LeakCanary原理分析
LeakCanary
class Helper {
}
class Utils {
public static Helper helper = new Helper();
}
static Helper helper = new Helper
class ExampleApplication : Application() {
val leakedViews = mutableListOf
}
class MainActivity : Activity() {
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
setContentView(R.layout.main_activity)
val textView = findViewById
val app = application as ExampleApplication
// This creates a leak, What a Terrible Failure!
app.leakedViews.add(textView)
}
}
ExampleApplication :Application
app.leakedViews.add(textView);
AppWatcher.Config config = AppWatcher.getConfig().newBuilder()
.watchFragmentViews(false)
.build();
AppWatcher.setConfig(config);
LeakCanary.Config config = LeakCanary.getConfig().newBuilder()
.retainedVisibleThreshold(3)
.build();
LeakCanary.setConfig(config);
.watchFragmentViews .retainedVisibleThreshold .build
class DebugExampleApplication : ExampleApplication() {
override fun onCreate() {
super.onCreate()
LeakCanary.config = LeakCanary.config.copy(onHeapAnalyzedListener = LeakUploader())
}
}
LeakCanary.config = LeakCanary.config.copy onHeapAnalyzedListener = LeakUploader
https://square.github.io/leakcanary/recipes/
class MyService : Service {
// ...
override fun onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy()
AppWatcher.objectWatcher.watch(
watchedObject = this,
description = "MyService received Service#onDestroy() callback"
)
}
}
AppWatcher.objectWatcher.watch (
watchob = this;
description = "";
);
./gradlew leakcanary-android-sample:connectedCheck
./gradlew leakcanary-android-sample:connectedCheck
class DebugExampleApplication : ExampleApplication() {
override fun onCreate() {
super.onCreate()
LeakCanary.config = LeakCanary.config.copy(
referenceMatchers = AndroidReferenceMatchers.appDefaults +
AndroidReferenceMatchers.staticFieldLeak(
className = "com.samsing.SomeSingleton",
fieldName = "sContext",
description = "SomeSingleton has a static field leaking a context.",
patternApplies = {
manufacturer == "Samsing" && sdkInt == 26
}
)
)
}
}
DebugExampleApplication ExampleApplication
LeakCanary referenceMatchers = AndroidReferenceMatchers staticFieldLeak )
patternApplies
class DebugExampleApplication : ExampleApplication() {
companion object {
@JvmStatic
lateinit var savedVersionName: String
}
override fun onCreate() {
super.onCreate()
val packageInfo = packageManager.getPackageInfo(packageName, 0)
savedVersionName = packageInfo.versionName
LeakCanary.config = LeakCanary.config.copy(
metadataExtractor = MetadataExtractor { graph ->
val companionClass =
graph.findClassByName("com.example.DebugExampleApplication")!!
val versionNameField = companionClass["savedVersionName"]!!
val versionName = versionNameField.valueAsInstance!!.readAsJavaString()!!
val defaultMetadata = AndroidMetadataExtractor.extractMetadata(graph)
mapOf("App Version Name" to versionName) + defaultMetadata
})
}
}
LeakCanary原理解析
https://www.jianshu.com/p/261e70f3083f
refWatcher = LeakCanary.install(this)
DebuggerControl debuggerControl = this.debuggerControl;
if (debuggerControl == null) {
debuggerControl = defaultDebuggerControl();
}
HeapDumper heapDumper = this.heapDumper;
if (heapDumper == null) {
heapDumper = defaultHeapDumper();
}
WatchExecutor watchExecutor = this.watchExecutor;
if (watchExecutor == null) {
watchExecutor = defaultWatchExecutor();
}
GcTrigger gcTrigger = this.gcTrigger;
if (gcTrigger == null) {
gcTrigger = defaultGcTrigger();
}
String mainProcess = packageInfo.applicationInfo.processName;
public RefWatcher buildAndInstall() {
if (LeakCanaryInternals.installedRefWatcher != null) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("buildAndInstall() should only be called once.");
}
RefWatcher refWatcher = build();
if (refWatcher != DISABLED) {
if (watchActivities) {
ActivityRefWatcher.install(context, refWatcher);
}
if (watchFragments) {
FragmentRefWatcher.Helper.install(context, refWatcher);
}
}
LeakCanaryInternals.installedRefWatcher = refWatcher;
return refWatcher;
}
ReferenceQueue
WeakReference
csdn
LeakCanary实现内存泄漏的主要判断逻辑是这样的。当我们观察的Activity或者Fragment销毁时,我们会使用一个弱引用去包装当前销毁的Activity或者Fragment,并且将它与本地的一个ReferenceQueue队列关联。我们知道如果GC触发了,系统会将当前的引用对象存入队列中。
如果没有被回收,队列中则没有当前的引用对象。所以LeakCanary会去判断,ReferenceQueue是否有当前观察的Activity或者Fragment的引用对象,第一次判断如果不存在,就去手动触发一次GC,然后做第二次判断,如果还是不存在,则表明出现了内存泄漏。
public class WeakReference
public WeakReference(T referent) {
super(referent);
}
public WeakReference(T referent, ReferenceQueue q) {
super(referent, q);
}
}
RefWatcher refWatcher = build();
return new RefWatcher(watchExecutor, debuggerControl, gcTrigger, heapDumper, heapDumpListener,
heapDumpBuilder);
queue = new ReferenceQueue<>();
private final Application.ActivityLifecycleCallbacks lifecycleCallbacks =
new ActivityLifecycleCallbacksAdapter() {
@Override public void onActivityDestroyed(Activity activity) {
refWatcher.watch(activity);
}
};
public void watch(Object watchedReference) {
watch(watchedReference, "");
}
final KeyedWeakReference reference =
new KeyedWeakReference(watchedReference, key, referenceName, queue);
WeakReference RefWatcher
install install buildAndInstall
private final FragmentManager.FragmentLifecycleCallbacks fragmentLifecycleCallbacks =
new FragmentManager.FragmentLifecycleCallbacks() {
@Override
public void onFragmentDestroyed(FragmentManager fm, Fragment fragment) {
refWatcher.watch(fragment);
}
};
onFragmentDestroyed KeyedWeakReference
static void add(Reference list) {
synchronized (ReferenceQueue.class) {
if (unenqueued == null) {
unenqueued = list;
} else {
// Find the last element in unenqueued.
Reference last = unenqueued;
while (last.pendingNext != unenqueued) {
last = last.pendingNext;
}
// Add our list to the end. Update the pendingNext to point back to enqueued.
last.pendingNext = list;
last = list;
while (last.pendingNext != list) {
last = last.pendingNext;
}
last.pendingNext = unenqueued;
}
ReferenceQueue.class.notifyAll();
}
}
last.pendingNext = list
last = list
synchronized void enqueue(Reference reference) {
if (tail == null) {
head = reference;
} else {
tail.queueNext = reference;
}
// The newly enqueued reference becomes the new tail, and always
// points to itself.
tail = reference;
tail.queueNext = reference;
notify();
}
enqueue
tail.queueNext = reference
Reference
final class KeyedWeakReference extends WeakReference
KeyedWeakReference(Object referent, String key, String name,
ReferenceQueue
public WeakReference(T r, ReferenceQueue q) {
super(r, q);
}
WeakReference
install constructor = newinstance
application.registerActivityLifecycleCallbacks(helper.activityLifecycleCallbacks)
@Override public void execute(Retryable retryable) {
if (Looper.getMainLooper().getThread() == Thread.currentThread()) {
waitForIdle(retryable, 0);
} else {
postWaitForIdle(retryable, 0);
}
}
public final RefWatcher build() {
if (isDisabled()) {
return RefWatcher.DISABLED;
}
if (heapDumpBuilder.excludedRefs == null) {
heapDumpBuilder.excludedRefs(defaultExcludedRefs());
}
HeapDump.Listener heapDumpListener = this.heapDumpListener;
if (heapDumpListener == null) {
heapDumpListener = defaultHeapDumpListener();
}
DebuggerControl debuggerControl = this.debuggerControl;
if (debuggerControl == null) {
debuggerControl = defaultDebuggerControl();
}
HeapDumper heapDumper = this.heapDumper;
if (heapDumper == null) {
//调用的是AndroidRefWatcherBuilder中的方法。所以这里创建的是一个AndroidHeapDumper对象
heapDumper = defaultHeapDumper();
}
WatchExecutor watchExecutor = this.watchExecutor;
if (watchExecutor == null) {
//调用的是AndroidRefWatcherBuilder中的方法。所以这里创建的是一个AndroidWatchExecutor对象
watchExecutor = defaultWatchExecutor();
}
GcTrigger gcTrigger = this.gcTrigger;
if (gcTrigger == null) {
//创建的是GcTrigger DEFAULT这个对象
gcTrigger = defaultGcTrigger();
}
if (heapDumpBuilder.reachabilityInspectorClasses == null) {
heapDumpBuilder.reachabilityInspectorClasses(defaultReachabilityInspectorClasses());
}
return new RefWatcher(watchExecutor, debuggerControl, gcTrigger, heapDumper, heapDumpListener,
heapDumpBuilder);
}
HeapDump DebuggerControl WatchExecutor GcTrigger
RefWatcher
public void watch(Object watchedReference, String referenceName) {
retainKeys.add(key);
Support
// AndroidOFragmentRefWatcher
private final FragmentManager.FragmentLifecycleCallbacks fragmentLifecycleCallbacks =
new FragmentManager.FragmentLifecycleCallbacks() {
@Override public void onFragmentViewDestroyed(FragmentManager fm, Fragment fragment) {
View view = fragment.getView();
if (view != null) {
refWatcher.watch(view);
}
}
@Override
public void onFragmentDestroyed(FragmentManager fm, Fragment fragment) {
refWatcher.watch(fragment);
}
};
@Override public void watchFragments(Activity activity) {
FragmentManager fragmentManager = activity.getFragmentManager();
fragmentManager.registerFragmentLifecycleCallbacks(fragmentLifecycleCallbacks, true);
}
onFragmentViewDestroyed onFragmentDestroyed
RefWatcher WatchExecutor DebuggerControl GcTrigger
HeapDump retainKeys ReferenceQueue
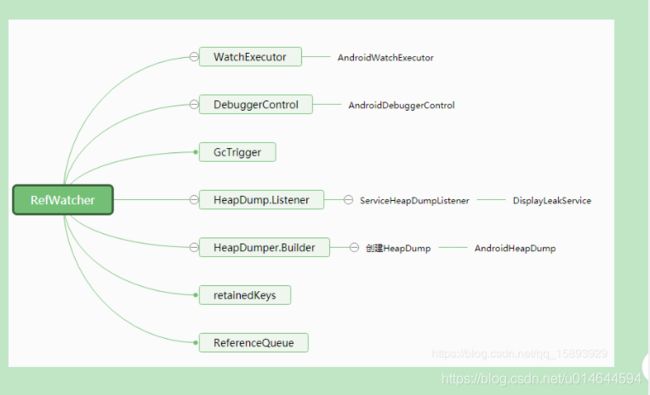
RefWatcher: 核心类,负责管理和提供入口watch(),由AndroidRefWatcherBuilder创建RefWatcher,建造者模式
WatchExecutor: 负责控制执行检测内存泄漏任务
DebuggerControl:判断是否处于debug
GcTrigger:负责触发一次GC
HeapDump:表示指定时刻的堆栈的快照,AndroidHeapDump为子类
HeapDump.Builder: 负责创建HeapDump
HeapDump.Listener:监听器,当发生内存泄漏的时候,会收到消息,需要触发分析AndroidHeapDump任务
ServiceHeapDumpListener:HeapDump.Listener的实现类,当触发分析任务,调用HeapAnalyzerService执行分析任务
HeapAnalyzerService:是一个Android中四大组件之一的Service,运行在独立的进程,负责执行分析任务和UI通知
HeapAnalyzer:在HeapAnalyzerService内部中,是对DumpHeap分析内存泄漏和找出引用链的工具
retainKeys: 是一个Set,保存着当前还没被回收的Reference的key
ReferenceQueue:引用队列,WeakReference可以关联引用队列,当reference被回收时,会被加入到ReferenceQueue,这样我们就可以判断哪些对象没有被回收了
DisplayLeakService:记录泄漏日志和展示通知的Service
其实,leakCanary的基本原理就是利用ReferenceQueue,在Activity销毁的时候判断对象有没有被加入ReferenceQueue,若没有则说明Activity还在存活,可能存在泄漏。
RefWatcher WatchExecutor DebuggerControl GcTrigger HeapDump
HeapDump.Builder HeapDump.Listener
ServiceHeapDumpListener:HeapDump
HeapAnalyzerService:是一个Android中四大组件之一的Service,运行在独立的进程,负责执行分析任务和UI通知
retainKeys ReferenceQueue DisplayLeakService:记录泄漏日志和展示通知的Service
AndroidHeapDumper为子类
AndroidDebuggerControl
ActivityRefWatcher.install
FragmentRefWatcher.install
removeWeakly
// RefWatcher
Retryable.Result ensureGone(final KeyedWeakReference reference, final long watchStartNanoTime) {
long gcStartNanoTime = System.nanoTime();
long watchDurationMs = NANOSECONDS.toMillis(gcStartNanoTime - watchStartNanoTime);
// 1. 从retainedKeys移除掉已经被会回收的弱引用的key
removeWeaklyReachableReferences();
// 2. 如果是debug模式,会继续重试
if (debuggerControl.isDebuggerAttached()) {
// The debugger can create false leaks.
return RETRY;
}
// 3. 若当前引用不在retainedKeys,说明不存在内存泄漏
if (gone(reference)) {
return DONE;
}
// 4. 触发一次gc
gcTrigger.runGc();
// 5.再次从retainedKeys移除掉已经被会回收的弱引用的key
removeWeaklyReachableReferences();
if (!gone(reference)) {
// 存在内存泄漏
long startDumpHeap = System.nanoTime();
long gcDurationMs = NANOSECONDS.toMillis(startDumpHeap - gcStartNanoTime);
// 6. 创建heapDump文件,还没写入
File heapDumpFile = heapDumper.dumpHeap();
if (heapDumpFile == RETRY_LATER) {
// Could not dump the heap.
return RETRY;
}
long heapDumpDurationMs = NANOSECONDS.toMillis(System.nanoTime() - startDumpHeap);
// 7. 创建heapDump
HeapDump heapDump = heapDumpBuilder.heapDumpFile(heapDumpFile).referenceKey(reference.key)
.referenceName(reference.name)
.watchDurationMs(watchDurationMs)
.gcDurationMs(gcDurationMs)
.heapDumpDurationMs(heapDumpDurationMs)
.build();
// 8.调用heapdumpListener分析
heapdumpListener.analyze(heapDump);
}
return DONE;
}
private boolean gone(KeyedWeakReference reference) {
return !retainedKeys.contains(reference.key);
}
private void removeWeaklyReachableReferences() {
KeyedWeakReference ref;
while ((ref = (KeyedWeakReference) queue.poll()) != null) {
retainedKeys.remove(ref.key);
}
}
removeWeaklyReachableReferences gone
gcTrigger.runGc
// RefWatcher
Retryable.Result ensureGone(final KeyedWeakReference reference, final long watchStartNanoTime) {
long gcStartNanoTime = System.nanoTime();
long watchDurationMs = NANOSECONDS.toMillis(gcStartNanoTime - watchStartNanoTime);
// 1. 从retainedKeys移除掉已经被会回收的弱引用的key
removeWeaklyReachableReferences();
// 2. 如果是debug模式,会继续重试
if (debuggerControl.isDebuggerAttached()) {
// The debugger can create false leaks.
return RETRY;
}
// 3. 若当前引用不在retainedKeys,说明不存在内存泄漏
if (gone(reference)) {
return DONE;
}
// 4. 触发一次gc
gcTrigger.runGc();
// 5.再次从retainedKeys移除掉已经被会回收的弱引用的key
removeWeaklyReachableReferences();
if (!gone(reference)) {
// 存在内存泄漏
long startDumpHeap = System.nanoTime();
long gcDurationMs = NANOSECONDS.toMillis(startDumpHeap - gcStartNanoTime);
// 6. 创建heapDump文件,还没写入
File heapDumpFile = heapDumper.dumpHeap();
if (heapDumpFile == RETRY_LATER) {
// Could not dump the heap.
return RETRY;
}
long heapDumpDurationMs = NANOSECONDS.toMillis(System.nanoTime() - startDumpHeap);
// 7. 创建heapDump
HeapDump heapDump = heapDumpBuilder.heapDumpFile(heapDumpFile).referenceKey(reference.key)
.referenceName(reference.name)
.watchDurationMs(watchDurationMs)
.gcDurationMs(gcDurationMs)
.heapDumpDurationMs(heapDumpDurationMs)
.build();
// 8.调用heapdumpListener分析
heapdumpListener.analyze(heapDump);
}
return DONE;
}
private boolean gone(KeyedWeakReference reference) {
return !retainedKeys.contains(reference.key);
}
gcTrigger之后 KeyedWeakReference(弱引用)消失,ref还在
private void removeWeaklyReachableReferences() {
KeyedWeakReference ref;
while ((ref = (KeyedWeakReference) queue.poll()) != null) {
retainedKeys.remove(ref.key);
}
}