一个绚丽的loading动效分析与实现!
转载:http://blog.csdn.net/tianjian4592
前两天我们这边的头儿给我说,有个 gif 动效很不错,可以考虑用来做项目里的loading,问我能不能实现,看了下效果确实不错,也还比较有新意,复杂度也不是非常高,所以就花时间给做了,我们先一起看下原gif图效果:
从效果上看,我们需要考虑以下几个问题:
1.叶子的随机产生;
2.叶子随着一条正余弦曲线移动;
3.叶子在移动的时候旋转,旋转方向随机,正时针或逆时针;
4.叶子遇到进度条,似乎是融合进入;
5.叶子不能超出最左边的弧角;
7.叶子飘出时的角度不是一致,走的曲线的振幅也有差别,否则太有规律性,缺乏美感;
总的看起来,需要注意和麻烦的地方主要是以上几点,当然还有一些细节问题,比如最左边是圆弧等等;
那接下来我们将效果进行分解,然后逐个击破:
整个效果来说,我们需要的图主要是飞动的小叶子和右边旋转的风扇,其他的部分都可以用色值进行绘制,当然我们为了方便,就连底部框一起切了;
先从gif 图里把飞动的小叶子和右边旋转的风扇、底部框抠出来,小叶子图如下:
我们需要处理的主要有两个部分:
1. 随着进度往前绘制的进度条;
2. 不断飞出来的小叶片;
我们先处理第一部分 - 随着进度往前绘制的进度条:
进度条的位置根据外层传入的 progress 进行计算,可以分为图中 1、2、3 三个阶段:
1. 当progress 较小,算出的当前距离还在弧形以内时,需要绘制如图所示 1 区域的弧形,其余部分用白色填充;
2. 当 progress 算出的距离到2时,需要绘制棕色半圆弧形,其余部分用白色矩形填充;
3. 当 progress 算出的距离到3 时,需要绘制棕色半圆弧形,棕色矩形,白色矩形;
4. 当 progress 算出的距离到头时,需要绘制棕色半圆弧形,棕色矩形;(可以合并到3中)
首先根据进度条的宽度和当前进度、总进度算出当前的位置:
//mProgressWidth为进度条的宽度,根据当前进度算出进度条的位置
mCurrentProgressPosition = mProgressWidth * mProgress / TOTAL_PROGRESS;
然后按照上面的逻辑进行绘制,其中需要计算上图中的红色弧角角度,计算方法如下:
// 单边角度
int angle = (int) Math.toDegrees(Math.acos((mArcRadius - mCurrentProgressPosition)/ (float) mArcRadius));
Math.acos() -反余弦函数;
Math.toDegrees() - 弧度转化为角度,Math.toRadians 角度转化为弧度
所以圆弧的起始点为:
int startAngle = 180 - angle;
圆弧划过的角度为:
2 * angle
这一块的代码如下:
// mProgressWidth为进度条的宽度,根据当前进度算出进度条的位置
mCurrentProgressPosition = mProgressWidth * mProgress / TOTAL_PROGRESS;
// 即当前位置在图中所示1范围内
if (mCurrentProgressPosition < mArcRadius) {
Log.i(TAG, "mProgress = " + mProgress + "---mCurrentProgressPosition = "
+ mCurrentProgressPosition
+ "--mArcProgressWidth" + mArcRadius);
// 1.绘制白色ARC,绘制orange ARC
// 2.绘制白色矩形
// 1.绘制白色ARC
canvas.drawArc(mArcRectF, 90, 180, false, mWhitePaint);
// 2.绘制白色矩形
mWhiteRectF.left = mArcRightLocation;
canvas.drawRect(mWhiteRectF, mWhitePaint);
// 3.绘制棕色 ARC
// 单边角度
int angle = (int) Math.toDegrees(Math.acos((mArcRadius - mCurrentProgressPosition)
/ (float) mArcRadius));
// 起始的位置
int startAngle = 180 - angle;
// 扫过的角度
int sweepAngle = 2 * angle;
Log.i(TAG, "startAngle = " + startAngle);
canvas.drawArc(mArcRectF, startAngle, sweepAngle, false, mOrangePaint);
} else {
Log.i(TAG, "mProgress = " + mProgress + "---transfer-----mCurrentProgressPosition = "
+ mCurrentProgressPosition
+ "--mArcProgressWidth" + mArcRadius);
// 1.绘制white RECT
// 2.绘制Orange ARC
// 3.绘制orange RECT
// 1.绘制white RECT
mWhiteRectF.left = mCurrentProgressPosition;
canvas.drawRect(mWhiteRectF, mWhitePaint);
// 2.绘制Orange ARC
canvas.drawArc(mArcRectF, 90, 180, false, mOrangePaint);
// 3.绘制orange RECT
mOrangeRectF.left = mArcRightLocation;
mOrangeRectF.right = mCurrentProgressPosition;
canvas.drawRect(mOrangeRectF, mOrangePaint);
}
接下来再来看叶子部分:
首先根据效果情况基本确定出 曲线函数,标准函数方程为:y = A(wx+Q)+h,其中w影响周期,A影响振幅 ,周期T= 2 * Math.PI/w;
根据效果可以看出,周期大致为总进度长度,所以确定w=(float) ((float) 2 * Math.PI /mProgressWidth);
仔细观察效果,我们可以发现,叶子飘动的过程中振幅不是完全一致的,产生一种错落的效果,既然如此,我们给叶子定义一个Type,根据Type 确定不同的振幅;
我们创建一个叶子对象:
private class Leaf {
// 在绘制部分的位置
float x, y;
// 控制叶子飘动的幅度
StartType type;
// 旋转角度
int rotateAngle;
// 旋转方向--0代表顺时针,1代表逆时针
int rotateDirection;
// 起始时间(ms)
long startTime;
}
类型采用枚举进行定义,其实就是用来区分不同的振幅:
private enum StartType {
LITTLE, MIDDLE, BIG
}
创建一个LeafFactory类用于创建一个或多个叶子信息:
private class LeafFactory {
private static final int MAX_LEAFS = 6;
Random random = new Random();
// 生成一个叶子信息
public Leaf generateLeaf() {
Leaf leaf = new Leaf();
int randomType = random.nextInt(3);
// 随时类型- 随机振幅
StartType type = StartType.MIDDLE;
switch (randomType) {
case 0:
break;
case 1:
type = StartType.LITTLE;
break;
case 2:
type = StartType.BIG;
break;
default:
break;
}
leaf.type = type;
// 随机起始的旋转角度
leaf.rotateAngle = random.nextInt(360);
// 随机旋转方向(顺时针或逆时针)
leaf.rotateDirection = random.nextInt(2);
// 为了产生交错的感觉,让开始的时间有一定的随机性
mAddTime += random.nextInt((int) (LEAF_FLOAT_TIME * 1.5));
leaf.startTime = System.currentTimeMillis() + mAddTime;
return leaf;
}
// 根据最大叶子数产生叶子信息
public List generateLeafs() {
return generateLeafs(MAX_LEAFS);
}
// 根据传入的叶子数量产生叶子信息
public List generateLeafs(int leafSize) {
List leafs = new LinkedList();
for (int i = 0; i < leafSize; i++) {
leafs.add(generateLeaf());
}
return leafs;
}
}
定义两个常亮分别记录中等振幅和之间的振幅差:
// 中等振幅大小
private static final int MIDDLE_AMPLITUDE = 13;
// 不同类型之间的振幅差距
private static final int AMPLITUDE_DISPARITY = 5;
// 中等振幅大小
private int mMiddleAmplitude = MIDDLE_AMPLITUDE;
// 振幅差
private int mAmplitudeDisparity = AMPLITUDE_DISPARITY;
有了以上信息,我们则可以获取到叶子的Y值:
// 通过叶子信息获取当前叶子的Y值
private int getLocationY(Leaf leaf) {
// y = A(wx+Q)+h
float w = (float) ((float) 2 * Math.PI / mProgressWidth);
float a = mMiddleAmplitude;
switch (leaf.type) {
case LITTLE:
// 小振幅 = 中等振幅 - 振幅差
a = mMiddleAmplitude - mAmplitudeDisparity;
break;
case MIDDLE:
a = mMiddleAmplitude;
break;
case BIG:
// 小振幅 = 中等振幅 + 振幅差
a = mMiddleAmplitude + mAmplitudeDisparity;
break;
default:
break;
}
Log.i(TAG, "---a = " + a + "---w = " + w + "--leaf.x = " + leaf.x);
return (int) (a * Math.sin(w * leaf.x)) + mArcRadius * 2 / 3;
}
接下来,我们开始绘制叶子:
/**
* 绘制叶子
*
* @param canvas
*/
private void drawLeafs(Canvas canvas) {
long currentTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < mLeafInfos.size(); i++) {
Leaf leaf = mLeafInfos.get(i);
if (currentTime > leaf.startTime && leaf.startTime != 0) {
// 绘制叶子--根据叶子的类型和当前时间得出叶子的(x,y)
getLeafLocation(leaf, currentTime);
// 根据时间计算旋转角度
canvas.save();
// 通过Matrix控制叶子旋转
Matrix matrix = new Matrix();
float transX = mLeftMargin + leaf.x;
float transY = mLeftMargin + leaf.y;
Log.i(TAG, "left.x = " + leaf.x + "--leaf.y=" + leaf.y);
matrix.postTranslate(transX, transY);
// 通过时间关联旋转角度,则可以直接通过修改LEAF_ROTATE_TIME调节叶子旋转快慢
float rotateFraction = ((currentTime - leaf.startTime) % LEAF_ROTATE_TIME)
/ (float) LEAF_ROTATE_TIME;
int angle = (int) (rotateFraction * 360);
// 根据叶子旋转方向确定叶子旋转角度
int rotate = leaf.rotateDirection == 0 ? angle + leaf.rotateAngle : -angle
+ leaf.rotateAngle;
matrix.postRotate(rotate, transX
+ mLeafWidth / 2, transY + mLeafHeight / 2);
canvas.drawBitmap(mLeafBitmap, matrix, mBitmapPaint);
canvas.restore();
} else {
continue;
}
}
}
最后,向外层暴露几个接口:
/**
* 设置中等振幅
*
* @param amplitude
*/
public void setMiddleAmplitude(int amplitude) {
this.mMiddleAmplitude = amplitude;
}
/**
* 设置振幅差
*
* @param disparity
*/
public void setMplitudeDisparity(int disparity) {
this.mAmplitudeDisparity = disparity;
}
/**
* 获取中等振幅
*
* @param amplitude
*/
public int getMiddleAmplitude() {
return mMiddleAmplitude;
}
/**
* 获取振幅差
*
* @param disparity
*/
public int getMplitudeDisparity() {
return mAmplitudeDisparity;
}
/**
* 设置进度
*
* @param progress
*/
public void setProgress(int progress) {
this.mProgress = progress;
postInvalidate();
}
/**
* 设置叶子飘完一个周期所花的时间
*
* @param time
*/
public void setLeafFloatTime(long time) {
this.mLeafFloatTime = time;
}
/**
* 设置叶子旋转一周所花的时间
*
* @param time
*/
public void setLeafRotateTime(long time) {
this.mLeafRotateTime = time;
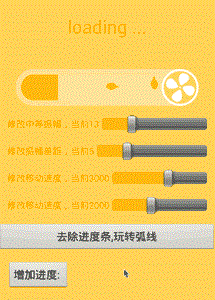
这些接口用来干嘛呢?用于把我们的动效做成完全可手动调节的,这样做有什么好处呢?
1. 更加便于产品、射鸡湿查看效果,避免YY,自己手动调节,不会出现要你一遍遍的改参数安装、查看、再改、再查看... ... N遍之后说 “这好像不是我想要的” -- 瞬间天崩地裂,天昏地暗,感觉被全世界抛弃;
2. 便于体现你是一个考虑全面,思维缜密,会编程、会设计的艺术家,当然这纯属YY,主要还是方便大家;
如此一来,射鸡湿们只需要不断的调节即可实时的看到展现的效果,最后只需要把最终的参数反馈过来即可,万事大吉,一了百了;
当然,如果对方是个漂亮的妹子,而你又苦于没有机会搭讪,以上内容就当我没说,尽情的不按要求写吧,她肯定会主动找你的,说不定连饭都反过来请了... ...
好啦,言归正传,完成收尾部分,我们让所有的参数都可调节起来:
把剩下的layout 和activity贴出来:
activity:
public class LeafLoadingActivity extends Activity implements OnSeekBarChangeListener,
OnClickListener {
Handler mHandler = new Handler() {
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
switch (msg.what) {
case REFRESH_PROGRESS:
if (mProgress < 40) {
mProgress += 1;
// 随机800ms以内刷新一次
mHandler.sendEmptyMessageDelayed(REFRESH_PROGRESS,
new Random().nextInt(800));
mLeafLoadingView.setProgress(mProgress);
} else {
mProgress += 1;
// 随机1200ms以内刷新一次
mHandler.sendEmptyMessageDelayed(REFRESH_PROGRESS,
new Random().nextInt(1200));
mLeafLoadingView.setProgress(mProgress);
}
break;
default:
break;
}
};
};
private static final int REFRESH_PROGRESS = 0x10;
private LeafLoadingView mLeafLoadingView;
private SeekBar mAmpireSeekBar;
private SeekBar mDistanceSeekBar;
private TextView mMplitudeText;
private TextView mDisparityText;
private View mFanView;
private Button mClearButton;
private int mProgress = 0;
private TextView mProgressText;
private View mAddProgress;
private SeekBar mFloatTimeSeekBar;
private SeekBar mRotateTimeSeekBar;
private TextView mFloatTimeText;
private TextView mRotateTimeText;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.leaf_loading_layout);
initViews();
mHandler.sendEmptyMessageDelayed(REFRESH_PROGRESS, 3000);
}
private void initViews() {
mFanView = findViewById(R.id.fan_pic);
RotateAnimation rotateAnimation = DXAnimationUtils.initRotateAnimation(false, 1500, true,
Animation.INFINITE);
mFanView.startAnimation(rotateAnimation);
mClearButton = (Button) findViewById(R.id.clear_progress);
mClearButton.setOnClickListener(this);
mLeafLoadingView = (LeafLoadingView) findViewById(R.id.leaf_loading);
mMplitudeText = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.text_ampair);
mMplitudeText.setText(getString(R.string.current_mplitude,
mLeafLoadingView.getMiddleAmplitude()));
mDisparityText = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.text_disparity);
mDisparityText.setText(getString(R.string.current_Disparity,
mLeafLoadingView.getMplitudeDisparity()));
mAmpireSeekBar = (SeekBar) findViewById(R.id.seekBar_ampair);
mAmpireSeekBar.setOnSeekBarChangeListener(this);
mAmpireSeekBar.setProgress(mLeafLoadingView.getMiddleAmplitude());
mAmpireSeekBar.setMax(50);
mDistanceSeekBar = (SeekBar) findViewById(R.id.seekBar_distance);
mDistanceSeekBar.setOnSeekBarChangeListener(this);
mDistanceSeekBar.setProgress(mLeafLoadingView.getMplitudeDisparity());
mDistanceSeekBar.setMax(20);
mAddProgress = findViewById(R.id.add_progress);
mAddProgress.setOnClickListener(this);
mProgressText = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.text_progress);
mFloatTimeText = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.text_float_time);
mFloatTimeSeekBar = (SeekBar) findViewById(R.id.seekBar_float_time);
mFloatTimeSeekBar.setOnSeekBarChangeListener(this);
mFloatTimeSeekBar.setMax(5000);
mFloatTimeSeekBar.setProgress((int) mLeafLoadingView.getLeafFloatTime());
mFloatTimeText.setText(getResources().getString(R.string.current_float_time,
mLeafLoadingView.getLeafFloatTime()));
mRotateTimeText = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.text_rotate_time);
mRotateTimeSeekBar = (SeekBar) findViewById(R.id.seekBar_rotate_time);
mRotateTimeSeekBar.setOnSeekBarChangeListener(this);
mRotateTimeSeekBar.setMax(5000);
mRotateTimeSeekBar.setProgress((int) mLeafLoadingView.getLeafRotateTime());
mRotateTimeText.setText(getResources().getString(R.string.current_float_time,
mLeafLoadingView.getLeafRotateTime()));
}
@Override
public void onProgressChanged(SeekBar seekBar, int progress, boolean fromUser) {
if (seekBar == mAmpireSeekBar) {
mLeafLoadingView.setMiddleAmplitude(progress);
mMplitudeText.setText(getString(R.string.current_mplitude,
progress));
} else if (seekBar == mDistanceSeekBar) {
mLeafLoadingView.setMplitudeDisparity(progress);
mDisparityText.setText(getString(R.string.current_Disparity,
progress));
} else if (seekBar == mFloatTimeSeekBar) {
mLeafLoadingView.setLeafFloatTime(progress);
mFloatTimeText.setText(getResources().getString(R.string.current_float_time,
progress));
}
else if (seekBar == mRotateTimeSeekBar) {
mLeafLoadingView.setLeafRotateTime(progress);
mRotateTimeText.setText(getResources().getString(R.string.current_rotate_time,
progress));
}
}
@Override
public void onStartTrackingTouch(SeekBar seekBar) {
}
@Override
public void onStopTrackingTouch(SeekBar seekBar) {
}
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
if (v == mClearButton) {
mLeafLoadingView.setProgress(0);
mHandler.removeCallbacksAndMessages(null);
mProgress = 0;
} else if (v == mAddProgress) {
mProgress++;
mLeafLoadingView.setProgress(mProgress);
mProgressText.setText(String.valueOf(mProgress));
}
}
}
layout:
最终效果如下,本来录了20+s,但是PS只能转5s,所以有兴趣的大家自己运行的玩吧:
github 源码地址:
https://github.com/Ajian-studio/GALeafLoading