Minimal search cost DP+平行四边形优化
Minimal search cost
Time Limit : 10000/4000ms (Java/Other) Memory Limit : 65536/32768K (Java/Other)
Total Submission(s) : 19 Accepted Submission(s) : 12
Font: Times New Roman | Verdana | Georgia
Font Size: ← →
Problem Description
As we know, we need to spend O(n) time in the abstract finding a key(every two keys are different) in a non-sorted array. But if we make up a BST(binary search tree) before, then for each access, you need to spend log(N) time to do it. And for each access, there exists a road from the root node to the target node, whose length Ci is the number of the edges of the road.
Because there is an accessing frequency Fi for each key. And the total value of the tree is defined as following rule: SUM=Sigma(Ci*Fi), for i from 0 to N-1, N is the number of the keys. You need to find the minimal value M_SUM to make up a tree.
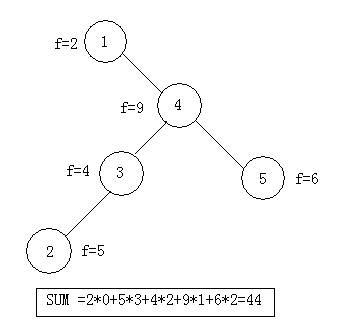

Because there is an accessing frequency Fi for each key. And the total value of the tree is defined as following rule: SUM=Sigma(Ci*Fi), for i from 0 to N-1, N is the number of the keys. You need to find the minimal value M_SUM to make up a tree.


Input
There are a lot of cases. In each case, in the first line, there is an integer N to represent the number of keys. In the second line, there are N sorted integers Ki. In the third line, there are N integers Fi, which are the accessing frequency. 0
Output
For each case, just output the minimal search cost.
Sample Input
5 1 2 3 4 5 2 5 4 9 6
Sample Output
23
Author
Source
2008 “Insigma International Cup” Zhejiang Collegiate Programming Contest - Warm Up(4)
思路:
跟石子归并换汤不换药,题目意思是根据访问频率构建一颗BST,我们很容易想到DP方程
dp[i][j]=min(dp[i][k-1]+dp[k+1][j]+sum(i,k-1)+sum(k+1,j))(i<=k<=j)
时间复杂度为O(n^3),这时我们需要用平行四边形来优化,
我们可以在枚举dp[i][j]时的k值是的范围上做文章;
用s[i][j]来记录i到j最小BST的根结点位置s[i][j],之后在i到j+1的话合并位置不可能在s[i][j]之前,否则s[i][j]更优;有此
我们可以确定k的范围为: s[i][j-1]<=k<=s[i+1][j];于是时间复杂度就降到O(n^2);
#include
#include
using namespace std;
#define N 1010
#define inf 0xfffffff
int dp[N][N];
int s[N][N];
int sum[N],dia[N];
int main(){
int i,n,j,k,pos;
while(scanf("%d",&n)!=EOF)
{
sum[0]=0;
for(i=0;i<=n+1;i++)
for(j=0;j<=n+1;j++)
dp[i][j]=inf;
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
scanf("%d",&pos);
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
scanf("%d",&dia[i]);
sum[i]=sum[i-1]+dia[i];
dp[i][i]=0;
s[i][i]=i;
}
int des;
for(k=2;k<=n;k++)
{
for(i=1;i+k-1<=n;i++)
{
des=i+k-1;
for(j=s[i][des-1];j<=s[i+1][des];j++)
{
if(j==i)
{
if(dp[i][des]>=dp[j+1][des]+sum[des]-sum[j])
{
dp[i][des]=dp[j+1][des]+sum[des]-sum[j];
s[i][des]=j;
}
}
else if(j==des)
{
if(dp[i][des]>=dp[i][j-1]+sum[j-1]-sum[i-1])
{
dp[i][des]=dp[i][j-1]+sum[j-1]-sum[i-1];
s[i][des]=j;
}
}
else
{
if(dp[i][des]>=dp[i][j-1]+dp[j+1][des]+sum[j-1]-sum[i-1]+sum[des]-sum[j])
{
dp[i][des]=dp[i][j-1]+dp[j+1][des]+sum[j-1]-sum[i-1]+sum[des]-sum[j];
s[i][des]=j;
}
}
}
}
}
cout<
}
return 0;
}