CoordinatorLayout+AppBarLayout+CollapsingToolbarLayout讲解
1,CoordinatorLayout协调布局
作用
根据一个layout(Dependency View)的操作来让另一个layout(child View)自动执行相关的操作,该child View具体执行什么相关操作取决于app:layout_behavior属性所指定的behavior类如何编写。
根据概念可以看出,协调布局的使用包含三个部分:
1.Dependency View
2.child View
3.behavior类
注意:被协调的2个view必须是CoordinatorLayout的直接子view。
使用案例
效果如下图:
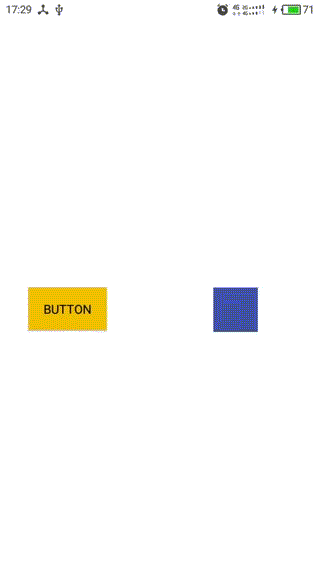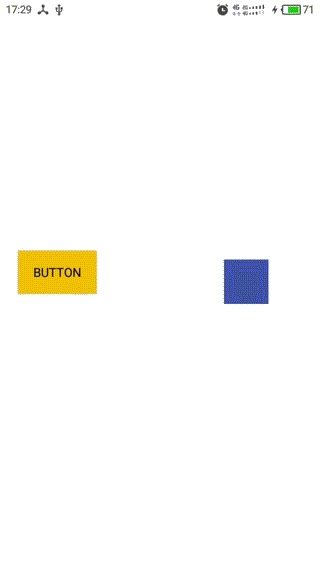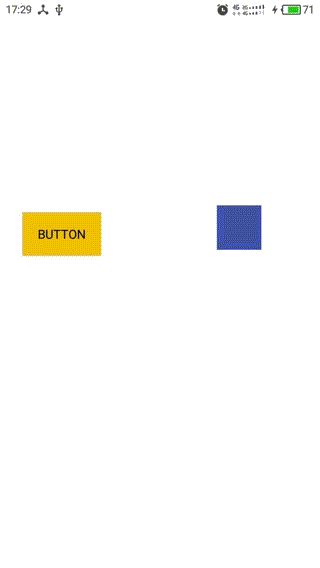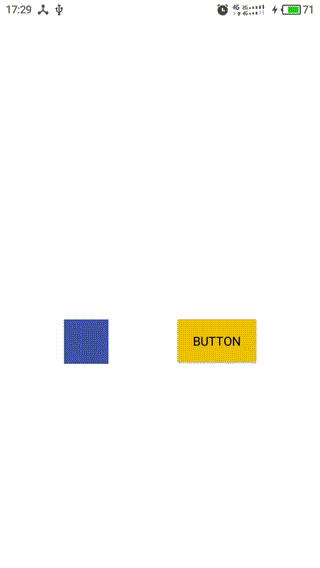
1,蓝色的是一个自定义View,可跟随手指移动,作为Dependency View
2,黄色的是一个Button,作为child View
3,Behavior中定义的child view的依赖规则:Button随着View的移动在竖直方向同步移动,在水平方向相反。
布局文件很简单,根布局使用CoordinatorLayout,如下所示:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<android.support.design.widget.CoordinatorLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="@color/colorPrimary"
app:layout_behavior="cn.xuexuan.newui.CoordinatorBehavior"/>
<cn.xuexuan.newui.MoveView
android:layout_width="50dp"
android:layout_height="50dp"
android:background="@color/colorAccent"
/>
</android.support.design.widget.CoordinatorLayout>
重点就是这个自定义Behavior的实现,要实现自定义的behavior类,我们需要继承CoordinatorLayout.Behavior < T>,其中泛型参数T是我们要执行动作的View类,也就是Child,注意必须加入一个MyBehavior的构造器,带有Context和AttributeSet参数,然后就是去实现Behavior的两个方法,该自定义Behavior的代码如下:
public class MyBehavior extends CoordinatorLayout.Behavior<Button> {
private int width;
public MyBehavior(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
DisplayMetrics display = context.getResources().getDisplayMetrics();
width = display.widthPixels;
}
/**
* 判断child的布局是否依赖dependency
* 根据逻辑判断rs的取值,返回false表示child不依赖dependency,ture表示依赖
*/
@Override
public boolean layoutDependsOn(CoordinatorLayout parent, Button child, View dependency) {
//如果dependency是TempView的实例,说明它就是我们所需要的Dependency
return dependency instanceof TempView;
}
/**
* 每次dependency位置发生变化,都会执行onDependentViewChanged方法
* 返回true表示child的位置或者是宽高也要发生改变,否则就返回false
*/
@Override
public boolean onDependentViewChanged(CoordinatorLayout parent, Button btn, View dependency) {
//根据dependency的位置,设置Button的位置
int top = dependency.getTop();
int left = dependency.getLeft();
int x = width - left - btn.getWidth();
int y = top;
setPosition(btn, x, y);
return true;
}
private void setPosition(View v, int x, int y) {
CoordinatorLayout.MarginLayoutParams layoutParams = (CoordinatorLayout.MarginLayoutParams) v.getLayoutParams();
layoutParams.leftMargin = x;
layoutParams.topMargin = y;
v.setLayoutParams(layoutParams);
}
}
OK,现在我们定义好了跟随Dependency一直变化的动作(Behavior),接下来我们就要指定哪个View来执行这些操作。方法很简单,直接在布局文件中通过app:layout_behavior属性指定就好了。
2,AppbarLayout
AppBarLayout 是继承LinerLayout实现的一个ViewGroup容器组件,它是为了Material Design设计的AppBar,支持手势滑动操作。默认的AppBarLayout是垂直方向的,它里面可以包含多个子View,它的作用是把AppBarLayout包裹的所有内容都作为AppBar来显示。
他的最主要特点是滑动,AppbarLayout要实现酷炫的滑动效果必须依赖于CoordinatorLayout使用,作为CoordinatorLayout的直接子view,如果父view是其他的viewGroup那么是没有效果的。
它可以让你定制,当指定的某个可滚动的View发生滚动时,AppBarLayout内部的某个子View实现何种动作。
这里说的某个可滚动的View就是NestedScrollView或者实现了NestedScrollView机制的其它控件, 如RecyclerView,使用ListView或者ScrollView是没有效果的,它有一个布局行为Layout_Behavior:
app:layout_behavior="@string/appbar_scrolling_view_behavior"
这个behavior是系统AppBarLayout帮我们定义好了的,我们直接拿来用即可。
而AppbarLayout中指定的子View要实现何种动作,是通过在布局中加app:layout_scrollFlags属性来指定的,layout_scrollFlags有如下5种选项:
1,scroll: 所有想滚动出屏幕的view都需要设置这个flag- 没有设置这个flag的view将被固定在屏幕顶部。
2,enterAlways: 这个flag让任意向下的滚动都会导致该view变为可见,启用快速“返回模式”。
3,enterAlwaysCollapsed: 当你的视图已经设置minHeight属性又使用此标志时,你的视图只能以最小高度进入,只有当滚动视图到达顶部时才扩大到完整高度。
4,exitUntilCollapsed: 当视图会在滚动时,它一直滚动到设置的minHeight时完全隐藏。
5,snap:在滚动结束后,如果view只是部分可见,它将滑动到最近的边界。比如,如果view的底部只有25%可见,它将滚动离开屏幕,而如果底部有75%可见,它将滚动到完全显示,类似于我们侧拉菜单的一个回弹效果,这个效果是可以和其他几个效果一起使用的。
3和4两种模式基本只有在CollapsingToolbarLayout才有用,关于CollapsingToolbarLayout的使用下一节我们会将,而前面两种模式是需要一起使用的。
综上所述,我们如果要实现AppbarLayout的滑动效果,必须满足如下条件:
1,结合协调布局一起使用,并作为协调布局的直接子View。
2,下方必须有可支持滚动的View,这里说的可滚动View指的是NestedScrollView或者实现了NestedScrollView机制的其它控件, 如RecyclerView,ViewPager等,scrollview和ListView不可以,并且为该可滚动View添加app:layout_behavior="@string/appbar_scrolling_view_behavior" 属性。
3,为AppbarLayout的某个需要滚动的子View设置app:layout_scrollFlags属性,并设置不同的属性值来指定需要响应的动作。
下面我们来看一个布局文件的例子:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<android.support.design.widget.CoordinatorLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
android:id="@+id/id_coordinatorlayout"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:fitsSystemWindows="true">
<android.support.design.widget.AppBarLayout
android:id="@+id/id_appbarlayout"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content">
<!--
属性解析:
app:theme:指定Toolbar的样式,包括ActionbarToggle和popupMenu的指示图标颜色
app:popupTheme:指定popupMenu溢出后的样式
app:title: 指定Toolbar中主Title的内容
-->
<android.support.v7.widget.Toolbar
android:id="@+id/id_toolbar"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="?attr/actionBarSize"
android:background="?attr/colorPrimary"
app:layout_scrollFlags="scroll|enterAlways"
app:popupTheme="@style/ThemeOverlay.AppCompat.Light"
app:theme="@style/ThemeOverlay.AppCompat.ActionBar"
app:title="@string/toolbar_title" />
<android.support.design.widget.TabLayout
android:id="@+id/id_tablayout"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
app:tabGravity="fill"
app:tabIndicatorColor="@color/main_white" />
</android.support.design.widget.AppBarLayout>
<!--
我们常用的ViewPager,不多说了。你会发现多了一个 app:layout_behavior 属性,没错,
如果你使用CoordinatorLayout来实现Toolbar滚动渐变消失动画效果,那就必须在它下面的那个控件中加入这个属性,
并且下面的这个控件必须是可滚动的。
当设置了layout_behavior的控件滑动时,就会触发设置了layout_scrollFlags的控件发生状态的改变。
-->
<android.support.v4.view.ViewPager
android:id="@+id/id_viewpager"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
app:layout_behavior="@string/appbar_scrolling_view_behavior" />
</android.support.design.widget.CoordinatorLayout>
上面的布局文件中,AppBarLayout中包含了两个子View:ToolBar和TabLayout,而我们只是设置了ToolBar可以滚动,这样在界面向上滚动时,ToolBar会隐藏,此时TabLayout会占据原本Toolbar的位置。
注意两种取值的区别:
1,scroll|enterAlways:当界面向上滚动时,AppBarLayout先滚动到ToolBar完全隐藏,然后滚动视图才开始向上滚动,界面向下滚动时也是一样,AppBarLayout先滚动到ToolBar完全显示,然后滚动视图才开始向下滚动。
2,scroll:去掉enterAlways会发现,当界面向上滚动时还是AppBarLayout先滚动到ToolBar完全隐藏,然后滚动视图才开始向上滚动,但是此时当界面向下滚动时,就不是AppBarLayout先滚动了,而是滚动视图先向下滚动到顶部,然后AppBarLayout才开始向下滚动直到ToolBar完全显示出来。
注意:enterAlways依赖于scroll,所以enterAlways必须与scroll搭配使用,单独使用是没有效果的。
以上两种取值不管是scroll|enterAlways还是scroll,都存在这种情况,就是当我们停止滚动时,ToolBar很可能只是部分可见,即一半显示一半隐藏的状态,为了避免这个问题我们可以结合snap一起使用,上面也说了snap会有一个回弹效果,根据我们滚动停在的ToolBar的位置来选择使ToolBar完全显示或者全完隐藏,即同时设置:scroll|enterAlways|snap或者scroll|snap。
案例:CoordinatorLayout+AppBarLayout实现TabLayout顶部悬浮效果
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<android.support.design.widget.CoordinatorLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:id="@+id/activity_toolbar"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
tools:context="com.gpf.mvp.ui.activity.ToolbarActivity">
<android.support.design.widget.AppBarLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content">
<LinearLayout
app:layout_scrollFlags="scroll|enterAlways|snap"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="vertical">
<ImageView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="140dp"
android:background="@mipmap/ic_launcher"/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="我是图片描述"/>
</LinearLayout>
<android.support.design.widget.TabLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content">
</android.support.design.widget.TabLayout>
</android.support.design.widget.AppBarLayout>
<android.support.v4.view.ViewPager
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
app:layout_behavior="@string/appbar_scrolling_view_behavior">
</android.support.v4.view.ViewPager>
</android.support.design.widget.CoordinatorLayout>
3,CollapsingToolbarLayout
CollapsingToolbarLayout是用来实现一个可以折叠的Toolbar,它继承自FrameLayout,可以让toolbar拉伸打开时显示的内容多样化,设置例如imageview,textview,button之类的使内容更丰富,作为AppbarLayout的直接子View使用。
1,通常作为AppBarLayout子View使用,所以可以给它设置layout_scrollFlags。
2,在CollapsingToolbarLayout的子View中可以设置以下属性:
layout_collapseMode (折叠模式) - 有两个值:
pin - 设置为这个模式时,当CollapsingToolbarLayout完全收缩后,Toolbar还可以保留在屏幕上。
parallax - 设置为这个模式时,在内容滚动时,CollapsingToolbarLayout中的View(比如ImageView)也可以同时滚动,实现视差滚动效果,和layout_collapseParallaxMultiplier搭配使用。
layout_collapseParallaxMultiplier(视差因子) - 设置视差滚动因子,值为:0~1。
之前在讲AppBarLayout的子View的layout_scrollFlags属性的时候,说道其中两个属性是配合CollapsingToolbarLayout来使用的,他们分别是:
enterAlwaysCollapsed: 当你的视图已经设置minHeight属性又使用此标志时,你的视图只能以最小高度进入,只有当滚动视图到达顶部时才扩大到完整高度。
exitUntilCollapsed: 当视图会在滚动时,它一直滚动到设置的minHeight时完全隐藏。
scroll|exitUntilCollapsed(必须一起使用):当界面在向上滚动时,AppBarLayout的子View先向上滚动直到最小高度,此时滚动视图才开始向上滚动,当界面向下滚动时,滚动视图先向下滚动到顶部,然后AppBarLayout的子View才开始从最小高度向下滚动直到完全显示。
scroll|enterAlways|enterAlwaysCollapsed(必须一起使用):界面在向上滚动时,AppBarLayout的子View先向上滚动直到完全隐藏,然后滚动视图才开始向上滚动,此时,界面向下滚动,AppBarLayout的子View先向下滚动到显示出最小高度,然后滚动视图开始向下滚动,当滚动视图向下滚动到顶部时,此时AppBarLayout的子View再继续向下滚动直到达到最大高度完全显示为止。
toolbar的默认最小高度minHeight就是"?attr/actionBarSize" , 很多时候我们可以不用设置。
我们来看以下布局:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<android.support.design.widget.CoordinatorLayout
...>
<android.support.design.widget.AppBarLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="150dp">
<android.support.design.widget.CollapsingToolbarLayout
android:id="@+id/collapsing_toolbar_layout"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:theme="@style/ThemeOverlay.AppCompat.Dark.ActionBar"
app:layout_scrollFlags="scroll|exitUntilCollapsed">
<android.support.v7.widget.Toolbar
android:id="@+id/toolbar"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="?attr/actionBarSize"
android:background="?attr/colorPrimary"
app:layout_collapseMode="parallax"
app:popupTheme="@style/ThemeOverlay.AppCompat.Light"
app:title="Title" />
</android.support.design.widget.CollapsingToolbarLayout>
</android.support.design.widget.AppBarLayout>
<android.support.v4.widget.NestedScrollView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
app:layout_behavior="@string/appbar_scrolling_view_behavior">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tv_content"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_margin="16dp"
android:lineSpacingMultiplier="2"
android:text="@string/textContent" />
</android.support.v4.widget.NestedScrollView>
</android.support.design.widget.CoordinatorLayout>
我们设置了CollapsingToolbarLayout的app:layout_scrollFlags=“scroll|exitUntilCollapsed” ,也就是说我们设置的150dp高的AppBarLayout在向上活动的过程中,子View也就是CollapsingToolbarLayout会先向上滑动,直到达到ToolBar默认的最小高度时会停止滑动,相应的我们在ToolBar中设置了app:layout_collapseMode=“parallax”,此时ToolBar不会留在屏幕上,所以最终的效果如下图:
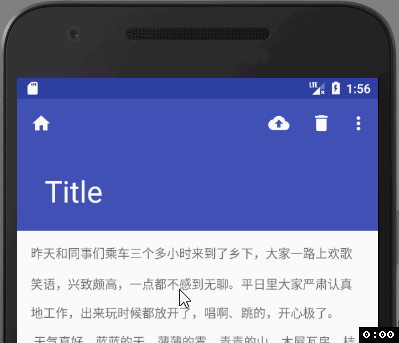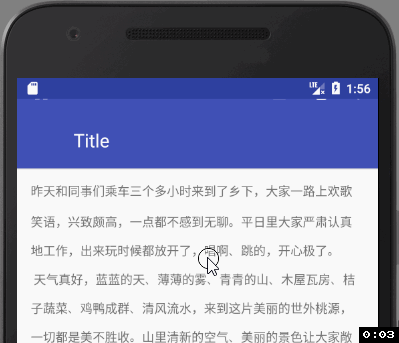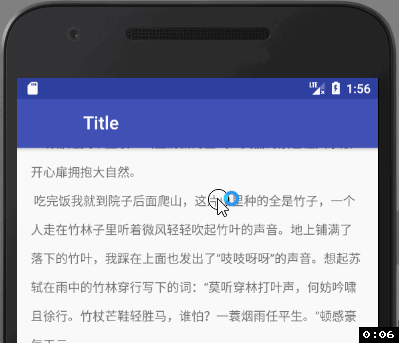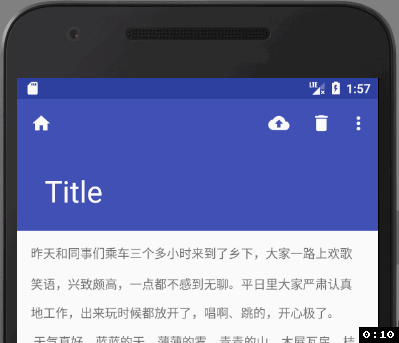
我们会发现,因为折叠模式的问题, toolbar的顶部图标没了, 我们改下折叠模式:app:layout_collapseMode=“pin”,再来看下效果:
接着我们再将app:layout_scrollFlags的值改为scroll|enterAlways|enterAlwaysCollapsed,从上面我们知道这样的属性组合,会使AppBarLayout在上滑时滚出屏幕,下滑时先到最小高度,然后滚动视图下滑,最后又是AppBarLayout继续下滑达到最大高度,效果如下:
上面我们在CollapsingToolbarLayout中只是添加了一个ToolBar,接下来我们在其中在添加一个ImageView,添加之后的布局如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<android.support.design.widget.CoordinatorLayout
...>
<android.support.design.widget.AppBarLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="200dp">
<android.support.design.widget.CollapsingToolbarLayout
...
android:theme="@style/ThemeOverlay.AppCompat.Dark.ActionBar"
app:layout_scrollFlags="scroll|enterAlways|enterAlwaysCollapsed">
<ImageView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:scaleType="centerCrop"
android:src="@drawable/darkbg"
app:layout_collapseMode="parallax"
app:layout_collapseParallaxMultiplier="0.7"/>
<android.support.v7.widget.Toolbar
android:id="@+id/toolbar"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="?attr/actionBarSize"
android:background="?attr/colorPrimary"
app:layout_collapseMode="pin"
app:popupTheme="@style/ThemeOverlay.AppCompat.Light"
app:title="Title" />
</android.support.design.widget.CollapsingToolbarLayout>
</android.support.design.widget.AppBarLayout>
<android.support.v4.widget.NestedScrollView
...
app:layout_behavior="@string/appbar_scrolling_view_behavior">
<TextView
... />
</android.support.v4.widget.NestedScrollView>
</android.support.design.widget.CoordinatorLayout>
可以看到在上面我们设置了AppBarLayout的高度为200dp,CollapsingToolbarLayout的app:layout_scrollFlags=“scroll|enterAlways|enterAlwaysCollapsed”,ImageView的折叠模式为parallax,ToolBar的折叠模式为pin,最终的效果如下:
折叠模式parallax可以用来实现视差滚动效果,通常和layout_collapseParallaxMultiplier(设置视差因子)搭配使用。
app:layout_collapseParallaxMultiplier="0.7"属性:设置视差滚动因子,值的范围是0~~1。
上面的ToolBar的背景和图片背景不搭,有点别扭,我们去掉ToolBar的背景看看效果:
接着我们给CollapsingToolbarLayout设置一下contentScrim属性
<android.support.design.widget.CollapsingToolbarLayout
...
app:contentScrim="?attr/colorPrimary"
...>
该属性设置的是当CollapsingToolbarLayout完全折叠时的背景颜色。
效果如下:
如果不想TooBar滑出屏幕,我们可以更改CollapsingToolbarLayout的app:layout_scrollFlags=“scroll|exitUntilCollapsed”,此时效果如下:
我们暂时去掉contentScrim属性,恢复CollapsingToolbarLayout的app:layout_scrollFlags="scroll|enterAlways|enterAlwaysCollapsed"的设置。
接下来,我们实现沉浸式设计,将状态栏设置成透明的,只需要在style主题中的AppTheme里增加一条:
<style name="AppTheme" parent="Theme.AppCompat.Light.NoActionBar">
...
<item name="android:statusBarColor">@android:color/transparent</item>
</style>
在布局里面, 将ImageView和所有它上面的父View都添加fitsSystemWindows属性:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<android.support.design.widget.CoordinatorLayout
...
android:fitsSystemWindows="true">
<android.support.design.widget.AppBarLayout
...
android:fitsSystemWindows="true">
<android.support.design.widget.CollapsingToolbarLayout
...
android:fitsSystemWindows="true">
<ImageView
...
android:fitsSystemWindows="true" />
<android.support.v7.widget.Toolbar
... />
</android.support.design.widget.CollapsingToolbarLayout>
</android.support.design.widget.AppBarLayout>
<android.support.v4.widget.NestedScrollView
...>
<TextView
... />
</android.support.v4.widget.NestedScrollView>
</android.support.design.widget.CoordinatorLayout>
我们来看下效果:
我们还可以通过在CollapsingToolbarLayout里设置statusBarScrim属性为透明色,然后更改layout_scrollFlags为 "scroll|exitUntilCollapsed"达到状态栏透明的效果,如下图:
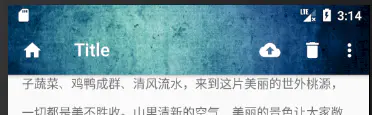
AppbarLayout整个做成沉浸式之后, 状态栏的图标可能会受到封面图片颜色过浅的影响, 可以给其加一个渐变的不透明层.
渐变遮罩设置方法:
在res/drawable文件夹下新建一个名为status_gradient的xml资源文件, 代码如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<shape xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android">
<gradient
android:angle="270"
android:endColor="@android:color/transparent"
android:startColor="#CC000000" />
<!-- shape节点中, 可以通过android:shape来设置形状, 默认是矩形.
gradient节点中angle的值270是从上到下,0是从左到右,90是从下到上。
此处的效果就是从下向上, 颜色逐渐由纯透明慢慢变成黑透色-->
</shape>
布局中, 在ImageView下面增加一个View, 背景设为上面的渐变遮罩:
<!-- 在顶部增加一个渐变遮罩, 防止出现status bar 状态栏看不清 -->
<View
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="40dp"
android:background="@drawable/status_gradient"
app:layout_collapseMode="pin"
android:fitsSystemWindows="true" />
给该遮罩层View设置折叠模式: app:layout_collapseMode=“pin” , 这样折叠到顶部会定住。来看下效果:

添加FloatingActionButton:
我们在布局中加一个悬浮按钮,让它的锚点挂载Appbar的右下角. 这样这个悬浮按钮就和Appbar关联起来了:
<android.support.design.widget.CoordinatorLayout
...>
<android.support.design.widget.AppBarLayout
...
</android.support.design.widget.AppBarLayout>
<android.support.v4.widget.NestedScrollView
...
</android.support.v4.widget.NestedScrollView>
<android.support.design.widget.FloatingActionButton
android:id="@+id/fab"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_margin="16dp"
android:src="@drawable/ic_share_white_24dp"
android:elevation="4dp"
app:pressedTranslationZ="16dp"
app:rippleColor="@android:color/white"
app:layout_anchor="@id/appbar"
app:layout_anchorGravity="bottom|end"/>
</android.support.design.widget.CoordinatorLayout>
我们来看下效果:
最后附上一个Activity代码供参考:
public class CollapsingToolbarLayoutActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(@Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_ctl);
Toolbar toolbar = (Toolbar) findViewById(R.id.ctl_toolbar);
setSupportActionBar(toolbar);
getSupportActionBar().setDisplayHomeAsUpEnabled(true);
toolbar.setNavigationIcon(getResources().getDrawable(R.drawable.back));
toolbar.setNavigationOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View view) {
finish();
}
});
CollapsingToolbarLayout collapsing_toolbar_layout = (CollapsingToolbarLayout) findViewById(R.id.collapsing_toolbar_layout);
collapsing_toolbar_layout.setTitle(getResources().getString(R.string.app_name));
//设置展开的时候标题显示字体颜色
collapsing_toolbar_layout.setExpandedTitleColor(Color.WHITE);
//设置折叠的时候标题显示字体颜色
collapsing_toolbar_layout.setCollapsedTitleTextColor(Color.WHITE);
//设置折叠时候标题对齐位置
collapsing_toolbar_layout.setCollapsedTitleGravity(Gravity.LEFT);
findViewById(R.id.ctl_fab).setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View view) {
Snackbar.make(view, "点击的是FAB", Snackbar.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
});
}
public static void start(Context mContext) {
mContext.startActivity(new Intent(mContext, CollapsingToolbarLayoutActivity.class));
}
}