Python 编译阶段 -- 从 CST 到 AST
CST TO AST
以后都在 github 更新,请戳 CST 到 AST
目录
- 相关位置文件
- pythonrun
- CST 到 AST
- 更多资料
相关位置文件
- Python/ast.c
- Python/pythonrun.c
- Include/Python-ast.h
- Python/Python-ast.c
- Python/asdl.c
- Include/asdl.h
下面的命令会从 Parser/Python.asdl 中生成 Include/Python-ast.h 和 Python/Python-ast.c, 这两个自动生成的文件的结构体会被用来从之前的 语法树 中生成 AST
% make regen-ast
# Regenerate Include/Python-ast.h using Parser/asdl_c.py -h
./install-sh -c -d ./Include
python3 ./Parser/asdl_c.py \
-h ./Include/Python-ast.h.new \
./Parser/Python.asdl
python3 ./Tools/scripts/update_file.py ./Include/Python-ast.h ./Include/Python-ast.h.new
# Regenerate Python/Python-ast.c using Parser/asdl_c.py -c
./install-sh -c -d ./Python
python3 ./Parser/asdl_c.py \
-c ./Python/Python-ast.c.new \
./Parser/Python.asdl
python3 ./Tools/scripts/update_file.py ./Python/Python-ast.c ./Python/Python-ast.c.new
- 小写名称是 non-terminals.
- 大写名称是 terminals
- 文本 tokens 用双引号引起来
[]表示 >= 0 个{}表示 >= 1 个?表示可能有可能没有,*表示 >= 0 个
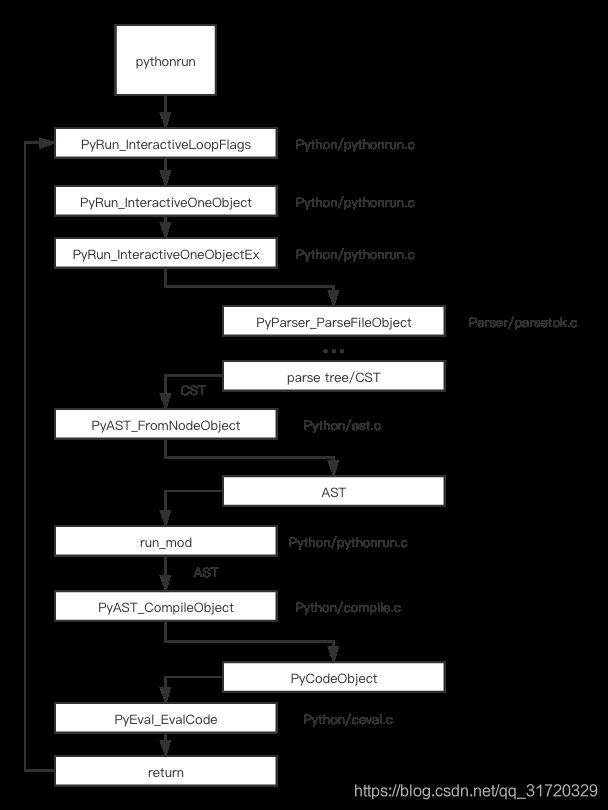
pythonrun
我们以交互式循环为例, 展开 pythonrun 的调用栈看看
CST 到 AST
我们把关注点放到 PyAST_FromNodeObject 上
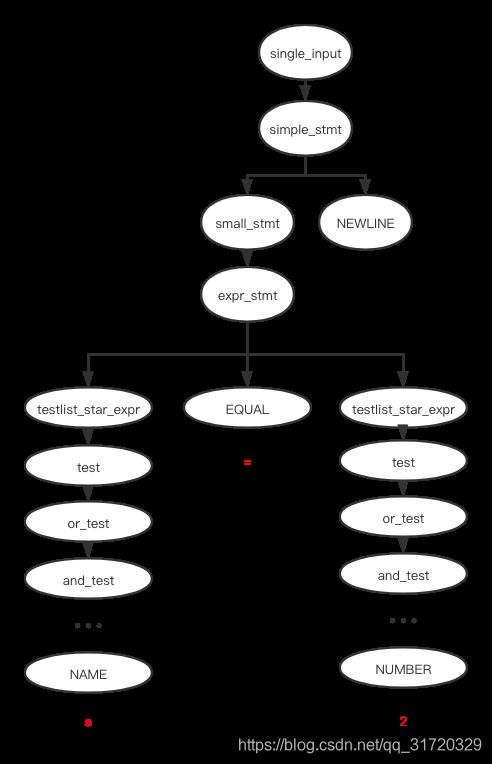
如果我们执行
a = 2
这是上述语句生成的 CST 结构
n_type: 256, n_type_str: single_input, n_str: (null), n_children: 1
n_type: 270, n_type_str: simple_stmt, n_str: (null), n_children: 2
n_type: 271, n_type_str: small_stmt, n_str: (null), n_children: 1
n_type: 272, n_type_str: expr_stmt, n_str: (null), n_children: 3
n_type: 274, n_type_str: testlist_star_expr, n_str: (null), n_children: 1
n_type: 305, n_type_str: test, n_str: (null), n_children: 1
n_type: 309, n_type_str: or_test, n_str: (null), n_children: 1
n_type: 310, n_type_str: and_test, n_str: (null), n_children: 1
n_type: 311, n_type_str: not_test, n_str: (null), n_children: 1
n_type: 312, n_type_str: comparison, n_str: (null), n_children: 1
n_type: 315, n_type_str: expr, n_str: (null), n_children: 1
n_type: 316, n_type_str: xor_expr, n_str: (null), n_children: 1
n_type: 317, n_type_str: and_expr, n_str: (null), n_children: 1
n_type: 318, n_type_str: shift_expr, n_str: (null), n_children: 1
n_type: 319, n_type_str: arith_expr, n_str: (null), n_children: 1
n_type: 320, n_type_str: term, n_str: (null), n_children: 1
n_type: 321, n_type_str: factor, n_str: (null), n_children: 1
n_type: 322, n_type_str: power, n_str: (null), n_children: 1
n_type: 323, n_type_str: atom_expr, n_str: (null), n_children: 1
n_type: 324, n_type_str: atom, n_str: (null), n_children: 1
n_type: 1, n_type_str: NAME, n_str: a, n_children: 0
n_type: 22, n_type_str: EQUAL, n_str: =, n_children: 0
n_type: 274, n_type_str: testlist_star_expr, n_str: (null), n_children: 1
n_type: 305, n_type_str: test, n_str: (null), n_children: 1
n_type: 309, n_type_str: or_test, n_str: (null), n_children: 1
n_type: 310, n_type_str: and_test, n_str: (null), n_children: 1
n_type: 311, n_type_str: not_test, n_str: (null), n_children: 1
n_type: 312, n_type_str: comparison, n_str: (null), n_children: 1
n_type: 315, n_type_str: expr, n_str: (null), n_children: 1
n_type: 316, n_type_str: xor_expr, n_str: (null), n_children: 1
n_type: 317, n_type_str: and_expr, n_str: (null), n_children: 1
n_type: 318, n_type_str: shift_expr, n_str: (null), n_children: 1
n_type: 319, n_type_str: arith_expr, n_str: (null), n_children: 1
n_type: 320, n_type_str: term, n_str: (null), n_children: 1
n_type: 321, n_type_str: factor, n_str: (null), n_children: 1
n_type: 322, n_type_str: power, n_str: (null), n_children: 1
n_type: 323, n_type_str: atom_expr, n_str: (null), n_children: 1
n_type: 324, n_type_str: atom, n_str: (null), n_children: 1
n_type: 2, n_type_str: NUMBER, n_str: 2, n_children: 0
n_type: 4, n_type_str: NEWLINE, n_str: , n_children: 0
图像表示的话如下, 你可以参数 Grammar/Grammar 语法文件
CST 到 AST 的转换部分是在 Python/ast.c 中写好的, 这个文件中对应的转换函数都是根据语法规则去进行对应的处理, 返回结构比如 expr_ty 则是上述自动生成的 C 文件生成的
// in Python/ast.c
static expr_ty
ast_for_atom(struct compiling *c, const node *n)
{
/* atom: '(' [yield_expr|testlist_comp] ')' | '[' [testlist_comp] ']'
| '{' [dictmaker|testlist_comp] '}' | NAME | NUMBER | STRING+
| '...' | 'None' | 'True' | 'False'
*/
node *ch = CHILD(n, 0);
switch (TYPE(ch)) {
case NAME: {
PyObject *name;
const char *s = STR(ch);
size_t len = strlen(s);
if (len >= 4 && len <= 5) {
if (!strcmp(s, "None"))
return Constant(Py_None, LINENO(n), n->n_col_offset, c->c_arena);
if (!strcmp(s, "True"))
return Constant(Py_True, LINENO(n), n->n_col_offset, c->c_arena);
if (!strcmp(s, "False"))
return Constant(Py_False, LINENO(n), n->n_col_offset, c->c_arena);
}
name = new_identifier(s, c);
if (!name)
return NULL;
/* All names start in Load context, but may later be changed. */
return Name(name, Load, LINENO(n), n->n_col_offset, c->c_arena);
}
// ...
case NUMBER: {
PyObject *pynum = parsenumber(c, STR(ch));
if (!pynum)
return NULL;
if (PyArena_AddPyObject(c->c_arena, pynum) < 0) {
Py_DECREF(pynum);
return NULL;
}
return Constant(pynum, LINENO(n), n->n_col_offset, c->c_arena);
}
// ...
default:
PyErr_Format(PyExc_SystemError, "unhandled atom %d", TYPE(ch));
return NULL;
}
}
Name 和 Load 在 Python/Python-ast.c 中定义好了
// Python/Python-ast.c
expr_ty
Name(identifier id, expr_context_ty ctx, int lineno, int col_offset, PyArena
*arena)
{
expr_ty p;
/* ... */
p->kind = Name_kind;
p->v.Name.id = id;
p->v.Name.ctx = ctx;
p->lineno = lineno;
p->col_offset = col_offset;
return p;
}
// Include/Python-ast.h
typedef enum _expr_context { Load=1, Store=2, Del=3, AugLoad=4, AugStore=5,
Param=6 } expr_context_ty;
// ...
typedef struct _expr *expr_ty;
_Py_asdl_seq_new 在 Python/asdl.c 中定义好了, 而 asdl_seq_SET 在 Include/asdl.h 中定义好了
// Python/ast.c
ast_for_global_stmt(struct compiling *c, const node *n)
{
/* global_stmt: 'global' NAME (',' NAME)* */
identifier name;
asdl_seq *s;
int i;
REQ(n, global_stmt);
s = _Py_asdl_seq_new(NCH(n) / 2, c->c_arena);
if (!s)
return NULL;
for (i = 1; i < NCH(n); i += 2) {
name = NEW_IDENTIFIER(CHILD(n, i));
if (!name)
return NULL;
asdl_seq_SET(s, i / 2, name);
}
return Global(s, LINENO(n), n->n_col_offset, c->c_arena);
}
// Include/asdl.h
typedef struct {
Py_ssize_t size;
void *elements[1];
} asdl_seq;
// ...
#define asdl_seq_SET(S, I, V) (S)->elements[I] = (V)
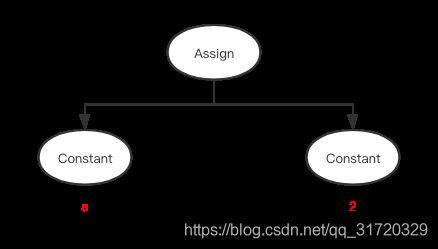
这是转换后的 AST 结构
这里的 函数 可以用来打印上述 AST 的结构内容
更多资料
- using-asdl-to-describe-asts-in-compilers
- What is Zephyr ASDL
- Python’s compiler - from CST to AST
- Design of CPython’s Compiler