源码基于logback 1.1.2
首先看个demo:
根据类名获取Logger,这里是用slf4j提供的工厂来获取logger的:
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger("className"); 进入getLogger方法:
public static Logger getLogger(String name) {
ILoggerFactory iLoggerFactory = getILoggerFactory();
return iLoggerFactory.getLogger(name);
}首先获取ILoggerFactory,然后根据name获取Logger。
getILoggerFactory方法:
public static ILoggerFactory getILoggerFactory() {
if (INITIALIZATION_STATE == UNINITIALIZED) {
INITIALIZATION_STATE = ONGOING_INITIALIZATION;
//执行初始化
performInitialization();
}
switch (INITIALIZATION_STATE) {
//初始化成功则调用logback的StaticLoggerBinder返回LoggerFactory
case SUCCESSFUL_INITIALIZATION:
return StaticLoggerBinder.getSingleton().getLoggerFactory();
//没有找到StaticLoggerBinder这个类
case NOP_FALLBACK_INITIALIZATION:
return NOP_FALLBACK_FACTORY;
//版本不对,或者StaticLoggerBinder包路径不对,或者其他
case FAILED_INITIALIZATION:
throw new IllegalStateException(UNSUCCESSFUL_INIT_MSG);
//线程A已经快执行完performInitialization的时候,INITIALIZATION_STATE设置成
SUCCESSFUL_INITIALIZATION,
//线程B刚开始调用performInitialization,又将INITIALIZATION_STATE修改成ONGOING_INITIALIZATION
//线程A执行到switch代码,就会跳转到这里,返回TEMP_FACTORY
//TEMP_FACTORY如其名,调用它的getLogger方法获取到SubstituteLogger。
//使用SubstituteLogger的info、error等方法打印日志的时候会判断它的_delegate属性是否为空
//一开始_delegate为空,返回一个临时的NOPLogger.NOP_LOGGER实例,该实例什么也不做
//后期performInitialization方法中会调用fixSubstitutedLoggers方法,重新设置_delegate为正确的logger。
case ONGOING_INITIALIZATION:
// support re-entrant behavior.
// See also http://bugzilla.slf4j.org/show_bug.cgi?id=106
return TEMP_FACTORY;
}
throw new IllegalStateException("Unreachable code");
}下面看看执行初始化的方法 performInitialization:
private final static void performInitialization() {
bind();
if (INITIALIZATION_STATE == SUCCESSFUL_INITIALIZATION) {
//版本检查
versionSanityCheck();
}
}
private final static void bind() {
try {
//查找org/slf4j/impl/StaticLoggerBinder.class,可能存在多个
Set staticLoggerBinderPathSet = findPossibleStaticLoggerBinderPathSet();
reportMultipleBindingAmbiguity(staticLoggerBinderPathSet);
// the next line does the binding
//如果没有StaticLoggerBinder class这里调用便会异常
StaticLoggerBinder.getSingleton();
//设置状态为成功初始化
INITIALIZATION_STATE = SUCCESSFUL_INITIALIZATION;
//如果StaticLoggerBinder class个数大于1个,则进行上报实际绑定的类型
reportActualBinding(staticLoggerBinderPathSet);
//修复并发调用getILoggerFactory时出现状态为ONGOING_INITIALIZATION且获取到的logger为
TEMP_FACTORY的问题
//解决方法是设置每个SubstituteLogger的_delegate为正确的logger
fixSubstitutedLoggers();
} catch (NoClassDefFoundError ncde) {
String msg = ncde.getMessage();
if (messageContainsOrgSlf4jImplStaticLoggerBinder(msg)) {
INITIALIZATION_STATE = NOP_FALLBACK_INITIALIZATION;
Util.report("Failed to load class \"org.slf4j.impl.StaticLoggerBinder\".");
Util.report("Defaulting to no-operation (NOP) logger implementation");
Util.report("See " + NO_STATICLOGGERBINDER_URL + " for further details.");
} else {
failedBinding(ncde);
throw ncde;
}
} catch (java.lang.NoSuchMethodError nsme) {
String msg = nsme.getMessage();
if (msg != null && msg.indexOf("org.slf4j.impl.StaticLoggerBinder.getSingleton()") != -1) {
INITIALIZATION_STATE = FAILED_INITIALIZATION;
Util.report("slf4j-api 1.6.x (or later) is incompatible with this binding.");
Util.report("Your binding is version 1.5.5 or earlier.");
Util.report("Upgrade your binding to version 1.6.x.");
}
throw nsme;
} catch (Exception e) {
failedBinding(e);
throw new IllegalStateException("Unexpected initialization failure", e);
}
} 执行完performInitialization方法后,状态被设置成SUCCESSFUL_INITIALIZATION,然后执行StaticLoggerBinder.getSingleton().getLoggerFactory()。
在这之前先看看StaticLoggerBinder的静态代码块:
private static StaticLoggerBinder SINGLETON = new StaticLoggerBinder();
private static Object KEY = new Object();
static {
//StaticLoggerBinder单例调用init方法
SINGLETON.init();
}
//生成默认的LoggerContext
private boolean initialized = false;
private LoggerContext defaultLoggerContext = new LoggerContext();
private final ContextSelectorStaticBinder contextSelectorBinder = ContextSelectorStaticBinder
.getSingleton();
private StaticLoggerBinder() {
defaultLoggerContext.setName(CoreConstants.DEFAULT_CONTEXT_NAME);
}
public static StaticLoggerBinder getSingleton() {
return SINGLETON;
}
void init() {
try {
try {
//创建ContextInitializer,调用autoConfig解析配置文件
new ContextInitializer(defaultLoggerContext).autoConfig();
} catch (JoranException je) {
Util.report("Failed to auto configure default logger context", je);
}
// logback-292
// logback-292
//打印logback内部error、warn信息
//如果没有配置StatusListener,则使用StatusPrinter的stdout方式打印
//配置StatusListener的代码实现在ContextInitializer#autoConfig()方法第一行
//内部产生的error、warn等日志在StaticLoggerBinder.defaultLoggerContext.sm中维护的。
//比如之前autoConfig方法中解析xml配置时出现error或者warn日志会在sm中存储,然后在此处打印
if(!StatusUtil.contextHasStatusListener(defaultLoggerContext)) {
StatusPrinter.printInCaseOfErrorsOrWarnings(defaultLoggerContext);
}
contextSelectorBinder.init(defaultLoggerContext, KEY);
//initialized初始为false,init成功设置成true
initialized = true;
} catch (Throwable t) {
// we should never get here
Util.report("Failed to instantiate [" + LoggerContext.class.getName()
+ "]", t);
}
}
接下来分析ContextInitializer.autoConfig:
public void autoConfig() throws JoranException {
//解析在环境变量中配置的StatusListener实现类,如果配置的话生成相应的实例,
//调用其start方法,上报过去一段时间logback内部日志
StatusListenerConfigHelper.installIfAsked(loggerContext);
//获取logback配置文件URL
URL url = findURLOfDefaultConfigurationFile(true);
if (url != null) {
//解析logback配置文件,核心
configureByResource(url);
} else {
//设置默认的config,后期日志直接输出到控制台
BasicConfigurator.configure(loggerContext);
}
}下面分析下ContextInitializer.configureByResource(url):
public void configureByResource(URL url) throws JoranException {
if (url == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("URL argument cannot be null");
}
//logback配置是groovy文件
if (url.toString().endsWith("groovy")) {
if (EnvUtil.isGroovyAvailable()) {
// avoid directly referring to GafferConfigurator so as to avoid
// loading groovy.lang.GroovyObject . See also http://jira.qos.ch/browse/LBCLASSIC-214
GafferUtil.runGafferConfiguratorOn(loggerContext, this, url);
} else {
StatusManager sm = loggerContext.getStatusManager();
sm.add(new ErrorStatus("Groovy classes are not available on the class path. ABORTING INITIALIZATION.",
loggerContext));
}
} else if (url.toString().endsWith("xml")) {
//logback配置文件是xml。我们主要分析该情况下的配置
//首先创建一个配置器,设置好loggerContext后,根据url进行配置解
JoranConfigurator configurator = new JoranConfigurator();
configurator.setContext(loggerContext);
configurator.doConfigure(url);
} else {
throw new LogbackException("Unexpected filename extension of file [" + url.toString() + "]. Should be either .groovy or .xml");
}
}JoranConfigurator.doConfigure(url)代码如下:
public final void doConfigure(URL url) throws JoranException {
InputStream in = null;
try {
//将该url添加到watch list中
informContextOfURLUsedForConfiguration(getContext(), url);
URLConnection urlConnection = url.openConnection();
// per http://jira.qos.ch/browse/LBCORE-105
// per http://jira.qos.ch/browse/LBCORE-127
//如果设置成true的话,当这个配置文件在一个jar中的时候,jar被锁住。如果应用需要重新加载的话会出现问题。
//所以设置成false。
urlConnection.setUseCaches(false);
//将logback配置转换成流进行解析
in = urlConnection.getInputStream();
doConfigure(in);
} catch (IOException ioe) {
String errMsg = "Could not open URL [" + url + "].";
addError(errMsg, ioe);
throw new JoranException(errMsg, ioe);
} finally {
if (in != null) {
try {
in.close();
} catch (IOException ioe) {
String errMsg = "Could not close input stream";
addError(errMsg, ioe);
throw new JoranException(errMsg, ioe);
}
}
}
}
//将InputStream转换成sax的InputSource对象,然后调用doConfigure进行解析
public final void doConfigure(InputStream inputStream) throws JoranException {
doConfigure(new InputSource(inputStream));
}
public final void doConfigure(final InputSource inputSource)
throws JoranException {
long threshold = System.currentTimeMillis();
if (!ConfigurationWatchListUtil.wasConfigurationWatchListReset(context)) {
informContextOfURLUsedForConfiguration(getContext(), null);
}
SaxEventRecorder recorder = new SaxEventRecorder(context);
//将xml的 bodyStr 解析成StartEvent,BodyEvent,EndEvent,保存到recorder.saxEventList中
//如果解析期间遇到warn、error、fatalError情况则会生成信息存入
StaticLoggerBinder.defaultLoggerContext.sm中
//后期将会将这些日志输出
recorder.recordEvents(inputSource);
//根据xml每个element对应的event来进行解析
doConfigure(recorder.saxEventList);
// no exceptions a this level
StatusUtil statusUtil = new StatusUtil(context);
if (statusUtil.noXMLParsingErrorsOccurred(threshold)) {
addInfo("Registering current configuration as safe fallback point");
registerSafeConfiguration();
}
}
public void doConfigure(final List eventList)
throws JoranException {
//将大部分的element path包装成ElementSelector并映射一个Action,比如xml中configuration/logger element
path映射成LoggerAction
//当解析到 时会触发LoggerAction的begin方法
//当解析到 bodyStr 时会触发LoggerAction的body方法,当然logger element是没有body的
//当解析到 bodyStr 时会触发LoggerAction的end方法
//action的映射关系存在JoranConfigurator#interpreter中
buildInterpreter();
// disallow simultaneous configurations of the same context
synchronized (context.getConfigurationLock()) {
//解析eventList
interpreter.getEventPlayer().play(eventList);
}
}
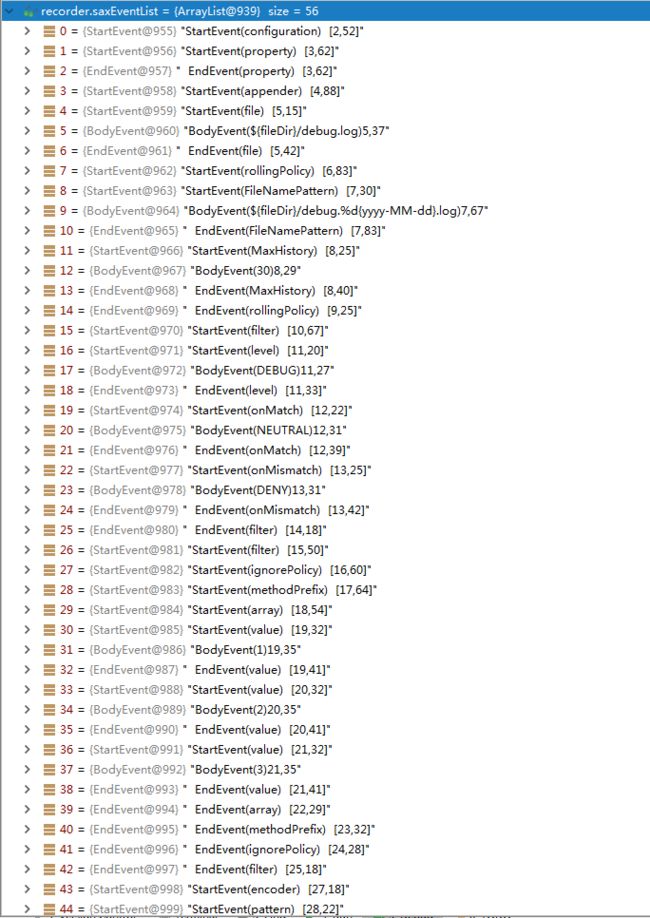
如下是一个简单的logback.xml demo
${fileDir}/debug.log
${fileDir}/debug.%d{yyyy-MM-dd}.log
30
DEBUG
NEUTRAL
DENY
1
2
3
%date [%thread] %-5level %logger{80} - %msg%n
转换成SaxEvent list便是这个样子:
对应56个event。
下面分析EventPlayer中play方法如何对event list进行遍历处理。
很清晰的看到event分成三种:StartEvent、BodyEvent、EndEvent。这个三种最终会调用对应action的begin、body、end方法
public void play(List aSaxEventList) {
eventList = aSaxEventList;
SaxEvent se;
for(currentIndex = 0; currentIndex < eventList.size(); currentIndex++) {
se = eventList.get(currentIndex);
if(se instanceof StartEvent) {
interpreter.startElement((StartEvent) se);
// invoke fireInPlay after startElement processing
interpreter.getInterpretationContext().fireInPlay(se);
}
if(se instanceof BodyEvent) {
// invoke fireInPlay before characters processing
interpreter.getInterpretationContext().fireInPlay(se);
interpreter.characters((BodyEvent) se);
}
if(se instanceof EndEvent) {
// invoke fireInPlay before endElement processing
interpreter.getInterpretationContext().fireInPlay(se);
interpreter.endElement((EndEvent) se);
}
}
} - satrtEvent
public void startElement(StartEvent se) {
//设置event在xml中的locator信息,比如在多少行多少列
setDocumentLocator(se.getLocator());
//处理start event
startElement(se.namespaceURI, se.localName, se.qName, se.attributes);
}
private void startElement(String namespaceURI, String localName,
String qName, Attributes atts) {
//首先选择localName为tagName,如果localName为空则选择qName
String tagName = getTagName(localName, qName);
//将这个startEvent的tagName推入elementPath栈中,后期处理对应的endEvent时,触发endElement方法弹出该tagName
elementPath.push(tagName);
if (skip != null) {
// every startElement pushes an action list
pushEmptyActionList();
return;
}
//根据elementPath查找相应的action list,
//比如elementPath推入了两个数据[configuration][appender],则会找到AppenderAction。
//Interpreter中ruleStore并不维护所有elementPath对应的action,
//比如[configuration][appender][file],在ruleStore中找不到对应的action。
//logback提供了两种隐式action:NestedComplexPropertyIA、NestedBasicPropertyIA,
//1.[configuration][appender][file]对应的action是NestedBasicPropertyIA,
//因为它属于简单的内嵌式action,file属于appender的一个属性,而file element没有内嵌element,只有一个body。
//2.[configuration][appender][rollingPolicy]对应的action是NestedComplexPropertyIA,
//因为它属于复杂的内嵌式action,rollingPolicy属于appender的一个属性,但是,rollingPolicy element还拥有自己的
内嵌element
List applicableActionList = getApplicableActionList(elementPath, atts);
if (applicableActionList != null) {
//将action list推入actionlistStacl栈中,后续会用到
actionListStack.add(applicableActionList);
//遍历applicableActionList,触发每个action的begin方法,正常applicableActionList中只有一个元素
callBeginAction(applicableActionList, tagName, atts);
} else {
// every startElement pushes an action list
pushEmptyActionList();
String errMsg = "no applicable action for [" + tagName
+ "], current ElementPath is [" + elementPath + "]";
cai.addError(errMsg);
}
}
void callBeginAction(List applicableActionList, String tagName,
Attributes atts) {
if (applicableActionList == null) {
return;
}
Iterator i = applicableActionList.iterator();
while (i.hasNext()) {
Action action = (Action) i.next();
// now let us invoke the action. We catch and report any eventual
// exceptions
try {
//真正的处理start event的逻辑,即该element path对应action的begin方法
action.begin(interpretationContext, tagName, atts);
} catch (ActionException e) {
skip = elementPath.duplicate();
cai.addError("ActionException in Action for tag [" + tagName + "]", e);
} catch (RuntimeException e) {
skip = elementPath.duplicate();
cai.addError("RuntimeException in Action for tag [" + tagName + "]", e);
}
}
} - bodyEvent
public void characters(BodyEvent be) {
setDocumentLocator(be.locator);
//获取body文本
String body = be.getText();
List applicableActionList = actionListStack.peek();
if (body != null) {
body = body.trim();
if (body.length() > 0) {
// System.out.println("calling body method with ["+body+ "]");
callBodyAction(applicableActionList, body);
}
}
}
private void callBodyAction(List applicableActionList, String body) {
if (applicableActionList == null) {
return;
}
Iterator i = applicableActionList.iterator();
while (i.hasNext()) {
Action action = i.next();
try {
//触发该element path对应action的body方法
action.body(interpretationContext, body);
} catch (ActionException ae) {
cai
.addError("Exception in end() methd for action [" + action + "]",
ae);
}
}
}
- endEvent
public void endElement(EndEvent endEvent) {
setDocumentLocator(endEvent.locator);
endElement(endEvent.namespaceURI, endEvent.localName, endEvent.qName);
}
private void endElement(String namespaceURI, String localName, String qName) {
// given that an action list is always pushed for every startElement, we
// need
// to always pop for every endElement
List applicableActionList = (List) actionListStack.pop();
if (skip != null) {
if (skip.equals(elementPath)) {
skip = null;
}
} else if (applicableActionList != EMPTY_LIST) {
callEndAction(applicableActionList, getTagName(localName, qName));
}
// given that we always push, we must also pop the pattern
//把在startElement方法中推入的元素弹出来
elementPath.pop();
}
private void callEndAction(List applicableActionList, String tagName) {
if (applicableActionList == null) {
return;
}
// logger.debug("About to call end actions on node: [" + localName + "]");
Iterator i = applicableActionList.iterator();
while (i.hasNext()) {
Action action = i.next();
// now let us invoke the end method of the action. We catch and report
// any eventual exceptions
try {
//触发当前element path对应action的end方法
action.end(interpretationContext, tagName);
} catch (ActionException ae) {
// at this point endAction, there is no point in skipping children as
// they have been already processed
cai.addError("ActionException in Action for tag [" + tagName + "]", ae);
} catch (RuntimeException e) {
// no point in setting skip
cai.addError("RuntimeException in Action for tag [" + tagName + "]", e);
}
}
} logback源码分析-配置文件解析