C#支持控制台调用的窗体程序思路
C#支持控制台调用的窗体程序思路
首先,谁特么现在还用客户端小程序啊……/(ㄒoㄒ)/~~
【START】
这类程序有两种情况,如果在入口函数Main中没有传任何参数进来,那么就启动界面进行处理,如果传了参数并且验证无误,就启动控制台界面来处理。
为了形象地进行说明,这里就写一个小的虚构的项目。流程如下:
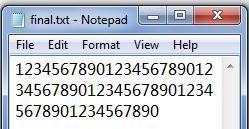
首先读取一个文件(源文件),然后复制其内容重复N次(N>=0),然后保存(目标文件)。
其中有这样几种情况:
1. N=0时,如果目标文件未指定,则清空源文件;否则创建空的目标文件。
2. N=1时,如果目标文件未指定,则不处理;否则复制源文件为目标文件。
3. N>1时,如果目标文件未指定,则更改源文件;否则更改目标文件。
创建每次转换所需参数的数据类:
public class ConvertInfo
{
public string InputFile { get; set; }
public string OutputFile { get; set; }
public uint Parameter { get; set; }
}添加实例化方法(包括验证),然后合并到唯一构造函数中:
//"input" 0 "output"
//"input" 2
private void tryParse(string[] args)
{
try
{
if (args.Length < 2)
{
throw new ArgumentException(
"more parameters should be specified.");
}
System.IO.FileInfo input = new System.IO.FileInfo(args[0]);
if (!input.Exists)
{
throw new ArgumentException(
"invalid input file.");
}
this.InputFile = input.FullName;
int param = -1;
int.TryParse(args[1], out param);
if (param < 0)
{
throw new ArgumentException(
"invalid parameter.");
}
this.Parameter = (uint)param;
if (args.Length > 2)
{
System.IO.FileInfo output = new System.IO.FileInfo(args[2]);
if (output.FullName != input.FullName)
{
this.OutputFile = output.FullName;
}
}
}
catch
{
throw;
}
}
public ConvertInfo(params string[] args)
{
if (args == null)
{ //should not fire.
throw new ArgumentNullException("args");
}
this.tryParse(args);
}再创建一个业务处理的类,添加处理数据类的方法:
public class Core
{
public static void Convert(ConvertInfo info)
{
try
{
if (info.Parameter == 0)
{
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(info.OutputFile))
{
System.IO.File.WriteAllBytes(info.InputFile, new byte[0]);
}
else
{
System.IO.File.Create(info.OutputFile);
}
}
else if (info.Parameter == 1)
{
if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(info.OutputFile))
{
System.IO.File.Copy(info.InputFile, info.OutputFile);
}
}
else
{
byte[] inputBuffer = System.IO.File.ReadAllBytes(info.InputFile);
if (inputBuffer.Length > 0)
{
int inputBufferLen = inputBuffer.Length;
byte[] outputBuffer = new byte[inputBufferLen * info.Parameter];
for (int i = 0; i < info.Parameter; i++)
{
inputBuffer.CopyTo(outputBuffer, inputBufferLen * i);
}
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(info.OutputFile))
{
System.IO.File.WriteAllBytes(info.InputFile, outputBuffer);
}
else
{
if (!System.IO.File.Exists(info.OutputFile))
{
System.IO.FileStream createStream =
System.IO.File.Create(info.OutputFile, outputBuffer.Length);
createStream.Close();
createStream.Dispose();
}
System.IO.File.WriteAllBytes(info.OutputFile, outputBuffer);
}
}
else
{
if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(info.OutputFile))
{
System.IO.File.Create(info.OutputFile);
}
}
}
}
catch
{
throw;
}
}
}再添加包含转换过程的数据类处理方法:
public static void Convert(string[] args)
{
try
{
ConvertInfo info = new ConvertInfo(args);
Convert(info);
}
catch
{
throw;
}
}由于强迫症的缘故,我把数据类放到业务处理类内部了……
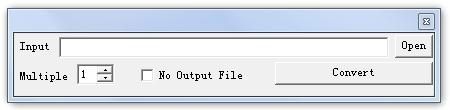
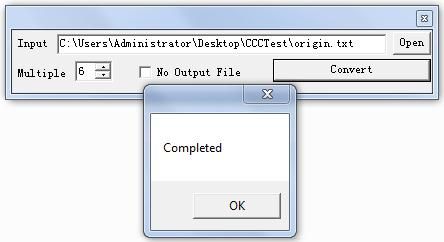
页面逻辑如下:
- 点击Open,设置源文件全路径,保存并显示在左边只读文本框里;
- 点击Convert,如果勾选了“No Output File”,表示将源文件做为目标文件,否则打开一个保存文件对话框,获取目标文件全路径,再加上Multipul中的重复次数值,组合成之前的那个数据类,最后调用数据处理方法进行处理,完成后提示。
对应于以上两点的方法代码如下:
//Open
private void button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
using (System.Windows.Forms.OpenFileDialog dialog
= new OpenFileDialog())
{
if (dialog.ShowDialog() ==
System.Windows.Forms.DialogResult.OK)
{
this.textBox1.Text = dialog.FileName;
}
}
}
//Convert
private void button2_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
string outputFile = null;
if (!this.checkBox1.Checked)
{
using (System.Windows.Forms.SaveFileDialog dialog
= new SaveFileDialog())
{
if (dialog.ShowDialog() ==
System.Windows.Forms.DialogResult.OK)
{
outputFile = dialog.FileName;
}
}
}
try
{
Core.ConvertInfo info = new Core.ConvertInfo(
this.textBox1.Text,
this.numericUpDown1.Value.ToString(),
outputFile);
Core.Convert(info);
MessageBox.Show("Completed");
}
catch
{
throw;
}
}然后是控制台端的处理方法。由于数据处理类中直接支持从字符串数组进行参数转换,所以直接调用对应的方法即可。
然后添加两个函数,分别为:
![]()
![]()
在Main函数中添加对应的流程控制:
static void Main(string[] args)
{
if (args != null && args.Length > 0)
{
runInConsole(args);
}
else
{
runInForm();
}
}接下来就只剩分别实现之前添加的两个空函数了。
对于UI流程,窗体控件必须在STA线程中创建,这里有两种选择:第一种是将Main函数改为STA的,这样对于控制台流程也没有影响,方便快捷;第二种就是再创建一个STA的新线程。我选择第二种(因为强迫症):
#region form
private static void runInForm()
{
try
{
System.Threading.Thread uiThread =
new System.Threading.Thread((System.Threading.ThreadStart)createForm);
uiThread.SetApartmentState(System.Threading.ApartmentState.STA);
uiThread.Start();
uiThread.Join();
}
catch
{
throw;
}
}
private static void createForm()
{
try
{
System.Windows.Forms.Application.Run(new AForm());
}
catch
{
throw;
}
}
#endregion form然而这里出现了点“意外”情况,程序进入UI流程后,控制台界面依旧存在。这时也有两种思路:第一种,调用WinAPI隐藏控制台窗体;第二种,将程序输出类型改为Windows应用程序。因为本人强迫症,对于这种还是会闪一下的控制台很不满,所以第一种方法不予考虑。那么只能选第二种,这么一来UI流程的问题就解决了,但是又遇到Console流程的问题,那就是控制台窗体怎么办。
对于这个问题,网上随便搜搜就一大堆(并不代表我这篇文章就是抄的,如果需要强行解释的话,那就是网上的文章大多复制粘贴源代码运行不了,一些关键细节的缺失导致想照着把程序做出来却发现不知道哪里少了……),这样一来目前遇到的问题就都解决了。
#region console
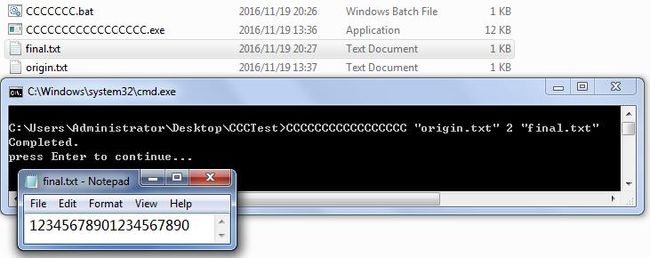
private static void runInConsole(string[] args)
{
try
{
attachOrCreateConsole();
try
{
Core.Convert(args);
Console.WriteLine("Completed.");
}
catch (Exception e)
{
Console.WriteLine(e);
}
finally
{
Console.WriteLine("press Enter to continue...");
Console.ReadLine();
}
FreeConsole();
}
catch
{
throw;
}
}
private static void attachOrCreateConsole()
{
try
{
IntPtr container = GetForegroundWindow();
int containerPID;
GetWindowThreadProcessId(container, out containerPID);
System.Diagnostics.Process process =
System.Diagnostics.Process.GetProcessById(containerPID);
if (process.ProcessName == "cmd") //opend from cmd
{
AttachConsole(process.Id);
}
else
{
AllocConsole(); //create new one
}
}
catch
{
throw;
}
}
#region console api
[System.Runtime.InteropServices.DllImport("kernel32.dll", SetLastError = true)]
static extern bool AllocConsole();
[System.Runtime.InteropServices.DllImport("kernel32.dll", SetLastError = true)]
static extern bool FreeConsole();
[System.Runtime.InteropServices.DllImport("kernel32", SetLastError = true)]
static extern bool AttachConsole(int dwProcessId);
[System.Runtime.InteropServices.DllImport("user32.dll")]
static extern IntPtr GetForegroundWindow();
[System.Runtime.InteropServices.DllImport("user32.dll", SetLastError = true)]
static extern uint GetWindowThreadProcessId(IntPtr hWnd, out int lpdwProcessId);
#endregion console api
#endregion console业务处理部分未处理的隐藏bug很多,但因为并不是本文关注的焦点,就不细化了。
整体来说,虽然谈不上是很好的方法,但是如果有这样的需求我这个新手首先就会想到用这种方法,虽然怎么可能会有这种奇葩需求吧……
【THE END】
源代码下载