leetcode刷题笔记-hashtable
939. Minimum Area Rectangle
给一些点,找最小的rectangle的面积。方法2比较简单明了。
https://leetcode.com/problems/minimum-area-rectangle/solution/
380. Insert Delete GetRandom O(1)
class RandomizedSet(object):
def __init__(self):
self.d = {}
self.length = 0
def insert(self, val):
if val not in self.d:
self.d[val] = True
self.length += 1
return True
return False
def remove(self, val):
if val in self.d:
del self.d[val]
self.length -= 1
return True
return False
def getRandom(self):
idx = random.randint(0, self.length-1)
return self.d.keys()[idx]方法2: 一个list存元素,一个dic记录元素的位置,删除的时候把最后一个元素放在删除的元素的位置,然后删除最后一个元素。
import random
class RandomizedSet(object):
def __init__(self):
self.nums, self.pos = [], {}
def insert(self, val):
if val not in self.pos:
self.nums.append(val)
self.pos[val] = len(self.nums) - 1
return True
return False
def remove(self, val):
if val in self.pos:
idx, last = self.pos[val], self.nums[-1]
self.nums[idx], self.pos[last] = last, idx
self.nums.pop(); self.pos.pop(val, 0)
return True
return False
def getRandom(self):
return self.nums[random.randint(0, len(self.nums) - 1)]49. Group Anagrams
class Solution(object):
def groupAnagrams(self, strs):
d = {}
for s in strs:
key = tuple(sorted(s)) # 注意这里有tuple
d[key] = d.get(key, []) + [s]
return d.values()
582. Kill Process
class Solution(object):
def killProcess(self, pid, ppid, kill):
res = []
childs = collections.defaultdict(list)
for i in xrange(len(ppid)):
childs[ppid[i]].append(pid[i])
q = [kill]
while q:
p = q.pop(0)
res.append(p)
for child in childs[p]:
q.append(child)
return res
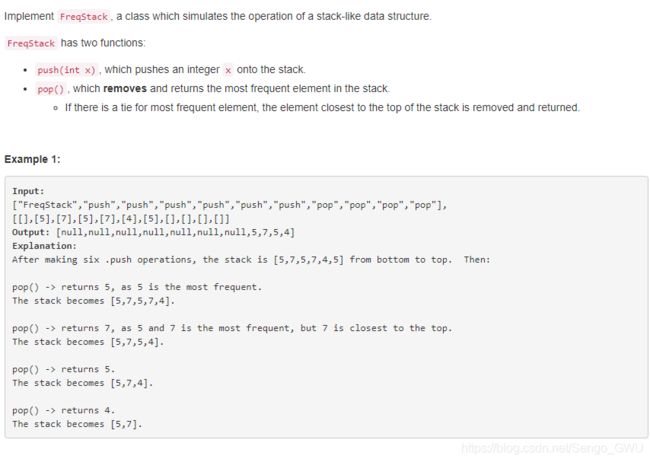
895. Maximum Frequency Stack
class FreqStack(object):
def __init__(self):
self.num2freq = collections.defaultdict(int)
self.freq2num = collections.defaultdict(list)
self.maxfreq = 0
def push(self, x):
self.num2freq[x] += 1
self.freq2num[self.num2freq[x]].append(x)
self.maxfreq = max(self.maxfreq, self.num2freq[x])
def pop(self):
num = self.freq2num[self.maxfreq].pop()
if not self.freq2num[self.maxfreq]:
self.maxfreq -= 1
self.num2freq[num] -= 1
return num299. Bulls and Cows
two pass解法:
import java.lang.StringBuffer;
public class Solution {
public String getHint(String secret, String guess) {
int [] all = new int[10];
int bulls = 0, cows = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < secret.length(); ++i)
{
// 如果当前位置值相等,bulls数量加1
if(secret.charAt(i) == guess.charAt(i)){
++bulls;
}else{
// 将secret中含有的数字放入
all[secret.charAt(i) - '0'] += 1;
}
}
for(int j = 0; j < secret.length(); ++j)
{
if(secret.charAt(j) != guess.charAt(j))
{
int charValue = guess.charAt(j) - '0';
// 还有待匹配的cows
if(all[charValue] > 0){
++cows;
all[charValue]-=1;
}
}
}
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();
// 拼接字符串
sb.append(bulls).append('A')
.append(cows).append('B');
return sb.toString();
}
}
one pass解法:
class Solution(object):
def getHint(self, secret, guess):
number = [0] * 10
bull = cow = 0
for i in xrange(len(secret)):
s = int(secret[i])
g = int(guess[i])
if s == g: bull += 1
else:
if number[g] > 0:
cow += 1
if number[s] < 0: # 可以加2次
cow += 1
number[s] += 1
number[g] -= 1
return ''.join([str(bull), 'A', str(cow), 'B'])
535. Encode and Decode TinyURL
class Codec:
alphabet = string.ascii_letters
def __init__(self):
self.url2code = {}
self.code2url = {}
def encode(self, longUrl):
while longUrl not in self.url2code:
code = ''.join(random.choice(Codec.alphabet) for _ in xrange(6)) # 注意random.choice
if code not in self.code2url:
self.url2code[longUrl] = code
self.code2url[code] = longUrl
return "http://tinyurl.com/" + self.url2code[longUrl]
def decode(self, shortUrl):
return self.code2url[shortUrl[-6:]]
403. Frog Jump
class Solution(object):
def canCross(self, stones):
if stones[1] != 1:
return False
d = {x: set() for x in stones}
d[1].add(1) # stone 1的 before jump 是1
for x in stones[:-1]:
for j in d[x]:
for k in xrange(j-1, j+2): # 之前的jump-1, jump+1之间
if k > 0 and x+k in d: # 这里是d 不是stones的话速度会比较快
d[x+k].add(k)
return bool(d[stones[-1]])957. Prison Cells After N Days
存在dict里面,直到遇到重复的情况结束循环。
class Solution(object):
def prisonAfterNDays(self, cells, N):
d = {}
re = [0] * len(cells)
for day in xrange(N):
for i in xrange(len(cells)):
if not (i == 0 or i == len(cells) -1):
if cells[i-1] == cells[i+1]:
re[i] = 1
else:
re[i] = 0
cells = re[:]
if str(cells) in d:
break
else:
d[str(cells)] = True
d[day] = cells
day = N%(len(d)/2)-1
return d[day if day > -1 else len(d)/2-1]347. Top K Frequent Elements
class Solution(object):
def topKFrequent(self, nums, k):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:type k: int
:rtype: List[int]
"""
d, q = {}, {}
for n in nums:
if d.get(n) is None:
d[n] = 1
else:
d[n] += 1
for n, c in d.items():
if q.get(c) is None:
q[c] = [n]
else:
q[c].append(n)
res = []
for i in xrange(len(nums), 0, -1):
if k < 0:
break
elif q.get(i):
res += [q[i][s] for s in xrange(min(k, len(q[i])))]
k -= len(q[i])
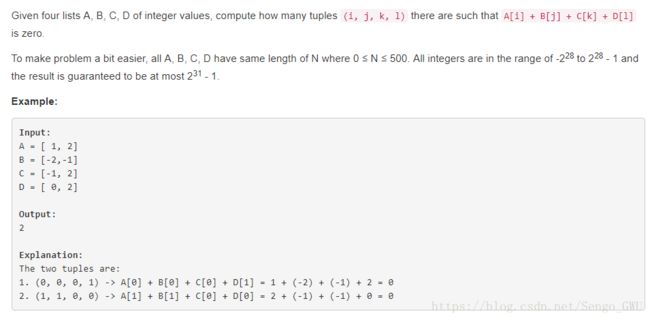
return res454. 4Sum II
第一次解法O(n^2),但是Memory Limit Exceeded
class Solution(object):
def fourSumCount(self, A, B, C, D):
"""
:type A: List[int]
:type B: List[int]
:type C: List[int]
:type D: List[int]
:rtype: int
"""
n, res = len(A), 0
mapAB = collections.defaultdict(list)
for i in xrange(n):
for j in xrange(n):
Sum = A[i] + B[j]
mapAB[Sum].append([i, j])
for i in xrange(n):
for j in xrange(n):
Sum = C[i] + D[j]
res += len(mapAB[0-Sum])
return res稍稍修改了下:
class Solution(object):
def fourSumCount(self, A, B, C, D):
"""
:type A: List[int]
:type B: List[int]
:type C: List[int]
:type D: List[int]
:rtype: int
"""
n, res = len(A), 0
mapAB = collections.defaultdict(int)
for i in xrange(n):
for j in xrange(n):
Sum = A[i] + B[j]
mapAB[Sum] += 1
for i in xrange(n):
for j in xrange(n):
Sum = C[i] + D[j]
res += mapAB[0-Sum]
return res138. Copy List with Random Pointer
# Definition for singly-linked list with a random pointer.
# class RandomListNode(object):
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.label = x
# self.next = None
# self.random = None
class Solution(object):
def copyRandomList(self, head):
"""
:type head: RandomListNode
:rtype: RandomListNode
"""
d = dict()
p1 = p2 = head
while p1:
d[p1] = RandomListNode(p1.label)
p1 = p1.next
while p2:
d[p2].next = d.get(p2.next)
d[p2].random = d.get(p2.random)
p2 = p2.next
return d.get(head)438. Find All Anagrams in a String
简单题但是是facebook的高频题,所以还是记录下
滑动窗口,用List 来当hashtable, 索引为key ord(c), value为出现次数。 滑动后加右边的,再减去左边的。
Hash the number of times each character appears in p. Iterate over s with a sliding window and maintain a similar hash. If these two hashes are ever the same, add that to the result.
Each of the hashes have a finite (a-z, A-Z) number of possible characters, so the space used is O(1)
We iterate over s linearly, comparing constant length hashes at each iteration so each iteration is also O(1), so the runtime is O(n)
class Solution(object):
def findAnagrams(self, s, p):
"""
:type s: str
:type p: str
:rtype: List[int]
"""
res = []
n, m = len(s), len(p)
if n < m: return res
phash, shash = [0]*123, [0]*123
for x in p:
phash[ord(x)] += 1
for x in s[:m-1]:
shash[ord(x)] += 1
for i in range(m-1, n):
shash[ord(s[i])] += 1
if i-m >= 0:
shash[ord(s[i-m])] -= 1
if shash == phash:
res.append(i - m + 1)
return res325. Maximum Size Subarray Sum Equals k
class Solution(object):
def maxSubArrayLen(self, nums, k):
mp = {0: -1}
re = acc = 0
for i in xrange(len(nums)):
acc += nums[i]
if acc - k in mp:
re = max(re, i - mp[acc-k])
if acc not in mp: # 重点,如果acc在后面也出现,也不需要记录,记录前面才能保证相减最长
mp[acc] = i
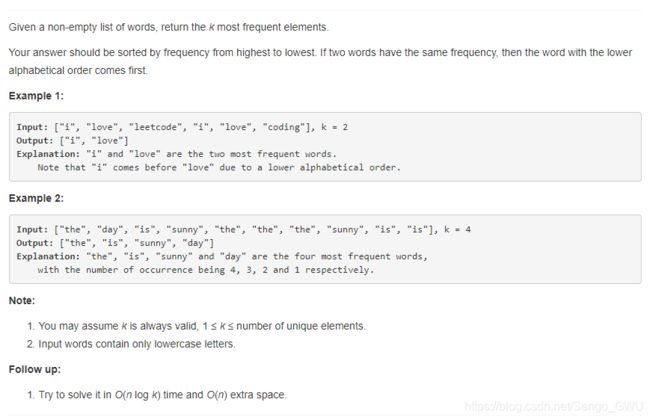
return re692. Top K Frequent Words
不是O(nlogk)
class Solution(object):
def topKFrequent(self, words, k):
d = {}
for w in words:
d[w] = d.get(w, 0) + 1
res = sorted(d, key=lambda w:(-d[w], w))
return res[:k]149. Max Points on a Line
import numpy
class Solution(object):
def maxPoints(self, points):
"""
:type points: List[Point]
:rtype: int
"""
points = sorted(points)
n = len(points)
re = 0
for i in xrange(n):
d = {'i': 1} # d在第一个循环里面,我做的时候在外面,单独斜率没法表示直线,要斜率+1个点
left = points[i]
same = 0
for j in xrange(i+1, n):
right = points[j]
if left.x == right.x and left.y == right.y:
same += 1
continue
if left.x == right.x:
slope = 'i' # slope = infinit
else:
slope = numpy.float128((right.y - left.y)) * 1.0 / numpy.float128((right.x - left.x))
if slope in d:
d[slope] += 1
else:
d[slope] = 2
re = max(re, max(d.values()) + same)
return re