求二叉树中两个节点的最近公共祖先(三叉链,搜索树,普通二叉树)
求二叉树中两个节点的最近公共祖先。
要求:分别考虑以下三种情况
1、二叉树每个节点有parent(三叉链)
2、二叉树是搜索二叉树。
3、就是普通二叉树。(尽可能实现时间复杂度为O(N))

节点:
struct Node
{
int _data;
Node* _left;
Node* _right;
Node* _parent;
Node(int x)
:_data(x)
, _left(NULL)
, _right(NULL)
, _parent(NULL)
{}
};一、二叉树每个节点有parent(三叉链)
这里介绍两种方法并提供代码实现。
第一种方法:
Node* CommonAncester0(Node* node1, Node* node2)
把从node1和node2到根节点分别看做两个单链表,定义一个指针tmp游走node2这条链表,node1每走一个节点将node2遍历一遍,同时将tmp->_parent对比,若相等,node1即为公共祖先节点;不相等继续游走。
代码如下:
Node* CommonAncester0(Node* node1, Node* node2)
{
if (node1 == NULL || node2 == NULL)
return NULL;
Node* tmp = node2;
while (node1)
{
node1 = node1->_parent;
tmp = node2;
while (tmp)
{
if (node1 == tmp->_parent)
return node1;
tmp = tmp->_parent;
}
}
return NULL;
}第二种方法:
把从node1和node2到根节点分别看做两个单链表,看做寻找两个相交单链表的交点问题来解决。

代码:
Node* CommonAncester1(Node* node1, Node* node2)
{
if (node1 == NULL || node2 == NULL)
return NULL;
//先计算链表长度
int len1 = Length(node1);
int len2 = Length(node2);
int sub = 0;
Node* fast = NULL;
Node* slow = NULL;
if (len1 >= len2)
{
sub = len1 - len2;
fast = node1;
slow = node2;
while (sub--)
fast = fast->_parent;
while (fast)
{
if (fast == slow)
return fast;
fast = fast->_parent;
slow = slow->_parent;
}
}
else
{
sub = len2 - len1;
fast = node2;
slow = node1;
while (sub--)
fast = fast->_parent;
while (fast)
{
if (fast == slow)
return fast;
fast = fast->_parent;
slow = slow->_parent;
}
}
return NULL;
}
二、二叉树是搜索二叉树
搜索二叉树特点:
任意一个节点的左子树的值都小于该节点的值,右子树的值都大于该节点的值。
从二叉树的根节点开始比较,若两个节点的值都比根节点值大,则公共祖先节点一定在右子树,继续在右子树中用相同方法查找;若都比根节点值小,则公共祖先节点一定在左子树,继续在左子树中查找;若两个节点的值一个大于根节点的值,一个小于根节点的值,则公共祖先节点为根节点。
代码:
Node* CommonAncester2(Node* root, Node* node1, Node* node2)
{
if (root == NULL || node1 == NULL || node2 == NULL)
return NULL;
if ((root->_data > node1->_data && root->_data < node2->_data) || (root->_data > node2->_data && root->_data < node1->_data))
return root;
else if (root->_data < node1->_data && root->_data < node2->_data)
return CommonAncester2(root->_right, node1, node2);
else if (root->_data == node1->_data || root->_data == node2->_data)
return root;
else
return CommonAncester2(root->_left, node1, node2);
}三、普通二叉树
方法1:
分别找到node1和node2到根节点的路径存储在两个vector中,然后遍历两个vector,直到找到不同的节点。
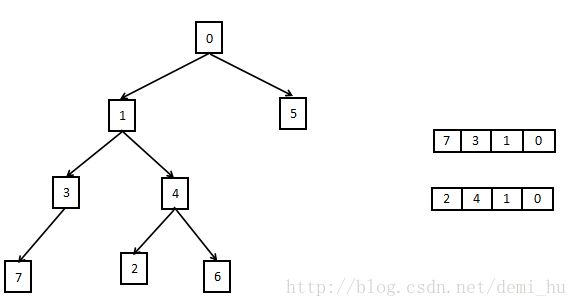
方法2:
先从根节点开始遍历,若node1或node2中一个与root相同,则根节点即为公共节点;递归查找节点 ,若一个节点在root左子树,一个节点在root右子树,root为公共祖先;如果两个节点都出现在左子树,则说明最低公共祖先在左子树中,否则在右子树。
Node* CommonAncester3(Node* root, Node* node1, Node* node2)
{
if (root == NULL || node1 == NULL || node2 == NULL)
return NULL;
if (node1 == root || node2 == root)
return root;
Node* cur = NULL;
Node* left = CommonAncester3(root->_left, node1, node2);
if (left)
{
cur = CommonAncester3(left->_left, node1, node2);
if (cur == NULL)
cur = CommonAncester3(left->_right, node1, node2);
if ((cur == node1&&left == node2) || (cur == node2&&left == node1))
return root;
}
Node* right = CommonAncester3(root->_right, node1, node2);
if (right)
{
cur = CommonAncester3(right->_left, node1, node2);
if (cur == NULL)
cur = CommonAncester3(right->_right, node1, node2);
if ((cur == node1&&right == node2) || (cur == node2&&right == node1))
return root;
}
if (left&&right)
return root;
if (left == NULL)
return right;
else
return left;
}