android ANR源码分析 --- 之三
4, inputDispatching Timeout
当input事件处理得慢就会触发ANR.
ANR时间区别便是指当前这次的事件dispatch过程中执行findFocusedWindowTargetsLocked()方法到下一次执行resetANRTimeoutsLocked()的时间区间.
在InputDispatcher.cpp的事件分发过程中, 如果是Key event事件,则会调用dispatchKeyLocked方法;
如果是Motion event事件,则会调用dispatchMotionLocked方法;
dispatchKeyLocked方法会调用findTouchedWindowTargetsLocked方法进行超时记录,如下,
int32_t injectionResult = findFocusedWindowTargetsLocked(currentTime,
entry, inputTargets, nextWakeupTime);
最后调用dispatchEventLocked继续处理事件。
dispatchEventLocked(currentTime, entry, inputTargets);dispatchMotionLocked方法中会根据触摸事件是点触摸还是轨迹球事件分别进行超时记录,
if (isPointerEvent) {
// Pointer event. (eg. touchscreen)
injectionResult = findTouchedWindowTargetsLocked(currentTime,
entry, inputTargets, nextWakeupTime, &conflictingPointerActions);
} else {
// Non touch event. (eg. trackball)
injectionResult = findFocusedWindowTargetsLocked(currentTime,
entry, inputTargets, nextWakeupTime);
}
如果是点触摸则调用findTouchedWindowTargetsLocked方法进行处理;
如果是其他,例如轨迹球事件则调用findFocusedWindowTargetsLocked方法进行处理。
最后都调用dispatchEventLocked继续处理事件,
dispatchEventLocked(currentTime, entry, inputTargets);最后无论是findTouchedWindowTargetsLocked还是findFocusedWindowTargetsLocked方法,都会调用handleTargetsNotReadyLocked方法。
injectionResult = handleTargetsNotReadyLocked(currentTime, entry,
mFocusedApplicationHandle, mFocusedWindowHandle, nextWakeupTime, reason.string());
4.1 handleTargetsNotReadyLocked
handleTargetsNotReadyLocked方法很关键,决定了是否调用onANRLocked方法,也就是ANR消息。
onANRLocked方法调用onANRLocked方法如下,
if (currentTime >= mInputTargetWaitTimeoutTime) {
onANRLocked(currentTime, applicationHandle, windowHandle,
entry->eventTime, mInputTargetWaitStartTime, reason);
逐步看onANRLocked方法执行的条件,
currentTime 就是系统的当前时间,这个没什么说的。主要是mInputTargetWaitTimeoutTime变量, mInputTargetWaitTimeoutTime 是一个全局变量,
1,如果applicationHandle和windowHandle 都为空,可能系统灭屏休眠了,这时候mInputTargetWaitTimeoutTime变量就设置一个比较大的值,
也就是说onANRLocked方法不会调用,
if (applicationHandle == NULL && windowHandle == NULL) {
if (mInputTargetWaitCause != INPUT_TARGET_WAIT_CAUSE_SYSTEM_NOT_READY) {
•••
mInputTargetWaitTimeoutTime = LONG_LONG_MAX;
2,如果不是上面的情况,并且apk已经完全启动,可以处理input事件,
else {
if (mInputTargetWaitCause != INPUT_TARGET_WAIT_CAUSE_APPLICATION_NOT_READY) {
•••
nsecs_t timeout; //获取等待的时间值
if (windowHandle != NULL) {
timeout = windowHandle->getDispatchingTimeout(DEFAULT_INPUT_DISPATCHING_TIMEOUT);
} else if (applicationHandle != NULL) {
timeout = applicationHandle->getDispatchingTimeout(
DEFAULT_INPUT_DISPATCHING_TIMEOUT);
} else {
timeout = DEFAULT_INPUT_DISPATCHING_TIMEOUT;
}
•••
mInputTargetWaitTimeoutTime = currentTime + timeout;// 为mInputTargetWaitTimeoutTime 赋值
Input事件ANR时间为5s,定义如下,
const nsecs_t DEFAULT_INPUT_DISPATCHING_TIMEOUT = 5000 * 1000000LL; // 5 sec到下次执行resetANRTimeoutsLocked方法时,就会重置时间,因此onANRLocked方法也不会执行,
// Reset input target wait timeout.
mInputTargetWaitCause = INPUT_TARGET_WAIT_CAUSE_NONE;
mInputTargetWaitApplicationHandle.clear();
在InputDispatcher.cpp中,有以下方法可能会调用resetANRTimeoutsLocked方法,
resetAndDropEverythingLocked
releasePendingEventLocked
setFocusedApplication
dispatchOnceInnerLocked
setInputDispatchMode
因此, 以下4个场景,可能会调用resetANRTimeoutsLocked方法,
1,解冻屏幕, 系统开/关机的时刻点 (thawInputDispatchingLw, setEventDispatchingLw)
2,wms聚焦app的改变 (WMS.setFocusedApp, WMS.removeAppToken)
3,设置input filter的过程 (IMS.setInputFilter)
4,再次分发事件的过程(dispatchOnceInnerLocked)
以上都运行于input native进程中,接下来看看如何从input native进程通过JNI回调到system_server进程的。
4.2 onANRLocked
InputDispatcher.cpp的onANRLocked方法调用流程图如下,
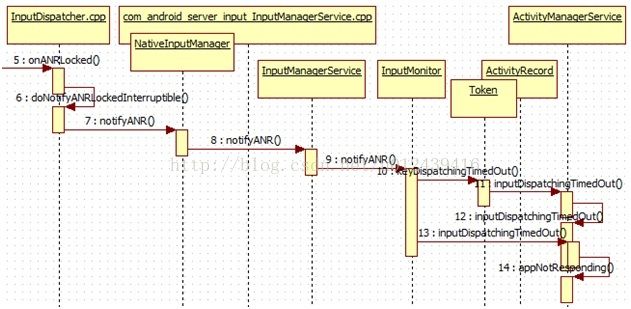
4.2.1 C++流程
onANRLocked方法主要逻辑如下,
1,首先捕获ANR的现场信息,
time_t t = time(NULL);
struct tm tm;
localtime_r(&t, &tm);
char timestr[64];
strftime(timestr, sizeof(timestr), "%F %T", &tm);
mLastANRState.clear();
mLastANRState.append(INDENT "ANR:\n");
mLastANRState.appendFormat(INDENT2 "Time: %s\n", timestr);
mLastANRState.appendFormat(INDENT2 "Window: %s\n",
getApplicationWindowLabelLocked(applicationHandle, windowHandle).string());
mLastANRState.appendFormat(INDENT2 "DispatchLatency: %0.1fms\n", dispatchLatency);
mLastANRState.appendFormat(INDENT2 "WaitDuration: %0.1fms\n", waitDuration);
mLastANRState.appendFormat(INDENT2 "Reason: %s\n", reason);
dumpDispatchStateLocked(mLastANRState);
2, 将ANR命令执行方法doNotifyANRLockedInterruptible加入mCommandQueue
CommandEntry* commandEntry = postCommandLocked(
& InputDispatcher::doNotifyANRLockedInterruptible);
commandEntry->inputApplicationHandle = applicationHandle;
commandEntry->inputWindowHandle = windowHandle;
commandEntry->reason = reason;
发生ANR调用onANRLocked()的过程会将doNotifyANRLockedInterruptible加入mCommandQueue。 在下一轮InputDispatcher.dispatchOnce的
过程中会先执行runCommandsLockedInterruptible()方法,取出 mCommandQueue队列的所有命令逐一执行。那么ANR所对应的
命令doNotifyANRLockedInterruptible,该方法如下,
nsecs_t newTimeout = mPolicy->notifyANR(
commandEntry->inputApplicationHandle, commandEntry->inputWindowHandle,
commandEntry->reason);
mPolicy是指NativeInputManager对象, NativeInputManager是com_android_server_input_InputManagerService.cpp的内部类,
NativeInputManager的notifyANR方法如下,
JNIEnv* env = jniEnv();
jobject inputApplicationHandleObj =
getInputApplicationHandleObjLocalRef(env, inputApplicationHandle);
jobject inputWindowHandleObj =
getInputWindowHandleObjLocalRef(env, inputWindowHandle);
jstring reasonObj = env->NewStringUTF(reason.string());
jlong newTimeout = env->CallLongMethod(mServiceObj,gServiceClassInfo.notifyANR, inputApplicationHandleObj, inputWindowHandleObj, reasonObj);
gServiceClassInfo是一个结构体,里面的变量一般指向InputManagerService.java中的方法,并且在register_android_server_InputManager方法中,给该结构体赋值,
GET_METHOD_ID(gServiceClassInfo.notifyANR, clazz,
"notifyANR",
"(Lcom/android/server/input/InputApplicationHandle;Lcom/android/server/input/InputWindowHandle;Ljava/lang/String;)J");
其中notifyANR变量指向的是InputManagerService的notifyANR方法,这样,流程终于走到Java层了。
4.2.2 Java层流程
InputManagerService的notifyANR方法如下,
return mWindowManagerCallbacks.notifyANR(
inputApplicationHandle, inputWindowHandle, reason);
WindowManagerCallbacks只是InputManagerService中的一个内部接口,具体的实现是在InputMonitor中,
InputMonitor继承了WindowManagerCallbacks接口,并且实现了相对应的方法, InputMonitor的notifyANR方法如下,
如果是key 事件,就跨进程调用ActivityRecord 的内部类Token 的keyDispatchingTimedOut方法,
boolean abort = appWindowToken.appToken.keyDispatchingTimedOut(reason);如果是触摸事件,跨进程调用AMS的inputDispatchingTimedOut方法,
long timeout = ActivityManagerNative.getDefault().inputDispatchingTimedOut(
windowState.mSession.mPid, aboveSystem, reason);
ActivityRecord的内部类Token 的keyDispatchingTimedOut方法最后也会调用AMS的inputDispatchingTimedOut方法,该方法如下,
mHandler.post(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
appNotResponding(proc, activity, parent, aboveSystem, annotation);
}
});