【linux驱动】USB子系统分析
本文针对Linux内核下USB子系统进行分析,主要会涉及一下几个方面:
-
USB基础知识:介绍USB设备相关的基础知识
-
Linux USB子系统分析:分析USB系统框架,USB HCD/ROOT HUB注册过程,USB新设备枚举过程
-
USB设备驱动案例:介绍常用的USB相关设备驱动
-
USB电源管理
一、USB基础知识
USB,是英文Universal Serial Bus(通用串行总线)、支持设备的即插即用和热插拔功能。在1994年底由英特尔、IBM、Microsoft等公司联合提出的,在此之前PC的接口杂乱,扩展能力差,热拔插不支持等。USB正是为了解决速度,扩展能力,易用性等而出现。
USB各版本速率对比
| USB版本 | 理论最大传输速率 | 速率称号 | 最大输出电流 | 推出时间 |
| USB 1.0 | 1.5Mbps(192KB/s) | 低速(Low-Speed) | 5V/500mA | 1996年1月 |
| USB 1.1 | 12Mbps(1.5MB/s) | 全速(Full-Speed) | 5V/500mA | 1998年9月 |
| USB 2.0 | 480Mbps(60MB/s) | 高速(High-Speed) | 5V/500mA | 2000年4月 |
| USB 3.0 | 5Gbps(500MB/s) | 超高速(Super-Speed) | 5V/900mA | 2008年11月 |
| USB 3.1 | 10Gbps(1280MB/s) | 超高速+(Super-speed+) | 20V/5A | 2013年12月 |
| USB 4.0 | 40Gbps | 协议(2019年9月) |
Linux 5.6将开始支持 USB 4 。
1.1 USB主从结构:通信都是主机端先发起通信
从设备端没有主动通知USB主机端的能力,从机插入后,主机控制器根据协议,获取设备描述符及驱动匹配。
1.2 USB描述符
定义路径:kernel\include\uapi\linux\usb\ch9.h
设备描述符
/* USB_DT_DEVICE: Device descriptor */
struct usb_device_descriptor {
__u8 bLength; //本结构体大小
__u8 bDescriptorType; //描述符类型
__le16 bcdUSB; //usb版本号 200->USB2.0
__u8 bDeviceClass; //设备类
__u8 bDeviceSubClass; //设备类子类
__u8 bDeviceProtocol; //设备协议,以上三点都是USB官方定义
__u8 bMaxPacketSize0; //端点0最大包大小
__le16 idVendor; //厂家id
__le16 idProduct; //产品id
__le16 bcdDevice; //设备出厂编号
__u8 iManufacturer; //设备厂商字符串索引
__u8 iProduct; //产品描述
__u8 iSerialNumber; //设备序列号字符串索引
__u8 bNumConfigurations; //配置的个数
} __attribute__ ((packed));配置描述符
struct usb_config_descriptor {
__u8 bLength; //自身长度
__u8 bDescriptorType;//描述符类型(本结构体中固定为0x02)
__le16 wTotalLength; //该配置下,信息的总长度
__u8 bNumInterfaces; //接口的个数
__u8 bConfigurationValue; //Set_Configuration命令所需要的参数值
__u8 iConfiguration; //描述该配置的字符串的索引值
__u8 bmAttributes;//供电模式的选择
__u8 bMaxPower;//设备从总线提取的最大电流
} __attribute__ ((packed));
接口描述符
struct usb_interface_descriptor {
__u8 bLength;
__u8 bDescriptorType;//接口描述符的类型编号(0x04)
__u8 bInterfaceNumber; //该接口的编号
__u8 bAlternateSetting; //备用的接口描述符编号
__u8 bNumEndpoints; //该接口使用的端点数,不包括端点0
__u8 bInterfaceClass; //接口类
__u8 bInterfaceSubClass; //子类
__u8 bInterfaceProtocol; //协议
__u8 iInterface;//描述该接口的字符串索引值
} __attribute__ ((packed));端点描述符
/* USB_DT_ENDPOINT: Endpoint descriptor */
struct usb_endpoint_descriptor {
__u8 bLength;//端点描述符字节数大小(7个字节)
__u8 bDescriptorType;//端点描述符类型编号(0x05)
__u8 bEndpointAddress; //端点地址及输入输出属性
__u8 bmAttributes; //属性,包含端点的传输类型,控制,中断...
__le16 wMaxPacketSize; //端点收、发的最大包大小
__u8 bInterval; //主机查询端点的时间间隔
/* NOTE: these two are _only_ in audio endpoints. */
/* use USB_DT_ENDPOINT*_SIZE in bLength, not sizeof. */
__u8 bRefresh;
__u8 bSynchAddress;
} __attribute__ ((packed));
https://www.cnblogs.com/myblesh/archive/2014/04/01/3637767.html
https://www.cnblogs.com/wangh0802PositiveANDupward/archive/2013/05/06/3061241.html
https://blog.csdn.net/michaelcao1980/article/details/51280736
1.3 USB传输:四种类型
- 控制传输:用于配置设备、获取设备信息、发送命令或者获取设备的状态报告,如:USB枚举阶段。
- 批量传输:
- 中断传输
- 实时传输
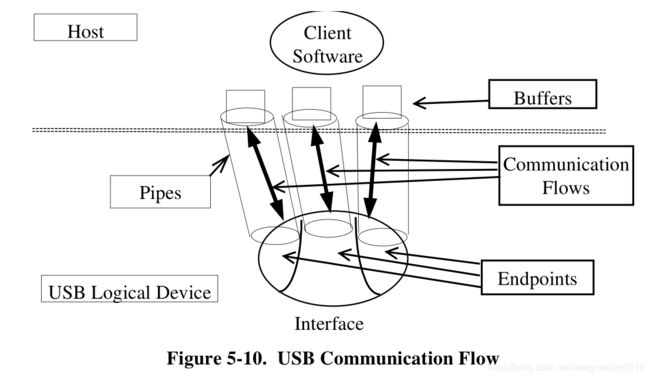
1.4 USB传输对象:端点
- 从端点接收和发送数据
- 每个端点都只有一个传输类型:控制,批量...
- 每个端点都只有一个传输方向:输入or输出 。端点0除外,端点0为双向(查询描述符,设置描述符)。
- 传输方向基于主机端而言,数据由从到主,则该端点为输入端点
二、Linux USB子系统分析
Linux内核USB子系统,以总线(Bus)、设备(device)、驱动(device_driver)模型来完成设备和驱动的绑定,实现USB业务逻辑。
本节在Linux USB驱动框架的基础上,分析USB子系统在内核中的整个初始化流程,以及内核对USB hub的监测及USB设备插入后的一系列初始化和驱动的匹配过程分析,从而分析USB业务实现的主要流程。
2.1 USB子系统框架
整个USB驱动模型可以总结为如上图,USB分为主机测和设备侧。本文重点分析主机测一端的USB驱动。
从主机HOST测来看,其包含:
-
USB设备驱动(RNDIS,HID,Mass Storagr...)
-
USB核心(Core init,Core API...)
-
USB主机控制器驱动HCD(Root Hub)
USB设备驱动:用于和枚举到的USB设备进行绑定,完成特定的功能。
USB Core:用于内核USB总线的初始化及USB相关API,为设备驱动和HCD的交互提供桥梁。
USB主机控制器HCD:完成主机控制器的初始化以及数据的传输,并监测外部设备插入,完成设备枚举。
接下来将从以上三个方面分析USB子系统在内核完成的初始化操作及USB业务实现的流程。
2.2 USB Core分析
Linux启动阶段,通过subsys_initcall会完成USB Core的加载,其代码位于kernel/drivers/usb/core/usb.c。
顺着驱动加载的入口函数,来分析USB被加载进内核的第一步。
2.2.1 入口函数usb_init分析
由于USB基于总线设备驱动模型来组织,其初始化阶段一个重点任务为完成USB总线的创建,usb_init代码如下:
static int __init usb_init(void)
{
int retval;
//通过command line传入nousb=1可禁止掉USB子模块的加载
if (nousb) {
pr_info("%s: USB support disabled\n", usbcore_name);
return 0;
}
retval = usb_debugfs_init();
if (retval)
goto out;
usb_acpi_register();
//注册USB总线(*****)
retval = bus_register(&usb_bus_type);
if (retval)
goto bus_register_failed;
retval = bus_register_notifier(&usb_bus_type, &usb_bus_nb);
if (retval)
goto bus_notifier_failed;
retval = usb_major_init();
if (retval)
goto major_init_failed;
retval = usb_register(&usbfs_driver);
if (retval)
goto driver_register_failed;
retval = usb_devio_init();
if (retval)
goto usb_devio_init_failed;
//usb hub的初始化,完成驱动注册和内核线程创建
retval = usb_hub_init();
if (retval)
goto hub_init_failed;
//加载一个通用的usb_device_driver驱动
retval = usb_register_device_driver(&usb_generic_driver, THIS_MODULE);
if (!retval)
goto out;
......
}usb_init主要完成USB相关的初始化操作,其重点工作:
-
通过bus_register注册USB总线usb_bus_type
struct bus_type usb_bus_type = {
.name = "usb",
.match = usb_device_match,
.uevent = usb_uevent,
};
bus_register中创建了两个链表,一端为设备链表,一端为驱动链表。
klist_init(&priv->klist_devices, klist_devices_get, klist_devices_put);
klist_init(&priv->klist_drivers, NULL, NULL);usb_bus_type提供了设备与驱动的匹配函数usb_device_match,这个函数很重要,后面用到的时候再详细分析。
-
完成USB Hub的初始化usb_hub_init()
int usb_hub_init(void)
{
if (usb_register(&hub_driver) < 0) {
printk(KERN_ERR "%s: can't register hub driver\n",
usbcore_name);
return -1;
}
khubd_task = kthread_run(hub_thread, NULL, "khubd");
if (!IS_ERR(khubd_task))
return 0;
/* Fall through if kernel_thread failed */
usb_deregister(&hub_driver);
printk(KERN_ERR "%s: can't start khubd\n", usbcore_name);
return -1;
}任务之1:是通过usb_register(&hub_driver),向USB总线添加一个hub驱动。指定了probe,disconnect,suspend,resume,id_table等相关函数。可以猜测,在root hub创建后,会执行此处的hub_probe函数。
任务之2:完成内核线程hub_thread的创建,该线程是检测USB端口插入设备后的处理函数,是完成USB设备识别到枚举的监控进程,十分重要。
static int hub_thread(void *__unused)
{
/* khubd needs to be freezable to avoid intefering with USB-PERSIST
* port handover. Otherwise it might see that a full-speed device
* was gone before the EHCI controller had handed its port over to
* the companion full-speed controller.
*/
set_freezable();
do {
hub_events();
wait_event_freezable(khubd_wait,
!list_empty(&hub_event_list) ||
kthread_should_stop());
} while (!kthread_should_stop() || !list_empty(&hub_event_list));
pr_debug("%s: khubd exiting\n", usbcore_name);
return 0;
}hub_events()是一个死循环,其任务是解析hub_event_list,来一个一个处理发生在hub上的事件,比如插入,拔出。当hub_event_list事件被处理完后,break跳出while,通过wait_event_freezable使进程进入休眠态。一旦hub_event_list上有新事件需要处理,此处khubd_wait会在事件中断中被唤醒,重新执行到此处的hub_events()来遍历执行事件,完成处理。
hub_events()十分庞大,且十分重要,后面分析到此处流程的时候再详细分析。
-
usb_register_device_driver完成一个usb_device_driver usb_generic_driver的注册
区别于usb_register函数,usb_register_device_driver完成一个device的注册,既然是一个device的驱动,那么在USB枚举之后,创建一个USB设备后,这个驱动就会被probe。
2.2.2 USB Core重点函数及数据结构
-
usb_register() 注册一个USB接口驱动
usb_register是一个宏,展开后:
#define usb_register(driver) usb_register_driver(driver, THIS_MODULE, KBUILD_MODNAME)/**
* usb_register_driver - register a USB interface driver
* @new_driver: USB operations for the interface driver
*
* Registers a USB interface driver with the USB core. The list of
* unattached interfaces will be rescanned whenever a new driver is
* added, allowing the new driver to attach to any recognized interfaces.
* Returns a negative error code on failure and 0 on success.
*
* NOTE: if you want your driver to use the USB major number, you must call
* usb_register_dev() to enable that functionality. This function no longer
* takes care of that.
*/
int usb_register_driver(struct usb_driver *new_driver, struct module *owner,
const char *mod_name)
{
...
new_driver->drvwrap.for_devices = 0;
new_driver->drvwrap.driver.name = (char *) new_driver->name;
new_driver->drvwrap.driver.bus = &usb_bus_type;
new_driver->drvwrap.driver.probe = usb_probe_interface;
new_driver->drvwrap.driver.remove = usb_unbind_interface;
...
retval = driver_register(&new_driver->drvwrap.driver);
retval = usb_create_newid_files(new_driver);
pr_info("%s: registered new interface driver %s\n",
usbcore_name, new_driver->name);
}-
int usb_register_device_driver(struct usb_device_driver *new_udriver, struct module *owner):注册USB设备驱动
/**
* usb_register_device_driver - register a USB device (not interface) driver
* @new_udriver: USB operations for the device driver
*
* Registers a USB device driver with the USB core. The list of
* unattached devices will be rescanned whenever a new driver is
* added, allowing the new driver to attach to any recognized devices.
* Returns a negative error code on failure and 0 on success.
*/
int usb_register_device_driver(struct usb_device_driver *new_udriver,
struct module *owner)
{
...
new_udriver->drvwrap.for_devices = 1;
new_udriver->drvwrap.driver.name = (char *) new_udriver->name;
new_udriver->drvwrap.driver.bus = &usb_bus_type;
new_udriver->drvwrap.driver.probe = usb_probe_device;
new_udriver->drvwrap.driver.remove = usb_unbind_device;
retval = driver_register(&new_udriver->drvwrap.driver);
if (!retval)
pr_info("%s: registered new device driver %s\n",
usbcore_name, new_udriver->name);
...
}对比两个驱动注册函数,一个为注册USB 接口驱动,一个为注册USB设备驱动,一个设备可以有多个接口,设备和接口的驱动在内核是有所区别的,他们都挂在usb_bus_type下,设备驱动的for_devices变量被置1,这个变量在总线的match函数usb_device_match的时候会用于判断是什么类型的驱动。且usb_device_match对接口和设备驱动进行了判断,走了不通的match分支。
由于总线的match函数通过for_devices进行匹配,可以猜测内核针对的USB设备驱动仅有usb_generic_driver一个,且USB枚举后产生的所有设备,都将被此驱动所probe。
-
struct usb_driver:USB接口驱动结构体
struct usb_driver {
const char *name;
int (*probe) (struct usb_interface *intf,
const struct usb_device_id *id);
void (*disconnect) (struct usb_interface *intf);
int (*unlocked_ioctl) (struct usb_interface *intf, unsigned int code,
void *buf);
int (*suspend) (struct usb_interface *intf, pm_message_t message);
int (*resume) (struct usb_interface *intf);
int (*reset_resume)(struct usb_interface *intf);
int (*pre_reset)(struct usb_interface *intf);
int (*post_reset)(struct usb_interface *intf);
const struct usb_device_id *id_table;
struct usb_dynids dynids;
struct usbdrv_wrap drvwrap;
unsigned int no_dynamic_id:1;
unsigned int supports_autosuspend:1;
unsigned int disable_hub_initiated_lpm:1;
unsigned int soft_unbind:1;
};USB分为:USB设备驱动,USB Core和HCD。在编写USB设备驱动的时候,一定也会向Core一样调用usb_register来向USB总线注册USB接口驱动。此时就需要实现一个usb_driver结构体,并填充里面重要的函数。
如上比较重要的成员,如probe匹配、id_table匹配的id表、supports_autosuspend休眠,对接设备驱动模型的drvwrap结构体等。
2.2.3 总结
可以将USB口的入口函数任务总结为如下:
-
创建并初始化了USB总线,usb_bus_type,提供了总线的匹配函数
-
向总线注册hub的驱动,并启动了内核线程hub_thread监控hub事件。
-
向总线注册USB设备驱动usb_generic_driver,用于USB设备插入后的设备驱动枚举。
2.3 USB主机控制器驱动分析
分析主机控制器驱动前,首先来看一个USB2.0协议 5.2.3 Physical Bus Topology 内的USB物理总线拓扑图。
(译:如下图)USB上的设备通过分层星形拓扑物理连接到主机,如中所示图5-5。USB连接点由一种特殊的USB设备(称为集线器hub)提供。这个集线器提供的附加连接点称为端口port。主机包括一个名为根集线器。主机通过根集线器提供一个或多个连接点。
从协议中可以看到,控制器上绑定了一个特殊的USB设备,称为root hub,根集线器提供的连接点称为port。所以可以总结出HCD需要完成的任务:
-
完成控制器硬件的初始化,使得USB PHY工作在主状态下。
-
从软件上构造出控制器结构体,并提供控制器驱动的操作函数,用于数据交互等。
-
既然root hub是一个USB设备,对于驱动中,一定需要创建一个USB设备来表示这个root hub。
-
外部设备插在root hub上,软件需要完成对root hub的监控,以及USB设备插入后的创建操作。
2.3.1 HCD入口函数分析
CPU一般在内部集成USB,可选的HCD也比较多,比如dwc2、dwc3、chipidea的等等,均在kernel/drivers/usb/目下可以找到其对应的目录。本文以dwc2为例,代码位置: kernel/drivers/usb/dwc2/core.c。
HCD控制器驱动一般以platform的形式将驱动注册进内核,本文HCD的入口函数中注册了两个platform_driver,并在板级代码中提供了platform_device。
本文将HCD控制器驱动可以从整体上分为两个大部分:
-
平台相关的硬件初始化
-
内核通用的USB HCD软件初始化流程
-
平台硬件相关初始化
第一部分:平台相关的硬件初始化,主要完成硬件相关初始化,devm_clk_get/clk_enable申请并使能时钟,phy_init对USB PHY寄存器进行初始化设置,devm_request_threaded_irq申请id引脚中断等。是与硬件相关的初始化。在完成平台硬件的初始化后,在probe的末尾部分,调用了dwc2_host_init()函数。
将dwc2_host_init()看做HCD驱动第二部分,其主要完成HCD控制器的创建注册以及ROOT HUB的注册和HUB的监测。由于内核该部分调用关系比较多,本文将第二部分分为多个层次,从dwc2_host_init()开始。
-
第一层:dwc2_host_init(dwc)
从最顶层名字上说明了整个代码最终是为了完成host控制器的初始化。在上面,我们知道主机控制器上绑定了一个ROOT HUB。
int dwc2_host_init(struct dwc2 *dwc) {
struct usb_hcd *hcd;
int ret;
...
hcd = usb_create_hcd(&dwc2_hc_driver, dwc->dev, dev_name(dwc->dev));
dev_set_drvdata(dwc->dev, dwc);
*(struct dwc2 **)(hcd->hcd_priv) = dwc;
dwc->hcd = hcd;
ret = usb_add_hcd(hcd, -1, 0);
...
}dwc2_host_init 主要调用了两个函数usb_create_hcd和usb_add_hcd
① usb_create_hcd(&dwc2_hc_driver, dwc->dev, dev_name(dwc->dev));
struct usb_hcd *usb_create_hcd(const struct hc_driver *driver,
struct device *dev, const char *bus_name)
{
return usb_create_shared_hcd(driver, dev, bus_name, NULL);
}/**
* usb_create_shared_hcd - create and initialize an HCD structure
* @driver: HC driver that will use this hcd
* @dev: device for this HC, stored in hcd->self.controller
* @bus_name: value to store in hcd->self.bus_name
* @primary_hcd: a pointer to the usb_hcd structure that is sharing the
* PCI device. Only allocate certain resources for the primary HCD
* Context: !in_interrupt()
*
* Allocate a struct usb_hcd, with extra space at the end for the
* HC driver's private data. Initialize the generic members of the
* hcd structure.
*
* If memory is unavailable, returns NULL.
*/
struct usb_hcd *usb_create_shared_hcd(const struct hc_driver *driver,
struct device *dev, const char *bus_name,
struct usb_hcd *primary_hcd)
{
struct usb_hcd *hcd;
hcd = kzalloc(sizeof(*hcd) + driver->hcd_priv_size, GFP_KERNEL);
...
usb_bus_init(&hcd->self);
hcd->self.controller = dev;
hcd->self.bus_name = bus_name;
hcd->self.uses_dma = (dev->dma_mask != NULL);
init_timer(&hcd->rh_timer);
hcd->rh_timer.function = rh_timer_func;
hcd->rh_timer.data = (unsigned long) hcd;
#ifdef CONFIG_PM_RUNTIME
INIT_WORK(&hcd->wakeup_work, hcd_resume_work);
#endif
hcd->driver = driver;
...
}根据注释该函数主要任务是创建并初始化一个HCD 结构体usb_hcd ,该函数主要实现:
-
完成usb_hcd内存申请
-
usb_bus总线初始化,usb_bus_init(&hcd->self);
-
填充控制器驱动hc_driver。
usb_hcd的第一个成员是:struct usb_bus self; /* hcd is-a bus */。
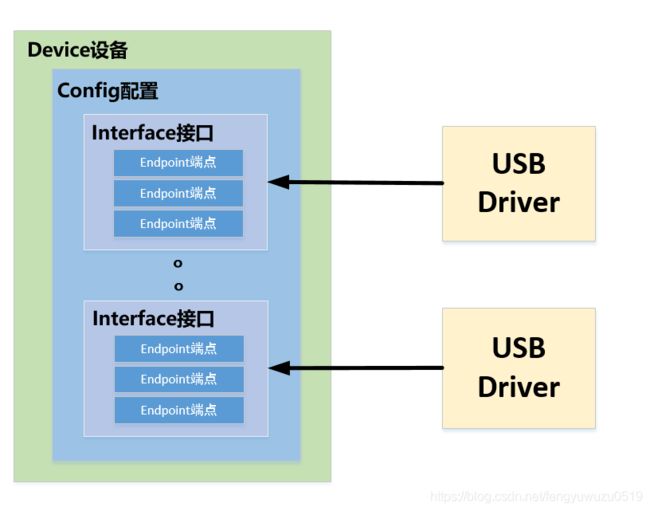
一个主控制器对应一条usb总线,一个主控制器绑定着一个root hub,一个root hub对应于一个usb_device,然后注册此root hub。
每个usb设备(usb_device)有一种或多种配置,每种配置有一个或多个接口,一个接口有一种或多种设置,一种设置有一个或多个端点。
hcd->driver = driver;中的driver=&dwc2_hc_driver(struct hc_driver)是主机控制器驱动函数,实现了通过主机控制器硬件向外通信的方法。类似于网卡设备驱动里面的net_device_ops结构体。后面用到再具体分析hc_driver。
② usb_add_hcd(hcd, -1, 0);
int usb_add_hcd(struct usb_hcd *hcd,
unsigned int irqnum, unsigned long irqflags)
{
int retval;
struct usb_device *rhdev;
if ((retval = usb_register_bus(&hcd->self)) < 0)
goto err_register_bus;
if ((rhdev = usb_alloc_dev(NULL, &hcd->self, 0)) == NULL) {
dev_err(hcd->self.controller, "unable to allocate root hub\n");
retval = -ENOMEM;
goto err_allocate_root_hub;
}
hcd->self.root_hub = rhdev;
if (hcd->driver->reset && (retval = hcd->driver->reset(hcd)) < 0) {
dev_err(hcd->self.controller, "can't setup\n");
goto err_hcd_driver_setup;
}
hcd->state = HC_STATE_RUNNING;
retval = hcd->driver->start(hcd);
/* starting here, usbcore will pay attention to this root hub */
retval = register_root_hub(hcd);
} 将hcd添加到USB总线,该函数主要实现
-
注册usb_bus总线
-
usb_alloc_dev申请一个usb_device,并赋给hcd->self.root_hub
-
register_root_hub
上面我们根据协议知道主机控制器上会被绑定一个特殊的USB设备叫做root hub,在hcd注册完成后,为了实现正常的usb功能,此处应该还要实现一个root hub并绑定在hcd上。当完成usb_bus总线的注册后,此处调用usb_alloc_dev来创建一个USB设备,并将该设备指给了控制器的root hub,hcd->self.root_hub = rhdev;并调用register_root_hub注册到usb总线。
-
第二层:register_root_hub()
/**
* register_root_hub - called by usb_add_hcd() to register a root hub
* @hcd: host controller for this root hub
*
* This function registers the root hub with the USB subsystem. It sets up
* the device properly in the device tree and then calls usb_new_device()
* to register the usb device. It also assigns the root hub's USB address
* (always 1).
*/
static int register_root_hub(struct usb_hcd *hcd)
{
struct device *parent_dev = hcd->self.controller;
struct usb_device *usb_dev = hcd->self.root_hub;
const int devnum = 1;
int retval;
usb_dev->devnum = devnum;
usb_dev->bus->devnum_next = devnum + 1;
usb_set_device_state(usb_dev, USB_STATE_ADDRESS);
mutex_lock(&usb_bus_list_lock);
retval = usb_get_device_descriptor(usb_dev, USB_DT_DEVICE_SIZE);
retval = usb_new_device (usb_dev);
mutex_unlock(&usb_bus_list_lock);
return retval;
}
usb_new_device创建一个usb设备并将其挂到usb_bus_type总线上,由于USB为总线设备驱动模型,在执行usb_new_device后,将执行总线的匹配函数如下。
usb_new_device->device_add->bus_probe_device->device_attach->bus_for_each_drv->__device_attach->driver_match_device->drv->bus->match(dev, drv)->usb_device_match
回顾USB2.0协议,这里确实是实现了一个绑定在控制器上的usb设备,并将其挂在USB总线上作为root hub来维护。
-
第三层:设备与驱动的匹配
USB总线的匹配函数usb_device_match这时就需要被调用到了,其代码如下:
static int usb_device_match(struct device *dev, struct device_driver *drv)
{
/* devices and interfaces are handled separately */
if (is_usb_device(dev)) {
/* interface drivers never match devices */
if (!is_usb_device_driver(drv))
return 0;
/* TODO: Add real matching code */
return 1;
} else if (is_usb_interface(dev)) {
struct usb_interface *intf;
struct usb_driver *usb_drv;
const struct usb_device_id *id;
/* device drivers never match interfaces */
if (is_usb_device_driver(drv))
return 0;
intf = to_usb_interface(dev);
usb_drv = to_usb_driver(drv);
id = usb_match_id(intf, usb_drv->id_table);
if (id)
return 1;
id = usb_match_dynamic_id(intf, usb_drv);
if (id)
return 1;
}
return 0;
}2.2章节我们分析了usb_register来注册一个usb接口驱动,usb_register_device_driver来注册一个usb设备驱动。同样在match函数里面也针对usb接口和设备进行了区分,形成了if else两个分支。
① USB设备&USB设备驱动
is_usb_device(dev)
static inline int is_usb_device(const struct device *dev)
{
return dev->type == &usb_device_type;
}usb_alloc_dev在创建usb hub的时候,其内部指定了dev->dev.type = &usb_device_type;
is_usb_device_driver(drv)
static inline int is_usb_device_driver(struct device_driver *drv)
{
return container_of(drv, struct usbdrv_wrap, driver)->
for_devices;
}回顾分析usb core入口函数,当时注册了一个usb设备驱动usb_generic_driver,其for_devices为1.此时显然root hub设备与usb_generic_driver驱动匹配成功,因此usb_generic_driver的generic_probe函数被调用。
① USB接口&USB接口驱动
我们继续分析usb root hub的注册,此时generic_probe被调用。
static int generic_probe(struct usb_device *udev)
{
int err, c;
/* Choose and set the configuration. This registers the interfaces
* with the driver core and lets interface drivers bind to them.
*/
c = usb_choose_configuration(udev);
err = usb_set_configuration(udev, c);
/* USB device state == configured ... usable */
usb_notify_add_device(udev);
return 0;
}其主要函数2个:usb_choose_configuration和usb_set_configuration,选择配置并设置配置。
-
第四层:usb配置选择和设置
https://blog.csdn.net/duan_xiaosu/article/details/68487314
https://www.linuxidc.com/Linux/2012-07/66670p3.htm
在usb_set_configuration的尾部,会将每一个接口设备注册到内核中。
for (i = 0; i < nintf; ++i) {
struct usb_interface *intf = cp->interface[i];
ret = device_add(&intf->dev);
create_intf_ep_devs(intf);
}在执行device_add后导致总线的匹配函数usb_device_match再次被调用,这次由于是接口设备,设备类型为usb_if_device_type,那么匹配的一定是接口驱动,于是会执行usb_device_match的else分支,去匹配接口驱动。根据上面对usb_device_match的分析,此时在core注册的hub_driver的hub_probe函数被调用。
-
第五层:hub_probe分析
static int hub_probe(struct usb_interface *intf, const struct usb_device_id *id)
{
struct usb_host_interface *desc;
struct usb_endpoint_descriptor *endpoint;
struct usb_device *hdev;
struct usb_hub *hub;
...
//分配usb_hub 结构体
hub = kzalloc(sizeof(*hub), GFP_KERNEL);
//填充结构体
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&hub->event_list);
hub->intfdev = &intf->dev;
hub->hdev = hdev;
usb_set_intfdata (intf, hub);
intf->needs_remote_wakeup = 1;
//配置hub
if (hub_configure(hub, endpoint) >= 0)
return 0;
}申请usb_hub ,填充,调用hub_configure配置hub
static int hub_configure(struct usb_hub *hub,
struct usb_endpoint_descriptor *endpoint)
{
struct usb_hcd *hcd;
struct usb_device *hdev = hub->hdev;
struct device *hub_dev = hub->intfdev;
u16 hubstatus, hubchange;
hub->descriptor = kmalloc(sizeof(*hub->descriptor), GFP_KERNEL);
//获取HUB的描述符
ret = get_hub_descriptor(hdev, hub->descriptor);
hub->ports = kzalloc(hdev->maxchild * sizeof(struct usb_port *),
//填充urb
hub->urb = usb_alloc_urb(0, GFP_KERNEL);
//初始化一个中断urb,回调函数为hub_irq
usb_fill_int_urb(hub->urb, hdev, pipe, *hub->buffer, maxp, hub_irq,
hub, endpoint->bInterval);
//激活hub
hub_activate(hub, HUB_INIT);
}-
填充hub的相关描述符信息
-
初始化一个urb中断,其回调函数为hub_irq
-
并激活hub
在当hub上存在事件的时候时候会触发hub_irq调用,hub_irq调用kick_khubd完成对hub_thread的唤醒,去执行hub_events。
/* completion function, fires on port status changes and various faults */
static void hub_irq(struct urb *urb)
{
struct usb_hub *hub = urb->context;
int status = urb->status;
unsigned i;
unsigned long bits;
switch (status) {
case -ENOENT: /* synchronous unlink */
case -ECONNRESET: /* async unlink */
case -ESHUTDOWN: /* hardware going away */
return;
default: /* presumably an error */
/* Cause a hub reset after 10 consecutive errors */
dev_dbg (hub->intfdev, "transfer --> %d\n", status);
if ((++hub->nerrors < 10) || hub->error)
goto resubmit;
hub->error = status;
/* FALL THROUGH */
/* let khubd handle things */
case 0: /* we got data: port status changed */
bits = 0;
for (i = 0; i < urb->actual_length; ++i)
bits |= ((unsigned long) ((*hub->buffer)[i]))
<< (i*8);
hub->event_bits[0] = bits;
break;
}
hub->nerrors = 0;
/* Something happened, let khubd figure it out */
kick_khubd(hub);
if ((status = usb_submit_urb (hub->urb, GFP_ATOMIC)) != 0
&& status != -ENODEV && status != -EPERM)
dev_err (hub->intfdev, "resubmit --> %d\n", status);
}
static void kick_khubd(struct usb_hub *hub)
{
unsigned long flags;
spin_lock_irqsave(&hub_event_lock, flags);
if (!hub->disconnected && list_empty(&hub->event_list)) {
list_add_tail(&hub->event_list, &hub_event_list);
/* Suppress autosuspend until khubd runs */
usb_autopm_get_interface_no_resume(
to_usb_interface(hub->intfdev));
wake_up(&khubd_wait);
}
spin_unlock_irqrestore(&hub_event_lock, flags);
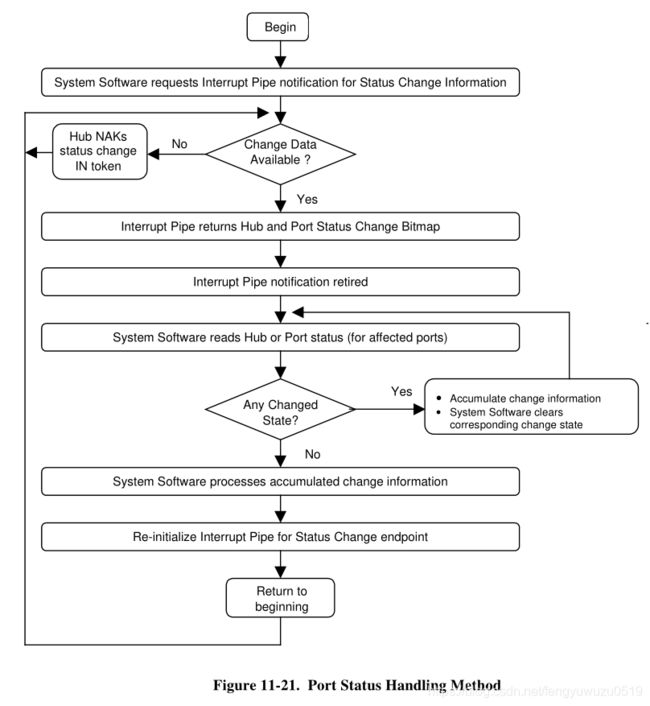
}usb协议:11.12.3 Port Change Information Processing
-
第六层 hub_events()事件处理
第五层,完成了root hub的初始化及相关hub监测的创建,当hub上存在新事件的时候,hub_events开始执行,进行hub事件处理。是hub功能最为核心的处理函数。
static void hub_events(void)
{
struct list_head *tmp;
struct usb_device *hdev;
struct usb_interface *intf;
struct usb_hub *hub;
struct device *hub_dev;
u16 hubstatus;
u16 hubchange;
u16 portstatus;
u16 portchange;
int i, ret;
int connect_change, wakeup_change;
/*
* We restart the list every time to avoid a deadlock with
* deleting hubs downstream from this one. This should be
* safe since we delete the hub from the event list.
* Not the most efficient, but avoids deadlocks.
*/
while (1) {
/* Grab the first entry at the beginning of the list */
spin_lock_irq(&hub_event_lock);
if (list_empty(&hub_event_list)) {
spin_unlock_irq(&hub_event_lock);
break;
}
tmp = hub_event_list.next;
list_del_init(tmp);
hub = list_entry(tmp, struct usb_hub, event_list);
kref_get(&hub->kref);
spin_unlock_irq(&hub_event_lock);
hdev = hub->hdev;
hub_dev = hub->intfdev;
intf = to_usb_interface(hub_dev);
dev_dbg(hub_dev, "state %d ports %d chg %04x evt %04x\n",
hdev->state, hub->descriptor
? hub->descriptor->bNbrPorts
: 0,
/* NOTE: expects max 15 ports... */
(u16) hub->change_bits[0],
(u16) hub->event_bits[0]);
/* Lock the device, then check to see if we were
* disconnected while waiting for the lock to succeed. */
usb_lock_device(hdev);
if (unlikely(hub->disconnected))
goto loop_disconnected;
/* If the hub has died, clean up after it */
if (hdev->state == USB_STATE_NOTATTACHED) {
hub->error = -ENODEV;
hub_quiesce(hub, HUB_DISCONNECT);
goto loop;
}
/* Autoresume */
ret = usb_autopm_get_interface(intf);
if (ret) {
dev_dbg(hub_dev, "Can't autoresume: %d\n", ret);
goto loop;
}
/* If this is an inactive hub, do nothing */
if (hub->quiescing)
goto loop_autopm;
if (hub->error) {
dev_dbg (hub_dev, "resetting for error %d\n",
hub->error);
ret = usb_reset_device(hdev);
if (ret) {
dev_dbg (hub_dev,
"error resetting hub: %d\n", ret);
goto loop_autopm;
}
hub->nerrors = 0;
hub->error = 0;
}
/* deal with port status changes */
for (i = 1; i <= hub->descriptor->bNbrPorts; i++) {
if (test_bit(i, hub->busy_bits))
continue;
connect_change = test_bit(i, hub->change_bits);
wakeup_change = test_and_clear_bit(i, hub->wakeup_bits);
if (!test_and_clear_bit(i, hub->event_bits) &&
!connect_change && !wakeup_change)
continue;
ret = hub_port_status(hub, i,
&portstatus, &portchange);
if (ret < 0)
continue;
if (portchange & USB_PORT_STAT_C_CONNECTION) {
usb_clear_port_feature(hdev, i,
USB_PORT_FEAT_C_CONNECTION);
connect_change = 1;
}
if (portchange & USB_PORT_STAT_C_ENABLE) {
if (!connect_change)
dev_dbg (hub_dev,
"port %d enable change, "
"status %08x\n",
i, portstatus);
usb_clear_port_feature(hdev, i,
USB_PORT_FEAT_C_ENABLE);
/*
* EM interference sometimes causes badly
* shielded USB devices to be shutdown by
* the hub, this hack enables them again.
* Works at least with mouse driver.
*/
if (!(portstatus & USB_PORT_STAT_ENABLE)
&& !connect_change
&& hub->ports[i - 1]->child) {
dev_err (hub_dev,
"port %i "
"disabled by hub (EMI?), "
"re-enabling...\n",
i);
connect_change = 1;
}
}
if (hub_handle_remote_wakeup(hub, i,
portstatus, portchange))
connect_change = 1;
if (portchange & USB_PORT_STAT_C_OVERCURRENT) {
u16 status = 0;
u16 unused;
dev_dbg(hub_dev, "over-current change on port "
"%d\n", i);
usb_clear_port_feature(hdev, i,
USB_PORT_FEAT_C_OVER_CURRENT);
msleep(100); /* Cool down */
hub_power_on(hub, true);
hub_port_status(hub, i, &status, &unused);
if (status & USB_PORT_STAT_OVERCURRENT)
dev_err(hub_dev, "over-current "
"condition on port %d\n", i);
}
if (portchange & USB_PORT_STAT_C_RESET) {
dev_dbg (hub_dev,
"reset change on port %d\n",
i);
usb_clear_port_feature(hdev, i,
USB_PORT_FEAT_C_RESET);
}
if ((portchange & USB_PORT_STAT_C_BH_RESET) &&
hub_is_superspeed(hub->hdev)) {
dev_dbg(hub_dev,
"warm reset change on port %d\n",
i);
usb_clear_port_feature(hdev, i,
USB_PORT_FEAT_C_BH_PORT_RESET);
}
if (portchange & USB_PORT_STAT_C_LINK_STATE) {
usb_clear_port_feature(hub->hdev, i,
USB_PORT_FEAT_C_PORT_LINK_STATE);
}
if (portchange & USB_PORT_STAT_C_CONFIG_ERROR) {
dev_warn(hub_dev,
"config error on port %d\n",
i);
usb_clear_port_feature(hub->hdev, i,
USB_PORT_FEAT_C_PORT_CONFIG_ERROR);
}
/* Warm reset a USB3 protocol port if it's in
* SS.Inactive state.
*/
if (hub_port_warm_reset_required(hub, portstatus)) {
int status;
struct usb_device *udev =
hub->ports[i - 1]->child;
dev_dbg(hub_dev, "warm reset port %d\n", i);
if (!udev || !(portstatus &
USB_PORT_STAT_CONNECTION)) {
status = hub_port_reset(hub, i,
NULL, HUB_BH_RESET_TIME,
true);
if (status < 0)
hub_port_disable(hub, i, 1);
} else {
usb_lock_device(udev);
status = usb_reset_device(udev);
usb_unlock_device(udev);
connect_change = 0;
}
}
if (connect_change)
hub_port_connect_change(hub, i,
portstatus, portchange);
} /* end for i */
/* deal with hub status changes */
if (test_and_clear_bit(0, hub->event_bits) == 0)
; /* do nothing */
else if (hub_hub_status(hub, &hubstatus, &hubchange) < 0)
dev_err (hub_dev, "get_hub_status failed\n");
else {
if (hubchange & HUB_CHANGE_LOCAL_POWER) {
dev_dbg (hub_dev, "power change\n");
clear_hub_feature(hdev, C_HUB_LOCAL_POWER);
if (hubstatus & HUB_STATUS_LOCAL_POWER)
/* FIXME: Is this always true? */
hub->limited_power = 1;
else
hub->limited_power = 0;
}
if (hubchange & HUB_CHANGE_OVERCURRENT) {
u16 status = 0;
u16 unused;
dev_dbg(hub_dev, "over-current change\n");
clear_hub_feature(hdev, C_HUB_OVER_CURRENT);
msleep(500); /* Cool down */
hub_power_on(hub, true);
hub_hub_status(hub, &status, &unused);
if (status & HUB_STATUS_OVERCURRENT)
dev_err(hub_dev, "over-current "
"condition\n");
}
}
loop_autopm:
/* Balance the usb_autopm_get_interface() above */
usb_autopm_put_interface_no_suspend(intf);
loop:
/* Balance the usb_autopm_get_interface_no_resume() in
* kick_khubd() and allow autosuspend.
*/
usb_autopm_put_interface(intf);
loop_disconnected:
usb_unlock_device(hdev);
kref_put(&hub->kref, hub_release);
} /* end while (1) */
}hub_events主要任务:
-
调用hub_port_status获取hub上发生的时间
-
调用hub_port_connect_change去处理事件
/* Handle physical or logical connection change events.
* This routine is called when:
* a port connection-change occurs;
* a port enable-change occurs (often caused by EMI);
* usb_reset_and_verify_device() encounters changed descriptors (as from
* a firmware download)
* caller already locked the hub
*/
static void hub_port_connect_change(struct usb_hub *hub, int port1,
u16 portstatus, u16 portchange)
{
struct usb_device *hdev = hub->hdev;
struct device *hub_dev = hub->intfdev;
struct usb_hcd *hcd = bus_to_hcd(hdev->bus);
unsigned wHubCharacteristics =
le16_to_cpu(hub->descriptor->wHubCharacteristics);
struct usb_device *udev;
int status, i;
unsigned unit_load;
dev_dbg (hub_dev,
"port %d, status %04x, change %04x, %s\n",
port1, portstatus, portchange, portspeed(hub, portstatus));
if (hub->has_indicators) {
set_port_led(hub, port1, HUB_LED_AUTO);
hub->indicator[port1-1] = INDICATOR_AUTO;
}
#ifdef CONFIG_USB_OTG
/* during HNP, don't repeat the debounce */
if (hdev->bus->is_b_host)
portchange &= ~(USB_PORT_STAT_C_CONNECTION |
USB_PORT_STAT_C_ENABLE);
#endif
/* Try to resuscitate an existing device */
udev = hub->ports[port1 - 1]->child;
if ((portstatus & USB_PORT_STAT_CONNECTION) && udev &&
udev->state != USB_STATE_NOTATTACHED) {
usb_lock_device(udev);
if (portstatus & USB_PORT_STAT_ENABLE) {
status = 0; /* Nothing to do */
#ifdef CONFIG_PM_RUNTIME
} else if (udev->state == USB_STATE_SUSPENDED &&
udev->persist_enabled) {
/* For a suspended device, treat this as a
* remote wakeup event.
*/
status = usb_remote_wakeup(udev);
#endif
} else {
status = -ENODEV; /* Don't resuscitate */
}
usb_unlock_device(udev);
if (status == 0) {
clear_bit(port1, hub->change_bits);
return;
}
}
/* Disconnect any existing devices under this port */
if (udev) {
if (hcd->phy && !hdev->parent &&
!(portstatus & USB_PORT_STAT_CONNECTION))
usb_phy_notify_disconnect(hcd->phy, udev->speed);
usb_disconnect(&hub->ports[port1 - 1]->child);
}
clear_bit(port1, hub->change_bits);
/* We can forget about a "removed" device when there's a physical
* disconnect or the connect status changes.
*/
if (!(portstatus & USB_PORT_STAT_CONNECTION) ||
(portchange & USB_PORT_STAT_C_CONNECTION))
clear_bit(port1, hub->removed_bits);
if (portchange & (USB_PORT_STAT_C_CONNECTION |
USB_PORT_STAT_C_ENABLE)) {
status = hub_port_debounce_be_stable(hub, port1);
if (status < 0) {
if (status != -ENODEV && printk_ratelimit())
dev_err(hub_dev, "connect-debounce failed, "
"port %d disabled\n", port1);
portstatus &= ~USB_PORT_STAT_CONNECTION;
} else {
portstatus = status;
}
}
/* Return now if debouncing failed or nothing is connected or
* the device was "removed".
*/
if (!(portstatus & USB_PORT_STAT_CONNECTION) ||
test_bit(port1, hub->removed_bits)) {
/* maybe switch power back on (e.g. root hub was reset) */
if ((wHubCharacteristics & HUB_CHAR_LPSM) < 2
&& !port_is_power_on(hub, portstatus))
set_port_feature(hdev, port1, USB_PORT_FEAT_POWER);
if (portstatus & USB_PORT_STAT_ENABLE)
goto done;
return;
}
if (hub_is_superspeed(hub->hdev))
unit_load = 150;
else
unit_load = 100;
status = 0;
for (i = 0; i < SET_CONFIG_TRIES; i++) {
/* reallocate for each attempt, since references
* to the previous one can escape in various ways
*/
udev = usb_alloc_dev(hdev, hdev->bus, port1);
if (!udev) {
dev_err (hub_dev,
"couldn't allocate port %d usb_device\n",
port1);
goto done;
}
usb_set_device_state(udev, USB_STATE_POWERED);
udev->bus_mA = hub->mA_per_port;
udev->level = hdev->level + 1;
udev->wusb = hub_is_wusb(hub);
/* Only USB 3.0 devices are connected to SuperSpeed hubs. */
if (hub_is_superspeed(hub->hdev))
udev->speed = USB_SPEED_SUPER;
else
udev->speed = USB_SPEED_UNKNOWN;
//选择设备号0.1.2...
choose_devnum(udev);
if (udev->devnum <= 0) {
status = -ENOTCONN; /* Don't retry */
goto loop;
}
/* reset (non-USB 3.0 devices) and get descriptor */
status = hub_port_init(hub, udev, port1, i);
if (status < 0)
goto loop;
usb_detect_quirks(udev);
if (udev->quirks & USB_QUIRK_DELAY_INIT)
msleep(1000);
/* consecutive bus-powered hubs aren't reliable; they can
* violate the voltage drop budget. if the new child has
* a "powered" LED, users should notice we didn't enable it
* (without reading syslog), even without per-port LEDs
* on the parent.
*/
if (udev->descriptor.bDeviceClass == USB_CLASS_HUB
&& udev->bus_mA <= unit_load) {
u16 devstat;
status = usb_get_status(udev, USB_RECIP_DEVICE, 0,
&devstat);
if (status < 2) {
dev_dbg(&udev->dev, "get status %d ?\n", status);
goto loop_disable;
}
le16_to_cpus(&devstat);
if ((devstat & (1 << USB_DEVICE_SELF_POWERED)) == 0) {
dev_err(&udev->dev,
"can't connect bus-powered hub "
"to this port\n");
if (hub->has_indicators) {
hub->indicator[port1-1] =
INDICATOR_AMBER_BLINK;
schedule_delayed_work (&hub->leds, 0);
}
status = -ENOTCONN; /* Don't retry */
goto loop_disable;
}
}
/* check for devices running slower than they could */
if (le16_to_cpu(udev->descriptor.bcdUSB) >= 0x0200
&& udev->speed == USB_SPEED_FULL
&& highspeed_hubs != 0)
check_highspeed (hub, udev, port1);
/* Store the parent's children[] pointer. At this point
* udev becomes globally accessible, although presumably
* no one will look at it until hdev is unlocked.
*/
status = 0;
/* We mustn't add new devices if the parent hub has
* been disconnected; we would race with the
* recursively_mark_NOTATTACHED() routine.
*/
spin_lock_irq(&device_state_lock);
if (hdev->state == USB_STATE_NOTATTACHED)
status = -ENOTCONN;
else
hub->ports[port1 - 1]->child = udev;
spin_unlock_irq(&device_state_lock);
/* Run it through the hoops (find a driver, etc) */
if (!status) {
status = usb_new_device(udev);
if (status) {
spin_lock_irq(&device_state_lock);
hub->ports[port1 - 1]->child = NULL;
spin_unlock_irq(&device_state_lock);
}
}
if (status)
goto loop_disable;
status = hub_power_remaining(hub);
if (status)
dev_dbg(hub_dev, "%dmA power budget left\n", status);
return;
loop_disable:
hub_port_disable(hub, port1, 1);
loop:
usb_ep0_reinit(udev);
release_devnum(udev);
hub_free_dev(udev);
usb_put_dev(udev);
if ((status == -ENOTCONN) || (status == -ENOTSUPP))
break;
}
if (hub->hdev->parent ||
!hcd->driver->port_handed_over ||
!(hcd->driver->port_handed_over)(hcd, port1)) {
if (status != -ENOTCONN && status != -ENODEV)
dev_err(hub_dev, "unable to enumerate USB device on port %d\n",
port1);
}
done:
hub_port_disable(hub, port1, 1);
if (hcd->driver->relinquish_port && !hub->hdev->parent)
hcd->driver->relinquish_port(hcd, port1);
}hub_port_connect_change主要任务
-
判断发生的事件的类型
-
若有新设备插入,则创建一个usb设备,并完成设备的信息获取和初始化。
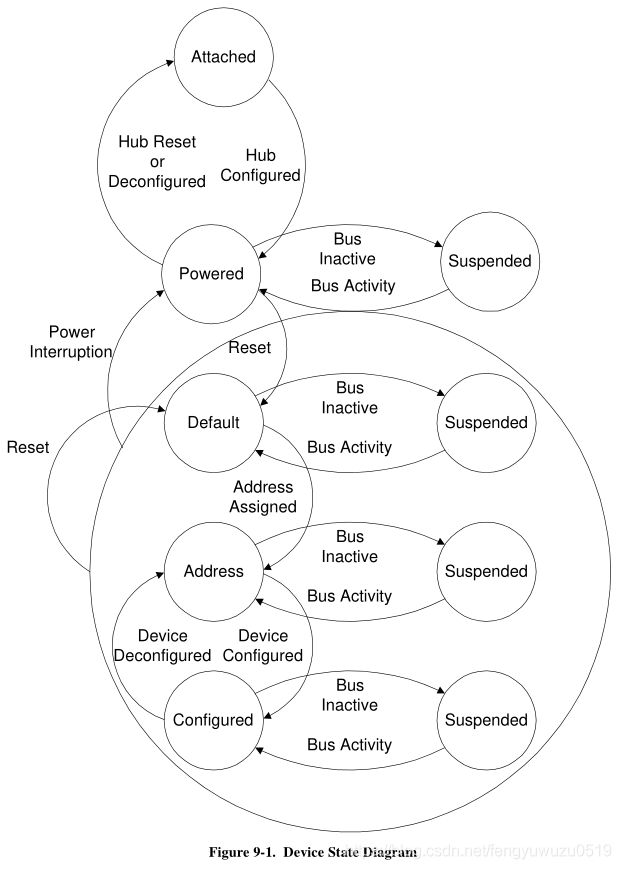
USB协议 9.1 USB设备状态
usb_alloc_dev
dev->state = USB_STATE_ATTACHED;
第七层 USB设备与驱动的枚举
2.3.2 HCD重点函数及结构体
/*-------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
/*
* USB Host Controller Driver (usb_hcd) framework
*
* Since "struct usb_bus" is so thin, you can't share much code in it.
* This framework is a layer over that, and should be more sharable.
*
* @authorized_default: Specifies if new devices are authorized to
* connect by default or they require explicit
* user space authorization; this bit is settable
* through /sys/class/usb_host/X/authorized_default.
* For the rest is RO, so we don't lock to r/w it.
*/
/*-------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
struct usb_hcd {
/*
* housekeeping
*/
struct usb_bus self; /* hcd is-a bus */
struct kref kref; /* reference counter */
const char *product_desc; /* product/vendor string */
int speed; /* Speed for this roothub.
* May be different from
* hcd->driver->flags & HCD_MASK
*/
char irq_descr[24]; /* driver + bus # */
struct timer_list rh_timer; /* drives root-hub polling */
struct urb *status_urb; /* the current status urb */
#ifdef CONFIG_PM_RUNTIME
struct work_struct wakeup_work; /* for remote wakeup */
#endif
/*
* hardware info/state
*/
const struct hc_driver *driver; /* hw-specific hooks */
/*
* OTG and some Host controllers need software interaction with phys;
* other external phys should be software-transparent
*/
struct usb_phy *phy;
/* Flags that need to be manipulated atomically because they can
* change while the host controller is running. Always use
* set_bit() or clear_bit() to change their values.
*/
unsigned long flags;
#define HCD_FLAG_HW_ACCESSIBLE 0 /* at full power */
#define HCD_FLAG_POLL_RH 2 /* poll for rh status? */
#define HCD_FLAG_POLL_PENDING 3 /* status has changed? */
#define HCD_FLAG_WAKEUP_PENDING 4 /* root hub is resuming? */
#define HCD_FLAG_RH_RUNNING 5 /* root hub is running? */
#define HCD_FLAG_DEAD 6 /* controller has died? */
/* The flags can be tested using these macros; they are likely to
* be slightly faster than test_bit().
*/
#define HCD_HW_ACCESSIBLE(hcd) ((hcd)->flags & (1U << HCD_FLAG_HW_ACCESSIBLE))
#define HCD_POLL_RH(hcd) ((hcd)->flags & (1U << HCD_FLAG_POLL_RH))
#define HCD_POLL_PENDING(hcd) ((hcd)->flags & (1U << HCD_FLAG_POLL_PENDING))
#define HCD_WAKEUP_PENDING(hcd) ((hcd)->flags & (1U << HCD_FLAG_WAKEUP_PENDING))
#define HCD_RH_RUNNING(hcd) ((hcd)->flags & (1U << HCD_FLAG_RH_RUNNING))
#define HCD_DEAD(hcd) ((hcd)->flags & (1U << HCD_FLAG_DEAD))
/* Flags that get set only during HCD registration or removal. */
unsigned rh_registered:1;/* is root hub registered? */
unsigned rh_pollable:1; /* may we poll the root hub? */
unsigned msix_enabled:1; /* driver has MSI-X enabled? */
/* The next flag is a stopgap, to be removed when all the HCDs
* support the new root-hub polling mechanism. */
unsigned uses_new_polling:1;
unsigned wireless:1; /* Wireless USB HCD */
unsigned authorized_default:1;
unsigned has_tt:1; /* Integrated TT in root hub */
unsigned int irq; /* irq allocated */
void __iomem *regs; /* device memory/io */
resource_size_t rsrc_start; /* memory/io resource start */
resource_size_t rsrc_len; /* memory/io resource length */
unsigned power_budget; /* in mA, 0 = no limit */
/* bandwidth_mutex should be taken before adding or removing
* any new bus bandwidth constraints:
* 1. Before adding a configuration for a new device.
* 2. Before removing the configuration to put the device into
* the addressed state.
* 3. Before selecting a different configuration.
* 4. Before selecting an alternate interface setting.
*
* bandwidth_mutex should be dropped after a successful control message
* to the device, or resetting the bandwidth after a failed attempt.
*/
struct mutex *bandwidth_mutex;
struct usb_hcd *shared_hcd;
struct usb_hcd *primary_hcd;
#define HCD_BUFFER_POOLS 4
struct dma_pool *pool[HCD_BUFFER_POOLS];
int state;
# define __ACTIVE 0x01
# define __SUSPEND 0x04
# define __TRANSIENT 0x80
# define HC_STATE_HALT 0
# define HC_STATE_RUNNING (__ACTIVE)
# define HC_STATE_QUIESCING (__SUSPEND|__TRANSIENT|__ACTIVE)
# define HC_STATE_RESUMING (__SUSPEND|__TRANSIENT)
# define HC_STATE_SUSPENDED (__SUSPEND)
#define HC_IS_RUNNING(state) ((state) & __ACTIVE)
#define HC_IS_SUSPENDED(state) ((state) & __SUSPEND)
/* more shared queuing code would be good; it should support
* smarter scheduling, handle transaction translators, etc;
* input size of periodic table to an interrupt scheduler.
* (ohci 32, uhci 1024, ehci 256/512/1024).
*/
/* The HC driver's private data is stored at the end of
* this structure.
*/
unsigned long hcd_priv[0]
__attribute__ ((aligned(sizeof(s64))));
};2.3.3 总结
三、USB驱动分析
根据以上对内核USB子系统分析,此时可以来分析USB驱动的案例,加强对USB的理解。
分析HCD的过程中,在控制器上绑定的root hub就是一个usb device,HCD初始化过程完成了对这个USB设备的一系列初始化,并使用usb_fill_int_urb初始化了一个中断urb,使用usb_submit_urb 进行提交。
首先分析一个usb鼠标驱动,其和root hub的过程相似,也是中断传输。
3.1 Usb Mouse驱动
代码位置:kernel\drivers\hid\usbhid\usbmouse.c
https://www.cnblogs.com/EaIE099/p/5124512.html
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
/* for apple IDs */
#ifdef CONFIG_USB_HID_MODULE
#include "../hid-ids.h"
#endif
/*
* Version Information
*/
#define DRIVER_VERSION "v1.6"
#define DRIVER_AUTHOR "Vojtech Pavlik "
#define DRIVER_DESC "USB HID Boot Protocol mouse driver"
#define DRIVER_LICENSE "GPL"
MODULE_AUTHOR(DRIVER_AUTHOR);
MODULE_DESCRIPTION(DRIVER_DESC);
MODULE_LICENSE(DRIVER_LICENSE);
struct usb_mouse {
char name[128];
char phys[64];
struct usb_device *usbdev;
struct input_dev *dev;
struct urb *irq;
signed char *data;
dma_addr_t data_dma;
};
static void usb_mouse_irq(struct urb *urb)
{
struct usb_mouse *mouse = urb->context;
signed char *data = mouse->data;
struct input_dev *dev = mouse->dev;
int status;
switch (urb->status) {
case 0: /* success */
break;
case -ECONNRESET: /* unlink */
case -ENOENT:
case -ESHUTDOWN:
return;
/* -EPIPE: should clear the halt */
default: /* error */
goto resubmit;
}
input_report_key(dev, BTN_LEFT, data[0] & 0x01);
input_report_key(dev, BTN_RIGHT, data[0] & 0x02);
input_report_key(dev, BTN_MIDDLE, data[0] & 0x04);
input_report_key(dev, BTN_SIDE, data[0] & 0x08);
input_report_key(dev, BTN_EXTRA, data[0] & 0x10);
input_report_rel(dev, REL_X, data[1]);
input_report_rel(dev, REL_Y, data[2]);
input_report_rel(dev, REL_WHEEL, data[3]);
input_sync(dev);
resubmit:
status = usb_submit_urb (urb, GFP_ATOMIC);
if (status)
dev_err(&mouse->usbdev->dev,
"can't resubmit intr, %s-%s/input0, status %d\n",
mouse->usbdev->bus->bus_name,
mouse->usbdev->devpath, status);
}
static int usb_mouse_open(struct input_dev *dev)
{
struct usb_mouse *mouse = input_get_drvdata(dev);
mouse->irq->dev = mouse->usbdev;
if (usb_submit_urb(mouse->irq, GFP_KERNEL))
return -EIO;
return 0;
}
static void usb_mouse_close(struct input_dev *dev)
{
struct usb_mouse *mouse = input_get_drvdata(dev);
usb_kill_urb(mouse->irq);
}
static int usb_mouse_probe(struct usb_interface *intf, const struct usb_device_id *id)
{
struct usb_device *dev = interface_to_usbdev(intf);
struct usb_host_interface *interface;
struct usb_endpoint_descriptor *endpoint;
struct usb_mouse *mouse;
struct input_dev *input_dev;
int pipe, maxp;
int error = -ENOMEM;
interface = intf->cur_altsetting;
if (interface->desc.bNumEndpoints != 1)
return -ENODEV;
endpoint = &interface->endpoint[0].desc;
if (!usb_endpoint_is_int_in(endpoint))
return -ENODEV;
pipe = usb_rcvintpipe(dev, endpoint->bEndpointAddress);
maxp = usb_maxpacket(dev, pipe, usb_pipeout(pipe));
mouse = kzalloc(sizeof(struct usb_mouse), GFP_KERNEL);
input_dev = input_allocate_device();
if (!mouse || !input_dev)
goto fail1;
mouse->data = usb_alloc_coherent(dev, 8, GFP_ATOMIC, &mouse->data_dma);
if (!mouse->data)
goto fail1;
mouse->irq = usb_alloc_urb(0, GFP_KERNEL);
if (!mouse->irq)
goto fail2;
mouse->usbdev = dev;
mouse->dev = input_dev;
if (dev->manufacturer)
strlcpy(mouse->name, dev->manufacturer, sizeof(mouse->name));
if (dev->product) {
if (dev->manufacturer)
strlcat(mouse->name, " ", sizeof(mouse->name));
strlcat(mouse->name, dev->product, sizeof(mouse->name));
}
if (!strlen(mouse->name))
snprintf(mouse->name, sizeof(mouse->name),
"USB HIDBP Mouse %04x:%04x",
le16_to_cpu(dev->descriptor.idVendor),
le16_to_cpu(dev->descriptor.idProduct));
usb_make_path(dev, mouse->phys, sizeof(mouse->phys));
strlcat(mouse->phys, "/input0", sizeof(mouse->phys));
input_dev->name = mouse->name;
input_dev->phys = mouse->phys;
usb_to_input_id(dev, &input_dev->id);
input_dev->dev.parent = &intf->dev;
input_dev->evbit[0] = BIT_MASK(EV_KEY) | BIT_MASK(EV_REL);
input_dev->keybit[BIT_WORD(BTN_MOUSE)] = BIT_MASK(BTN_LEFT) |
BIT_MASK(BTN_RIGHT) | BIT_MASK(BTN_MIDDLE);
input_dev->relbit[0] = BIT_MASK(REL_X) | BIT_MASK(REL_Y);
input_dev->keybit[BIT_WORD(BTN_MOUSE)] |= BIT_MASK(BTN_SIDE) |
BIT_MASK(BTN_EXTRA);
input_dev->relbit[0] |= BIT_MASK(REL_WHEEL);
input_set_drvdata(input_dev, mouse);
input_dev->open = usb_mouse_open;
input_dev->close = usb_mouse_close;
usb_fill_int_urb(mouse->irq, dev, pipe, mouse->data,
(maxp > 8 ? 8 : maxp),
usb_mouse_irq, mouse, endpoint->bInterval);
mouse->irq->transfer_dma = mouse->data_dma;
mouse->irq->transfer_flags |= URB_NO_TRANSFER_DMA_MAP;
error = input_register_device(mouse->dev);
if (error)
goto fail3;
usb_set_intfdata(intf, mouse);
return 0;
fail3:
usb_free_urb(mouse->irq);
fail2:
usb_free_coherent(dev, 8, mouse->data, mouse->data_dma);
fail1:
input_free_device(input_dev);
kfree(mouse);
return error;
}
static void usb_mouse_disconnect(struct usb_interface *intf)
{
struct usb_mouse *mouse = usb_get_intfdata (intf);
usb_set_intfdata(intf, NULL);
if (mouse) {
usb_kill_urb(mouse->irq);
input_unregister_device(mouse->dev);
usb_free_urb(mouse->irq);
usb_free_coherent(interface_to_usbdev(intf), 8, mouse->data, mouse->data_dma);
kfree(mouse);
}
}
//用于驱动的匹配:
//match_flags 匹配哪些项,USB_DEVICE_ID_MATCH_INT_INFO:接口信息
//bInterfaceClass 、bInterfaceSubClass 、bInterfaceProtocol 所属的类,子类,及设备协议是否匹配
//#define USB_INTERFACE_INFO(cl, sc, pr) \
.match_flags = USB_DEVICE_ID_MATCH_INT_INFO, \
.bInterfaceClass = (cl), \
.bInterfaceSubClass = (sc), \
.bInterfaceProtocol = (pr)
static struct usb_device_id usb_mouse_id_table [] = {
{ USB_INTERFACE_INFO(USB_INTERFACE_CLASS_HID, USB_INTERFACE_SUBCLASS_BOOT,
USB_INTERFACE_PROTOCOL_MOUSE) },
{ } /* Terminating entry */
};
MODULE_DEVICE_TABLE (usb, usb_mouse_id_table);
static struct usb_driver usb_mouse_driver = {
.name = "usbmouse",
.probe = usb_mouse_probe,
.disconnect = usb_mouse_disconnect,
.id_table = usb_mouse_id_table,
};
module_usb_driver(usb_mouse_driver);
3.2 USB网卡
USB设备信息
设备电源管理信息
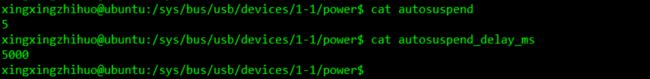
参数1:autosuspend & autosuspend_delay_ms
运行时期休眠的超时时间,即但总线挂起设备后,多久之后设备开始进入休眠。
参数2:runtime_enabled &
runtime_enabled :是否允许运行时期的休眠,状态有4中:disabled、forbidden、disabled & forbidden、enabled
disabled:dev->power.disable_depth
forbidden:dev->power.runtime_auto
runtime_status:当前状态
参数3:runtime_status
当前设备状态有四种:suspended、suspending、resuming、active。见上图。
参数:runtime_usage:&dev->power.usage_count
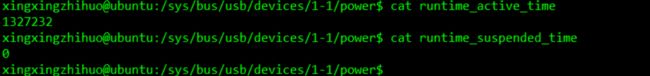
参数:runtime_suspended_time & runtime_active_time
设备活跃时间和挂起的时间
https://blog.csdn.net/ll148305879/article/details/91578189