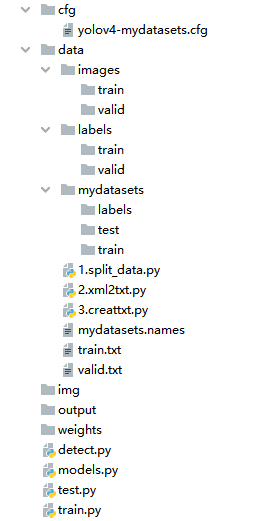
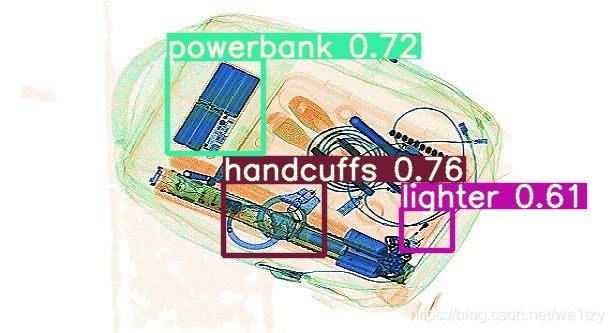
使用yolov4训练自己的数据集——科大讯飞X光安检图像识别baseline
文章目录
- 一、cfg文件修改
- 二、data/下新建配置文件
- 三、创建标注文件
- 四、划分训练集、验证集与对应标签
- 4.1 split_data.py
- 4.2 xml2txt.py
- 4.3 creattxt.py
- 五、训练
- 六、推理
一、cfg文件修改
创建yolov4-mydatasets.cfg,因为我用了yolov4.cfg训练太吃显存,2080TI的机子batchsize设置为2也会爆显存。其主要原因是mish函数太占显存了。
修改的地方:
将mish函数替代为relu函数,大大降低显存使用!
另外filters设置为:(class数目 + 4 +1) × 3 = 45(我这里10个类别)分别对应三个detect header
classes=10 修改为类别数目,我这里是10(所以这里和filters一共修改6处)
其他的超参数可以适当修改。
[convolutional]
size=1
stride=1
pad=1
filters=45
activation=linear
[yolo]
mask = 0,1,2
anchors = 12, 16, 19, 36, 40, 28, 36, 75, 76, 55, 72, 146, 142, 110, 192, 243, 459, 401
classes=10
num=9
jitter=.3
ignore_thresh = .7
truth_thresh = 1
scale_x_y = 1.2
iou_thresh=0.213
cls_normalizer=1.0
iou_normalizer=0.07
iou_loss=ciou
nms_kind=greedynms
beta_nms=0.6
[route]
layers = -4
[convolutional]
batch_normalize=1
size=3
stride=2
pad=1
filters=256
activation=leaky
[route]
layers = -1, -16
[convolutional]
batch_normalize=1
filters=256
size=1
stride=1
pad=1
activation=leaky
[convolutional]
batch_normalize=1
size=3
stride=1
pad=1
filters=512
activation=leaky
[convolutional]
batch_normalize=1
filters=256
size=1
stride=1
pad=1
activation=leaky
[convolutional]
batch_normalize=1
size=3
stride=1
pad=1
filters=512
activation=leaky
[convolutional]
batch_normalize=1
filters=256
size=1
stride=1
pad=1
activation=leaky
[convolutional]
batch_normalize=1
size=3
stride=1
pad=1
filters=512
activation=leaky
[convolutional]
size=1
stride=1
pad=1
filters=45
activation=linear
[yolo]
mask = 3,4,5
anchors = 12, 16, 19, 36, 40, 28, 36, 75, 76, 55, 72, 146, 142, 110, 192, 243, 459, 401
classes=10
num=9
jitter=.3
ignore_thresh = .7
truth_thresh = 1
scale_x_y = 1.1
iou_thresh=0.213
cls_normalizer=1.0
iou_normalizer=0.07
iou_loss=ciou
nms_kind=greedynms
beta_nms=0.6
[route]
layers = -4
[convolutional]
batch_normalize=1
size=3
stride=2
pad=1
filters=512
activation=leaky
[route]
layers = -1, -37
[convolutional]
batch_normalize=1
filters=512
size=1
stride=1
pad=1
activation=leaky
[convolutional]
batch_normalize=1
size=3
stride=1
pad=1
filters=1024
activation=leaky
[convolutional]
batch_normalize=1
filters=512
size=1
stride=1
pad=1
activation=leaky
[convolutional]
batch_normalize=1
size=3
stride=1
pad=1
filters=1024
activation=leaky
[convolutional]
batch_normalize=1
filters=512
size=1
stride=1
pad=1
activation=leaky
[convolutional]
batch_normalize=1
size=3
stride=1
pad=1
filters=1024
activation=leaky
[convolutional]
size=1
stride=1
pad=1
filters=45
activation=linear
[yolo]
mask = 6,7,8
anchors = 12, 16, 19, 36, 40, 28, 36, 75, 76, 55, 72, 146, 142, 110, 192, 243, 459, 401
classes=10
num=9
jitter=.3
ignore_thresh = .7
truth_thresh = 1
random=1
scale_x_y = 1.05
iou_thresh=0.213
cls_normalizer=1.0
iou_normalizer=0.07
iou_loss=ciou
nms_kind=greedynms
beta_nms=0.6
二、data/下新建配置文件
在data下新建mydatasets.names文件,把自己的类别写进去即可
knife
scissors
lighter
zippooil
pressure
slingshot
handcuffs
nailpolish
powerbank
firecrackers
在data/下新建mydatasets.data文件,填入以下内容即可:
classes= 10
train=data/train.txt
valid=data/valid.txt
names=data/mydatasets.names
三、创建标注文件
可以使用LabelImg,Labme,Labelbox, CVAT来标注数据,对于目标检测而言需要标注bounding box即可。然后需要将标注转换为和darknet format相同的标注形式,每一个图像生成一个*.txt的标注文件(如果该图像没有标注目标则不用创建*.txt文件)。创建的*.txt文件遵循如下规则:
- 每一行存放一个标注类别
- 每一行的内容包括class x_center y_center width height
- Bounding box 的坐标信息是归一化之后的(0-1)
- class label转化为index时计数是从0开始的
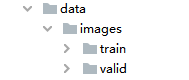
四、划分训练集、验证集与对应标签
在data/下,新建文件夹命名为“mydatasets”。即:data/mydatasets/,再划分train文件夹(训练数据集),labels文件夹(标签集),test文件夹。数据集、测试集与标签分别放到对应位置。如下图所示:

再先划分训练数据集train,将train数据集划分为train/valid数据集:
4.1 split_data.py
import os
import glob
import json
import shutil
import numpy as np
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
img_train = './images/train/'
img_val = './images/valid/'
label_train = './labels/train/'
label_val = './labels/valid/'
allimgs = glob.glob('mydatasets/train/' + "/*.jpg")
allimgs = np.sort(allimgs)
np.random.seed(100)
np.random.shuffle(allimgs)
train_ratio = 0.9
train_num = int(len(allimgs) * train_ratio)
# 得到训练和验证数据集列表
img_list_train = allimgs[:train_num]
img_list_val = allimgs[train_num:]
# 创建文件夹
if os.path.exists(img_train):
shutil.rmtree(img_train)
os.mkdir(img_train)
else:
os.mkdir(img_train)
if os.path.exists(img_val):
shutil.rmtree(img_val)
os.mkdir(img_val)
else:
os.mkdir(img_val)
if os.path.exists(label_train):
shutil.rmtree(label_train)
os.mkdir(label_train)
else:
os.mkdir(label_train)
if os.path.exists(label_val):
shutil.rmtree(label_val)
os.mkdir(label_val)
else:
os.mkdir(label_val)
# 移动val数据到指定位置
for i in img_list_val:
print(i.split('.')[0].split('/')[1][6:])
img_id = i.split('.')[0].split('/')[1][6:]
print(img_id)
# jpg
shutil.copy(i, img_val + img_id + '.jpg')
# xml
shutil.copy('mydatasets/label/' + 'new_' + img_id + '.xml', label_val + img_id + '.xml')
# 移动train数据到指定位置
for i in img_list_train:
img_id = i.split('.')[0].split('/')[1][6:]
print(img_id)
# jpg
shutil.copy(i, img_train + img_id + '.jpg')
# xml
shutil.copy('mydatasets/label/' + 'new_' + img_id + '.xml', label_train + img_id + '.xml')
4.2 xml2txt.py
yolo的标签格式是txt格式,所以我们还需将xml标签转为txt格式。先新建txt_train、txt_valid文件夹,用于存放转换后的txt标签文件。
注意:
- 第一次运行xml2txt.py,得到训练集的txt文件,再修改/labels/train/为/labels/valid/,得到验证集的txt文件。
- 转换完成后将原来的train,valid文件夹删除,并将txt_train,txt_valid文件夹重命名为train,valid。
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
import pickle
import os
from os import listdir, getcwd
from os.path import join
import bs4
from PIL import Image
classes = ["knife","scissors","lighter","zippooil",
"pressure","slingshot","handcuffs","nailpolish",
"powerbank","firecrackers"] #为了获得cls id
def convert(size, box):
dw = 1. / (size[0])
dh = 1. / (size[1])
x = (box[0] + box[1]) / 2.0 - 1
y = (box[2] + box[3]) / 2.0 - 1
w = box[1] - box[0]
h = box[3] - box[2]
x = x * dw
w = w * dw
y = y * dh
h = h * dh
return (x, y, w, h)
def convert_annotation(image_id):
global none_counts
# 输入文件xml
in_file = open('./labels/train/%s.xml' % (image_id))
# 输出label txt
out_file = open('./labels/train/%s.txt' % (image_id), 'w')
tree = ET.parse(in_file)
root = tree.getroot()
size = root.find('size')
print(image_id)
w = int(size.find('width').text)
h = int(size.find('height').text)
for obj in root.iter('object'):
cls = obj.find('name').text
if cls not in classes:
continue
cls_id = classes.index(cls)
xmlbox = obj.find('bndbox')
b = (float(xmlbox.find('xmin').text), float(xmlbox.find('xmax').text), float(xmlbox.find('ymin').text),
float(xmlbox.find('ymax').text))
bb = convert((w, h), b)
out_file.write(str(cls_id) + " " + " ".join([str(a) for a in bb]) + '\n')
if __name__=='__main__':
xml_count = 0
none_counts = 0
list_file = os.listdir('./labels/train/')
for file in list_file:
print(file)
# image_id = file.replace('.xml', '')
image_id = file.split('.')[0]
convert_annotation(image_id)
xml_count = xml_count + 1
print('没有size字段的xml文件数目:{}'.format(none_counts))
print('总xml个数是 {}'.format(xml_count))
4.3 creattxt.py
这一步需要生成train.txt和valid.txt
# 根据训练数据集和验证数据集persontrain.txt and personvalid.txt
import os, random, shutil
trainDir = 'images/train/'
validDir = 'images/valid/'
train_pathDir = os.listdir(trainDir) # 取图片的原始路径
print('训练集图片数目: {}'.format(len(train_pathDir)))
valid_pathDir = os.listdir(validDir) # 取图片的原始路径
print('验证集图片数目: {}'.format(len(valid_pathDir)))
# 删除persontrain.txt and personvalid.txt
if(os.path.exists('train.txt')):
os.remove('train.txt')
print('删除train.txt成功')
if(os.path.exists('valid.txt')):
os.remove('valid.txt')
print('删除valid.txt成功')
def text_save(root, filename, data): # filename为写入CSV文件的路径,data为要写入数据列表.
file = open(filename, 'a')
for i in range(len(data)):
s = str(data[i]).replace('[', '').replace(']', '') # 去除[],这两行按数据不同,可以选择
s = 'data/' + root + s.replace("'", '').replace(',', '') + '\n' # 去除单引号,逗号,每行末尾追加换行符
file.write(s)
file.close()
print("保存文件成功")
if __name__ == '__main__':
text_save(trainDir, './train.txt', train_pathDir)
text_save(validDir, './valid.txt', valid_pathDir)
print('train.txt 有 {} 行'.format(len([i for i in open('./train.txt', 'r')])))
print('valid.txt 有 {} 行'.format(len([i for i in open('./valid.txt', 'r')])))
得到的txt文件格式部分内容如下:
data/images/train/1.jpg
data/images/train/10.jpg
data/images/train/1000.jpg
data/images/train/1001.jpg
data/images/train/1002.jpg
data/images/train/1005.jpg
data/images/train/1006.jpg
data/images/train/1007.jpg
data/images/train/1008.jpg
data/images/train/1009.jpg
data/images/train/101.jpg
data/images/train/1010.jpg
data/images/train/1011.jpg
data/images/train/1012.jpg
data/images/train/1015.jpg
data/images/train/1018.jpg
data/images/train/1019.jpg
五、训练
完成上述步骤后即可训练,在train.py下运行
if __name__ == '__main__':
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument('--epochs', type=int, default=300) # 500200 batches at bs 16, 117263 COCO images = 273 epochs
parser.add_argument('--batch-size', type=int, default=16) # effective bs = batch_size * accumulate = 16 * 4 = 64
parser.add_argument('--cfg', type=str, default='cfg/yolov4-mydatasets.cfg', help='*.cfg path')
parser.add_argument('--data', type=str, default='data/mydatasets.data', help='*.data path')
parser.add_argument('--multi-scale', action='store_true', help='adjust (67%% - 150%%) img_size every 10 batches')
parser.add_argument('--img-size', nargs='+', type=int, default=[320, 640], help='[min_train, max-train, test]')
parser.add_argument('--rect', action='store_true', help='rectangular training')
parser.add_argument('--resume', action='store_true', help='resume training from last.pt')
parser.add_argument('--nosave', action='store_true', help='only save final checkpoint')
parser.add_argument('--notest', action='store_true', help='only test final epoch')
parser.add_argument('--evolve', action='store_true', help='evolve hyperparameters')
parser.add_argument('--bucket', type=str, default='', help='gsutil bucket')
parser.add_argument('--cache-images', action='store_true', help='cache images for faster training')
parser.add_argument('--weights', type=str, default='weights/yolov4.weights', help='initial weights path')
parser.add_argument('--name', default='', help='renames results.txt to results_name.txt if supplied')
parser.add_argument('--device', default='', help='device id (i.e. 0 or 0,1 or cpu)')
parser.add_argument('--adam', action='store_true', help='use adam optimizer')
parser.add_argument('--single-cls', action='store_true', help='train as single-class dataset')
opt = parser.parse_args()
opt.weights = last if opt.resume else opt.weights
check_git_status()
print(opt)
六、推理
运行detect.py
import argparse
from models import * # set ONNX_EXPORT in models.py
from utils.datasets import *
from utils.utils import *
def detect(save_img=False):
img_size = (320, 192) if ONNX_EXPORT else opt.img_size # (320, 192) or (416, 256) or (608, 352) for (height, width)
out, source, weights, half, view_img, save_txt = opt.output, opt.source, opt.weights, opt.half, opt.view_img, opt.save_txt
webcam = source == '0' or source.startswith('rtsp') or source.startswith('http') or source.endswith('.txt')
# Initialize
device = torch_utils.select_device(device='cpu' if ONNX_EXPORT else opt.device)
if os.path.exists(out):
shutil.rmtree(out) # delete output folder
os.makedirs(out) # make new output folder
# Initialize model
model = Darknet(opt.cfg, img_size)
# Load weights
attempt_download(weights)
if weights.endswith('.pt'): # pytorch format
model.load_state_dict(torch.load(weights, map_location=device)['model'])
else: # darknet format
load_darknet_weights(model, weights)
# Second-stage classifier
classify = False
if classify:
modelc = torch_utils.load_classifier(name='resnet101', n=2) # initialize
modelc.load_state_dict(torch.load('weights/resnet101.pt', map_location=device)['model']) # load weights
modelc.to(device).eval()
# Eval mode
model.to(device).eval()
# Fuse Conv2d + BatchNorm2d layers
# model.fuse()
# Export mode
if ONNX_EXPORT:
model.fuse()
img = torch.zeros((1, 3) + img_size) # (1, 3, 320, 192)
f = opt.weights.replace(opt.weights.split('.')[-1], 'onnx') # *.onnx filename
torch.onnx.export(model, img, f, verbose=False, opset_version=11,
input_names=['images'], output_names=['classes', 'boxes'])
# Validate exported model
import onnx
model = onnx.load(f) # Load the ONNX model
onnx.checker.check_model(model) # Check that the IR is well formed
print(onnx.helper.printable_graph(model.graph)) # Print a human readable representation of the graph
return
# Half precision
half = half and device.type != 'cpu' # half precision only supported on CUDA
if half:
model.half()
# Set Dataloader
vid_path, vid_writer = None, None
if webcam:
view_img = True
torch.backends.cudnn.benchmark = True # set True to speed up constant image size inference
dataset = LoadStreams(source, img_size=img_size)
else:
save_img = True
dataset = LoadImages(source, img_size=img_size)
# Get names and colors
names = load_classes(opt.names)
colors = [[random.randint(0, 255) for _ in range(3)] for _ in range(len(names))]
# Run inference
t0 = time.time()
img = torch.zeros((1, 3, img_size, img_size), device=device) # init img
_ = model(img.half() if half else img.float()) if device.type != 'cpu' else None # run once
for path, img, im0s, vid_cap in dataset:
img = torch.from_numpy(img).to(device)
img = img.half() if half else img.float() # uint8 to fp16/32
img /= 255.0 # 0 - 255 to 0.0 - 1.0
if img.ndimension() == 3:
img = img.unsqueeze(0)
# Inference
t1 = torch_utils.time_synchronized()
pred = model(img, augment=opt.augment)[0]
t2 = torch_utils.time_synchronized()
# to float
if half:
pred = pred.float()
# Apply NMS
pred = non_max_suppression(pred, opt.conf_thres, opt.iou_thres,
multi_label=False, classes=opt.classes, agnostic=opt.agnostic_nms)
# Apply Classifier
if classify:
pred = apply_classifier(pred, modelc, img, im0s)
# Process detections
for i, det in enumerate(pred): # detections per image
if webcam: # batch_size >= 1
p, s, im0 = path[i], '%g: ' % i, im0s[i]
else:
p, s, im0 = path, '', im0s
save_path = str(Path(out) / Path(p).name)
s += '%gx%g ' % img.shape[2:] # print string
if det is not None and len(det):
# Rescale boxes from img_size to im0 size
det[:, :4] = scale_coords(img.shape[2:], det[:, :4], im0.shape).round()
# Print results
for c in det[:, -1].unique():
n = (det[:, -1] == c).sum() # detections per class
s += '%g %ss, ' % (n, names[int(c)]) # add to string
# Write results
for *xyxy, conf, cls in det:
if save_txt: # Write to file
with open(save_path + '.txt', 'a') as file:
file.write(('%g ' * 6 + '\n') % (*xyxy, cls, conf))
if save_img or view_img: # Add bbox to image
label = '%s %.2f' % (names[int(cls)], conf)
plot_one_box(xyxy, im0, label=label, color=colors[int(cls)])
# Print time (inference + NMS)
print('%sDone. (%.3fs)' % (s, t2 - t1))
# Stream results
if view_img:
cv2.imshow(p, im0)
if cv2.waitKey(1) == ord('q'): # q to quit
raise StopIteration
# Save results (image with detections)
if save_img:
if dataset.mode == 'images':
cv2.imwrite(save_path, im0)
else:
if vid_path != save_path: # new video
vid_path = save_path
if isinstance(vid_writer, cv2.VideoWriter):
vid_writer.release() # release previous video writer
fps = vid_cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FPS)
w = int(vid_cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_WIDTH))
h = int(vid_cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_HEIGHT))
vid_writer = cv2.VideoWriter(save_path, cv2.VideoWriter_fourcc(*opt.fourcc), fps, (w, h))
vid_writer.write(im0)
if save_txt or save_img:
print('Results saved to %s' % os.getcwd() + os.sep + out)
if platform == 'darwin': # MacOS
os.system('open ' + save_path)
print('Done. (%.3fs)' % (time.time() - t0))
if __name__ == '__main__':
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument('--cfg', type=str, default='cfg/yolov4-mydatasets.cfg', help='*.cfg path')
parser.add_argument('--names', type=str, default='data/mydatasets.names', help='*.names path')
parser.add_argument('--weights', type=str, default='weights/best.pt', help='weights path')
parser.add_argument('--source', type=str, default='img', help='source') # input file/folder, 0 for webcam
parser.add_argument('--output', type=str, default='output', help='output folder') # output folder
parser.add_argument('--img-size', type=int, default=512, help='inference size (pixels)')
parser.add_argument('--conf-thres', type=float, default=0.3, help='object confidence threshold')
parser.add_argument('--iou-thres', type=float, default=0.6, help='IOU threshold for NMS')
parser.add_argument('--fourcc', type=str, default='mp4v', help='output video codec (verify ffmpeg support)')
parser.add_argument('--half', action='store_true', help='half precision FP16 inference')
parser.add_argument('--device', default='', help='device id (i.e. 0 or 0,1) or cpu')
parser.add_argument('--view-img', action='store_true', help='display results')
parser.add_argument('--save-txt', action='store_true', help='save results to *.txt')
parser.add_argument('--classes', nargs='+', type=int, help='filter by class')
parser.add_argument('--agnostic-nms', action='store_true', help='class-agnostic NMS')
parser.add_argument('--augment', action='store_true', help='augmented inference')
opt = parser.parse_args()
print(opt)
with torch.no_grad():
detect()