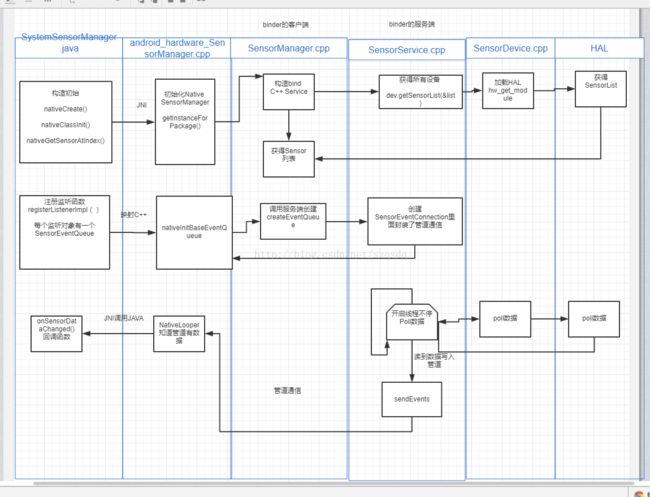
Android Sensor从FWK到HAL至Driver纵线分析处理
VR ROM要在HAL层兼容MPU6500芯片的Sensor模块借此机会从FWK到HAL 到Driver分析了Sensor模块
首先看APP--》HAL
1:底层数据如何实时上报给APP?
2:SensorService怎么跟HAL交互?
3:SensorEventListener本质是什么
下面是我的结论:
1APP注册监听对象
2每个监听对象在FWK都有一个包含管道通信功能的Receiver对象被注册
3SnesorService.cpp开了线程不停的poll HAL层数据,一旦得到数据就写入管道,然后Receiver通过Native Looper 机制收到数据通过JNI调用监听对象的回调实现实时获得数据的功能
核心技术难点,看具体逻辑前可以准备下面的知识点就很方便了
1进程通信方式:Binder C++实现系统Service 通过JNI进行函数调用
2Linux Poll机制:HAL层Poll数据给Service 不停Poll驱动的Sensor数据
3Linux Pipe管道通信机制:Service poll数据后写入管道
4Native Looper机制:Service写入数据到管道,怎么通知监听Sensor的对象
上面就是具体的时序图了
核心类SensorService.cpp分析
为C++系统Service实现的接口如下:
class ISensorServer : public IInterface
{
public:
DECLARE_META_INTERFACE(SensorServer);
virtual Vector getSensorList(const String16& opPackageName) = 0;
virtual sp createSensorEventConnection(const String8& packageName,
int mode, const String16& opPackageName) = 0;
virtual int32_t isDataInjectionEnabled() = 0;
};
// ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
class BnSensorServer : public BnInterface
{
public:
virtual status_t onTransact( uint32_t code,
const Parcel& data,
Parcel* reply,
uint32_t flags = 0);
};
// ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
}; // namespace android
getSensorList获得所有设备
createSensorEventConnection创建通信管道
class SensorService : public BinderService,//创建的时候注册到ServiceManager public BnSensorServer,//实现接口 protected Thread//继承线程 在onfirstRef()里面初始化sensordevice.cpp
void SensorService::onFirstRef()
{
char value[PROPERTY_VALUE_MAX];
property_get("ro.target.product", value, "0");
if(!strcmp("box",value))
{
ALOGD("----box product do not have sensor,skip----");
return;
}
SensorDevice& dev(SensorDevice::getInstance()); //这里创建了SensorDevice.cpp
//.................................
if (dev.initCheck() == NO_ERROR) {
sensor_t const* list;
ssize_t count = dev.getSensorList(&list);
if (count > 0) {
mInitCheck = NO_ERROR;
mAckReceiver = new SensorEventAckReceiver(this);
mAckReceiver->run("SensorEventAckReceiver", PRIORITY_URGENT_DISPLAY);
run("SensorService", PRIORITY_URGENT_DISPLAY); //这里开启线程循环调用自己的loop()函数
}
}
}
因为sensorservice继承了thread,会不停的循环执行threadLoop()函数去poll数据
bool SensorService::threadLoop()
{
SensorDevice& device(SensorDevice::getInstance());
const size_t vcount = mVirtualSensorList.size();
const int halVersion = device.getHalDeviceVersion();
do {
ssize_t count = device.poll(mSensorEventBuffer, numEventMax); //device.cpp poll数据
if (count < 0) {
ALOGE("sensor poll failed (%s)", strerror(-count));
break;
}
size_t numConnections = activeConnections.size();
for (size_t i=0 ; i < numConnections; ++i) {
if (activeConnections[i] != 0) {
activeConnections[i]->sendEvents(mSensorEventBuffer, count, mSensorEventScratch, //将数据写入管道
mMapFlushEventsToConnections);
}
}
}
if (mWakeLockAcquired && !needsWakeLock) {
setWakeLockAcquiredLocked(false);
}
} while (!Thread::exitPending());
ALOGW("Exiting SensorService::threadLoop => aborting...");
abort();
return false;
}
sensordevice.cpp封装了加载HAL层和调用HAL层的API
根据HAL 标准找到Sensor的操作接口
Module定义
struct sensors_module_t HAL_MODULE_INFO_SYM = {
common: {
tag:
HARDWARE_MODULE_TAG,
version_major: 1,
version_minor: 0,
id:
SENSORS_HARDWARE_MODULE_ID,
name: "Invensense module",
author: "Invensense Inc.",
methods:
&sensors_module_methods,
dso: NULL,
reserved: {0}
},
get_sensors_list: sensors__get_sensors_list,
set_operation_mode: NULL,
};
static struct hw_module_methods_t sensors_module_methods = {
open: open_sensors
}操作接口
static int open_sensors(const struct hw_module_t* module, const char* id,
struct hw_device_t** device)
{
FUNC_LOG;
int status = -EINVAL;
sensors_poll_context_t *dev = new sensors_poll_context_t();
memset(&dev->device, 0, sizeof(sensors_poll_device_t));
dev->device.common.tag = HARDWARE_DEVICE_TAG;
dev->device.common.version = 0;
dev->device.common.module = const_cast(module);
dev->device.common.close = poll__close;
dev->device.activate = poll__activate;
dev->device.setDelay = poll__setDelay;
dev->device.poll = poll__poll;
*device = &dev->device.common;
status = 0;
return status;
}
Driver提供read write ioctl poll API来帮助用户空间与内核空间进行设备节点的数据交互
Sensor构造的时候会打开对应的属性节点
InvnAccelSensor::InvnAccelSensor()
: SensorBase(NULL, "/dev/invn_accel"),
mHasPendingEvent(false)
{
memset(mPendingEvent.data, 0, sizeof(mPendingEvent.data));
mPendingEvent.version = sizeof(sensors_event_t);
mPendingEvent.sensor = ID_A;
mPendingEvent.type = SENSOR_TYPE_ACCELEROMETER;
mPendingEvent.acceleration.status = SENSOR_STATUS_ACCURACY_HIGH;
ALOGD("InvnTAG %s,data_fd = %d", __func__, data_fd);
if (data_fd > 0) {
sprintf(sysfs_path, "/sys/class/misc/invn_accel/");
sysfs_path_len = strlen(sysfs_path);
ALOGD("InvnTAG %s:%s", __func__,sysfs_path);
}
}
驱动模块加载流程