Spring学习笔记(一)
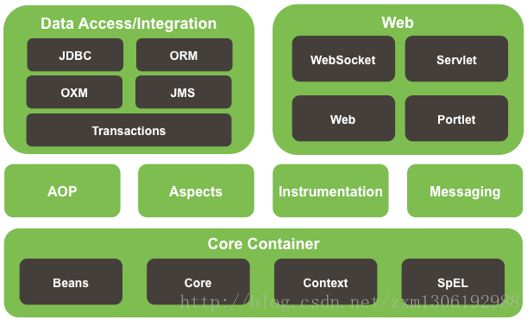
Spring是什么
- Spring是一个开源框架。
- Spring为简化企业级应用开发而生。(使简单的JavaBean实现EJB的功能)
- Spring是一个IOC(DI)和AOP容器框架。
具体描述Spring:
- 轻量级:Spring是非侵入性的-基于Spring开发的应用中的对象可以不依赖于Spring的API。(不用继承或实现接口)
- 依赖注入(DI—dependency injection、IOC—Inversion of Control)
- 面向切面编程(AOP—aspect oriented programming)
- 容器:Spring是一个容器,因为它包含并且管理应用对象的生命周期。
- 框架:Spring实现了使用简单的组件配置组合成一个复制的应用。(使用XML或Java注解组合对象)
- 一站式:在IOC和AOP的基础上可以整合各种企业应用的开源框架,自身的展示层SpringMVC和持久层Spring JDBC或者第三方类库。
安装SPRING TOOL SUITE
SPRING TOOL SUITE 是一个 Eclipse 插件,利用该插件可以更方便的在 Eclipse 平台上开发基于 Spring 的应用。
下载地址:https://spring.io/tools/sts/all
在Update Site Archives中查找相应eclipse版本的安装地址,到eclipse中安装。
只选择后面是 /Spring IDE 的安装项
取消Contact all updates sites during install … 自动更新选项。

搭建Spring开发环境
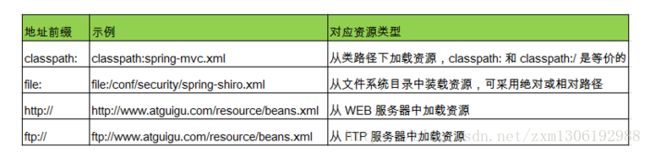
Spring 的配置文件: 一个典型的 Spring 项目需要创建一个或多个 Bean 配置文件, 这些配置文件用于在 Spring IOC 容器里配置 Bean. Bean 的配置文件可以放在 classpath 下, 也可以放在其它目录下.
建立 Spring 项目
HelloWorld.java
public class HelloWorld {
private String user;
public HelloWorld(){
System.out.println("HelloWorld's constructor...");
}
public HelloWorld(String user){
this.user=user;
}
public String getUser() {
return user;
}
public void setUser(String user) {
this.user = user;
}
public void hello(){
System.out.println("Hello:"+user);
}
}Main.java
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// //创建类的对象
// HelloWorld helloWorld=new HelloWorld();
// //给类对象属性赋值
// helloWorld.setUser("atguigu");
//1.创建Spring的IOC容器对象
ApplicationContext ctx=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml");//创建IOC容器时,对配置文件中的bean进行初识化创建对象,并赋值
//2.从IOC容器中获取Bean实例
HelloWorld helloWorld=(HelloWorld) ctx.getBean("helloworld");
//调用对象方法
helloWorld.hello();
}
}新建一个 Spring Bean Configuration File 文件
beans.xml
property 下的name 属性值user 对应HelloWorld.java 中的 setUser 方法。
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:util="http://www.springframework.org/schema/util"
xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/util http://www.springframework.org/schema/util/spring-util-4.0.xsd">
<bean id="helloworld" class="com.atguigu.spring.helloword.HelloWorld">
<property name="user" value="Spring">property>
bean>
beans>IOC和DI
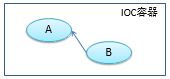
IOC(Inversion of Control,控制反转):其思想是反转资源获取的方向。传统的资源查找方式要求组件向容器发起请求查找资源,容器适时的返回资源。而应用了IOC之后,则是容器主动将资源送给它所管理的组件,组件所要做的仅是选择一种合适的方式来接受资源。这种行为也被称为查找的被动形式。
DI(Dependency Injection,依赖注入),IOC的另一种表述方式:组件以一些预先定义好的方式(例如:setter方法)接受来自如容器的资源注入。
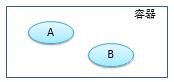
示例:
从容器中获取B对象,并使B对象的a属性被赋值为容器中A对象的引用。

class A{}
class B{
private A a;
public void setA(A a){
this.a = a;
}
}
A a=getA();
B b=getB();
b.setA(a);B b=getB();IOC的前生
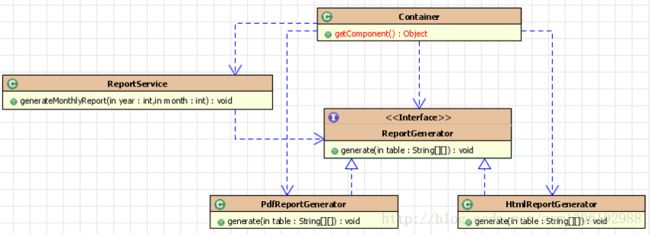
需求:生成 HTML 或 PDF 格式的不同类型的报表。
分离接口和实现
service需要知道接口和接口每个实现类的细节,耦合度高。

采用工厂设计模式
service需要知道接口和工厂,工厂负责生成接口的实现类。

采用控制翻转
Spring中Bean的配置
Bean的配置
Bean 的配置方式:通过全类名(反射)、通过工厂方法(静态工厂方法 & 实例工厂方法)、FactoryBean
- 在 xml 文件中通过 bean 节点来配置 bean
- id:Bean 的名称
- 在 IOC 容器中必须是唯一的
- 若 id 没有指定,Spring 自动将全限定性类名(class=”X.X.X”)作为 Bean 的名字
- id 可以指定多个名字,名字之间可用逗号、分号、或空格分隔
创建Spring 容器
在 Spring IOC 容器读取 Bean 配置创建 Bean 实例之前, 必须对它进行实例化.
Spring 提供了两种类型的 IOC 容器实现.
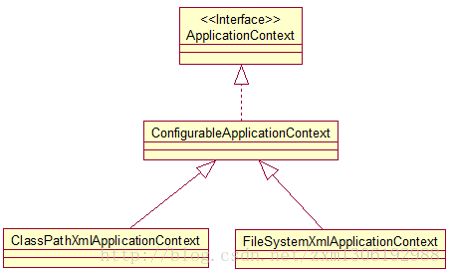
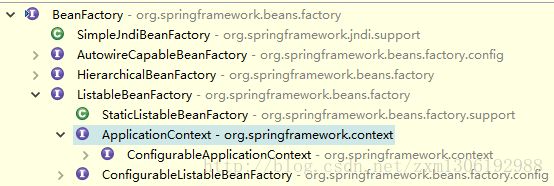
- BeanFactory: IOC 容器的基本实现.(基础设施,面向 Spring 本身)
- ApplicationContext: 提供了更多的高级特性. 是 BeanFactory 的子接口.(面向开发者)
ConfigurableApplicationContext 扩展于 ApplicationContext,新增加两个主要方法:refresh() 和 close(), 让 ApplicationContext 具有启动、刷新和关闭上下文的能力
ApplicationContext 在初始化上下文时就实例化所有单例的 Bean。
ApplicationContext 的主要实现类:
- ClassPathXmlApplicationContext:从类路径下加载配置文件
- FileSystemXmlApplicationContext: 从文件系统中加载配置文件
- WebApplicationContext 是专门为 WEB 应用而准备的,它允许从相对于 WEB 根目录的路径中完成初始化工作。
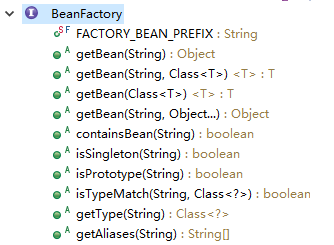
从 IOC 容器中获取 Bean
调用 ApplicationContext 的 getBean() 方法
该方法实际是其父接口BeanFactory中定义的方法
//根据ID定位到IOC的bean
HelloWorld helloWord=(HelloWorld)ctx.getBean("helloWorld");
//根据类型返回IOC容器中的Bean,但如果xml中配置了两个HelloWorld.java 类型的Bean 就会报错,因为它不知道引用哪个bean,所有用此方法要求IOC容器中只有一个该类型的Bean
HelloWorld helloWord=ctx.getBean(HelloWorld.class);依赖注入的方式
Spring 支持 3 种依赖注入的方式
属性注入
构造器注入
工厂方法注入(很少使用,不推荐)
属性注入
通过setter方法注入Bean的属性值或依赖的对象。
对应的实体类中一定要有getter和setter方法,如果写了带参的构造器,一定要有空参的构造器,因为容器用此方法创建对象时会调用空参的构造器。
使用< property>元素, 使用 name 属性指定 Bean 的属性名称,value 属性或 子节点指定属性值
id="helloworld" class="com.atguigu.spring.helloword.HelloWorld">
<property name="user" value="Spring">property>
构造方法注入
通过构造方法注入Bean 的属性值或依赖的对象
构造器注入在 < constructor-arg> 元素里声明属性, < constructor-arg> 中没有 name 属性
public Car(String name, String band, double price) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.band = band;
this.price = price;
}
public Car(String name, String band, int speed) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.band = band;
this.speed = speed;
}
<bean id="car" class="com.atguigu.spring.helloword.Car">
<constructor-arg value="Audi" index="0">constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg value="Shanghai" index="1">constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg value="300000" type="double">constructor-arg>
bean>
<bean id="car2" class="com.atguigu.spring.helloword.Car">
<constructor-arg value="Audi" type="java.lang.String">constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg value="Shanghai" type="java.lang.String">constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg value="240" type="int">constructor-arg>
bean>注入属性值细节
字面值
字面值:可用字符串表示的值,可以通过< value>元素标签或value属性进行注入。
基本数据类型及其包装类、String等类型都可以采取字面值注入的方式。
若字面值中包含特殊字符,可以使用< ![CDATA[ ]]>把字面值包裹进去。
<property name="user">
<value>]]>value>
property>引用其它Bean
在 Bean 的配置文件中, 可以 ref 属性 或通过 < ref> 元素为Bean的属性或构造器参数指定对 Bean 的引用.
<bean id="person" class="com.atguigu.spring.helloword.Person">
<property name="name" value="Tom">property>
<property name="age" value="24">property>
<property name="car" ref="car2">property>
<property name="car">
<ref bean="car2"/>
property>
bean>也可以在属性或构造器里包含 Bean 的声明, 这样的 Bean 称为内部 Bean。
<bean id="person" class="com.atguigu.spring.helloword.Person">
<property name="name" value="Tom">property>
<property name="age" value="24">property>
<property name="car">
<bean class="com.atguigu.spring.helloword.Car">
<constructor-arg value="Audi" index="0">constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg value="Shanghai" index="1">constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg value="300000" type="double">constructor-arg>
bean>
property>
bean>null 值和级联属性
通过构造器方法来配置bean的属性时,参数传null值,可以使用专用的 < null/> 元素标签为 Bean 的字符串或其它对象类型的属性注入 null 值
<bean id="car" class="com.atguigu.spring.helloword.Car">
<constructor-arg value="Audi" index="0">constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg index="1"><null/>constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg value="300000" type="double">constructor-arg>
bean>和 Struts、Hiberante 等框架一样,Spring 支持级联属性的配置。
<bean id="person2" class="com.atguigu.spring.helloword.Person">
<constructor-arg value="Jerry">constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg value="25">constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg ref="car2">constructor-arg>
<property name="car.price" value="3000">property>
bean>集合属性
在 Spring中可以通过一组内置的 xml 标签(例如: < list>, < set> 或 < map>) 来配置集合属性.
配置 java.util.List 类型的属性, 需要指定 < list> 标签, 在标签里包含一些元素. 这些标签可以通过 < value> 指定简单的常量值, 通过 < ref> 指定对其他 Bean 的引用. 通过< bean> 指定内置 Bean 定义. 通过 < null/> 指定空元素. 甚至可以内嵌其他集合.
数组的定义和 List 一样, 都使用 < list>
配置 java.util.Set 需要使用 < set> 标签, 定义元素的方法与 List 一样.
<bean id="person3" class="com.atguigu.spring.helloword.collections.Person">
<property name="name" value="Mike">property>
<property name="age" value="27">property>
<property name="cars" >
<list>
<ref bean="car"/>
<ref bean="car2"/>
<bean class="com.atguigu.spring.helloword.Car">
<constructor-arg value="Audi" index="0">constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg value="Shanghai" index="1">constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg value="300000" type="double">constructor-arg>
bean>
list>
property>
bean>Java.util.Map 通过 < map> 标签定义, 标签里可以使用多个 < entry> 作为子标签. 每个条目包含一个键和一个值.
因为键和值的类型没有限制, 所以可以自由地为它们指定 < value>, < ref>, < bean> 或 < null> 元素.
可以将 Map 的键和值作为 < entry> 的属性定义: 简单常量使用 key 和 value 来定义; Bean 引用通过 key-ref 和 value-ref 属性定义
<bean id="newperson" class="com.atguigu.spring.helloword.collections.NewPerson">
<property name="name" value="Mike">property>
<property name="age" value="27">property>
<property name="cars">
<map>
<entry key="AA" value-ref="car">entry>
<entry key="BB" value-ref="car2">entry>
map>
property>
bean>使用 < props> 定义 java.util.Properties, 该标签使用多个 < prop> 作为子标签. 每个 < prop> 标签必须定义 key 属性.
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.atguigu.spring.helloword.collections.DataSource">
<property name="properties">
<props>
<prop key="user">rootprop>
<prop key="password">1234prop>
<prop key="jdbcUrl">jdbc:mysql:///testprop>
<prop key="driverClass">com.sql.jdbc.Driverprop>
props>
property>
bean>使用 utility scheme 定义集合
使用基本的集合标签定义集合时, 不能将集合作为独立的 Bean 定义, 导致其他 Bean 无法引用该集合, 所以无法在不同 Bean 之间共享集合.
可以使用 util schema 里的集合标签定义独立的集合 Bean. 需要注意的是, 必须在 < beans> 根元素里添加 util schema 定义
<util:list id="cars">
<ref bean="car"/>
<ref bean="car2"/>
util:list>
<bean id="person4" class="com.atguigu.spring.helloword.collections.Person">
<property name="name" value="Mike">property>
<property name="age" value="29">property>
<property name="cars" ref="cars">property>
bean>使用p命名空间
为了简化 XML 文件的配置,越来越多的 XML 文件采用属性而非子元素配置信息。
Spring 从 2.5 版本开始引入了一个新的 p 命名空间,可以通过 < bean> 元素属性的方式配置 Bean 的属性。
使用 p 命名空间后,基于 XML 的配置方式将进一步简化。
<bean id="person5" class="com.atguigu.spring.helloword.collections.Person" p:age="30"
p:name="Queen" p:cars-ref="cars">
bean>XML 配置里的 Bean 自动装配
Spring IOC 容器可以自动装配 Bean. 需要做的仅仅是在 < bean> 的 autowire 属性里指定自动装配的模式
- byName(根据名称自动装配): 必须将目标 Bean 的名称和属性名设置的完全相同.
- byType(根据类型自动装配): 若 IOC 容器中有多个与目标 Bean 类型一致的 Bean. 在这种情况下, Spring 将无法判定哪个 Bean 最合适该属性, 所以不能执行自动装配.
- constructor(通过构造器自动装配): 当 Bean 中存在多个构造器时, 此种自动装配方式将会很复杂. 不推荐使用
不使用自动装配的情况
<bean id="address" class="com.atguigu.spring.beans.autowire.Address"
p:city="Beijing" p:street="HuiLongGuan">bean>
<bean id="car" class="com.atguigu.spring.beans.autowire.Car"
p:brand="Audi" p:price="300000">bean>
<bean id="person" class="com.atguigu.spring.beans.autowire.Person"
p:name="Tom" p:address-ref="address" p:car-ref="car">bean>
<bean id="person" class="com.atguigu.spring.beans.autowire.Person"
p:name="Tom" autowire="byName">bean>
<bean id="person" class="com.atguigu.spring.beans.autowire.Person"
p:name="Tom" autowire="byType">bean>自动装配的缺点:
- 在 Bean 配置文件里设置 autowire 属性进行自动装配将会装配 Bean 的所有属性. 然而, 若只希望装配个别属性时, autowire 属性就不够灵活了.
- autowire 属性要么根据类型自动装配, 要么根据名称自动装配, 不能两者兼而有之.
- 一般情况下,在实际的项目中很少使用自动装配功能,因为和自动装配功能所带来的好处比起来,明确清晰的配置文档更有说服力一些
Bean之间的关系:继承、依赖
继承Bean配置
- Spring 允许继承 bean 的配置, 被继承的 bean 称为父 bean. 继承这个父 Bean 的 Bean 称为子 Bean
- 子 Bean 从父 Bean 中继承配置, 包括 Bean 的属性配置
- 子 Bean 也可以覆盖从父 Bean 继承过来的配置
- 父 Bean 可以作为配置模板, 也可以作为 Bean 实例. 若只想把父 Bean 作为模板, 可以设置 < bean> 的abstract 属性为 true, 这样 Spring 将不会实例化这个 Bean
- 并不是 < bean> 元素里的所有属性都会被继承. 比如: autowire, abstract 等.
- 如果父 Bean 没有 class 属性, 那它必须是一个抽象Bean,此时 abstract 必须设为 true。
<bean id="address" class="com.atguigu.spring.beans.autowire.Address"
p:city="Beijing" p:street="WuDaoKou" abstract="true">bean>
<bean id="address2" p:street="DaZhongSi" parent="address">bean>依赖Bean配置
- Spring允许用户通过depends-on属性设定Bean前置依赖的Bean,前置依赖的Bean会在本Bean实例化之前创建好。
- 如果前置依赖于多个Bean,则可以通过逗号,或者空格的方式指定配置依赖与的Bean的名称。
<bean id="car" class="com.atguigu.spring.beans.autowire.Car"
p:brand="Audi" p:price="300000">bean>
<bean id="person" class="com.atguigu.spring.beans.autowire.Person"
p:name="Tom" p:address-ref="address2" depends-on="car">bean>Bean的作用域
在Spring中,可以在< bean>元素的scope属性里设置Bean的作用域。
默认情况下,Spring只为每个在IOC容器里声明的Bean创建唯一一个实例(singleton),整个IOC容器范围内都可共享该实例:所有后续的getBean()调用和Bean引用都将返回这个唯一的Bean实例。该作用域被称为singleton,它是所有Bean的默认作用域。

<bean id="car" class="com.atguigu.spring.beans.autowire.Car" scope="prototype">
<property name="brand" value="Audi">property>
<property name="price" value="300000">property>
bean>使用外部属性文件
在配置文件里配置Bean时,有时需要在Bean的配置里混入系统部署的细节信息(如:文件路径,数据源配置信息等)。而这些部署细节实际上需要和Bean配置相分离。
Spring提供了一个PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer的BeanFactory后置处理器,这个处理器允许用户将Bean配置的部分内容后移到属性文件中。可以在Bean配置问价里使用形式为${var} 的变量,PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer 从属性文件里加载属性,并使用这些属性替换变量。
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:db.properties"/>
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource">
<property name="user" value="${user}">property>
<property name="password" value="${password}">property>
<property name="driverClass" value="${driverClass}">property>
<property name="jdbcUrl" value="${jdbcUrl}">property>
bean>如果出现cvc-complex-type.2.4.c: The matching wildcard is strict, but no declaration错误,则在xml头加入
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.0.xsd"Spring表达式语言:SpEL
Spring表达式语言(简称SpEL):是一个支持运行时查询和操作对象图的强大的表达式语言。
语法类似于EL:SpEL使用 #{…} 作为限定符,所有在大框号中的字符都将被认为是SpEL
SpEL为bean的属性进行动态赋值提供了便利
通过SpEL可以实现:
- 通过bean的id对bean进行引用
- 调用方法以及引用对象中的属性
- 计算表达式的值
- 正则表达式的匹配
SpEL:字面值
字面值的表示:
- 整数:< property name=”count” value=”#{5}”/>
- 小数:< property name=”frequency” value=”#{89.7}”/>
- 科学计数法:< property name=”capacity” value=”#{1e4}”/>
- String可以使用单引号或者双引号作为字符串的界定符号:< property name=”name” value=”#{Chuck}”/>或< property name=’name’ value=’#{“Chuck”}’>
- Boolean:< property name=”enabled” value=”#{false}”/>
此处使用SpEL的意义不大
SpEL:引用Bean、属性和方法
- 引用其他对象:
<property name="car" value="#{car}">property>- 引用其他对象的属性:
<property name="city" value="#{address.city}">property>- 调用其他方法,还可以链式操作:
<property name="suffix" value="#{sequenceGenerator2.toString()}">
<property name="suffix" value="#{sequenceGenerator2.toString().toUpperCase()}">- 调用静态方法或静态属性:
通过 T() 调用一个类的静态方法,它将返回一个 Class Object,然后再调用相应的方法或属性:
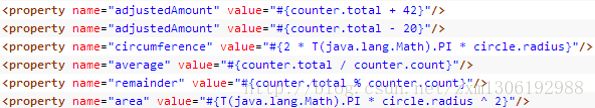
<property name="tyrePerimeter" value="#{T(java.lang.Math).PI*80}">property>SpEL支持的运算符号
算数运算符:+, -, *, /, %, ^:
加号还可以用作字符串连接:
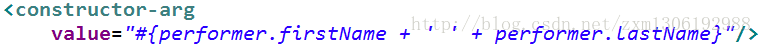
比较运算符: <, >, ==, <=, >=, lt, gt, eq, le, ge

逻辑运算符号: and, or, not, |

if-else 运算符:?: (ternary), ?: (Elvis)

if-else 的变体

正则表达式:matches

IOC容器中Bean的生命周期
SpringIOC容器可以管理Bean的生命周期,Spring允许在Bean生命周期的特定点执行定制的任务。
Spring IOC容器对Bean的生命周期进行管理的过程:
- 通过构造器或工厂方法创建Bean实例
- 为Bean的属性设置值和对其他Bean的引用
- 调用Bean的初始化方法
- Bean可以使用了
- 当容器关闭时,调用Bean的销毁方法
Car’s Constructor…
setBrand…
init…
com.atguigu.spring.beans.cycle.Car@5f1843c0
destroy…
在Bean的声明里设置 init-method 和 destroy-method 属性,为Bean指定 初始化 和 销毁方法
创建Bean后置处理器
Bean后置处理器允许在调用初始化方法前后对Bean进行额外的处理。
Bean后置处理器对IOC容器里的所有Bean实例逐一处理,而非单一实例。其典型应用是:检查Bean属性的正确性或根据特定的标准更改Bean的属性。
对Bean后置处理器而言,需要实现 org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanPostProcessor接口。在初始化方法被调用前后,Spring将把每个Bean实例分别传递给上述接口的以下两个方法:
public class MyBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor{
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("postProcessAfterInitialization:"+bean+","+beanName);
if("car".equals(beanName)){
//对不同的bean类型进行处理
}
return bean;
}
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("postProcessBeforeInitialization:"+bean+","+beanName);
// Car car=new Car();
// car.setBrand("Ford");
// return car;
return bean;
}
} <bean id="car" class="com.atguigu.spring.beans.cycle.Car"
init-method="init"
destroy-method="destroy">
<property name="brand" value="Audi">property>
bean>
<bean class="com.atguigu.spring.beans.cycle.MyBeanPostProcessor">bean>Spring IOC 容器对 Bean 的生命周期进行管理的过程:
- 通过构造器或工厂方法创建Bean实例
- 为Bean的属性设置值和对其他Bean的引用
- 将Bean实例传递给Bean后置处理器的postProcessBeforeInitialization 方法
- 调用Bean的初始化方法
- 将Bean实例传递给Bean后置处理器的postProcessAfterInitialization方法
- Bean可以使用了
- 当容器关闭是,调用Bean的销毁方法
Car’s Constructor…
setBrand…
postProcessBeforeInitialization:Car [brand=Audi],car
init…
postProcessAfterInitialization:Car [brand=Audi],car
destroy…
详细版:
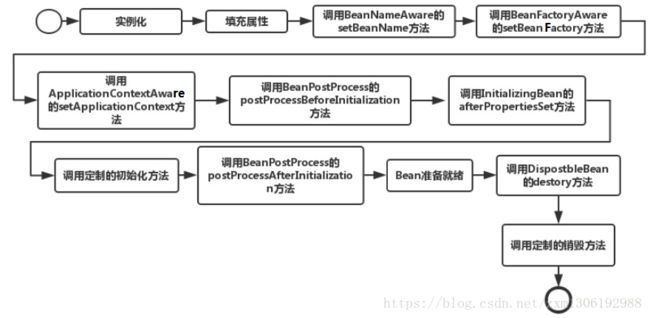
1.Spring对Bean进行实例化(相当于程序中的new Xx())
2.Spring将 值 和 Bean的引用 注入进Bean对应的属性中
3.如果Bean实现了BeanNameAware接口,Spring将Bean的ID传递给setBeanName()方法
(实现BeanNameAware主要是为了通过Bean的引用来获得Bean的ID,一般业务中是很少有用到Bean的ID的)
4.如果Bean实现了BeanFactoryAware接口,Spring将调用setBeanFactory(BeanFactory bf)方法并把BeanFactory容器实例作为参数传入。
(实现BeanFactoryAware 主要目的是为了获取Spring容器,如Bean通过Spring容器发布事件等)
5.如果Bean实现了ApplicationContextAware接口,Spring容器将调用setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext ctx)方法,把应用上下文作为参数传入。
(作用与BeanFactory类似都是为了获取Spring容器,不同的是Spring容器在调用setApplicationContext方法时会把它自己作为setApplicationContext 的参数传入,而Spring容器在调用setBeanFactory前需要程序员自己指定(注入)setBeanFactory里的参数BeanFactory )
6.如果Bean实现了BeanPostProcess接口,Spring将调用它们的postProcessBeforeInitialization(预初始化)方法
(作用是在Bean实例创建成功后对进行增强处理,如对Bean进行修改,增加某个功能)
7.如果Bean实现了InitializingBean接口,Spring将调用它们的afterPropertiesSet方法,作用与在配置文件中对Bean使用init-method声明初始化的作用一样,都是在Bean的全部属性设置成功后执行的初始化方法。
8.如果Bean实现了BeanPostProcess接口,Spring将调用它们的postProcessAfterInitialization(后初始化)方法
(作用与6的一样,只不过6是在Bean初始化前执行的,而这个是在Bean初始化后执行的,时机不同 )
9.经过以上的工作后,Bean将一直驻留在应用上下文中给应用使用,直到应用上下文被销毁
10.如果Bean实现了DispostbleBean接口,Spring将调用它的destory方法,作用与在配置文件中对Bean使用destory-method属性的作用一样,都是在Bean实例销毁前执行的方法。
通过调用静态工厂方法创建Bean
调用静态工厂方法创建Bean是将对象创建的过程封装到静态方法中。当客户端需要对象时,只需要简单地调用静态方法,而不用关心创建对象的细节。
要声明通过静态方法创建的Bean,需要在Bean的class属性里指定拥有该工厂的方法的类,同时在Factory-method属性里指定工厂方法的名称。最后,使用< constructor-arg>元素为该方法传递方法参数。
//静态工厂方法:直接调用某个类的静态方法就可以返回Bean的实例
public class StaticCarFactory {
private static Map cars=new HashMap();
//使用静态代码块,对cars进行初始化
static{
cars.put("audi", new Car("audi",300000));
cars.put("ford", new Car("ford",400000));
}
//静态工厂方法。
public static Car getCar(String name){
return cars.get(name);
}
}
<bean id="car1" class="com.atguigu.spring.beans.factory.StaticCarFactory" factory-method="getCar">
<constructor-arg value="audi">constructor-arg>
bean>通过调用实例工厂方法创建Bean
实例工厂方法:将对象的创建过程封装到另外一个对象实例的方法里。当客户端需要请求对象时,只需要简单的调用该实例方法而不需要关心对象的创建细节。
要声明通过实例工厂方法创建的Bean
- 在 bean 的 factory-bean 属性里指定拥有该工厂方法的 Bean
- 在 factory-method 属性里指定该工厂方法的名称
- 使用 constructor-arg 元素为工厂方法传递方法参数
//实例工厂方法:实例工厂的方法,即现需要创建工厂本身,再调用工厂的实例方法来返回bean的实例
public class InstanceCarFactory {
private Map cars=null;
public InstanceCarFactory(){
cars=new HashMap();
cars.put("audi", new Car("audi",300000));
cars.put("audi", new Car("ford",400000));
}
public Car getCar(String brand){
return cars.get(brand);
}
}
<bean id="carFactory" class="com.atguigu.spring.beans.factory.InstanceCarFactory">bean>
<bean id="car2" factory-bean="carFactory" factory-method="getCar">
<constructor-arg value="ford">constructor-arg>
bean>实现FactoryBean 接口在容器中配置Bean
Spring中有两种类型的Bean,一种是普通Bean,另一种是工厂Bean,即FactoryBean。
工厂Bean跟普通Bean不同,其返回的对象不是指定类的一个实例,其返回的是该工厂Bean的getObject 方法所返回的对象
//自定义的FactoryBean 需要实现FactoryBean接口
public class CarFactoryBean implements FactoryBean<Car>{
private String brand;
public void setBrand(String brand){
this.brand=brand;
}
//返回bean的对象
@Override
public Car getObject() throws Exception {
return new Car(brand,500000);
}
//返回bean的类型
@Override
public Class getObjectType() {
return Car.class;
}
//返回实例是否是单例
@Override
public boolean isSingleton() {
return false;
}
}
<bean id="car" class="com.atguigu.spring.beans.factorybean.CarFactoryBean">
<property name="brand" value="BMW">property>
bean>基于注解的方式
基于注解配置Bean
组件扫描(component scanning): Spring 能够从 classpath 下自动扫描, 侦测和实例化具有特定注解的组件.
特定组件包括:
- @Component: 基本注解, 标识了一个受 Spring 管理的组件
- @Controller: 标识表现层组件
- @Service: 标识服务层(业务层)组件
- @Respository: 标识持久层组件
对于扫描到的组件, Spring 有默认的命名策略: 使用非限定类名, 第一个字母小写. 也可以在注解中通过 value 属性值标识组件的名称
当在组件类上使用了特定的注解之后, 还需要在 Spring 的配置文件中声明
- base-package 属性指定一个需要扫描的基类包,Spring 容器将会扫描这个基类包里及其子包中的所有类.
- 当需要扫描多个包时, 可以使用逗号分隔.
如果仅希望扫描特定的类而非基包下的所有类,可使用 resource-pattern 属性过滤特定的类,示例:
<context:component-scan base-package="com.atguigu.spring.beans.annotation" resource-pattern="repository/*.class"> context:component-scan><context:component-scan base-package="com.atguigu.spring.beans.annotation" use-default-filters="false"> <context:include-filter type="annotation" expression="org.springframework.stereotype.Repository"/> context:component-scan><context:component-scan base-package="com.atguigu.spring.beans.annotation"> <context:exclude-filter type="annotation" expression="org.springframework.stereotype.Repository"/> context:component-scan>--><context:component-scan base-package="com.atguigu.spring.beans.annotation"> <context:exclude-filter type="assignable" expression="com.atguigu.spring.beans.annotation.repository.User"/> context:component-scan>

注意:使用主键扫描,必须添加 spring-aop-4.0.0.RELEASE.jar 包,不然会报Caused by: java.lang.ClassNotFoundException: org.springframework.aop.TargetSource错误
基于注解来装配 Bean
使用 @Autowired 自动装配 Bean
@Autowired 注解自动装配IOC容器中具有兼容类型的单个 Bean属性
构造器, 普通字段(即使是非 public), 一切具有参数的方法都可以应用@Authwired 注解
@Autowired private UserDao userDao; 或 @Autowired public void setUserDao(UserDao userDao) { this.userDao = userDao; }默认情况下, 所有使用 @Authwired 注解的对象都需要被设置. 当 Spring 找不到匹配的 Bean 装配Bean时, 会抛出异常, 若某一对象允许不被设置, 可以设置 @Authwired 注解的 required 属性为 false
默认情况下, 当 IOC 容器里存在多个类型兼容的 Bean 时(通常是给接口装配,有多个实现类), 通过类型的自动装配将无法工作. 此时可以在 @Qualifier 注解里提供 Bean 的名称.
@Autowired @Qualifier("userRepositoryImp") private UserRepository userRepository;@Authwired 注解也可以应用在数组类型的属性上, 此时 Spring 将会把所有匹配的 Bean 进行自动装配.
- @Authwired 注解也可以应用在集合属性上, 此时 Spring 读取该集合的类型信息, 然后自动装配所有与之兼容的 Bean.
- @Authwired 注解用在 java.util.Map 上时, 若该 Map 的键值为 String, 那么 Spring 将自动装配与之 Map 值类型兼容的 Bean, 此时 Bean 的名称作为键值
Spring 还支持 @Resource 和 @Inject 注解,这两个注解和 @Autowired 注解的功用类似,建议使用 @Autowired 注解
@Resource 注解要求提供一个 Bean 名称的属性,若该属性为空,则自动采用标注处的变量或方法名作为 Bean 的名称
@Inject 和 @Autowired 注解一样也是按类型匹配注入的 Bean, 但没有 reqired 属性
Spring 4.X 新特性:泛型依赖注入
父类之间有引用关系,子类在继承父类时,传入了泛型的具体类型,Spring可以为子类注入 子类对应的泛型类型的成员变量的引用。
整合多个配置文件
Spring 允许通过