Runtime面试题与栈区参数
Python实战社群
Java实战社群
长按识别下方二维码,按需求添加
![]()
扫码关注添加客服
进Python社群▲
![]()
扫码关注添加客服
进Java社群▲
作者丨收納箱
来源丨知识小集(zsxjtip)
https://juejin.im/post/5f0dcc676fb9a07e5a1c43d4
1. 面试题
朋友发给我一到面试题,问:
下面代码执行 ⌘+R 后会 Compile Error 、Runtime Crash 或者 NSLog 输出?
如果 [(__bridge id)obj speak]; 能调用成功,输出什么?
@interface Speaker : NSObject
@property (nonatomic, copy) NSString *name;
- (void)speak;
@end
@implementation Speaker
- (void)speak {
NSLog(@"Speaker's name: %@", self.name);
}
@end
@implementation ViewController
- (void)viewDidLoad {
[super viewDidLoad];
id cls = [Speaker class]; // 1
void *obj = &cls; // 2
[(__bridge id)obj speak]; // 3
}
@end
当然,本着 反正不是真面试 的态度,直接跑一下不就行了,嘿嘿。
//输出
Speaker's name:
可以看到运行时成功的,但输出的结果让我有点懵逼???原因有2点:
为什么 [(__bridge id)obj speak] 不会崩溃,而且感觉看着像给 类对象发消息 ,这应该解析不了啊?
为什么 self.name 是ViewController对象?
下面我们仔细分析一下。
2. 分析
2.1 为什么可以发消息?
第一步
id cls = [Speaker class]; // 1
这一步获取到了Speaker的类对象,id表示将其转换为一个对象指针,实际类型为struct objc_object *。
struct objc_object {
Class _Nonnull isa OBJC_ISA_AVAILABILITY;
};
typedef struct objc_object *id;
而 [Speaker class] 的返回类型为Class,其实类型为struct objc_class *。
typedef struct objc_class *Class;
虽然,我们写的类型为struct objc_object *,但其本质还是 struct objc_class *。
id cls = [Speaker class];
if (object_isClass(cls)) {
NSLog(@"object_isClass");
}
// 输出
object_isClass
复制代码也就是说这一步拿到的 本质还是类对象。
id cls = [Speaker class];
[cls speak];
// 直接发送消息,是会崩溃的
+[Speaker speak]: unrecognized selector sent to class 0x106824f08
第二步、第三步
void *obj = &cls; // 2
这一步才是关键。
struct objc_object {
Class _Nonnull isa OBJC_ISA_AVAILABILITY;
};
可以看到struct objc_object这个结构体的首字段是 isa 指向一个Class。
也就是说,我们如果有一个指向Class的地址的指针,相当于这个对象就已经可以使用了。
@interface Speaker : NSObject
@property (nonatomic, copy) NSString *name;
- (void)speak;
@end
@implementation Speaker
- (void)speak {
NSLog(@"speak");
}
@end
struct my_object {
Class isa;
};
struct my_object *getObject() {
// id cls = [Speaker class]; id类型的实质是一个指针,所以cls是一个指针
// void *obj = &cls; 这里取cls的地址,相当于[Speaker class]现在被一个 指针 的 指针 所指向
// 下面 struct my_object * 是一个指针,isa 是一个也是一个指针
// 所以也等效于[Speaker class]现在被一个 指针 的 指针 所指向
struct my_object *obj = (struct my_object *)malloc(sizeof(struct my_object));
obj->isa = [Speaker class];
return obj;
}
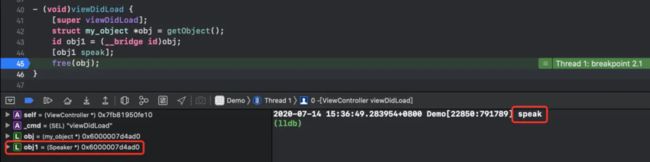
- (void)viewDidLoad {
[super viewDidLoad];
struct my_object *obj = getObject();
id obj1 = (__bridge id)obj;
[obj1 speak]; // 3
free(obj);
}
我们可以看到,通过id类型转换obj1也被Xcode识别为了Speaker实例对象,而且我们调用 [obj1 speak] 也顺利输出了。
相当于消息 objc_msgSend 执行过程中通过 obj1 顺利访问到了 isa 对象,在Speaker类中找到了speak实例方法,并成功调用。
2.2 为什么输出的name是ViewController实例对象?
2.2.1 等价代码
#import
#import
@interface Speaker : NSObject
@property (nonatomic, copy) NSString *name;
- (void)speak;
@end
@implementation Speaker
- (void)speak {
NSLog(@"my name's %@", self.name);
}
@end
@interface ViewController : UIViewController
@end
@implementation ViewController
- (void)viewDidLoad {
[super viewDidLoad];
id cls = [Speaker class];
void *obj = &cls;
[(__bridge id)obj speak];
}
@end
我们将这个 ViewController.m 文件编译为 ViewController.cpp 来看一下。
在 终端 中切换到 ViewController.m 所在目录,并输入以下命令:
xcrun -sdk iphoneos clang -arch arm64 -w -rewrite-objc -fobjc-arc -mios-version-min=8.0.0 -fobjc-runtime=ios-8.0.0 ViewController.m
执行完毕后我们可以在同一个目录下找到 ViewController.cpp 文件。
打开 ViewController.cpp ,并搜索 ViewController_viewDidLoad 即可找到下面的方法:
static void _I_ViewController_viewDidLoad(ViewController * self, SEL _cmd) {
((void (*)(__rw_objc_super *, SEL))(void *)objc_msgSendSuper)((__rw_objc_super){(id)self, (id)class_getSuperclass(objc_getClass("ViewController"))}, sel_registerName("viewDidLoad"));
id cls = ((Class (*)(id, SEL))(void *)objc_msgSend)((id)objc_getClass("Speaker"), sel_registerName("class"));
void *obj = &cls;
((void (*)(id, SEL))(void *)objc_msgSend)((id)(__bridgeid)obj, sel_registerName("speak"));
}
看起来有点复杂,我们把非必要的格式转换去掉:
static void _I_ViewController_viewDidLoad(ViewController * self, SEL _cmd) {
objc_msgSendSuper((__rw_objc_super){self, class_getSuperclass(objc_getClass("ViewController"))}, sel_registerName("viewDidLoad")); // 1
id cls = objc_msgSend(objc_getClass("Speaker"), sel_registerName("class")); // 2
void *obj = &cls; // 3
objc_msgSend(obj, sel_registerName("speak")); // 4
}
可以看到:
对应 [super viewDidLoad]
对应 id cls = [Speaker class];
对应 void *obj = &cls;
对应 [(__bridge id)obj speak];
objc_msgSend 会传入两个隐式参数self和_cmd,想必大家已经很熟悉了。
objc_msgSend(void /* id self, SEL op, ... */ )
OBJC_AVAILABLE(10.0, 2.0, 9.0, 1.0, 2.0);
objc_msgSendSuper(void /* struct objc_super *super, SEL op, ... */ )
OBJC_AVAILABLE(10.0, 2.0, 9.0, 1.0, 2.0);
而 objc_msgSendSuper 需要传入另一个结构体 struct objc_super *。
/// Specifies the superclass of an instance.
struct objc_super {
/// Specifies an instance of a class.
__unsafe_unretained _Nonnull id receiver;
/// Specifies the particular superclass of the instance to message.
#if !defined(__cplusplus) && !__OBJC2__
/* For compatibility with old objc-runtime.h header */
__unsafe_unretained _Nonnull Class class;
#else
__unsafe_unretained _Nonnull Class super_class;
#endif
/* super_class is the first class to search */
};
{self, class_getSuperclass(objc_getClass("ViewController"))} 实际上就是在初始化一个struct objc_super结构体。
知道这些之后,再阅读上面的代码就没有什么难度了。
2.2.2 参数顺序
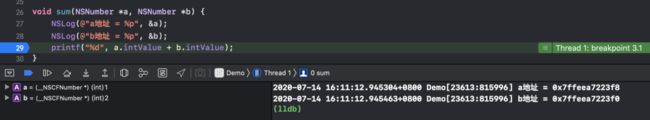
void sum(NSNumber *a, NSNumber *b) {
NSLog(@"a地址 = %p", &a);
NSLog(@"b地址 = %p", &b);
printf("%d", a.intValue + b.intValue);
}
- (void)viewDidLoad {
[super viewDidLoad];
sum(@(1), @(2));
NSNumber *c = @(4);
NSLog(@"c地址 = %p", &c);
}
我们在给函数传入参数时,参数会作为自动变量入栈 :
而且我们可以看到入栈的顺序是a先入栈,b后入栈,因为 栈从高地址到低地址分配内存 。
但是在初始化一个结构体的时候,这个顺序是相反的:
我们看到 two_number tn = {@(1), @(2)}; 先传入的是1后传入的2,但实际情况是2先入栈,1后入栈。
按照上面2条规则,下面代码第5步之前的变量入栈的顺序应该是:
static void _I_ViewController_viewDidLoad(ViewController * self, SEL _cmd) { // 1
objc_msgSendSuper((__rw_objc_super){self, class_getSuperclass(objc_getClass("ViewController"))}, sel_registerName("viewDidLoad")); // 2
id cls = objc_msgSend(objc_getClass("Speaker"), sel_registerName("class")); // 3
void *obj = &cls; // 4
objc_msgSend(obj, sel_registerName("speak")); // 5
}
self、_cmd为函数的隐式参数,依次先入栈。
objc_msgSendSuper 初始化了一个结构体,这个结构体的参数会入栈。
又因为参数入栈是从右到左的顺序入栈:
class_getSuperclass(objc_getClass("ViewController"))
self后入栈
cls本地变量赋值为Speaker类,最后入栈
那么入栈的顺序为self、_cmd、class_getSuperclass(objc_getClass("ViewController"))、self、Speaker类。下面我们验证一下:
@interface Speaker : NSObject
@property (nonatomic, copy) NSString *name;
- (void)speak;
@end
@implementation Speaker
- (void)speak {
NSLog(@"Speaker self: %p, _name: %p", self, &_name);
NSLog(@"Speaker's name: %@", self.name);
}
@end
@implementation ViewController
- (void)viewDidLoad {
[super viewDidLoad];
id cls = [Speaker class]; // 1
void *obj = &cls; // 2
NSLog(@"栈区变量");
void *start = (void *)&self;
void *end = (void *)&obj;
long count = (start - end) / 0x8;
for (long i = 0; i < count; i++) {
void *address = start - 0x8 * i;
if (i == 1) {
NSLog(@"%p: %s", address, *(char **)(address));
} else {
NSLog(@"%p: %@", address, *(void **)address);
}
}
NSLog(@"obj speak");
[(__bridge id)obj speak]; // 3
}
@end
// 打印
Demo[32768:1105890] 栈区变量
Demo[32768:1105890] 0x7ffeec17c648:
Demo[32768:1105890] 0x7ffeec17c640: viewDidLoad
Demo[32768:1105890] 0x7ffeec17c638: ViewController //这里比较怪
Demo[32768:1105890] 0x7ffeec17c630:
Demo[32768:1105890] 0x7ffeec17c628: Speaker
Demo[32768:1105890] obj speak
Demo[32768:1105890] Speaker self: 0x7ffeec17c628, _name: 0x7ffeec17c630
Demo[32768:1105890] Speaker's name:
从输出可以看到,栈区的打印顺序和我们的分析基本吻合。
下面我们看一下为什么Speaker实例对象的 self.name 访问到的是ViewController实例对象。
Speaker实例对象,如果我们通过 [[Speaker alloc] init] 初始化的话,会在堆区分配内存。但现在,我们是使用栈区指针指向了Speaker类对象地址,"伪装"成了一个Speaker实例对象,所以传入的self值为栈区的地址:0x7ffeec17c628 。
从上面的输出我们可以看到,name属性的实例变量_name在Speaker实例对象 self + 0x8 的地址,即 0x7ffeec17c630 。
根据输出_name实例变量访问的地址 0x7ffeec17c630 ,找到栈区对应的数据 0x7ffeec17c630:
3. 总结
通过这个面试题我们得出了一下结论:
Objective-C中的对象是一个指向class_object地址的变量,即 id obj = &class_object
对象的实例变量 void *ivar = &obj + offset(N)
但这里还有一个疑问:
我们看到直接调用 [super viewDidLoad]; ,栈区的第3个变量为ViewController类。
但根据我们用Clang重写的代码 [super viewDidLoad]; 实现做替换:
- (void)viewDidLoad {
((void (*)(struct objc_super *, SEL))(void *)objc_msgSendSuper)(&((struct objc_super){(id)self, (id)class_getSuperclass(objc_getClass("ViewController"))}), sel_registerName("viewDidLoad"));
id cls = [Speaker class]; // 1
void *obj = &cls; // 2
NSLog(@"栈区变量");
void *start = (void *)&self;
void *end = (void *)&obj;
long count = (start - end) / 0x8;
for (long i = 0; i < count; i++) {
void *address = start - 0x8 * i;
if (i == 1) {
NSLog(@"%p: %s", address, *(char **)(address));
} else {
NSLog(@"%p: %@", address, *(void **)address);
}
}
NSLog(@"obj speak");
[(__bridge id)obj speak]; // 3
}
// 输出
Demo[33008:1114325] 栈区变量
Demo[33008:1114325] 0x7ffee4983648:
Demo[33008:1114325] 0x7ffee4983640: viewDidLoad
Demo[33008:1114325] 0x7ffee4983638: UIViewController // 这里符合预期
Demo[33008:1114325] 0x7ffee4983630:
Demo[33008:1114325] 0x7ffee4983628: Speaker
Demo[33008:1114325] obj speak
Demo[33008:1114325] Speaker self: 0x7ffee4983628, _name: 0x7ffee4983630
Demo[33008:1114325] Speaker's name:
我们看到栈区的第3个变量为UIViewController类,这个输出是符合预期的,因为class_getSuperclass(objc_getClass("ViewController"))我们获取的就是父类。
但为什么直接调用 [super viewDidLoad]; ,栈区的第3个变量为ViewController类,这个问题难道是Xcode的Bug???
![]()
程序员专栏 扫码关注填加客服 长按识别下方二维码进群
![]()
近期精彩内容推荐:
![]() 牛逼!北京后厂村惊现互联网工厂,007. ICU
牛逼!北京后厂村惊现互联网工厂,007. ICU
![]() 从月薪2300女工到年薪80万谷歌工程师的女孩
从月薪2300女工到年薪80万谷歌工程师的女孩
![]() 8个流行的Python可视化工具包
8个流行的Python可视化工具包
![]() 分布式锁(数据库、Redis、ZK)拍了拍你
分布式锁(数据库、Redis、ZK)拍了拍你
![]()
![]()
在看点这里![]() 好文分享给更多人↓↓
好文分享给更多人↓↓