stanford cs144 networks lab 0 networking warmup
文章目录
- Networking by hand
- Fetch a Web page
- Listening and connecting
- Writing a network program using an OS stream socket
- Let’s get started—fetching and building the starter code
- Modern C++: mostly safe but still fast and low-level
- Reading the Sponge documentation
- FileDescriptor
- Socket
- TCPSocket
- Address
- `file_descriptor.hh`
- `socket.hh`
- `address.hh`
- Writing webget \verb|webget| webget
- An in-memory reliable byte stream
Networking by hand
Fetch a Web page
在虚拟机上运行 telnet cs144.keithw.org http ,这句话的意思是让 telnet 程序在你的计算机和另外一个计算机(名字叫 cs144.keithw.org)之间建立一个可靠的字节流连接,并且该计算机上运行着特定的服务:http (Hyper-Text Transfer Protocol 超文本传输服务)
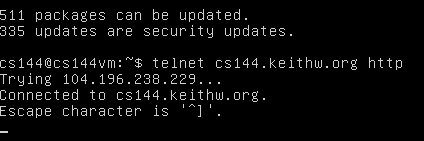
键入 GET /hello HTTP/1.1 ,这句话告诉服务器 URL 的路径(path)
键入 Host: cs144.keithw.org 这告诉服务器 URL 的主机(host)
然后再敲一次回车,则这个 HTTP 请求就会被发出。
效果如下:

这等价于获取网页 http://cs144.keithw.org/hello 的信息
Listening and connecting
现在我们已经知道 telnet 可以作为客户端程序,现在可以试一下服务器端:可以等待用户连接。
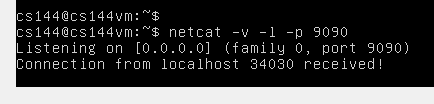
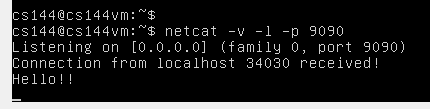
运行:netcat -v -l -p 9090 ( netcat 是一个能够读写TCP、UDP连接的工具, -v 是 verbose ,显示详细信息,-l 表示 listen,是在监听是否有客户端连接,-p 指的是监听端口)
效果如下:

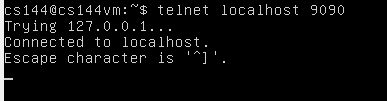
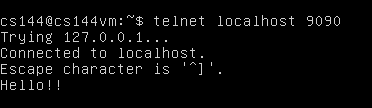
打开另一个终端,运行 telnet localhost 9090
Writing a network program using an OS stream socket
下面来写一个程序来读一个网页,用的是操作系统提供的 stream socket ,这个 socket 看起来就像一个普通的文件描述子(和磁盘上的文件相似,也和 stdin,stdout 相似)当两个 stream sockets 连接起来时,写到其中一个 socket 中的字节会以相同的顺序从另一个 socket 中出来。
但是现实里因特网并不提供一个可靠的字节传输,Internet 做的事情叫做尽最大可能(best effort)地向目的地交付短数据,叫做 Internet datagrams 。每个数据报文都包含一些元信息(headers),指定了源地址和目标地址,以及一些净荷载(payload)(最大约为 1500 字节)。
尽管网络尽可能地去发所有地报文,但是这些报文会:
- 丢失
- 失序
- 出错
- 重复
通常是由源和目标处地计算机操作系统来将这些“尽可能”交付地报文转化为“可靠的字节流传输”。
两个计算机必须共同协作来确保流中的每个字节都最终能够按照顺序交付。并且他们要告诉彼此自己准备接收的数据大小,这些是通过 1981 年建立的 Transmission Control Protocol (TCP)来实现的。
Let’s get started—fetching and building the starter code
首先 git clone https://github.com/cs144/sponge ,假如慢的话可以先把仓库移到 gitee.com 上,然后再 clone。注意 cs144 提供的虚拟机是可以通过 ssh -p 2222 cs144@localhost 从外面连上的,配合 xshell 这类的工具,用起来不要太爽hhh
然后是一系列的命令:
Modern C++: mostly safe but still fast and low-level
作业主要用的是现代的 C++ 风格,参考 http://isocpp.github.io/CppCoreGuidelines/CppCoreGuidelines
其基础思想是使每一个对象都有尽可能少的公有接口(public interface),其内部有很多安全检查,使得很难被误用,并且能够自己释放资源(而不是需要成对的 malloc/free,new/delete)
这种风格叫做:“Resource acquisition is initialization” (RAII,资源获取即为初始化 )
Reading the Sponge documentation
https://cs144.github.io/doc/lab0
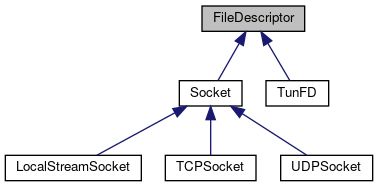
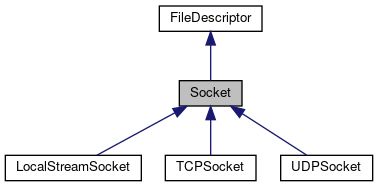
其中 Socket 是一种 FileDescriptor,TCPSocket 是一种 Socket
FileDescriptor
这个类是一个 reference-count handle to a file descriptor
继承关系:
Socket
这是网络 socket(TCP,UDP,…) 的基类,继承关系如下:
TCPSocket
是 TCP socket 的一个 wrapper ,继承关系如下:
Address
Wrapper around IPv4 addresses and DNS operations.
Inside libsponge/util :
file_descriptor.hh
#ifndef SPONGE_LIBSPONGE_FILE_DESCRIPTOR_HH
#define SPONGE_LIBSPONGE_FILE_DESCRIPTOR_HH
#include "buffer.hh"
#include socket.hh
#ifndef SPONGE_LIBSPONGE_SOCKET_HH
#define SPONGE_LIBSPONGE_SOCKET_HH
#include "address.hh"
#include "file_descriptor.hh"
#include address.hh
#ifndef SPONGE_LIBSPONGE_ADDRESS_HH
#define SPONGE_LIBSPONGE_ADDRESS_HH
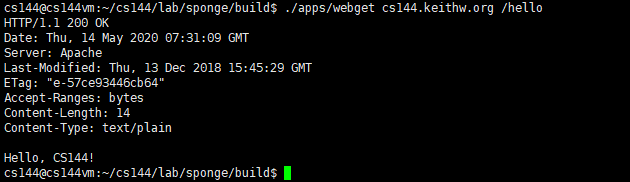
#include Writing webget \verb|webget| webget
填空的代码如下:
TCPSocket sock1{};
sock1.connect(Address(host, "http"));
sock1.write("GET "+path+" HTTP/1.1\r\nHost: "+host+"\r\n\r\n");
sock1.shutdown(SHUT_WR);
while(!sock1.eof()){
auto recvd = sock1.read();
cout << recvd ;
}
An in-memory reliable byte stream
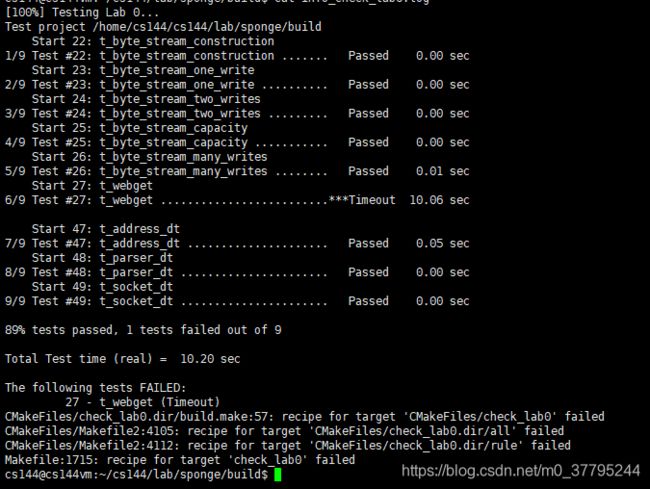
这部分的实现我出现的问题是 EOF 的判定,相关初始化以及改变以及整体代码如下:
// byte_stream.hh
#ifndef SPONGE_LIBSPONGE_BYTE_STREAM_HH
#define SPONGE_LIBSPONGE_BYTE_STREAM_HH
#include
#include // byte_stream.cc
#include "byte_stream.hh"
#include 但是有一个 test 是超时的… 我怀疑可能是测试抓取了一个墙外的网站吧。。