入门Struts1第一讲——Struts1入门就这么简单
现在终于进入框架的学习中了,后面还有好几个框架等待着我们呢!我们先来学习Struts1框架,然后再过渡到Struts2框架的学习中。下面我们开始学习Struts1框架之旅。
Struts1简介
Struts1是Apache开发的一个web层的框架,它主要用于简化web层的开发,Struts1针对web层的一些常用操作,例如:
- 表单数据的封装、校验和数据的回显;
- 国际化开发;
- 文件上传;
- 异常处理;
- 等等…
Struts1都提供了相应的简化,因此,很多web开发人员都会选用Struts1进行web开发。我们不禁就要问,Struts1是如何做到简化web层开发的呢?传统方式上都是在Servlet中编写请求处理代码,如下图:
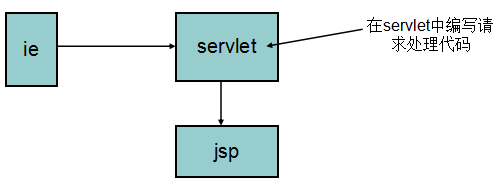
学了Struts1之后,是在Action中编写请求处理代码,为什么这样做呢?因为Struts1作者帮我们写好了一个ActionServlet,他写这个Servlet的目的是希望所有请求都交给它预处理,它预处理完后,再调用你写的Action处理请求。当然,Struts1的ActionServlet在对请求进行预处理时,会帮我们做好一些基础性的工作,我们编写Action处理请求时,就可以省去一些编码量了,从而简化开发。如下图:

学了Struts1框架时,初学者需要明确的几个问题:
- Struts1只是一个web层的框架,它用于规范并简化web层的开发,它是对Servlet、JSP等web开发技术的封装。在开发中大家遇到问题,如果发现Struts1不给力,照样可以使用web技术解决,两种技术混用不会有任何问题;
- web基础最重要;
- Struts1只是一个web层的框架,它只是用于解决web层的问题,千万不要想着用Struts1去操纵数据库。
Struts1开发快速入门
现在以一个我们常见的用户注册案例来快速入门Struts1。首先,编写register.jsp注册页面,表单提交给register.do处理。register.jsp页面内容如下:
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8"
pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8">
<title>用户注册页面title>
head>
<body>
<form action="${pageContext.request.contextPath }/register.do" method="post">
用户名:<input type="text" name="username" /><br/>
密码:<input type="password" name="password" /><br/>
电子邮箱:<input type="text" name="email" /><br/>
<input type="submit" value="注册" />
form>
body>
html>
温馨提示:Struts1框架规定了若是提交请求,请求应交给xxx.do去处理,大家只须记住即可,不要问为何,因为我也不知道。
然后,用户填写完注册信息,点击注册按钮,请求就要交给Struts1去处理,这时需要在web工程中导入Struts1开发包。那我们怎么知道要导入哪些jar包呢?可以在struts-1.3.8-all\struts-1.3.8\lib目录下查找到我们所需的Struts1开发包,如下图:
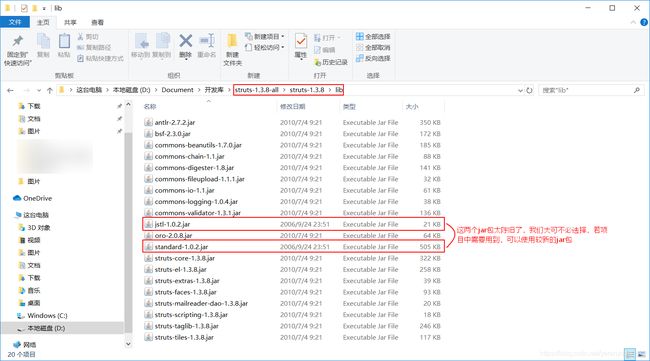
从lib目录中我们可以看到,Struts1开发所需的jar包,有些是我们非常熟悉的,比如:
- commons-beanutils-1.7.0.jar
- commons-fileupload-1.1.1.jar
- commons-io-1.1.jar
- commons-logging-1.0.4.jar
只不过是这些jar包的版本比较低而已,但是如下的两个jar包由于版本太低了,我们遗弃了。
- jstl-1.0.2.jar
- standard-1.0.2.jar
若要是项目中需要使用到JSTL标签,可以使用较新的jar包。那这样,在lib目录下,除了以上两个jar包,我们将所有jar包拷贝到项目中去,作为Struts1开发包。
接着,要在web.xml文件中配置Struts1框架提供的ActionServlet,使其处理所有以.do为结尾的请求。
<servlet>
<servlet-name>ActionServletservlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.apache.struts.action.ActionServletservlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>configparam-name>
<param-value>/WEB-INF/struts-config.xmlparam-value>
init-param>
<load-on-startup>1load-on-startup>
servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>ActionServletservlet-name>
<url-pattern>*.dourl-pattern>
servlet-mapping>
顺其自然地,还应在WEB-INF目录下编写ActionServlet工作时使用的配置文件struts-config.xml,配置当ActionServlet收到register.do请求时,调用一个名称为RegisterAction的Action处理。这样配置文件struts-config.xml的内容为:
<struts-config>
<action-mappings>
<action path="/register" type="cn.liayun.web.action.RegisterAction">action>
action-mappings>
struts-config>
还记得以前,我们做用户注册的案例时,需要将用户提交过来的注册信息封装到一个formbean中吧!现在学了Struts1之后,Struts1会自动封装请求数据。Struts1的ActionServlet的功能非常强大,我们只需要在它的配置文件(struts-config.xml文件)中配置一下,它就可以自动把请求数据封装到用户指定的formbean中。并且Struts1在调用开发人员编写的Action时,会把封装了数据的formbean传给Action。这样,可以省去开发人员在Action中手工获取客户端提交的数据,减轻编码工作量。这样配置文件struts-config.xml的内容就为:
<struts-config>
<form-beans>
<form-bean name="registerForm" type="cn.liayun.web.formbean.RegisterFormBean">form-bean>
form-beans>
<action-mappings>
<action path="/register" name="registerForm" type="cn.liayun.web.action.RegisterAction">action>
action-mappings>
struts-config>
接着要在cn.liayun.web.formbean包下创建出封装用户提交过来的注册信息的formbean(RegisterFormBean.java)了。
package cn.liayun.web.formbean;
import org.apache.struts.action.ActionForm;
public class RegisterFormBean extends ActionForm {
private String username;
private String password;
private String email;
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
public String getEmail() {
return email;
}
public void setEmail(String email) {
this.email = email;
}
}
温馨提示:用于封装数据的formbean要继承Struts1的ActionForm类。
紧接着,我们要编写处理请求的Action——RegisterAction.java,在其execute方法内编码,采用传统方式获取数据,并调用service层完成用户注册,然后转发给相应的jsp页面。
package cn.liayun.web.action;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import org.apache.struts.action.Action;
import org.apache.struts.action.ActionForm;
import org.apache.struts.action.ActionForward;
import org.apache.struts.action.ActionMapping;
import cn.liayun.web.formbean.RegisterFormBean;
//该RegisterAction是由Struts1来调用,Struts1会调用它的execute方法处理请求
public class RegisterAction extends Action {
@Override
public ActionForward execute(ActionMapping mapping, ActionForm form, HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
RegisterFormBean registerForm = (RegisterFormBean) form;
String username = registerForm.getUsername();
String password = registerForm.getPassword();
String email = registerForm.getEmail();
try {
System.out.println("向数据库中注册" + username + "用户");
request.setAttribute("message", "注册成功!!");
} catch (Exception e) {
request.setAttribute("message", "注册失败!!");
}
request.getRequestDispatcher("/message.jsp").forward(request, response);//使用传统技术来跳转
return null;
}
}
最后,编写用于显示全局消息的message.jsp页面。
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8"
pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8">
<title>全局消息显示页面title>
head>
<body>
${message }
body>
html>
编写完这样一个小程序,我们就算入门Struts1框架了。学习一门技术最重要的是入门,入门之后剩下的就好说了。
让Struts1实现请求转发
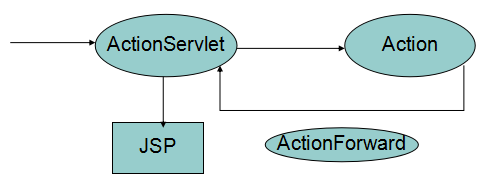
我们编写处理请求的RegisterAction时,使用的是传统方式的请求转发。但现在我们让Struts1实现请求转发,我们在编写Action时,无须在Action内手工编码进行请求转发,Struts1的ActionServlet在调用Action的execute方法时,可以根据它的返回值,决定调用哪个jsp页面响应用户请求。
Action.execute方法的返回值ActionForward代表一个转发对象,Struts1的ActionServlet在收到Action.execute方法的返回值——ActionForward后,会取出该对象封装的转发地址,进行请求转发。用图表示即为:
这样,RegisterAction类的代码可以修改为:
package cn.liayun.web.action;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import org.apache.struts.action.Action;
import org.apache.struts.action.ActionForm;
import org.apache.struts.action.ActionForward;
import org.apache.struts.action.ActionMapping;
import cn.liayun.web.formbean.RegisterFormBean;
//该RegisterAction是由Struts1来调用,Struts1会调用它的execute方法处理请求
public class RegisterAction extends Action {
@Override
public ActionForward execute(ActionMapping mapping, ActionForm form, HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
RegisterFormBean registerForm = (RegisterFormBean) form;
String username = registerForm.getUsername();
String password = registerForm.getPassword();
String email = registerForm.getEmail();
try {
System.out.println("向数据库中注册" + username + "用户");
request.setAttribute("message", "注册成功!!");
} catch (Exception e) {
request.setAttribute("message", "注册失败!!");
}
//request.getRequestDispatcher("/message.jsp").forward(request, response);//使用传统技术来跳转
ActionForward forward = new ActionForward("/message.jsp");//转发地址写死了,并不好
return forward;
}
}
我们也可以让Struts1根据配置实现转发。在Struts1的配置文件(struts-config.xml文件)中,可以配置forward标签,它用于封装一个转发地址。如:

这样,Struts1的配置文件(struts-config.xml文件)就要修改为:
<struts-config>
<form-beans>
<form-bean name="registerForm" type="cn.liayun.web.formbean.RegisterFormBean">form-bean>
form-beans>
<action-mappings>
<action path="/register" name="registerForm" type="cn.liayun.web.action.RegisterAction">
<forward name="message" path="message.jsp" />
action>
action-mappings>
struts-config>
Struts1的ActionServlet在调用Action时,会把Action的配置信息封装到一个ActionMapping对象中,并传递给Action。因此,开发人员在编写Action时,无须硬编码指定转发地址,可以通过ActionMapping对象,获得配置文件中配置的转发地址,从而实现转发。如下图:

这样,RegisterAction类的代码又将修改为:
package cn.liayun.web.action;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import org.apache.struts.action.Action;
import org.apache.struts.action.ActionForm;
import org.apache.struts.action.ActionForward;
import org.apache.struts.action.ActionMapping;
import cn.liayun.web.formbean.RegisterFormBean;
//该RegisterAction是由Struts1来调用,Struts1会调用它的execute方法处理请求
public class RegisterAction extends Action {
@Override
public ActionForward execute(ActionMapping mapping, ActionForm form, HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
RegisterFormBean registerForm = (RegisterFormBean) form;
String username = registerForm.getUsername();
String password = registerForm.getPassword();
String email = registerForm.getEmail();
try {
System.out.println("向数据库中注册" + username + "用户");
request.setAttribute("message", "注册成功!!");
} catch (Exception e) {
request.setAttribute("message", "注册失败!!");
}
ActionForward forward = new ActionForward(mapping.getForward());//处理完了,到底要跳到哪儿去,不需要在程序中写死,就在配置文件里面配置好就行了!
return forward;
}
}
甚至,我们也可以写成下面这个样子:
package cn.liayun.web.action;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import org.apache.struts.action.Action;
import org.apache.struts.action.ActionForm;
import org.apache.struts.action.ActionForward;
import org.apache.struts.action.ActionMapping;
import cn.liayun.web.formbean.RegisterFormBean;
//该RegisterAction是由Struts1来调用,Struts1会调用它的execute方法处理请求
public class RegisterAction extends Action {
@Override
public ActionForward execute(ActionMapping mapping, ActionForm form, HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
RegisterFormBean registerForm = (RegisterFormBean) form;
String username = registerForm.getUsername();
String password = registerForm.getPassword();
String email = registerForm.getEmail();
try {
System.out.println("向数据库中注册" + username + "用户");
request.setAttribute("message", "注册成功!!");
} catch (Exception e) {
request.setAttribute("message", "注册失败!!");
}
return mapping.findForward("message");
}
}
Struts1工作原理与源码分析
我们一定要读Struts1的源码,然后分析Struts1的工作流程,这对我们深入理解Struts1有极大的帮助。在读Struts1的源码时,有一个小细节需要我们注意:由于我们使用的是struts-1.3.8-all,这个版本是Struts1的最终版本,所以我们读它的源码时,挺费劲的,为了让其源码比较好读一点,我们可以在Struts1的配置文件(struts-config.xml文件)中配置Struts1.2采用的请求处理器,并且在实际开发中,若真有项目是用的Struts1框架,那么使用的一般都是Struts1.2版本的。
<struts-config>
<form-beans>
<form-bean name="registerForm" type="cn.liayun.web.formbean.RegisterFormBean">form-bean>
form-beans>
<action-mappings>
<action path="/register" name="registerForm" type="cn.liayun.web.action.RegisterAction">
<forward name="message" path="message.jsp" />
action>
action-mappings>
<controller processorClass="org.apache.struts.action.RequestProcessor">controller>
struts-config>
然后大家就可以使用断点跟踪的方式查看Struts1的源码了。读了Struts1的源码之后,我们可以得出一些结论:


Struts1的配置
Struts1配置文件常用属性
Struts1配置文件常用属性有:

下面我们来逐一地详解这些属性。
- path:指定action处理的地址;
- type:指定处理请求的Action的完整类名;
- name:指定使用哪个formbean封装请求参数。
以上三个参数我们都知道了,就没有说的必要了,接下来看看我们并未熟知的属性。
-
scope:指定把formbean存放到哪个域对象中,默认为session。
我们还是举用户注册的案例来讲解这个属性。若要是不指定这个属性,默认把formbean存放到session这个域中,是不是真是这样呢?我们可以用以下代码来测试:package cn.liayun.web.action; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse; import org.apache.struts.action.Action; import org.apache.struts.action.ActionForm; import org.apache.struts.action.ActionForward; import org.apache.struts.action.ActionMapping; import cn.liayun.web.formbean.RegisterFormBean; //该RegisterAction是由Struts1来调用,Struts1会调用它的execute方法处理请求 public class RegisterAction extends Action { @Override public ActionForward execute(ActionMapping mapping, ActionForm form, HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception { RegisterFormBean registerForm = (RegisterFormBean) request.getSession().getAttribute("registerForm"); String username = registerForm.getUsername(); String password = registerForm.getPassword(); String email = registerForm.getEmail(); try { System.out.println("向数据库中注册" + username + "用户"); request.setAttribute("message", "注册成功!!"); } catch (Exception e) { request.setAttribute("message", "注册失败!!"); } return mapping.findForward("message"); } }经测试,发现若要是不指定这个属性,真是默认把formbean对象存放到session这个域中。但是session域的生命周期比较长,把formbean对象存到其中并不太好,session域中将来要存储的东西很多,要是什么东西都往session域中存,难不保计算机内存会溢出。所以,一般来说,我们把formbean存放到request域中,这样就要修改Struts1的配置文件了。
<struts-config> <form-beans> <form-bean name="registerForm" type="cn.liayun.web.formbean.RegisterFormBean">form-bean> form-beans> <action-mappings> <action path="/register" name="registerForm" type="cn.liayun.web.action.RegisterAction" scope="request"> <forward name="message" path="message.jsp" /> action> action-mappings> <controller processorClass="org.apache.struts.action.RequestProcessor">controller> struts-config>这样我们处理请求的RegisterAction就要写为:
package cn.liayun.web.action; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse; import org.apache.struts.action.Action; import org.apache.struts.action.ActionForm; import org.apache.struts.action.ActionForward; import org.apache.struts.action.ActionMapping; import cn.liayun.web.formbean.RegisterFormBean; //该RegisterAction是由Struts1来调用,Struts1会调用它的execute方法处理请求 public class RegisterAction extends Action { @Override public ActionForward execute(ActionMapping mapping, ActionForm form, HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception { RegisterFormBean registerForm = (RegisterFormBean) request.getAttribute("registerForm"); String username = registerForm.getUsername(); String password = registerForm.getPassword(); String email = registerForm.getEmail(); try { System.out.println("向数据库中注册" + username + "用户"); request.setAttribute("message", "注册成功!!"); } catch (Exception e) { request.setAttribute("message", "注册失败!!"); } return mapping.findForward("message"); } } -
attribute:指定formbean存储的key,不设默认为name属性的值。
从上面的代码中可知,formbean存放在request域中的key默认就是name属性的值,但大家也可以修改formbean存放在request域中的key,如:<struts-config> <form-beans> <form-bean name="registerForm" type="cn.liayun.web.formbean.RegisterFormBean">form-bean> form-beans> <action-mappings> <action path="/register" name="registerForm" type="cn.liayun.web.action.RegisterAction" scope="request" attribute="liayun"> <forward name="message" path="message.jsp" /> action> action-mappings> <controller processorClass="org.apache.struts.action.RequestProcessor">controller> struts-config>那么处理请求的RegisterAction就要写为:
package cn.liayun.web.action; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse; import org.apache.struts.action.Action; import org.apache.struts.action.ActionForm; import org.apache.struts.action.ActionForward; import org.apache.struts.action.ActionMapping; import cn.liayun.web.formbean.RegisterFormBean; //该RegisterAction是由Struts1来调用,Struts1会调用它的execute方法处理请求 public class RegisterAction extends Action { @Override public ActionForward execute(ActionMapping mapping, ActionForm form, HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception { RegisterFormBean registerForm = (RegisterFormBean) request.getAttribute("liayun"); String username = registerForm.getUsername(); String password = registerForm.getPassword(); String email = registerForm.getEmail(); try { System.out.println("向数据库中注册" + username + "用户"); request.setAttribute("message", "注册成功!!"); } catch (Exception e) { request.setAttribute("message", "注册失败!!"); } return mapping.findForward("message"); } } -
input:指定formbean的数据是由哪个页面提供的,提供此属性的目的在于formbean校验失败时,程序方便跳回formbean的输入页面,显示校验失败信息。在这儿,我就不举例说明了,因为后面在借助Struts1完成表单校验时就会用到这个属性;
-
forward:指定收到请求时,跳转到相应的jsp页面,如果配置了此属性,则Action将不再被调用。
这个属性还是比较实用的,试想我们浏览一个网站,都是首页给我们提供这个网站的一些功能,例如该网站会在首页挂一个注册的超链接,首页index.jsp的内容如下:<%@ page language="java" import="java.util.*" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%> <%@ taglib uri="http://struts.apache.org/tags-html" prefix="html" %> <html> <head> <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8"> <title>网站首页title> head> <body> <a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath }/registerUI.do">注册a> body> html>用户点击注册超链接,以前都是将请求交给一个Servlet,然后通过这个Servlet跳转到注册页面,现在学了Struts1之后,就不用这么做了,我们只须这样修改Struts1的配置文件:
<struts-config> <form-beans> <form-bean name="registerForm" type="cn.liayun.web.formbean.RegisterFormBean">form-bean> form-beans> <action-mappings> <action path="/register" name="registerForm" type="cn.liayun.web.action.RegisterAction" scope="request" attribute="liayun"> <forward name="message" path="message.jsp" /> action> <action path="/registerUI" forward="/register.jsp">action> action-mappings> <controller processorClass="org.apache.struts.action.RequestProcessor">controller> struts-config>这样当用户点击注册超链接时,就会跳转到用户注册页面。
-
include:指定收到请求时,进行页面包含。这个属性不是很常用;
-
unknown:如果Action把该属性设置为true,则它可以处理客户机发出的所有无效的
.do请求,默认值为false。
例如有些人吃饱了没事干,会通过这样的URL地址访问web服务器,如http://localhost:8080/Struts1Sample/dertettytuyiioioip.do,明显web服务器就没有对应的Action对这样的请求进行处理,所以会报这样的错误:

而要想不向用户弹出这样不友好的错误页面,可以在Struts1的配置文件中添加:

这样Struts1的配置文件就为:<struts-config> <form-beans> <form-bean name="registerForm" type="cn.liayun.web.formbean.RegisterFormBean">form-bean> form-beans> <action-mappings> <action path="/register" name="registerForm" type="cn.liayun.web.action.RegisterAction" scope="request" attribute="liayun"> <forward name="message" path="message.jsp" /> action> <action path="/registerUI" forward="/register.jsp">action> <action path="/error" unknown="true" forward="/WEB-INF/jsp/error.jsp">action> action-mappings> <controller processorClass="org.apache.struts.action.RequestProcessor">controller> struts-config>接下来就要创建出专门处理错误的页面了,error.jsp页面的内容如下:
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%> <html> <head> <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8"> <title>专门处理错误的页面title> head> <body> 出错了!!! body> html>这样,当有些人吃饱了没事干,通过这样的URL地址,如
http://localhost:8080/Struts1Sample/dertettytuyiioioip.do访问web服务器,那么就会跳转到error.jsp页面中。
其实在实际生活中人们并不会通过这样的URL地址去访问web服务器,更加常见的是使用这样的URL地址(如http://localhost:8080/Struts1Sample/dertettytuyiioioip)去访问web服务器,这时由于并不是.do请求,所以Struts1就起不了任何作用了。如果要避免这样的情况,我们还是要像以前一样在web.xml文件中配置这样的代码:<error-page> <error-code>404error-code> ... error-page> <error-page> <error-code>500error-code> ... error-page> -
parameter:配置Action参数,调用ActionMapping.getParameter方法可以获得这里配置的参数。我们修改Struts1的配置文件为:
<struts-config> <form-beans> <form-bean name="registerForm" type="cn.liayun.web.formbean.RegisterFormBean">form-bean> form-beans> <action-mappings> <action path="/register" name="registerForm" type="cn.liayun.web.action.RegisterAction" scope="request" attribute="liayun" parameter="method"> <forward name="message" path="message.jsp" /> action> <action path="/registerUI" forward="/register.jsp">action> <action path="/error" unknown="true" forward="/WEB-INF/jsp/error.jsp">action> action-mappings> <controller processorClass="org.apache.struts.action.RequestProcessor">controller> struts-config>然后为了获得配置Action的参数,我们要修改RegisterAction类的代码为:
package cn.liayun.web.action; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse; import org.apache.struts.action.Action; import org.apache.struts.action.ActionForm; import org.apache.struts.action.ActionForward; import org.apache.struts.action.ActionMapping; import cn.liayun.web.formbean.RegisterFormBean; //该RegisterAction是由Struts1来调用,Struts1会调用它的execute方法处理请求 public class RegisterAction extends Action { @Override public ActionForward execute(ActionMapping mapping, ActionForm form, HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception { RegisterFormBean registerForm = (RegisterFormBean) request.getAttribute("liayun"); String username = registerForm.getUsername(); String password = registerForm.getPassword(); String email = registerForm.getEmail(); System.out.println(mapping.getParameter()); try { System.out.println("向数据库中注册" + username + "用户"); request.setAttribute("message", "注册成功!!"); } catch (Exception e) { request.setAttribute("message", "注册失败!!"); } return mapping.findForward("message"); } }这样会在Eclipse的控制台中输出method。
-
classname:
-
validate:请求参数封装到formbean中后,是否让Struts1自动调用formbean的validate方法进行数据校验。默认为true。
这样我们就把Struts1配置文件的常用属性过了一遍了。这就是Struts1入门了,涉及到的知识还是蛮多的哟!写到这里给自己一个赞!!
