ugui ui相对位置的计算,以及如何把ui限制在屏幕内
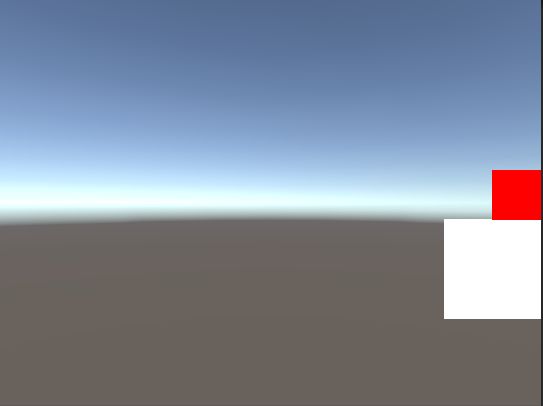
今天写关于ui位置的计算,举个例子:在我之前做的项目中背包的物品都可以点出一个属性面板,这个属性面板的左上角最齐图标的右下角,如图(红是物品图标,白是属性面板)

原理:计算出两个ui的包围盒就可以算出【白image】相对于【红image】的偏差多少坐标,然后用【红image】的position+偏差的坐标赋值给【白image】的世界坐标
如上图的方式,我这边举个例子(【红】的右下角对齐【白】的左上角)
【白】position.x =【红】position.x +【红】包围盒extents.x+【白】包围盒extents.x
【白】position.y =【红】position.x -【红】包围盒extents.y -【白】包围盒extents.y
这样就可以求出【白】的position,这里只给出一种情况,其他情况可以看下面代码
//枚举8个方向
public enum UGUISide
{
Bottom,
BottomLeft,
BottomRight,
Left,
Right,
Top,
TopLeft,
TopRight,
}
public class MathEx
{
/// 包围盒计算:RectTransformUtility.CalculateRelativeRectTransformBounds(canvas, ui)两个参数都是Transform。【包围盒的中心点是从屏幕中心作为原点计算出来的】
位置计算比较简单我觉得看看代码就知道,不过如果物品图标右边对齐屏幕右边,这样计算就会超出屏幕,不过我想要的效果就如下图
这里就涉及到ugui的屏幕大小,知道ugui屏幕大小就知道它是否超出屏幕。如果超出屏幕,可以计算靠边位置。
ugui的屏幕大小与屏幕大小有点区别,不同的ui缩放模式就有ugui屏幕大小不同
现在讲解一下不同ui缩放模式,怎么计算ugui屏幕大小
二、在不同Ui Scale Mode下屏幕的rect的计算,以【屏幕中心为原点】(上面说了ui包围盒按照屏幕中心作为原点计算的)
1.Constant Pixel Size
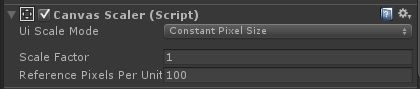
这种模式下屏幕分辨率多大,ugui屏幕就多大
rect = new Rect(-Screen.width / 2, -Screen.height / 2, Screen.width , Screen.height);2.Scale With Screen Size
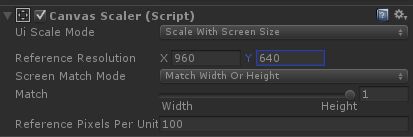
match为1,就是高度适应,
Reference Resolution设置为960*640,因为美术出图都是按照这个分辨率
这样设置无论那种分辨率,ugui屏幕的高度都是640,所以根据屏幕Height和ugui屏幕的Height算出比例,来计算ugui屏幕的Width
rect = new Rect(-Screen.width / 2,
-Screen.height / 2,
Screen.width ,
Screen.height);
float scale = CanvasScaler.matchWidthOrHeight == 1 ?
CanvaScaler.referenceResolution.y / (float)Screen.height :
CanvaScaler.referenceResolution.x / (float)Screen.width;
rect = new Rect(rect.x * scale,
rect.y * scale,
rect.width * scale,
rect.height * scale);第三种就不算,重点是第二种,用得最多还是第二种
三、区域比较
直接上代码,第一个参数就是【白】,第二个参数就是ugui屏幕的rect,第三个是画布
代码比较简单,我就不一一说明。
public static bool SetUIArea(RectTransform target, Rect area, Transform canvas)
{
Bounds bounds = RectTransformUtility.CalculateRelativeRectTransformBounds(canvas, target);
if (null == area)
{
return false;
}
Vector2 delta = default(Vector2);
if (bounds.center.x - bounds.extents.x < area.x)//target超出area的左边框
{
delta.x += Mathf.Abs(bounds.center.x - bounds.extents.x - area.x);
}
else if (bounds.center.x + bounds.extents.x > area.width / 2)//target超出area的右边框
{
delta.x -= Mathf.Abs(bounds.center.x + bounds.extents.x - area.width / 2);
}
if (bounds.center.y - bounds.extents.y < area.y)//target超出area上边框
{
delta.y += Mathf.Abs(bounds.center.y - bounds.extents.y - area.y);
}
else if (bounds.center.y + bounds.extents.y > area.height / 2)//target超出area的下边框
{
delta.y -= Mathf.Abs(bounds.center.y + bounds.extents.y - area.height / 2);
}
//加上偏移位置算出在屏幕内的坐标
target.anchoredPosition += delta;
return delta != default(Vector2);
}最后我这边上完整代码
using UnityEngine;
using System.Collections;
public enum UGUISide
{
Bottom,
BottomLeft,
BottomRight,
Left,
Right,
Top,
TopLeft,
TopRight,
}
public class MathEx
{
/// 测试脚本
using UnityEngine;
using System.Collections;
using System.Data;
using Mono.Data.Sqlite;
using UnityEngine.UI;
using DG.Tweening;
public class Test : MonoBehaviour
{
public RectTransform rt1;
public RectTransform rt2;
private Rect rect;
CanvasScaler canvaScaler;
void Awake()
{
canvaScaler = GetComponent();
rect = new Rect(-Screen.width / 2, -Screen.height / 2, Screen.width , Screen.height);
float scale = canvaScaler.matchWidthOrHeight == 1 ? canvaScaler.referenceResolution.y / (float)Screen.height : canvaScaler.referenceResolution.x / (float)Screen.width;
rect = new Rect(rect.x * scale, rect.y * scale, rect.width * scale, rect.height * scale);
}
void Update()
{
if (null == rt1 || null == rt2) { return; }
MathEx.AnchorTo(rt1, UGUISide.TopLeft, rt2, UGUISide.BottomRight, transform);
MathEx.SetUIArea(rt1, rect, transform);
}
} 测试结构
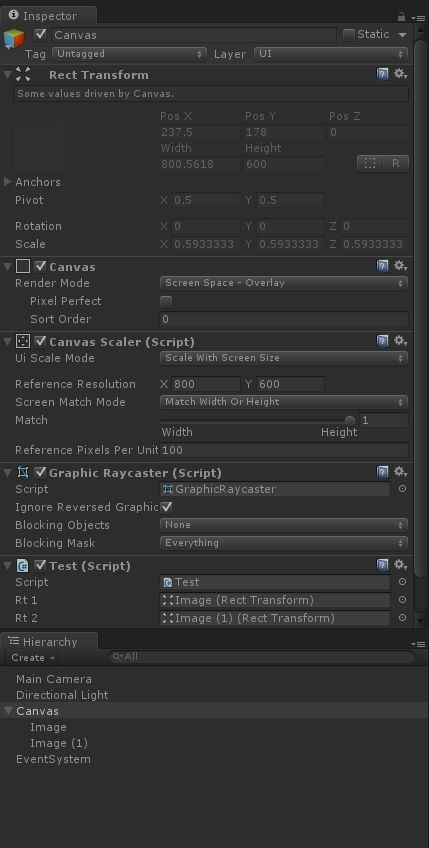


这样子就可以把ui限制在某个区域内。
下一期分享,世界坐标转屏幕坐标,不用设置描点为左下角,也可以做。以及拖拽坐标的计算