DFS个人总结
本人写了十道左右的深搜题,感觉这种题实际就是一种模板题,有套路可寻,故挑了几题做个小总结。
①DFS代码大体上可以分为两种,一是走后再判,二是判后再走。现在分别举出用这两种方式解的题:
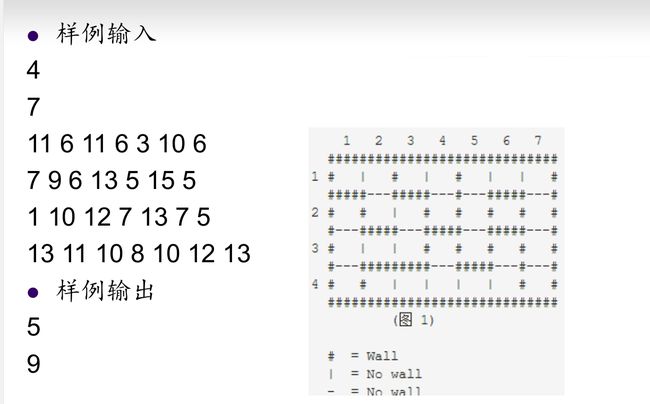
第一题: :百练 2815 城堡问题(网址:点击打开链接)
AC代码:
#include
#include
#include
#include
#define N 100
using namespace std;
int x,y;
int map[N][N];
int color[N][N];
int roomnum,temp,maxnum;
void DFS(int i,int j) //类型一:走后再判
{
if(color[i][j]!=0) //判断(i,j)是否可以走
return ;
temp++;
color[i][j]=roomnum; //做标记
if((map[i][j]&1)==0) DFS(i,j-1); //先走到(i,j-1)上,而后在判断是否走过
if((map[i][j]&2)==0) DFS(i-1,j);
if((map[i][j]&4)==0) DFS(i,j+1);
if((map[i][j]&8)==0) DFS(i+1,j);
}
int main()
{
//freopen("E:\\in.txt","r",stdin);
cin>>x>>y;
memset(map,0,sizeof(map));
memset(color,0,sizeof(color));
for(int i=0;i>map[i][j];
for(int i=0;i AC代码:
#include
#include
using namespace std;
int visited[30][50];
int dfs ( int i,int j,int n) //类型二:先判再走
{
if( n == 0) //终止条件
return 1;
visited[i][j] = 1; //做标记
int num = 0;
if( ! visited[i][j-1] ) //先(i,j-1)判断是否可以走
num+= dfs(i,j-1,n-1);
if( ! visited[i][j+1] )
num+= dfs(i,j+1,n-1);
if( ! visited[i+1][j] )
num+= dfs(i+1,j,n-1);
visited[i][j] = 0; //消除标记
return num;
}
int main()
{
int n;
cin >> n;
memset(visited,0,sizeof(visited));
cout << dfs(0,25,n) << endl;
return 0;
} ②上面两个DFS格式虽然都可以解题,也可以互相转化,不过最好根据具体题目具体做出题目,一般而言,第二种(先判后走)一般耗时更少些,下面举出Poj一个题目,我通过两个格式都交了一次,而且这题也涉及到了两种剪枝类型:可行性剪枝和最优性剪枝
题目:Poj Roads(地址:点击打开链接)
AC代码(先判后走):
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
struct Roads
{
int d;
int l;
int t;
};
vector city[105]; //定义向量,相当于一个二维数组,其中第一维的长度无限大,第二维的长度是105,数组中的各个元素是之前定义的Roads结构体
int K,N,R;
int totallen,totalcost,minlen;
int minn[105][10005]; //minn[i][j]表示到达i城市且花费了j时所走的最小路程 ,用于下面每走到一个城市都可以进行剪枝
int visited[105]; //由于本题是求最短路径长度,而若是走的过程中,对一个城市走了不止一遍,那么肯定不再是最短路径长度,所以每一个城市都不可以重复走
void dfs( int c )
{
if( c == N ) //走到了终点
{
minlen = min( minlen , totallen ); //结束递归之前,先更新minlen的值
return ;
}
int rnum = city[c].size();
for( int i = 0 ; i < rnum ; ++i ) //遍历c城市所能走的所有路
{
if( visited[city[c][i].d] || totalcost + city[c][i].t > K ) //可行性剪枝
continue;
if( totallen + city[c][i].l >= minlen || totallen + city[c][i].l >= minn[city[c][i].d][totalcost + city[c][i].t] ) //最优性剪枝
continue;
totalcost += city[c][i].t;
totallen += city[c][i].l;
minn[city[c][i].d][totalcost] = totallen;
visited[city[c][i].d] = 1; //更新状态
dfs(city[c][i].d);
totallen -= city[c][i].l;
totalcost -= city[c][i].t;
visited[city[c][i].d] = 0; //还原状态
}
}
int main()
{
freopen( "E:\\in.txt", "r" , stdin );
cin >> K; //总共的钱
cin >> N >> R;
for(int i = 0; i < R ; ++i) //构建图(连接表)
{
int s;
cin>>s;
Roads r;
cin>>r.d>>r.l>>r.t;
city[s].push_back(r);
}
totalcost = 0; //初始化
totallen = 0;
minlen = 1 << 30;
for(int i = 0 ; i < 105 ; ++i)
for(int j = 0 ; j < 10005 ; ++j)
minn[i][j] = 1 << 30;
memset(visited,0,sizeof(visited));
visited[1]=1;
dfs(1); //深搜开始
if(minlen == 1 << 30) //minlen的值没有被改变 说明并没有找到合适的路
cout << "-1" << endl;
else
cout << minlen << endl;
return 0;
} AC代码(走后再判):
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
typedef struct Roads
{
int D;
int L;
int T;
}r;
int K;
int N;
int R;
int minlen;
int totallen;
int totalcost;
int visited[105];
int minn[105][10005];
vector map[10005];
void dfs(int n)
{
if( visited[n] || totalcost > K ) //可行性剪枝
return ;
if( totallen >= minlen || totallen >= minn[n][totalcost] ) //最优性剪枝
return ;
minn[n][totalcost] = totallen;
visited[n] = 1; //判断可走后,做标记
if( n == N )
{
minlen = min(minlen,totallen);
return ;
}
for( int i = 0 ; i < map[n].size() ; ++i )
{
int d = map[n][i].D;
totallen += map[n][i].L;
totalcost += map[n][i].T; //走后再判,所以直接先跟新状态量
dfs(d); //回退到d后,还原状态值以及清除标记
visited[d] = 0;
totallen -= map[n][i].L;
totalcost -= map[n][i].T;
}
}
int main()
{
freopen("E:\\in.txt","r",stdin);
cin>>K>>N>>R;
for(int i = 0; i < R; ++i)
{
int s;
r R;
cin >> s >> R.D >> R.L >> R.T;
if(s != R.D)
map[s].push_back(R);
}
minlen=1<<30;
totalcost=0;
totallen=0;
memset(visited,0,sizeof(visited));
for(int i = 0; i < 105 ; ++i)
for(int j = 0; j < 10005 ; ++j)
minn[i][j]=1<<30;
dfs(1); //由于是走后再判,所以dfs(1)之前不能将visited[1]=1
if(minlen == 1<<30)
cout << "-1" << endl;
else
cout< PS:①运行结果显示第一个代码比第二种快,见图
②由于“判”和“走”的先后次序不同,所以在main函数中第一步走之前,visited数组是否标记存在差异,需引起注意
最后附上北大郭炜老师在他课程里的总结的几种dfs模板:
①判断从V出发是否能走到终点:
bool Dfs(V) {
if( V 为终点)
return true;
if( V 为旧点)
return false;
将V 标记为旧点;
对和V 相邻的每个节点U {
if( Dfs(U) == true)
return true;
}
return false;
}
int main()
{
将所有点都标记为新点;
起点 = 1
终点 = 8
cout << Dfs( 起点);
}
将其转化为另一种格式:
bool Dfs(V) {
if( V 为终点)
return true;
将V 标记为旧点;
对和V 相邻的每个节点U {
if(U是新点)
{
if( Dfs(U) == true)
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
int main()
{
将所有点都标记为新点;
起点 = 1
终点 = 8
cout << Dfs( 起点);
}
②判断从V出发是否能走到终点,如果能,要记录路径:
Node path[MAX_LEN]; //MAX_LEN 取节点总数即可
int depth;
bool Dfs(V) {
if( V 为终点){
path[depth] = V;
return true;
}
if( V 为旧点)
return false;
将V 标记为旧点;
path[depth]=V;
++depth;
在图上寻找路径
13
对和V 相邻的每个节点U {
if( Dfs(U) == true)
return true;
}
--depth;
return false;
}
int main()
{
将所有点都标记为新点;
depth = 0;
if( Dfs( 起点)) {
for(int i = 0;i <= depth; ++ i)
cout << path[i] << endl;
}
}
③遍历图上所有节点
Dfs(V) {
if( V 是旧点)
return;
将V 标记为旧点;
对和V 相邻的每个点 U {
Dfs(U);
}
}
int main() {
将所有点都标记为新点;
while( 在图中能找到新点k)
Dfs(k);
}