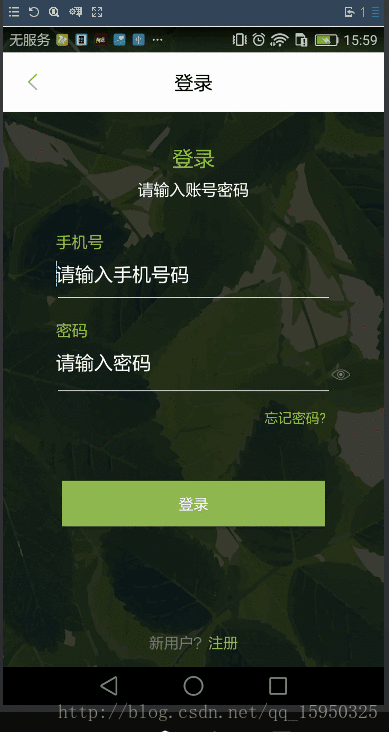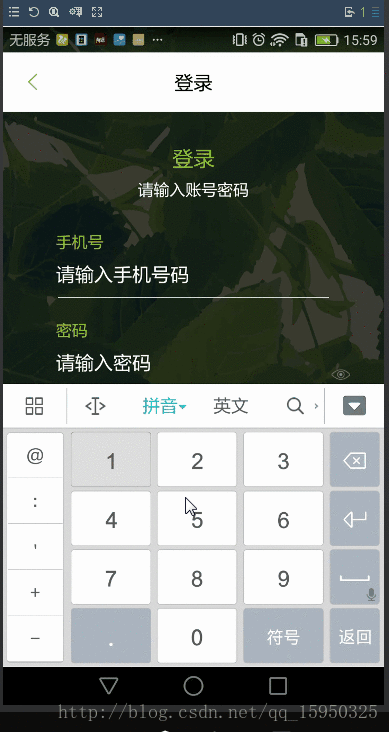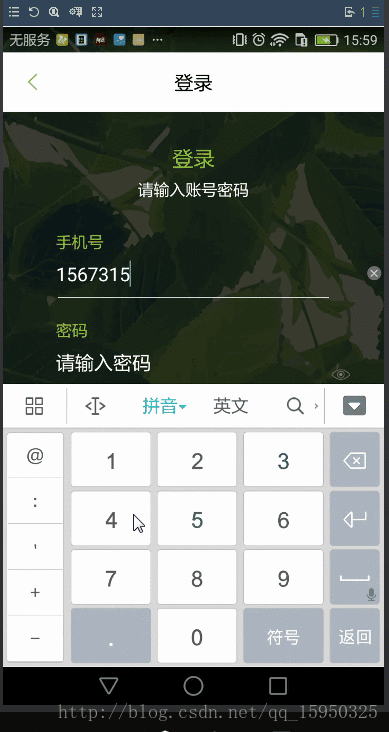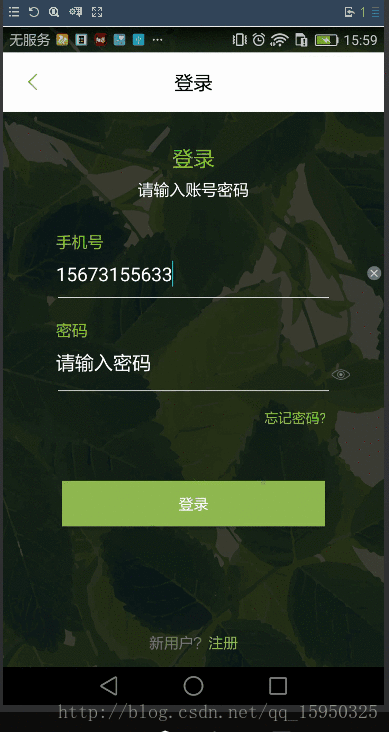
Android EditText 中hint文字大小以及与输入文字颜色保存一致
SpannableString 这个就是用来处理android 文本信息 可编辑 可点击 感兴趣的自己去看!
/*
* Copyright (C) 2006 The Android Open Source Project
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package android.text;
/**
* This is the interface for text that has markup objects attached to
* ranges of it. Not all text classes have mutable markup or text;
* see {@link Spannable} for mutable markup and {@link Editable} for
* mutable text.
*/
public interface Spanned
extends CharSequence
{
/**
* Bitmask of bits that are relevent for controlling point/mark behavior
* of spans.
*
* MARK and POINT are conceptually located between two adjacent characters.
* A MARK is "attached" to the character before, while a POINT will stick to the character
* after. The insertion cursor is conceptually located between the MARK and the POINT.
*
* As a result, inserting a new character between a MARK and a POINT will leave the MARK
* unchanged, while the POINT will be shifted, now located after the inserted character and
* still glued to the same character after it.
*
* Depending on whether the insertion happens at the beginning or the end of a span, the span
* will hence be expanded to include the new character (when the span is using a MARK at
* its beginning or a POINT at its end) or it will be excluded.
*
* Note that before and after here refer to offsets in the String, which are
* independent from the visual representation of the text (left-to-right or right-to-left).
*/
public static final int SPAN_POINT_MARK_MASK = 0x33;
/**
* 0-length spans with type SPAN_MARK_MARK behave like text marks:
* they remain at their original offset when text is inserted
* at that offset. Conceptually, the text is added after the mark.
*/
public static final int SPAN_MARK_MARK = 0x11;
/**
* SPAN_MARK_POINT is a synonym for {@link #SPAN_INCLUSIVE_INCLUSIVE}.
*/
public static final int SPAN_MARK_POINT = 0x12;
/**
* SPAN_POINT_MARK is a synonym for {@link #SPAN_EXCLUSIVE_EXCLUSIVE}.
*/
public static final int SPAN_POINT_MARK = 0x21;
/**
* 0-length spans with type SPAN_POINT_POINT behave like cursors:
* they are pushed forward by the length of the insertion when text
* is inserted at their offset.
* The text is conceptually inserted before the point.
*/
public static final int SPAN_POINT_POINT = 0x22;
/**
* SPAN_PARAGRAPH behaves like SPAN_INCLUSIVE_EXCLUSIVE
* (SPAN_MARK_MARK), except that if either end of the span is
* at the end of the buffer, that end behaves like _POINT
* instead (so SPAN_INCLUSIVE_INCLUSIVE if it starts in the
* middle and ends at the end, or SPAN_EXCLUSIVE_INCLUSIVE
* if it both starts and ends at the end).
*
* Its endpoints must be the start or end of the buffer or
* immediately after a \n character, and if the \n
* that anchors it is deleted, the endpoint is pulled to the
* next \n that follows in the buffer (or to the end of
* the buffer). If a span with SPAN_PARAGRAPH flag is pasted
* into another text and the paragraph boundary constraint
* is not satisfied, the span is discarded.
*/
public static final int SPAN_PARAGRAPH = 0x33;
/**
* Non-0-length spans of type SPAN_INCLUSIVE_EXCLUSIVE expand
* to include text inserted at their starting point but not at their
* ending point. When 0-length, they behave like marks.
*/
public static final int SPAN_INCLUSIVE_EXCLUSIVE = SPAN_MARK_MARK;
/**
* Spans of type SPAN_INCLUSIVE_INCLUSIVE expand
* to include text inserted at either their starting or ending point.
*/
public static final int SPAN_INCLUSIVE_INCLUSIVE = SPAN_MARK_POINT;
/**
* Spans of type SPAN_EXCLUSIVE_EXCLUSIVE do not expand
* to include text inserted at either their starting or ending point.
* They can never have a length of 0 and are automatically removed
* from the buffer if all the text they cover is removed.
*/
public static final int SPAN_EXCLUSIVE_EXCLUSIVE = SPAN_POINT_MARK;
/**
* Non-0-length spans of type SPAN_EXCLUSIVE_INCLUSIVE expand
* to include text inserted at their ending point but not at their
* starting point. When 0-length, they behave like points.
*/
public static final int SPAN_EXCLUSIVE_INCLUSIVE = SPAN_POINT_POINT;
/**
* This flag is set on spans that are being used to apply temporary
* styling information on the composing text of an input method, so that
* they can be found and removed when the composing text is being
* replaced.
*/
public static final int SPAN_COMPOSING = 0x100;
/**
* This flag will be set for intermediate span changes, meaning there
* is guaranteed to be another change following it. Typically it is
* used for {@link Selection} which automatically uses this with the first
* offset it sets when updating the selection.
*/
public static final int SPAN_INTERMEDIATE = 0x200;
/**
* The bits numbered SPAN_USER_SHIFT and above are available
* for callers to use to store scalar data associated with their
* span object.
*/
public static final int SPAN_USER_SHIFT = 24;
/**
* The bits specified by the SPAN_USER bitfield are available
* for callers to use to store scalar data associated with their
* span object.
*/
public static final int SPAN_USER = 0xFFFFFFFF << SPAN_USER_SHIFT;
/**
* The bits numbered just above SPAN_PRIORITY_SHIFT determine the order
* of change notifications -- higher numbers go first. You probably
* don't need to set this; it is used so that when text changes, the
* text layout gets the chance to update itself before any other
* callbacks can inquire about the layout of the text.
*/
public static final int SPAN_PRIORITY_SHIFT = 16;
/**
* The bits specified by the SPAN_PRIORITY bitmap determine the order
* of change notifications -- higher numbers go first. You probably
* don't need to set this; it is used so that when text changes, the
* text layout gets the chance to update itself before any other
* callbacks can inquire about the layout of the text.
*/
public static final int SPAN_PRIORITY = 0xFF << SPAN_PRIORITY_SHIFT;
/**
* Return an array of the markup objects attached to the specified
* slice of this CharSequence and whose type is the specified type
* or a subclass of it. Specify Object.class for the type if you
* want all the objects regardless of type.
*/
public T[] getSpans(int start, int end, Class type);
/**
* Return the beginning of the range of text to which the specified
* markup object is attached, or -1 if the object is not attached.
*/
public int getSpanStart(Object tag);
/**
* Return the end of the range of text to which the specified
* markup object is attached, or -1 if the object is not attached.
*/
public int getSpanEnd(Object tag);
/**
* Return the flags that were specified when {@link Spannable#setSpan} was
* used to attach the specified markup object, or 0 if the specified
* object has not been attached.
*/
public int getSpanFlags(Object tag);
/**
* Return the first offset greater than start where a markup
* object of class type begins or ends, or limit
* if there are no starts or ends greater than start but less
* than limit. Specify null or Object.class for
* the type if you want every transition regardless of type.
*/
public int nextSpanTransition(int start, int limit, Class type);
}
xml布局设置 两个属性
一个文本颜色textcolor 是指你输入文本的颜色
一个是textcolorhint 隐藏表单域的颜色
<com.visoport.medicine.view.input.ClearEditText
android:id="@+id/et_pwd"
android:layout_width="260dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginLeft="50dp"
android:layout_marginTop="8dp"
android:clickable="true"
android:ellipsize="end"
android:background="@null"
android:focusable="true"
android:inputType="textPassword"
android:maxLength="16"
android:maxLines="1"
android:hint="请输入账号密码"
android:textColorHint="@color/white"
android:textColor="#ffffff"
android:textSize="18sp" />代码设置
package com.visoport.medicine.util;
import android.text.SpannableString;
import android.text.Spanned;
import android.text.SpannedString;
import android.text.style.AbsoluteSizeSpan;
import android.widget.EditText;
/**
* 去除EditTexthint文本与输入的输入不一致
*/
public class EditTextUtil {
public static void showHintTextColor(EditText phoneText,EditText pwdText)
{
// 添加属性的文本对象
SpannableString ss = new SpannableString("请输入手机号码");
// 属性对象,设置文字的大小
AbsoluteSizeSpan ass = new AbsoluteSizeSpan(18,true);
// 附加属性到文本
ss.setSpan(ass, 0, ss.length(), Spanned.SPAN_EXCLUSIVE_EXCLUSIVE);
// 设置hint
phoneText.setHint(new SpannedString(ss)); // 一定要进行转换,否则属性会消失
// 添加属性的文本对象
ss = new SpannableString("请输入密码");
// 属性对象,设置文字的大小
ass = new AbsoluteSizeSpan(18,true);
// 附加属性到文本
ss.setSpan(ass, 0, ss.length(), Spanned.SPAN_EXCLUSIVE_EXCLUSIVE);
// 设置hint
pwdText.setHint(new SpannedString(ss)); // 一定要进行转换,否则属性会消失
}
}
效果如下