树的前中后序遍历
文章目录
- LeetCode 94.二叉树的中序遍历
- 题目描述
- 方法一 递归
- 方法二 基于栈的遍历
- LeetCode 144.二叉树的前序遍历
- 题目描述
- 方法一 递归
- 方法二 基于栈的遍历
- 模板化非递归的前中后序遍历(推荐)
- 前序遍历
- 中序遍历
- 后序遍历
- LeetCode 589.N叉树的前序遍历
- 题目描述
- 方法一 递归
- 方法二 基于栈的遍历
- LeetCode 590.N叉树的后序遍历
- 题目描述
- 方法一 递归
- 方法二 基于栈的遍历
- LeetCode 429.N叉树的层序遍历
- 题目描述
- 广度优先搜索(BFS)
LeetCode 94.二叉树的中序遍历
题目描述
题目链接
给定一个二叉树,返回它的中序 遍历。
示例:
输入: [1,null,2,3]
1
\
2
/
3
输出: [1,3,2]
进阶: 递归算法很简单,你可以通过迭代算法完成吗?
方法一 递归
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
helper(root, list);
return list;
}
private void helper(TreeNode root, List<Integer> list){
if(root != null){
if(root.left != null)
helper(root.left, list);
list.add(root.val);
if(root.right != null)
helper(root.right, list);
}
}
}
方法二 基于栈的遍历
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List < Integer > list = new ArrayList < > ();
Stack < TreeNode > stack = new Stack < > ();
TreeNode curr = root;
while (curr != null || !stack.isEmpty()) {
while (curr != null) {
stack.push(curr);
curr = curr.left;
}
curr = stack.pop();
list.add(curr.val);
curr = curr.right;
}
return list;
}
}
LeetCode 144.二叉树的前序遍历
题目描述
题目链接
给定一个二叉树,返回它的 前序 遍历。
示例:
输入: [1,null,2,3]
1
\
2
/
3
输出: [1,2,3]
方法一 递归
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public List<Integer> preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
helper(root, list);
return list;
}
private void helper(TreeNode root, List<Integer> list){
if(root != null){
list.add(root.val);
if(root.left != null)
helper(root.left, list);
if(root.right != null)
helper(root.right, list);
}
}
}
方法二 基于栈的遍历
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public List<Integer> preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
TreeNode curr = root;
while(curr != null || !stack.isEmpty()){
while(curr != null){
stack.push(curr);
list.add(curr.val);
curr = curr.left;
}
curr = stack.pop();
curr = curr.right;
}
return list;
}
}
模板化非递归的前中后序遍历(推荐)
这里的方法参考于LeetCode上PualKing的题解
前序遍历
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public List<Integer> preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
//前序遍历顺序为:根->左->右
//入栈的顺序应和遍历的顺序相反(先进后出): 右->左->根
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
if(root != null)
stack.push(root);
while(!stack.isEmpty()){
TreeNode curr = stack.pop();
if(curr != null){
if(curr.right != null)
stack.push(curr.right);//右节点先进栈,最后处理
if(curr.left != null)
stack.push(curr.left);
stack.push(curr);//当前节点重新压栈
stack.push(null);//在当前节点之前加入一个空节点表示已经访问过了
}else{
list.add(stack.pop().val);
}
}
return list;
}
}
中序遍历
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
//前序遍历顺序为:左->根->右
//入栈的顺序应和遍历的顺序相反(先进后出):右->根->左
List < Integer > list = new ArrayList < > ();
Stack < TreeNode > stack = new Stack < > ();
if(root != null)
stack.push(root);
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode curr = stack.pop();
if(curr != null){
if(curr.right != null)
stack.push(curr.right);
stack.push(curr);//在左节点之前重新插入当前节点
stack.push(null);
if(curr.left != null)
stack.push(curr.left);
}else{
list.add(stack.pop().val);
}
}
return list;
}
}
后序遍历
题目链接
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public List<Integer> postorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
//后序遍历顺序为:左->右->根
//入栈的顺序应和遍历的顺序相反(先进后出): 根->右->左
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
if(root != null)
stack.push(root);
while(!stack.isEmpty()){
TreeNode curr = stack.pop();
if(curr != null){
stack.push(curr);//当前节点重新压栈
stack.push(null);//在当前节点之前加入一个空节点表示已经访问过了
if(curr.right != null)
stack.push(curr.right);//右节点先进栈,最后处理
if(curr.left != null)
stack.push(curr.left);
}else{
list.add(stack.pop().val);
}
}
return list;
}
}
LeetCode 589.N叉树的前序遍历
题目描述
题目链接
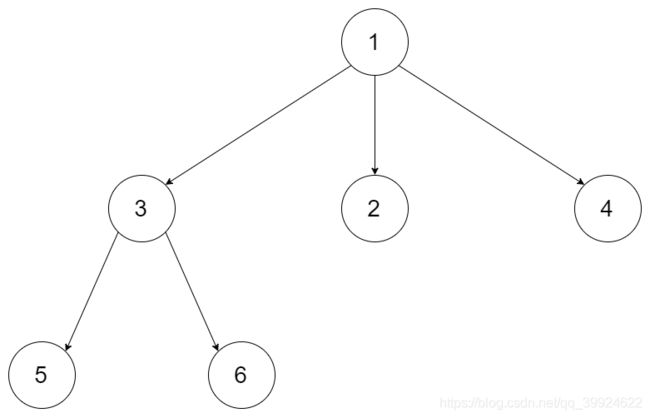
给定一个 N 叉树,返回其节点值的前序遍历。
例如,给定一个 3叉树 :
方法一 递归
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
public int val;
public List children;
public Node() {}
public Node(int _val) {
val = _val;
}
public Node(int _val, List _children) {
val = _val;
children = _children;
}
};
*/
class Solution {
public List<Integer> preorder(Node root) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
helper(root, list);
return list;
}
private void helper(Node root, List<Integer> list){
if(root == null)
return;
list.add(root.val);
for(Node child : root.children)
helper(child, list);
}
}
方法二 基于栈的遍历
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
public int val;
public List children;
public Node() {}
public Node(int _val) {
val = _val;
}
public Node(int _val, List _children) {
val = _val;
children = _children;
}
};
*/
class Solution {
public List<Integer> preorder(Node root) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
Deque<Node> deque = new ArrayDeque<>();
if(root == null)
return list;
deque.addLast(root);
while(!deque.isEmpty()){
Node cur = deque.pollLast();
list.add(cur.val);
//翻转孩子节点
Collections.reverse(cur.children);
for(Node child : cur.children){
deque.addLast(child);
}
}
return list;
}
}
LeetCode 590.N叉树的后序遍历
题目描述
题目链接
给定一个 N 叉树,返回其节点值的后序遍历。
例如,给定一个 3叉树 :

返回其后序遍历: [5,6,3,2,4,1].
方法一 递归
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
public int val;
public List children;
public Node() {}
public Node(int _val) {
val = _val;
}
public Node(int _val, List _children) {
val = _val;
children = _children;
}
};
*/
class Solution {
public List<Integer> postorder(Node root) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
helper(root, list);
return list;
}
private void helper(Node root, List<Integer> list){
if(root == null)
return;
//先遍历孩子节点
for(Node child : root.children){
helper(child, list);
}
list.add(root.val);
}
}
方法二 基于栈的遍历
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
public int val;
public List children;
public Node() {}
public Node(int _val) {
val = _val;
}
public Node(int _val, List _children) {
val = _val;
children = _children;
}
};
*/
class Solution {
public List<Integer> postorder(Node root) {
LinkedList<Integer> list = new LinkedList<>();
Deque<Node> deque = new ArrayDeque<>();
if(root == null)
return list;
deque.addLast(root);
while(!deque.isEmpty()){
Node cur = deque.pollLast();
list.offerFirst(cur.val);
for(Node child : cur.children)
deque.addLast(child);
}
return list;
}
}
LeetCode 429.N叉树的层序遍历
题目描述
题目链接
给定一个 N 叉树,返回其节点值的层序遍历。 (即从左到右,逐层遍历)。
[
[1],
[3,2,4],
[5,6]
]
说明:
树的深度不会超过 1000。
树的节点总数不会超过 5000。
广度优先搜索(BFS)
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
public int val;
public List children;
public Node() {}
public Node(int _val) {
val = _val;
}
public Node(int _val, List _children) {
val = _val;
children = _children;
}
};
*/
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(Node root) {
List<List<Integer>> list = new ArrayList<>();
if(root == null)
return list;
Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(root);
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
List<Integer> curLevel = new ArrayList<>();
int len = queue.size();
for(int i = 0; i < len; i++){
Node curr = queue.poll();
curLevel.add(curr.val);
for(Node child : curr.children)
queue.offer(child);
}
list.add(curLevel);
}
return list;
}
}