Android A/B system - update_engine(一)
Android A/B System的升级过程是怎样的?理解这一过程就需要理解update_engine的逻辑。
首先来看Android.mk,这里截取了一些关键信息
- 入口函数:
main.cc - 依赖的c文件/动态库/静态库
# update_engine (type: executable)
# ========================================================
# update_engine daemon.
include $(CLEAR_VARS)
LOCAL_MODULE := update_engine
LOCAL_MODULE_CLASS := EXECUTABLES
LOCAL_REQUIRED_MODULES := \
cacerts_google
LOCAL_CPP_EXTENSION := .cc
LOCAL_CFLAGS := $(ue_common_cflags)
LOCAL_CPPFLAGS := $(ue_common_cppflags)
LOCAL_LDFLAGS := $(ue_common_ldflags)
LOCAL_C_INCLUDES := \
$(ue_common_c_includes)
LOCAL_SHARED_LIBRARIES := \
$(ue_common_shared_libraries)
LOCAL_STATIC_LIBRARIES := \
$(ue_common_static_libraries)
LOCAL_SRC_FILES := \
main.cc
# 依赖的c文件/动态库/静态库
ue_common_c_includes := \
$(LOCAL_PATH)/client_library/include \
system
ue_common_shared_libraries := \
libbrillo-stream \
libbrillo \
libchrome
ue_common_static_libraries := \
libgtest_prod \
首先来看main.cc,main.cc主要做了这些事:
- log相关
- 初始化crc-32 table
- 调用
update_engine_daemon.Run()
/system/update_engine/main.cc
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
DEFINE_bool(logtofile, false, "Write logs to a file in log_dir.");
DEFINE_bool(logtostderr, false,
"Write logs to stderr instead of to a file in log_dir.");
DEFINE_bool(foreground, false,
"Don't daemon()ize; run in foreground.");
chromeos_update_engine::Terminator::Init();
brillo::FlagHelper::Init(argc, argv, "Chromium OS Update Engine");
// We have two logging flags "--logtostderr" and "--logtofile"; and the logic
// to choose the logging destination is:
// 1. --logtostderr --logtofile -> logs to both
// 2. --logtostderr -> logs to system debug
// 3. --logtofile or no flags -> logs to file
bool log_to_system = FLAGS_logtostderr;
bool log_to_file = FLAGS_logtofile || !FLAGS_logtostderr;
chromeos_update_engine::SetupLogging(log_to_system, log_to_file);
if (!FLAGS_foreground)
PLOG_IF(FATAL, daemon(0, 0) == 1) << "daemon() failed";
LOG(INFO) << "Chrome OS Update Engine starting";
// xz-embedded requires to initialize its CRC-32 table once on startup.
xz_crc32_init();
// Ensure that all written files have safe permissions.
// This is a mask, so we _block_ all permissions for the group owner and other
// users but allow all permissions for the user owner. We allow execution
// for the owner so we can create directories.
// Done _after_ log file creation.
umask(S_IRWXG | S_IRWXO);
chromeos_update_engine::UpdateEngineDaemon update_engine_daemon;
int exit_code = update_engine_daemon.Run();
LOG(INFO) << "Chrome OS Update Engine terminating with exit code "
<< exit_code;
return exit_code;
}
在/system/update_engine/daemon.h没有找到Run()函数,所以去找父类。
/system/update_engine/daemon.h
class UpdateEngineDaemon : public brillo::Daemon{}
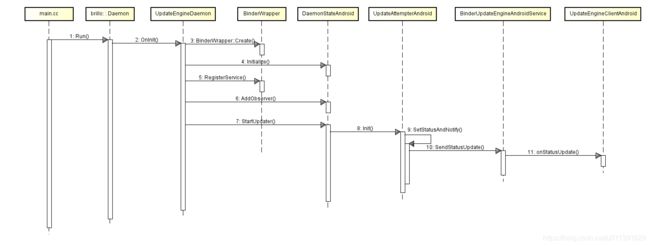
可以看到这里Run()函数,首先执行了OnInit()函数。
/external/libbrillo/brillo/daemons/daemon.cc
int Daemon::Run() {
int exit_code = OnInit();
if (exit_code != EX_OK)
return exit_code;
message_loop_.Run();
OnShutdown(&exit_code_);
// base::RunLoop::QuitClosure() causes the message loop to quit
// immediately, even if pending tasks are still queued.
// Run a secondary loop to make sure all those are processed.
// This becomes important when working with D-Bus since dbus::Bus does
// a bunch of clean-up tasks asynchronously when shutting down.
while (message_loop_.RunOnce(false /* may_block */)) {}
return exit_code_;
}
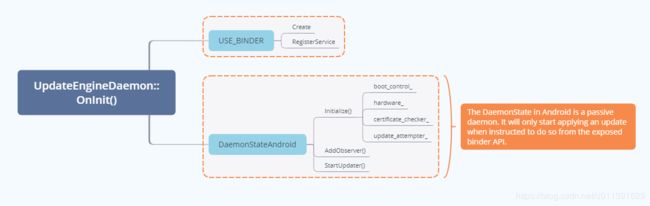
OnInit()函数做了两件事:
- Binder初始化(创建/注册)
- 调用
DaemonStateAndroid的函数AddObserver()StartUpdater()Initialized()
/system/update_engine/daemon.cc
int UpdateEngineDaemon::OnInit() {
// Register the |subprocess_| singleton with this Daemon as the signal
// handler.
subprocess_.Init(this);
int exit_code = Daemon::OnInit();
if (exit_code != EX_OK)
return exit_code;
#if USE_BINDER
android::BinderWrapper::Create();
binder_watcher_.Init();
#endif // USE_BINDER
#if USE_OMAHA
// Initialize update engine global state but continue if something fails.
// TODO(deymo): Move the daemon_state_ initialization to a factory method
// avoiding the explicit re-usage of the |bus| instance, shared between
// D-Bus service and D-Bus client calls.
RealSystemState* real_system_state = new RealSystemState();
daemon_state_.reset(real_system_state);
LOG_IF(ERROR, !real_system_state->Initialize())
<< "Failed to initialize system state.";
#else // !USE_OMAHA
DaemonStateAndroid* daemon_state_android = new DaemonStateAndroid();
daemon_state_.reset(daemon_state_android);
LOG_IF(ERROR, !daemon_state_android->Initialize())
<< "Failed to initialize system state.";
#endif // USE_OMAHA
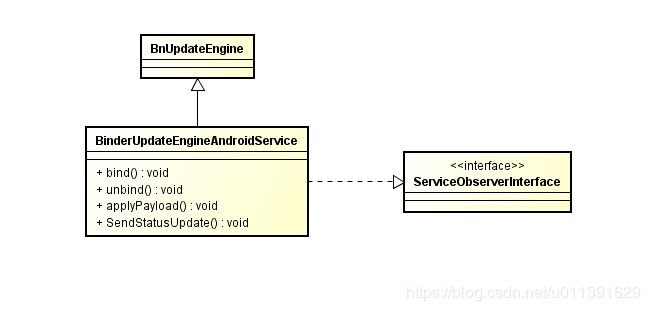
#if USE_BINDER
// Create the Binder Service.
#if USE_OMAHA
binder_service_ = new BinderUpdateEngineBrilloService{real_system_state};
#else // !USE_OMAHA
binder_service_ = new BinderUpdateEngineAndroidService{
daemon_state_android->service_delegate()};
#endif // USE_OMAHA
auto binder_wrapper = android::BinderWrapper::Get();
if (!binder_wrapper->RegisterService(binder_service_->ServiceName(),
binder_service_)) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Failed to register binder service.";
}
daemon_state_->AddObserver(binder_service_.get());
#endif // USE_BINDER
#if USE_DBUS
// Create the DBus service.
dbus_adaptor_.reset(new UpdateEngineAdaptor(real_system_state));
daemon_state_->AddObserver(dbus_adaptor_.get());
dbus_adaptor_->RegisterAsync(base::Bind(&UpdateEngineDaemon::OnDBusRegistered,
base::Unretained(this)));
LOG(INFO) << "Waiting for DBus object to be registered.";
#else // !USE_DBUS
daemon_state_->StartUpdater();
#endif // USE_DBUS
return EX_OK;
}
#if USE_DBUS
void UpdateEngineDaemon::OnDBusRegistered(bool succeeded) {
if (!succeeded) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Registering the UpdateEngineAdaptor";
QuitWithExitCode(1);
return;
}
// Take ownership of the service now that everything is initialized. We need
// to this now and not before to avoid exposing a well known DBus service
// path that doesn't have the service it is supposed to implement.
if (!dbus_adaptor_->RequestOwnership()) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Unable to take ownership of the DBus service, is there "
<< "other update_engine daemon running?";
QuitWithExitCode(1);
return;
}
daemon_state_->StartUpdater();
}
#endif // USE_DBUS
} // namespace chromeos_update_engine
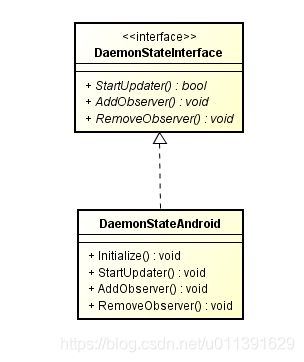
来看DaemonStateAndroid这个类做了什么,首先来看Initialize()这个函数,从名字可以看出做了一些初始化的工作,包括boot_control_,hardware_,ceritficate_checker_,update_attempter_。boot_control_可以看Android A/B System Updates,是google提供的接口,在启动的过程中会用到,每个芯片厂商自己去实现这部分的内容;hardware_与硬件相关;ceritficate_checker_,update_attempter_是UpdateAttempter会使用到,这是A/B升级的核心。
bool DaemonStateAndroid::Initialize() {
boot_control_ = boot_control::CreateBootControl();
if (!boot_control_) {
LOG(WARNING) << "Unable to create BootControl instance, using stub "
<< "instead. All update attempts will fail.";
boot_control_.reset(new BootControlStub());
}
hardware_ = hardware::CreateHardware();
if (!hardware_) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Error intializing the HardwareInterface.";
return false;
}
LOG_IF(INFO, !hardware_->IsNormalBootMode()) << "Booted in dev mode.";
LOG_IF(INFO, !hardware_->IsOfficialBuild()) << "Booted non-official build.";
// Initialize prefs.
base::FilePath non_volatile_path;
// TODO(deymo): Fall back to in-memory prefs if there's no physical directory
// available.
if (!hardware_->GetNonVolatileDirectory(&non_volatile_path)) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Failed to get a non-volatile directory.";
return false;
}
Prefs* prefs = new Prefs();
prefs_.reset(prefs);
if (!prefs->Init(non_volatile_path.Append(kPrefsSubDirectory))) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Failed to initialize preferences.";
return false;
}
// The CertificateChecker singleton is used by the update attempter.
certificate_checker_.reset(
new CertificateChecker(prefs_.get(), &openssl_wrapper_));
certificate_checker_->Init();
// Initialize the UpdateAttempter before the UpdateManager.
update_attempter_.reset(new UpdateAttempterAndroid(
this, prefs_.get(), boot_control_.get(), hardware_.get()));
return true;
}
再来看StartUpdater()做了什么,它继续调用了update_attempter_->Init(),所以还要往下看。
/system/update_engine/daemon_state_android.cc
bool DaemonStateAndroid::StartUpdater() {
// The DaemonState in Android is a passive daemon. It will only start applying
// an update when instructed to do so from the exposed binder API.
update_attempter_->Init();
return true;
}
/system/update_engine/update_attempter_android.cc
void UpdateAttempterAndroid::Init() {
// In case of update_engine restart without a reboot we need to restore the
// reboot needed state.
if (UpdateCompletedOnThisBoot()) {
SetStatusAndNotify(UpdateStatus::UPDATED_NEED_REBOOT);
} else {
SetStatusAndNotify(UpdateStatus::IDLE);
UpdatePrefsAndReportUpdateMetricsOnReboot();
}
}
Init()函数。它分为两种情况:
- 如果升级已经完成,设置
UPDATED_NEED_REBOOT状态,表示升级已经完成,需要重启。 - 否则,设置
IDLE状态,并且更新并检查版本信息。
/system/update_engine/update_attempter_android.cc
void UpdateAttempterAndroid::Init() {
// In case of update_engine restart without a reboot we need to restore the
// reboot needed state.
if (UpdateCompletedOnThisBoot()) {
SetStatusAndNotify(UpdateStatus::UPDATED_NEED_REBOOT);
} else {
SetStatusAndNotify(UpdateStatus::IDLE);
UpdatePrefsAndReportUpdateMetricsOnReboot();
}
}
SetStatusAndNotify()函数先获取payload.bin(升级包中的一个核心文件)的大小,然后更新的情况发出(这里是观察者模式,所有的观察者都能接收到信息)。
/system/update_engine/update_attempter_android.cc
void UpdateAttempterAndroid::SetStatusAndNotify(UpdateStatus status) {
status_ = status;
size_t payload_size =
install_plan_.payloads.empty() ? 0 : install_plan_.payloads[0].size;
UpdateEngineStatus status_to_send = {.status = status_,
.progress = download_progress_,
.new_size_bytes = payload_size};
for (auto observer : daemon_state_->service_observers()) {
observer->SendStatusUpdate(status_to_send);
}
last_notify_time_ = TimeTicks::Now();
}
这里的每个观察者对应一个客户端,客户端接收到了更新信息。
/system/update_engine/update_engine_client_android.cc
void UpdateAttempterAndroid::SetStatusAndNotify(UpdateStatus status) {
status_ = status;
size_t payload_size =
install_plan_.payloads.empty() ? 0 : install_plan_.payloads[0].size;
UpdateEngineStatus status_to_send = {.status = status_,
.progress = download_progress_,
.new_size_bytes = payload_size};
for (auto observer : daemon_state_->service_observers()) {
observer->SendStatusUpdate(status_to_send);
}
last_notify_time_ = TimeTicks::Now();
}
这一篇就分析到这,下一篇继续分析,以下是这一篇涉及到的流程图和类图,可以对照着看。