单调栈及其应用(leetcode 42&84&85解析)
单调栈
摘录于lucky52529
从名字上就听的出来,单调栈中存放的数据应该是有序的,所以单调栈也分为单调递增栈和单调递减栈
- 单调递增栈:数据出栈的序列为单调递增序列
- 单调递增栈:数据出栈的序列为单调递增序列
举个例子:
现在有一组数10,3,7,4,12。从左到右依次入栈,则如果栈为空或入栈元素值小于栈顶元素值,则入栈;否则,如果入栈则会破坏栈的单调性,则需要把比入栈元素小的元素全部出栈。单调递减的栈反之。
- 10入栈时,栈为空,直接入栈,栈内元素为10。
- 3入栈时,栈顶元素10比3大,则入栈,栈内元素为10,3。
- 7入栈时,栈顶元素3比7小,则栈顶元素出栈,此时栈顶元素为10,比7大,则7入栈,栈内元素为10,7。
- 4入栈时,栈顶元素7比4大,则入栈,栈内元素为10,7,4。
- 12入栈时,栈顶元素4比12小,4出栈,此时栈顶元素为7,仍比12小,栈顶元素7继续出栈,此时栈顶元素为10,仍比12小,10出栈,此时栈为空,12入栈,栈内元素为12。
再举一个通俗的例子(摘自Grandyang):比如有一天,某家店在发 free food,很多人在排队,于是你也赶过去凑热闹。但是由于来晚了,队伍已经很长了,想着不然就插个队啥的。但发现排在队伍最前面的都是一些有纹身的大佬,惹不起,只能赞美道,小猪佩奇身上纹,来世还做社会人。于是往队伍后面走,发现是一群小屁孩,直接全部撵走,然后排在了社会大佬们的后面。那么这就是一个单调递减的栈,按实力递减。由于栈元素是后进先出的,所以上面的例子正确的检查顺序应该是从队尾往前遍历,小屁孩都撵走,直到遇到大佬停止,然后排在大佬后面(假设这个队列已经事先按实力递减排好了)。
明白了单调栈的加入元素的过程后,我们来看看它的性质,以及为啥要用单调栈。单调栈的一大优势就是线性的时间复杂度,所有的元素只会进栈一次,而且一旦出栈后就不会再进来了。
应用示例
(摘自https://www.acwing.com/user/myspace/solution/index/leetcode/21/2/)
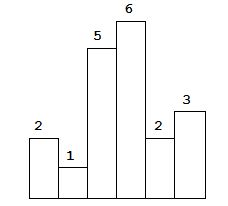
LeetCode 84. Largest Rectangle in Histogram
https://leetcode.com/problems/largest-rectangle-in-histogram/
题目描述
- 给定n个非负整数代表n个柱形条的高度,每个柱形条的宽度都是1,返回该柱形图中最大矩形的面积。
样例
Input: [2,1,5,6,2,3]
Output: 10
解释:如下图显示的最大矩形位置
算法(使用单调栈)
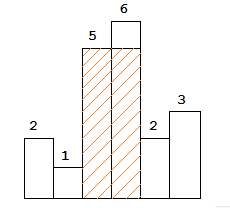
- 此题的本质是找到每个柱形条左边和右边最近的比自己低的矩形条,然后用宽度乘上当前柱形条的高度作为备选答案。
- 解决此类问题的经典做法是单调栈,维护一个单调递增的栈,如果当前柱形条i的高度比栈顶要低,则栈顶元素cur出栈。出栈后,cur右边第一个比它低的柱形条就是i,左边第一个比它低的柱形条是当前栈中的top。不断出栈直到栈为空或者柱形条i不再比top低。
- 满足2之后,当前矩形条i进栈。
C++代码
class Solution {
public:
int largestRectangleArea(vector& heights) {
int n = heights.size(), ans = 0;
heights.push_back(-1);
// 为了算法书写方便,在数组末尾添加高度 -1
// 这会使得栈中所有数字在最后出栈。
stack st;
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) {
while (!st.empty() && heights[i] < heights[st.top()]) {
int cur = st.top();
st.pop();
if (st.empty())
ans = max(ans, heights[cur] * i);
else
ans = max(ans, heights[cur]
* (i - st.top() - 1));
}
st.push(i);
}
return ans;
}
};
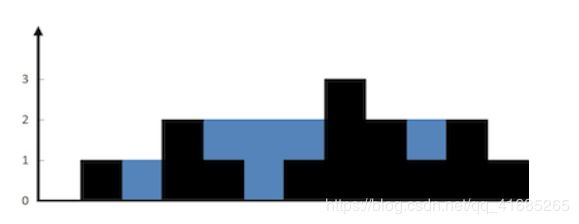
LeetCode 42.Trapping Rain Water
https://leetcode.com/problems/trapping-rain-water/description/
题目描述
给定n个非负整数,代表一个高度地图,每个位置的矩形条宽度为1,计算该图形能装下多少单位的水。
样例
Input: [0,1,0,2,1,0,1,3,2,1,2,1]
Output: 6
算法(单调栈)
- 考虑每个位置左边和右边第一个比它高的位置的矩形条,以及三个矩形条构成的U型。
- 维护单调递减的单调栈,在每次出栈时,i即为当前栈顶st.top()位置第一个比它高的矩形的位置,弹出栈顶,并将当前栈顶记为top。
- 假设此时栈中仍然存在矩形,现在st.top()、top与i三个位置构成一个U型,其中top位置代表U型的底部,此时可以计算出该U型所能接受的水的面积为(i−st.top()−1)∗(min(height[st.top()],height[i])−height[top])
- 如果想不清楚,建议根据代码在纸上模拟一下数据[3, 0, 0, 1, 0, 2, 0, 4],这个例子中总共会出现五次U型。
C++代码
class Solution {
public:
int trap(vector& height) {
int n = height.size(), ans = 0;
stack st;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
while (!st.empty() && height[st.top()] < height[i]) {
int top = st.top();
st.pop();
if (st.empty()) break;
ans += (i - st.top() - 1) * (min(height[st.top()], height[i]) - height[top]);
}
st.push(i);
}
return ans;
}
};
LeetCode 85. Maximal Rectangle
https://leetcode.com/problems/maximal-rectangle
题目描述
给定一个二维的矩阵,矩阵只包含0和1。找到最大的只包含1的矩形,返回它的面积。
样例
输入:
[
["1","0","1","0","0"],
["1","0","1","1","1"],
["1","1","1","1","1"],
["1","0","0","1","0"]
]
输出:6
算法(单调栈) O(nm)O(nm)
- 将 Largest Rectangle in Histogram 问题扩展到二维。
- 一行一行考虑,类比 上一题,一行内所有柱形条的高度 heights 就是当前 (i,j) 位置能往上延伸的最大高度。
- 直接套用 Largest Rectangle in Histogram 的单调栈算法即可。
C++ 代码
class Solution {
public:
int maximalRectangle(vector>& matrix) {
int n = matrix.size(), m, ans = 0;
if (n == 0)
return 0;
m = matrix[0].size();
vector heights(m + 1, 0);
heights[m] = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++)
if (matrix[i][j] == '0')
heights[j] = 0;
else
heights[j]++;
stack st;
for (int j = 0; j <= m; j++) {
while (!st.empty() && heights[j] < heights[st.top()]) {
int cur = st.top();
st.pop();
if (st.empty())
ans = max(ans, heights[cur] * j);
else
ans = max(ans, heights[cur] * (j - st.top() - 1));
}
st.push(j);
}
}
return ans;
}
};