable task.
//找到top-most activity没有finishing的栈顶activity
final ActivityRecord next = topRunningActivityLocked(true /* focusableOnly */);
final boolean hasRunningActivity = next != null;
// TODO: Maybe this entire condition can get removed?
//栈顶有stack,但是却没有显示的ActivityDisplay,说明可能此activity已经被移除
if (hasRunningActivity && getDisplay() == null) {
return false;
}
//top running之后的任意处于初始化状态且有显示startingWindow,则移除startingWindow
mStackSupervisor.cancelInitializingActivities();
// Remember how we'll process this pause/resume situation, and ensure
// that the state is reset however we wind up proceeding.
final boolean userLeaving = mStackSupervisor.mUserLeaving;
mStackSupervisor.mUserLeaving = false;
if (!hasRunningActivity) {
// There are no activities left in the stack, let's look somewhere else.
//如果栈顶没有对应的stack,就显示下个stack
return resumeTopActivityInNextFocusableStack(prev, options, "noMoreActivities");
}
next.delayedResume = false;
// If the top activity is the resumed one, nothing to do.
//处于睡眠或者关机状态,top activity已经暂停的情况
if (mResumedActivity == next && next.state == ActivityState.RESUMED &&
mStackSupervisor.allResumedActivitiesComplete()) {
// Make sure we have executed any pending transitions, since there
// should be nothing left to do at this point.
executeAppTransition(options);
if (DEBUG_STATES) Slog.d(TAG_STATES,
"resumeTopActivityLocked: Top activity resumed " + next);
if (DEBUG_STACK) mStackSupervisor.validateTopActivitiesLocked();
return false;
}
final TaskRecord nextTask = next.getTask();
final TaskRecord prevTask = prev != null ? prev.getTask() : null;
//prev!=null的情况
if (prevTask != null && prevTask.getStack() == this &&
prevTask.isOverHomeStack() && prev.finishing && prev.frontOfTask) {
if (DEBUG_STACK) mStackSupervisor.validateTopActivitiesLocked();
if (prevTask == nextTask) {
prevTask.setFrontOfTask();
} else if (prevTask != topTask()) {
// This task is going away but it was supposed to return to the home stack.
// Now the task above it has to return to the home task instead.
final int taskNdx = mTaskHistory.indexOf(prevTask) + 1;
mTaskHistory.get(taskNdx).setTaskToReturnTo(HOME_ACTIVITY_TYPE);
} else if (!isOnHomeDisplay()) {
return false;
} else if (!isHomeStack()){
if (DEBUG_STATES) Slog.d(TAG_STATES,
"resumeTopActivityLocked: Launching home next");
return isOnHomeDisplay() &&
mStackSupervisor.resumeHomeStackTask(prev, "prevFinished");
}
}
// If we are sleeping, and there is no resumed activity, and the top
// activity is paused, well that is the state we want.
//拥有该activity的用户没有启动则直接返回
if (shouldSleepOrShutDownActivities()
&& mLastPausedActivity == next
&& mStackSupervisor.allPausedActivitiesComplete()) {
// Make sure we have executed any pending transitions, since there
// should be nothing left to do at this point.
executeAppTransition(options);
if (DEBUG_STATES) Slog.d(TAG_STATES,
"resumeTopActivityLocked: Going to sleep and all paused");
if (DEBUG_STACK) mStackSupervisor.validateTopActivitiesLocked();
return false;
}
// Make sure that the user who owns this activity is started. If not,
// we will just leave it as is because someone should be bringing
// another user's activities to the top of the stack.
if (!mService.mUserController.hasStartedUserState(next.userId)) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Skipping resume of top activity " + next
+ ": user " + next.userId + " is stopped");
if (DEBUG_STACK) mStackSupervisor.validateTopActivitiesLocked();
return false;
}
// The activity may be waiting for stop, but that is no longer
// appropriate for it.
//从mStoppingActivities ,mGoingToSleepActivities移除他,这两个链表是保持stop和休眠的actvity
mStackSupervisor.mStoppingActivities.remove(next);
mStackSupervisor.mGoingToSleepActivities.remove(next);
next.sleeping = false;
mStackSupervisor.mActivitiesWaitingForVisibleActivity.remove(next);
if (DEBUG_SWITCH) Slog.v(TAG_SWITCH, "Resuming " + next);
// If we are currently pausing an activity, then don't do anything until that is done.
if (!mStackSupervisor.allPausedActivitiesComplete()) {//当处于暂停activity,则直接返回
if (DEBUG_SWITCH || DEBUG_PAUSE || DEBUG_STATES) Slog.v(TAG_PAUSE,
"resumeTopActivityLocked: Skip resume: some activity pausing.");
if (DEBUG_STACK) mStackSupervisor.validateTopActivitiesLocked();
return false;
}
//设置PowerManager.WakeLock就是保持在启动activity这段时间系统不休眠
mStackSupervisor.setLaunchSource(next.info.applicationInfo.uid);
boolean lastResumedCanPip = false;
final ActivityStack lastFocusedStack = mStackSupervisor.getLastStack();//得到最近的stack
if (lastFocusedStack != null && lastFocusedStack != this) {//如果新的stack跟最近的stack不是同一个stack的情况
// So, why aren't we using prev here??? See the param comment on the method. prev doesn't
// represent the last resumed activity. However, the last focus stack does if it isn't null.
final ActivityRecord lastResumed = lastFocusedStack.mResumedActivity;
lastResumedCanPip = lastResumed != null && lastResumed.checkEnterPictureInPictureState(
"resumeTopActivity", userLeaving /* beforeStopping */);
}
// If the flag RESUME_WHILE_PAUSING is set, then continue to schedule the previous activity
// to be paused, while at the same time resuming the new resume activity only if the
// previous activity can't go into Pip since we want to give Pip activities a chance to
// enter Pip before resuming the next activity.
final boolean resumeWhilePausing = (next.info.flags & FLAG_RESUME_WHILE_PAUSING) != 0
&& !lastResumedCanPip;
boolean pausing = mStackSupervisor.pauseBackStacks(userLeaving, next, false);
if(DEBUG_ACTIVITY_START)Log.i("ActivityManagerService-xiao", "ActivityActivity resumeTopActivityInnerLocked mResumedActivity:"+mResumedActivity
+", pausing:"+ pausing+",resumeWhilePausing:"+resumeWhilePausing);
if (mResumedActivity != null) {
if (DEBUG_STATES) Slog.d(TAG_STATES,
"resumeTopActivityLocked: Pausing " + mResumedActivity);
pausing |= startPausingLocked(userLeaving, false, next, false);//调用thread.schedulePauseActivity方法最终会调用onpause
}
/// M: onBeforeActivitySwitch @{
mService.mAmsExt.onBeforeActivitySwitch(mService.mLastResumedActivity, next, pausing,
next.mActivityType);
/// M: onBeforeActivitySwitch @}
if (pausing && !resumeWhilePausing) {
if (DEBUG_SWITCH || DEBUG_STATES) Slog.v(TAG_STATES,
"resumeTopActivityLocked: Skip resume: need to start pausing");
// At this point we want to put the upcoming activity's process
// at the top of the LRU list, since we know we will be needing it
// very soon and it would be a waste to let it get killed if it
// happens to be sitting towards the end.
if (next.app != null && next.app.thread != null) {
mService.updateLruProcessLocked(next.app, true, null);//更新进程lru值
}
if (DEBUG_STACK) mStackSupervisor.validateTopActivitiesLocked();
return true;
} else if (mResumedActivity == next && next.state == ActivityState.RESUMED &&
mStackSupervisor.allResumedActivitiesComplete()) {
// It is possible for the activity to be resumed when we paused back stacks above if the
// next activity doesn't have to wait for pause to complete.
// So, nothing else to-do except:
// Make sure we have executed any pending transitions, since there
// should be nothing left to do at this point.
executeAppTransition(options);
if (DEBUG_STATES) Slog.d(TAG_STATES,
"resumeTopActivityLocked: Top activity resumed (dontWaitForPause) " + next);
if (DEBUG_STACK) mStackSupervisor.validateTopActivitiesLocked();
return true;
}
// If the most recent activity was noHistory but was only stopped rather
// than stopped+finished because the device went to sleep, we need to make
// sure to finish it as we're making a new activity topmost.
//finish那些已经stop的activity
if (shouldSleepActivities() && mLastNoHistoryActivity != null &&
!mLastNoHistoryActivity.finishing) {
if (DEBUG_STATES) Slog.d(TAG_STATES,
"no-history finish of " + mLastNoHistoryActivity + " on new resume");
requestFinishActivityLocked(mLastNoHistoryActivity.appToken, Activity.RESULT_CANCELED,
null, "resume-no-history", false);
mLastNoHistoryActivity = null;
}
if (prev != null && prev != next) {
if (!mStackSupervisor.mActivitiesWaitingForVisibleActivity.contains(prev)
&& next != null && !next.nowVisible) {
mStackSupervisor.mActivitiesWaitingForVisibleActivity.add(prev);
if (DEBUG_SWITCH) Slog.v(TAG_SWITCH,
"Resuming top, waiting visible to hide: " + prev);
} else {
// The next activity is already visible, so hide the previous
// activity's windows right now so we can show the new one ASAP.
// We only do this if the previous is finishing, which should mean
// it is on top of the one being resumed so hiding it quickly
// is good. Otherwise, we want to do the normal route of allowing
// the resumed activity to be shown so we can decide if the
// previous should actually be hidden depending on whether the
// new one is found to be full-screen or not.
if (prev.finishing) {
prev.setVisibility(false);
if (DEBUG_SWITCH) Slog.v(TAG_SWITCH,
"Not waiting for visible to hide: " + prev + ", waitingVisible="
+ mStackSupervisor.mActivitiesWaitingForVisibleActivity.contains(prev)
+ ", nowVisible=" + next.nowVisible);
} else {
if (DEBUG_SWITCH) Slog.v(TAG_SWITCH,
"Previous already visible but still waiting to hide: " + prev
+ ", waitingVisible="
+ mStackSupervisor.mActivitiesWaitingForVisibleActivity.contains(prev)
+ ", nowVisible=" + next.nowVisible);
}
}
}
// Launching this app's activity, make sure the app is no longer
// considered stopped.
try {
//通知PKMS修改该Package stop状态
AppGlobals.getPackageManager().setPackageStoppedState(
next.packageName, false, next.userId); /* TODO: Verify if correct userid */
} catch (RemoteException e1) {
} catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Failed trying to unstop package "
+ next.packageName + ": " + e);
}
// We are starting up the next activity, so tell the window manager
// that the previous one will be hidden soon. This way it can know
// to ignore it when computing the desired screen orientation.
boolean anim = true;
//通知WMS停止绘画动画
if (prev != null) {
if (prev.finishing) {
if (DEBUG_TRANSITION) Slog.v(TAG_TRANSITION,
"Prepare close transition: prev=" + prev);
if (mNoAnimActivities.contains(prev)) {
anim = false;
mWindowManager.prepareAppTransition(TRANSIT_NONE, false);
} else {
mWindowManager.prepareAppTransition(prev.getTask() == next.getTask()
? TRANSIT_ACTIVITY_CLOSE
: TRANSIT_TASK_CLOSE, false);
}
prev.setVisibility(false);
} else {
if (DEBUG_TRANSITION) Slog.v(TAG_TRANSITION,
"Prepare open transition: prev=" + prev);
if (mNoAnimActivities.contains(next)) {
anim = false;
mWindowManager.prepareAppTransition(TRANSIT_NONE, false);
} else {
mWindowManager.prepareAppTransition(prev.getTask() == next.getTask()
? TRANSIT_ACTIVITY_OPEN
: next.mLaunchTaskBehind
? TRANSIT_TASK_OPEN_BEHIND
: TRANSIT_TASK_OPEN, false);
}
}
} else {
if (DEBUG_TRANSITION) Slog.v(TAG_TRANSITION, "Prepare open transition: no previous");
if (mNoAnimActivities.contains(next)) {
anim = false;
mWindowManager.prepareAppTransition(TRANSIT_NONE, false);
} else {
mWindowManager.prepareAppTransition(TRANSIT_ACTIVITY_OPEN, false);
}
}
Bundle resumeAnimOptions = null;
if (anim) {
ActivityOptions opts = next.getOptionsForTargetActivityLocked();
if (opts != null) {
resumeAnimOptions = opts.toBundle();
}
next.applyOptionsLocked();
} else {
next.clearOptionsLocked();
}
ActivityStack lastStack = mStackSupervisor.getLastStack();
//如果该ActivityRecord已有对应的进程存在,则只需要重启Activity,对于新创建的activity next.app=null
if (next.app != null && next.app.thread != null) {
if(DEBUG_ACTIVITY_START)Log.i("ActivityManagerService-xiao", "ActivityStack resumeTopActivityInnerLocked Resume running:"+next + " stopped=" + next.stopped + " visible=" + next.visible);
if (DEBUG_SWITCH) Slog.v(TAG_SWITCH, "Resume running: " + next
+ " stopped=" + next.stopped + " visible=" + next.visible);
// If the previous activity is translucent, force a visibility update of
// the next activity, so that it's added to WM's opening app list, and
// transition animation can be set up properly.
// For example, pressing Home button with a translucent activity in focus.
// Launcher is already visible in this case. If we don't add it to opening
// apps, maybeUpdateTransitToWallpaper() will fail to identify this as a
// TRANSIT_WALLPAPER_OPEN animation, and run some funny animation.
final boolean lastActivityTranslucent = lastStack != null
&& (!lastStack.mFullscreen
|| (lastStack.mLastPausedActivity != null
&& !lastStack.mLastPausedActivity.fullscreen));
// The contained logic must be synchronized, since we are both changing the visibility
// and updating the {@link Configuration}. {@link ActivityRecord#setVisibility} will
// ultimately cause the client code to schedule a layout. Since layouts retrieve the
// current {@link Configuration}, we must ensure that the below code updates it before
// the layout can occur.
synchronized(mWindowManager.getWindowManagerLock()) {
// This activity is now becoming visible.
if (!next.visible || next.stopped || lastActivityTranslucent) {
next.setVisibility(true);//设置activity的可见性
}
// schedule launch ticks to collect information about slow apps.
//计算activity的启动时间launchTickTime
next.startLaunchTickingLocked();
ActivityRecord lastResumedActivity =
lastStack == null ? null :lastStack.mResumedActivity;
ActivityState lastState = next.state;
mService.updateCpuStats();
if (DEBUG_STATES) Slog.v(TAG_STATES, "Moving to RESUMED: " + next
+ " (in existing)");
//更新ActivityRecord的resume的状态
setResumedActivityLocked(next, "resumeTopActivityInnerLocked");
/// M: onAfterActivityResumed @{
mService.mAmsExt.onAfterActivityResumed(next);
/// M: onAfterActivityResumed @}
mService.updateLruProcessLocked(next.app, true, null);//更新app进程的lru值
updateLRUListLocked(next);
mService.updateOomAdjLocked();
// Have the window manager re-evaluate the orientation of
// the screen based on the new activity order.
boolean notUpdated = true;
if (mStackSupervisor.isFocusedStack(this)) {
// We have special rotation behavior when Keyguard is locked. Make sure all
// activity visibilities are set correctly as well as the transition is updated
// if needed to get the correct rotation behavior.
// TODO: Remove this once visibilities are set correctly immediately when
// starting an activity.
if (mStackSupervisor.mKeyguardController.isKeyguardLocked()) {
mStackSupervisor.ensureActivitiesVisibleLocked(null /* starting */,
0 /* configChanges */, false /* preserveWindows */);
}
final Configuration config = mWindowManager.updateOrientationFromAppTokens(
mStackSupervisor.getDisplayOverrideConfiguration(mDisplayId),
next.mayFreezeScreenLocked(next.app) ? next.appToken : null,
mDisplayId);
if (config != null) {
next.frozenBeforeDestroy = true;
}
notUpdated = !mService.updateDisplayOverrideConfigurationLocked(config, next,
false /* deferResume */, mDisplayId);
}
if (notUpdated) {
// The configuration update wasn't able to keep the existing
// instance of the activity, and instead started a new one.
// We should be all done, but let's just make sure our activity
// is still at the top and schedule another run if something
// weird happened.
ActivityRecord nextNext = topRunningActivityLocked();
if (DEBUG_SWITCH || DEBUG_STATES) Slog.i(TAG_STATES,
"Activity config changed during resume: " + next
+ ", new next: " + nextNext);
if (nextNext != next) {
// Do over!
mStackSupervisor.scheduleResumeTopActivities();
}
if (!next.visible || next.stopped) {
next.setVisibility(true);
}
next.completeResumeLocked();
if (DEBUG_STACK) mStackSupervisor.validateTopActivitiesLocked();
return true;
}
try {
// Deliver all pending results.
ArrayList a = next.results;
if (a != null) {
final int N = a.size();
if (!next.finishing && N > 0) {
if (DEBUG_RESULTS) Slog.v(TAG_RESULTS,
"Delivering results to " + next + ": " + a);
next.app.thread.scheduleSendResult(next.appToken, a);//最终调用onActivityResult方法
}
}
//触发onNewIntent 方法
if (next.newIntents != null) {
next.app.thread.scheduleNewIntent(
next.newIntents, next.appToken, false /* andPause */);
}
// Well the app will no longer be stopped.
// Clear app token stopped state in window manager if needed.
//WMS 改变next stop的状态。
next.notifyAppResumed(next.stopped);
EventLog.writeEvent(EventLogTags.AM_RESUME_ACTIVITY, next.userId,
System.identityHashCode(next), next.getTask().taskId,
next.shortComponentName);
//next的状态的更新,为了启动做准备
next.sleeping = false;
mService.showUnsupportedZoomDialogIfNeededLocked(next);
mService.showAskCompatModeDialogLocked(next);
next.app.pendingUiClean = true;
next.app.forceProcessStateUpTo(mService.mTopProcessState);
next.clearOptionsLocked();
if(DEBUG_ACTIVITY_START)Log.i("ActivityManagerService-xiao", "ActivityStack resumeTopActivityInnerLocked scheduleResumeActivity" );
//启动activity ,最终会调用onResume方法
next.app.thread.scheduleResumeActivity(next.appToken, next.app.repProcState,
mService.isNextTransitionForward(), resumeAnimOptions);
if (DEBUG_STATES) Slog.d(TAG_STATES, "resumeTopActivityLocked: Resumed "
+ next);
} catch (Exception e) {
// Whoops, need to restart this activity!
if (DEBUG_STATES) Slog.v(TAG_STATES, "Resume failed; resetting state to "
+ lastState + ": " + next);
next.state = lastState;
if (lastStack != null) {
lastStack.mResumedActivity = lastResumedActivity;
}
Slog.i(TAG, "Restarting because process died: " + next);
if (!next.hasBeenLaunched) {
next.hasBeenLaunched = true;
} else if (SHOW_APP_STARTING_PREVIEW && lastStack != null &&
mStackSupervisor.isFrontStackOnDisplay(lastStack)) {
next.showStartingWindow(null /* prev */, false /* newTask */,
false /* taskSwitch */);
}
mStackSupervisor.startSpecificActivityLocked(next, true, false);
if (DEBUG_STACK) mStackSupervisor.validateTopActivitiesLocked();
return true;
}
}
// From this point on, if something goes wrong there is no way
// to recover the activity.
try {
next.completeResumeLocked();
} catch (Exception e) {
// If any exception gets thrown, toss away this
// activity and try the next one.
Slog.w(TAG, "Exception thrown during resume of " + next, e);
requestFinishActivityLocked(next.appToken, Activity.RESULT_CANCELED, null,
"resume-exception", true);
if (DEBUG_STACK) mStackSupervisor.validateTopActivitiesLocked();
return true;
}
} else {
// Whoops, need to restart this activity!
//第一次启动
if (!next.hasBeenLaunched) {
next.hasBeenLaunched = true;
} else {
if (SHOW_APP_STARTING_PREVIEW) {
next.showStartingWindow(null /* prev */, false /* newTask */,
false /* taskSwich */);
}
if (DEBUG_SWITCH) Slog.v(TAG_SWITCH, "Restarting: " + next);
}
if (DEBUG_STATES) Slog.d(TAG_STATES, "resumeTopActivityLocked: Restarting " + next);
//创建进程
mStackSupervisor.startSpecificActivityLocked(next, true, true);
}
if (DEBUG_STACK) mStackSupervisor.validateTopActivitiesLocked();
return true;
} 这个函数代码量很大,但是也是非常重要,主要工作是:
1.mService.mBooting 为false 也就是系统没启动完成,不让显示Acitivity的。
2.如果启动的activity正在启动,而在它上面的task已被清除,就显示next task
3.如果是休眠状态,没有启动的Activity,或者task的Activity都暂停了
4.做一些动画处理
5. 如果要启动这个activity则需要暂停或者finish其他的activity,并且更新进程的lru值和OomAdj值。
1.2.1 ActivityStackSuppervisor startSpecificActivityLocked
void startSpecificActivityLocked(ActivityRecord r,
boolean andResume, boolean checkConfig) {
// Is this activity's application already running?
//第一次启动,查询结果应该为null
ProcessRecord app = mService.getProcessRecordLocked(r.processName,
r.info.applicationInfo.uid, true);
r.getStack().setLaunchTime(r);//设置启动时间
//已经启动过或者创建过相应的进程
if (app != null && app.thread != null) {
try {
if ((r.info.flags&ActivityInfo.FLAG_MULTIPROCESS) == 0
|| !"android".equals(r.info.packageName)) {
// Don't add this if it is a platform component that is marked
// to run in multiple processes, because this is actually
// part of the framework so doesn't make sense to track as a
// separate apk in the process.
app.addPackage(r.info.packageName, r.info.applicationInfo.versionCode,
mService.mProcessStats);
}
//真正启动Activity
realStartActivityLocked(r, app, andResume, checkConfig);
return;
} catch (RemoteException e) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Exception when starting activity "
+ r.intent.getComponent().flattenToShortString(), e);
}
// If a dead object exception was thrown -- fall through to
// restart the application.
}
//如果第一次启动没有进程的话就创建
mService.startProcessLocked(r.processName, r.info.applicationInfo, true, 0,
"activity", r.intent.getComponent(), false, false, true);
}
启动一些特殊情况的Activity,比如没有进程的Activity。
由于CSDN排版原因,Activity启动流程后半部分在另一篇博文:ActivityManagerService之深入理解Activity启动流程(三)