【8】python-opencv3教程:边缘检测(Roberts算子边缘检测,Prewitt算子边缘检测,Sobel算子边缘检测)
第八节:边缘检测
边缘检测:边缘检测指的是灰度值发生急剧变化的位置,边缘检测的目的是制作一个线图,在不会损害理解图像内容的情况下, 有大大减少了图像的数据量,提供了对图像数据的合适概述。
一:Roberts算子
代码实现:
import cv2
import numpy as np
from scipy import signal
def roberts(I, _boundary='fill', _fillvalue=0):
# 图像的高,宽
H1, W1 = I.shape[0:2]
# 卷积核的尺寸
H2, W2 = 2, 2
# 卷积核1 和 锚点的位置
R1 = np.array([[1, 0], [0, -1]], np.float32)
kr1, kc1 = 0, 0
# 计算full卷积
IconR1 = signal.convolve2d(I, R1, mode='full', boundary=_boundary, fillvalue=_fillvalue)
IconR1 = IconR1[H2-kr1-1:H1+H2-kr1-1, W2-kc1-1:W1+W2-kc1-1]
# 卷积核2 和 锚点的位置
R2 = np.array([[0, 1], [-1, 0]], np.float32)
kr2, kc2 = 0, 1
# 再计算full卷积
IconR2 = signal.convolve2d(I, R2, mode='full', boundary=_boundary, fillvalue=_fillvalue)
IconR2 = IconR2[H2-kr2-1:H1+H2-kr2-1, W2-kc2-1:W1+W2-kc2-1]
return (IconR1, IconR2)
if __name__ == '__main__':
I = cv2.imread('img3.png', cv2.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE)
# 显示原图
cv2.imshow('origin', I)
# 卷积,注意边界一般扩充采用的symm
IconR1, IconR2 = roberts(I, 'symm')
# 45度方向上的边缘强度的灰度级显示
IconR1 = np.abs(IconR1)
edge45 = IconR1.astype(np.uint8)
cv2.imshow('edge45', edge45)
# 135度方向上的边缘强度的灰度级显示
IconR2 = np.abs(IconR2)
edge135 = IconR2.astype(np.uint8)
cv2.imshow('edge135', edge135)
# 用平方和的开方来衡量最后输出的边缘
edge = np.sqrt(np.power(IconR1, 2.0) + np.power(IconR2, 2.0))
edge = np.round(edge)
edge[edge > 255] = 255
edge = edge.astype(np.uint8)
# 显示边缘
cv2.imshow('edge', edge)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
输出结果:
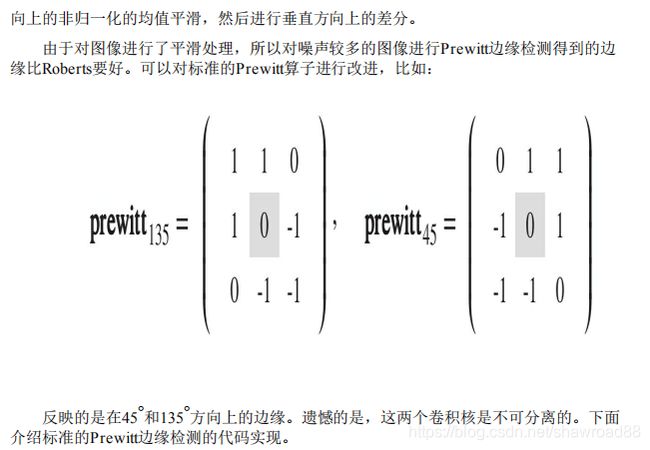
二: Prewitt边缘检测
代码实现:
import cv2
import numpy as np
from scipy import signal
def prewitt(I, _boundary = 'symm', ):
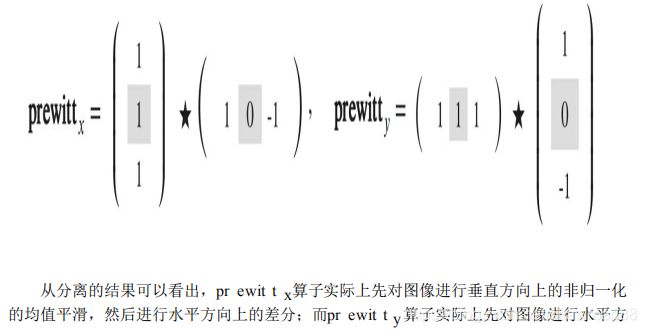
# prewitt算子是可分离的。 根据卷积运算的结合律,分两次小卷积核运算
# 算子分为两部分,这是对第一部分操作
# 1: 垂直方向上的均值平滑
ones_y = np.array([[1], [1], [1]], np.float32)
i_conv_pre_x = signal.convolve2d(I, ones_y, mode='same', boundary=_boundary)
# 2: 水平方向上的差分
diff_x = np.array([[1, 0, -1]], np.float32)
i_conv_pre_x = signal.convolve2d(i_conv_pre_x, diff_x, mode='same', boundary=_boundary)
# 算子分为两部分,这是对第二部分操作
# 1: 水平方向上的均值平滑
ones_x = np.array([[1, 1, 1]], np.float32)
i_conv_pre_y = signal.convolve2d(I, ones_x, mode='same', boundary=_boundary)
# 2: 垂直方向上的差分
diff_y = np.array([[1], [0], [-1]], np.float32)
i_conv_pre_y = signal.convolve2d(i_conv_pre_y, diff_y, mode='same', boundary=_boundary)
return (i_conv_pre_x, i_conv_pre_y)
if __name__ == '__main__':
I = cv2.imread('img7.jpg', cv2.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE)
cv2.imshow('origin', I)
i_conv_pre_x, i_conv_pre_y = prewitt(I)
# 取绝对值,分别得到水平方向和垂直方向的边缘强度
abs_i_conv_pre_x = np.abs(i_conv_pre_x)
abs_i_conv_pre_y = np.abs(i_conv_pre_y)
# 水平方向和垂直方向上的边缘强度的灰度级显示
edge_x = abs_i_conv_pre_x.copy()
edge_y = abs_i_conv_pre_y.copy()
# 将大于255的值截断为255
edge_x[edge_x > 255] = 255
edge_y[edge_y > 255] = 255
# 数据类型转换
edge_x = edge_x.astype(np.uint8)
edge_y = edge_y.astype(np.uint8)
# 显示
cv2.imshow('edge_x', edge_x)
cv2.imshow('edge_y', edge_y)
# 利用abs_i_conv_pre_x 和 abs_i_conv_pre_y 求最终的边缘强度
# 求边缘强度有多重方法, 这里使用的是插值法
edge = 0.5 * abs_i_conv_pre_x + 0.5 * abs_i_conv_pre_y
# 边缘强度灰度级显示
edge[edge > 255] = 255
edge = edge.astype(np.uint8)
cv2.imshow('edge', edge)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()输出结果:
三:Sobel边缘检测
代码实现:
import math
import cv2
import numpy as np
from scipy import signal
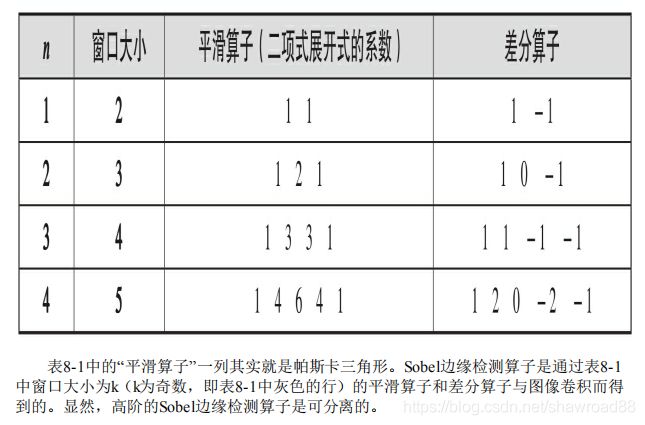
def pascalSmooth(n):
# 返回n阶的非归一化的高斯平滑算子
pascalSmooth = np.zeros([1, n], np.float32)
for i in range(n):
pascalSmooth[0][i] = math.factorial(n - 1) / (math.factorial(i) * math.factorial(n-1-i))
return pascalSmooth
def pascalDiff(n): # 在一半之前是逐差法。。后半部分的值和前半部分对应
# 返回n阶差分算子
pascalDiff = np.zeros([1, n], np.float32)
pascalSmooth_previous = pascalSmooth(n - 1)
for i in range(n):
if i == 0:
# 恒等于1
pascalDiff[0][i] = pascalSmooth_previous[0][i]
elif i == n-1:
pascalDiff[0][i] = pascalSmooth_previous[0][i-1]
else:
pascalDiff[0][i] = pascalSmooth_previous[0][i] - pascalSmooth_previous[0][i-1]
return pascalDiff
def getSmoothKernel(n):
# 返回两个sobel算子
pascalSmoothKernel = pascalSmooth(n)
pascalDiffKernel = pascalDiff(n)
# 水平方向上的卷积核
sobelKernel_x = signal.convolve2d(pascalSmoothKernel.transpose(), pascalDiffKernel, mode='full')
# 垂直方向上的卷积核
sobelKernel_y = signal.convolve2d(pascalSmoothKernel, pascalDiffKernel.transpose(), mode='full')
return (sobelKernel_x, sobelKernel_y)
def sobel(image, n):
rows, cols = image.shape
# 得到平滑算子
pascalSmoothKernel = pascalSmooth(n)
# 得到差分算子
pascalDiffKernel = pascalDiff(n)
# 与水平方向的sobel核卷积
# 先进行垂直方向的平滑
image_sobel_x = signal.convolve2d(image, pascalSmoothKernel.transpose(), mode='same')
# 再进行水平方向的差分
image_sobel_x = signal.convolve2d(image_sobel_x, pascalDiffKernel, mode='same')
# 与垂直方向的sobel核卷积
# 先进行水平方向的平滑
image_sobel_y = signal.convolve2d(image, pascalSmoothKernel, mode='same')
image_sobel_y = signal.convolve2d(image_sobel_y, pascalDiffKernel.transpose(), mode='same')
return (image_sobel_x, image_sobel_y)
if __name__ == '__main__':
I = cv2.imread('img7.jpg', cv2.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE)
cv2.imshow('origin', I)
# 卷积
image_sobel_x, image_sobel_y = sobel(I, 7)
# cv2.imshow('image_sobel_x', image_sobel_x)
# cv2.imshow('image_sobel_y', image_sobel_y)
# 平方和的方式展开
edge = np.sqrt(np.power(image_sobel_x, 2.0) + np.power(image_sobel_y, 2.0))
# 边缘强度的灰度级显示
edge = edge / np.max(edge)
edge = np.power(edge, 1)
edge = edge * 255
edge = edge.astype(np.uint8)
cv2.imshow('edge', edge)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
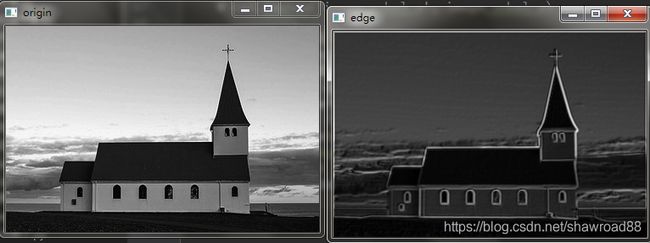
输出结果:
后面出一节,狂调API。。。无需实现这些算法,只需知道在opencv中怎么调用。