ansible剧本的编写 和 playbook配置web--nfs--rsync架构环境
简述
学会写playbook剧本,使用ansible-playbook执行可以实现的就是自动化运维,playbook由一个或多个模块组成,完成统一的目的,实现自动化操作,
剧本编写遵循yaml语法
配置文件的概述
playbook配置文件使用YAML语法,具有简洁 明了,结构清晰等特点,playbook配置文件类似于shell脚本,是一个YAML格式的文件,用于保存对特定的需求的人物列表。YAML的文件扩展名通常是.yaml或.yml
yaml的三要素
缩进:两个字符,默认的tab键是四个字符,所以要使用tab键,需要修改.vimrc
vim /root/.vimrc
添加:
set tabstop=2
保存退出
冒号:冒号后面需要
空格: 除非以冒号结尾
短横杠: 列表项,后面跟空格
playbook的核心元素
hosts:任务的目标主机,多个主机用冒号分隔,一般/etc/ansible/hosts分组信息
remote_user:远程主机 上,运行此任务的身份默认为root
tasks:任务,自定义的具体任务
handlers:触发器,可通过“notify”通知给相应的handlers进行触发执行
roles:角色,由tasks,handlers等所一组特定的集合
templates:存放模板文件的目录
vars:存放变量的目录
files:存放由copy或script等模块调用的文件
对于playbook怎末学,都看多练就是好方法,就跟shell脚本类似,灵活掌握好他能使用的模块。
下面以安装httpd为例介绍:
---
- hosts: web #针对web群组的操作
tasks: #任务列表
- name: install httpd #任务名称
yum: name=httpd state=latest #任务:yum安装最新httpd
- name: httpd config
copy: src=/etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf #任务:复制配置文件,其中端口改成了8080 dest=/etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
notify: restart httpd #设置触发条件,即完成该剧本任务后,调用"restart httpd "的触发器
- name: start httpd
service: name=httpd state=started #保证能开启服务
handlers: #触发器
- name: restart httpd
service: name=httpd state=restarted
测试剧本,不会发生改变:
ansible-playbook -C 绝对路径 httpd.yaml
执行剧本:
ansible-playbook 绝对路径 httpd.yaml
[root@localhost roles]# ansible-playbook ./httpd.yaml
PLAY [web] ***********************************************************************
TASK [Gathering Facts] ***********************************************************
ok: [node1]
TASK [install httpd] *************************************************************
ok: [node1]
TASK [httpd config] **************************************************************
changed: [node1]
TASK [start httpd] ***************************************************************
changed: [node1]
RUNNING HANDLER [restart httpd] **************************************************
changed: [node1]
PLAY RECAP ***********************************************************************
node1 : ok=5 changed=3 unreachable=0 failed=0 skirescued=0 ignored=0
部署nginx例子:
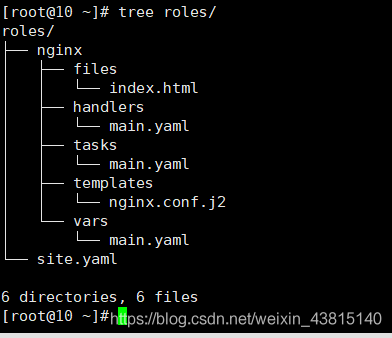
分开里面的核心组件进行编写playbook,更通俗易懂每个组件是干嘛的;将多种不同的tasks的文件集中存储在某个目录下,这个目录就是角色,角色存放在/etc/ansible/roles目录,roles可以有很多子目录,每个子目录对应一个角色,每个角色有自己的目录结构。
在roles目录下建立nginx目录和自己的目录结构,如下图:
编写主剧本tasks/main.yaml
---
- name: install nginx packge
yum: name={{ item }} state=latest #定义一个item的变量,yum要安装的东西
with_items:
- epel-release
- nginx
- name: copy index.html
copy: src=index.html dest=/usr/share/nginx/html/
- name: copy nginx.conf tempalte
template: src=nginx.conf.j2 dest=/etc/nginx/nginx.conf #调用nginx.conf.j2这个模板
notify: restart nginx #任务执行完成后开始执行restart nginx的触发器
- name: make sure nginx service running
service: name=nginx state=started enabled=yes
准备模板文件
[root@localhost roles]# cp /etc/nginx/nginx.conf /etc/ansible/roles/nginx/templates/
[root@localhost roles]#
[root@localhost roles]# cd nginx/templates/
[root@localhost templates]# ls
nginx.conf
[root@localhost templates]# mv nginx.conf nginx.conf.j2
在模板文件添加设置变量
worker_processes {{ansible_processor_cores}}; 为系统变量,值取决于你的设备
worker_connections {{worker_connections}}; 自定义变量
自定义变量需要修改/var/main.yaml文件

编辑触发器文件

最后site.yaml就像是开关一样,只要编辑完后执行,nginx就会安装上来;
hosts:定义目标主机
roles:就是定义的nginx角色
以后可能会有装有很多角色,一部分装nginx,一部分装 nfs ,一部分装mysql等等,都分别建好目录,方便区分和管理

ansible-playbook执行剧本

例:playbook配置web–nfs–rsync架构环境
搭建rsync服务器,使其web客户端在发生变化时能快速的备份到rsync服务器,nfs服务器负责同步数据到各个web节点,保证数据的一致性
web节点搭建参考第一个例子
nfs搭建
nfs详细学习参考博文:
https://editor.csdn.net/md/?articleId=105769837
编写playbook剧本

nfs服务器搭建非常简单,用不到很多组件和参数,只需把一份样例文件copy过去就好
---
- name: install nfs-utils rpcbind
yum: name={{ item }} state=installed
with_items:
- rpcbind
- nfs-utils
- name: copy exports
copy: src=exports dest=/etc/exports
- name: create share_directory
file: path=/nfs state=directory recurse=yes owner=root group=root mode=755
- name: start rpcbind
service: name=rpcbind state=restarted
- name: start nfs
service: name=nfs state=restarted
在files目录放置需要copy或script文件会直接调用或者使用绝对路径指定位置

因为Centos7的图形化界面会默认自带rpcbind,不需要手动下载了,
其他的web节点可以直接挂载使用,若是最小化安装,需要安装rpcbind才能访问
最小化安装的也可以使用ansible批量安装一下:
ansible web -m shell -a 'yum -y install rpcbind nfs-utils'
开启rpcbind,nfs服务:
ansible web -m shell -a 'systemctl start rpcbind nfs'
ansible web -m shell -a 'mount 192.168.10.7:/nfs /var/www/html'
搭建rsync+inotify实时同步备份
详细了解参考:
https://editor.csdn.net/md/?articleId=105788030
使用ansible搭建多台rsync备份服务器,在web端安装上inotify工具,会根据自己的变动向rsync服务器发送同步,结合nfs在web端的作用,实现全网备份数据。
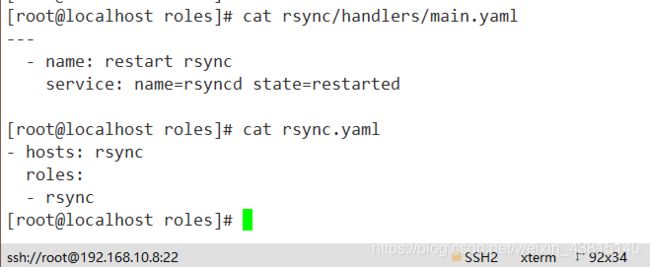
rsync剧本结构:
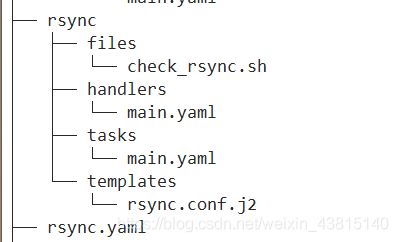
check_rsync.sh脚本是web客户端要使用的实时监测脚本
rsync剧本参考如下:
[root@localhost roles]# cat rsync/tasks/main.yaml
---
- name: install rsync
yum: name=rsync state=installed
- name: config rsync.conf
template: src=rsync.conf.j2 dest=/etc/rsync.conf
notify: restart rsync
- name: create rsync_directory
file: path=/rsync state=directory
- name: start rsync
service: name=rsyncd state=started enabled=yes
模板文件如下:
[root@localhost roles]# cat rsync/templates/rsync.conf.j2
uid = nobody
gid = nobody
port 873
address = 192.168.10.4
hosts allow = 192.168.10.0/24
max connections = 4
pid file = /var/run/rsyncd.pid
timeout = 900
dont compress = *.gz *.tgz *.zip *.z *.Z *.rpm *.deb *.bz2
[rsync]
path = /rsync
read only = yes
配置web端
编写实时同步剧本
---
- hosts: web
tasks:
- name: install inotify-tools
yum: name=inotify-tools state=installed
- name: copy script
copy: src=/root/check_rsync.sh dest=/root/
- name: chmod
shell: chmod +x /root/check_rsync.sh
- name: run script
shell: sh /root/check_rsync.sh & #放到后台运行
把在/rsync里面的脚本拷贝到/root目录下
脚本内容为
#!/bin/bash
#2020年4月27日15:28:39
#Slave to master script
inotifywait -mrq -e create,delete,modify,move /var/www/html/ | while read a b c #将检测到的结果赋值给变量aaa,当成功后开始循环do...done内容
do
rsync -avz --delete /var/www/html [email protected]:/rsync
done
执行剧本
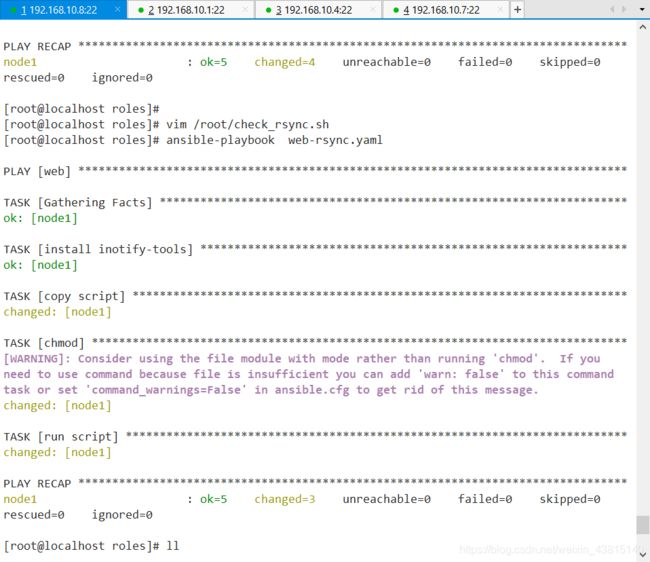
此时,我们在web节点上的网页根目录/var/www/html下创建删除文件,观察rsync服务器的/rsync目录和nfs服务器/nfs目录