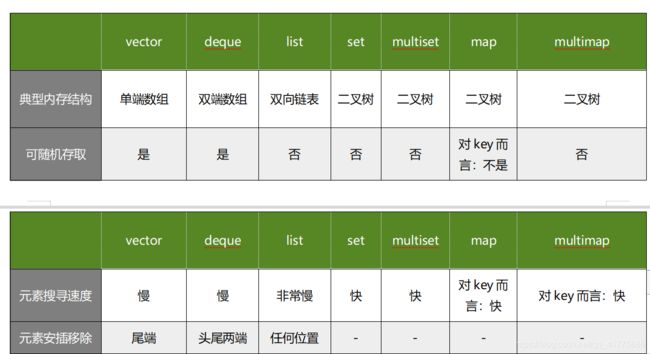
alin的学习之路(STL篇:二)(stack,queue,list,set,map)
alin的学习之路(STL篇:二)(stack,queue,list,set,map)
1.stack容器
stack容器模拟了栈的结构,先进后出,没有迭代器,只能对栈顶进行操作
void test01()
{
stack s;
s.push(10);
s.push(20);
s.push(30);
s.push(40);
cout << "栈的大小为:" << s.size() << endl;
while (!s.empty())
{
cout << "栈顶元素:" << s.top() << endl;
s.pop();
}
cout << "栈的大小为:" << s.size() << endl;
}
2.queue容器
queue容器模拟了队列的结构,先进后出,它有两端开口,一端插入数据,一端移出数据
class Person {
public:
Person(string name, int age)
{
this->m_Name = name;
this->m_Age = age;
}
string m_Name;
int m_Age;
};
void test01()
{
queue q;
Person p1("aaa", 10);
Person p2("bbb", 20);
Person p3("ccc", 30);
Person p4("ddd", 40);
q.push(p1);
q.push(p2);
q.push(p3);
q.push(p4);
while (!q.empty())
{
cout << "队头元素: 姓名:" << q.front().m_Name << " 年龄:" << q.front().m_Age << endl;
cout << "队尾元素: 姓名:" << q.back().m_Name << " 年龄:" << q.back().m_Age << endl;
q.pop();
}
}
3.list容器
list容器模拟了链表的结构,它不会有空间的浪费,有几个元素就占多大的内存空间,支持头插尾插头删尾删和指定位置插入删除
- list构造函数
list lstT;//list采用采用模板类实现,对象的默认构造形式:
list(beg,end);//构造函数将[beg, end)区间中的元素拷贝给本身。
list(n,elem);//构造函数将n个elem拷贝给本身。
list(const list &lst);//拷贝构造函数。 - list数据元素插入和删除操作
push_back(elem);//在容器尾部加入一个元素
pop_back();//删除容器中最后一个元素
push_front(elem);//在容器开头插入一个元素
pop_front();//从容器开头移除第一个元素
insert(pos,elem);//在pos位置插elem元素的拷贝,返回新数据的位置。
insert(pos,n,elem);//在pos位置插入n个elem数据,无返回值。
insert(pos,beg,end);//在pos位置插入[beg,end)区间的数据,无返回值。
clear();//移除容器的所有数据
erase(beg,end);//删除[beg,end)区间的数据,返回下一个数据的位置。
erase(pos);//删除pos位置的数据,返回下一个数据的位置。
remove(elem);//删除容器中所有与elem值匹配的元素。
void printList(list & L)
{
for (list::iterator it = L.begin(); it != L.end(); ++it)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void test01()
{
list L;
L.push_back(10);
L.push_back(20);
L.push_back(30);
L.push_front(100);
L.push_front(200);
L.push_front(300);
//正序遍历
printList(L);
//逆序遍历
for (list::reverse_iterator it = L.rbegin(); it != L.rend(); ++it)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
list::iterator itBegin = L.begin();
itBegin++;
itBegin--;
//itBegin = itBegin + 1; //测试说明list容器的迭代器是双向迭代器,不是随机访问迭代器
}
void test02()
{
listL;
L.push_back(10);
L.push_back(20);
L.push_back(30);
L.push_front(100);
L.push_front(200);
L.push_front(300);
//300 200 100 10 20 30
printList(L);
L.pop_back();
L.pop_front();
// 200 100 10 20
printList(L);
L.insert(L.begin(), 1000);
//1000 200 100 10 20
printList(L);
L.erase(L.begin());
//200 100 10 20
printList(L);
L.push_back(100);
L.push_front(100);
//100 200 100 10 20 100
printList(L);
L.remove(100); //删除容器中所有与elem值匹配的元素。
//200 10 20
printList(L);
}
- list反转排序
reverse();//反转链表,比如lst包含1,3,5元素,运行此方法后,lst就包含5,3,1元素。
sort(); //list排序
//reverse
void test03()
{
listL;
L.push_back(10);
L.push_back(20);
L.push_back(30);
L.push_front(100);
L.push_front(200);
L.push_front(300);
//300 200 100 10 20 30
printList(L);
L.reverse();
//30 20 10 100 200 300
printList(L);
}
//sort
bool compareInt(int v1, int v2)
{
return v1 > v2;
}
void test04()
{
listL;
L.push_back(10);
L.push_back(20);
L.push_back(30);
L.push_front(100);
L.push_front(200);
L.push_front(300);
//300 200 100 10 20 30
printList(L);
L.sort(compareInt); //默认提供的算法函数只适用于支持随机访问迭代器的容器,list是双向迭代器,所以要用容器调用其自身的sort函数
//10 20 30 100 200 300
//300 200 100 30 20 10
printList(L);
}
class Person
{
public:
Person(string name,int age,int height)
{
this->m_Name = name;
this->m_Age = age;
this->m_Height = height;
}
bool operator==(const Person& p) const
{
return this->m_Name == p.m_Name && this->m_Age == p.m_Age && this->m_Height == p.m_Height;
}
string m_Name;
int m_Age;
int m_Height;
};
bool comparePerson(Person& p1, Person& p2)
{
//按年龄升序排序,如果年龄相同,按身高降序排序
return p1.m_Age == p2.m_Age ? p1.m_Height > p2.m_Height : p1.m_Age < p2.m_Age;
}
void test05()
{
list L;
Person p1("刘备", 30, 170);
Person p2("关羽", 29, 180);
Person p3("张飞", 28, 188);
Person p4("赵云", 31, 185);
Person p5("吕布", 32, 177);
Person p6("曹操", 32, 160);
Person p7("孙权", 32, 190);
L.push_back(p1);
L.push_back(p2);
L.push_back(p3);
L.push_back(p4);
L.push_back(p5);
L.push_back(p6);
L.push_back(p7);
cout << "排序前打印的结果为:" << endl;
for (list::iterator it = L.begin(); it != L.end(); ++it)
{
cout << "姓名:" << it->m_Name << " 年龄:" << it->m_Age << " 身高:" << it->m_Height << endl;
}
L.sort(comparePerson);
cout << "排序后打印的结果为:" << endl;
for (list::iterator it = L.begin(); it != L.end(); ++it)
{
cout << "姓名:" << it->m_Name << " 年龄:" << it->m_Age << " 身高:" << it->m_Height << endl;
}
//删除曹操
L.remove(p6); //注意要重载==号
cout << "删除曹操后的结果为:" << endl;
for (list::iterator it = L.begin(); it != L.end(); ++it)
{
cout << "姓名:" << it->m_Name << " 年龄:" << it->m_Age << " 身高:" << it->m_Height << endl;
}
}
4.set容器
set容器是关联式容器,底层是用红黑树实现,插入其中的数据会自动进行排序,默认升序排序,如果插入了自定义类型的数据,则需要指定排序规则
-
set构造函数
set st;//set默认构造函数:
mulitset mst; //multiset默认构造函数:
set(const set &st);//拷贝构造函数
set赋值操作
set& operator=(const set &st);//重载等号操作符
swap(st);//交换两个集合容器
set大小操作
size();//返回容器中元素的数目
empty();//判断容器是否为空set插入和删除操作
insert(elem);//在容器中插入元素。
clear();//清除所有元素
erase(pos);//删除pos迭代器所指的元素,返回下一个元素的迭代器。
erase(beg, end);//删除区间[beg,end)的所有元素 ,返回下一个元素的迭代器。
erase(elem);//删除容器中值为elem的元素。
void printSet(set& s)
{
for (set::iterator it = s.begin(); it != s.end(); ++it)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void test01()
{
set s;
s.insert(10);
s.insert(30);
s.insert(20);
s.insert(50);
s.insert(40);
printSet(s);
//插入重复元素不会插进去
s.insert(30);
s.erase(s.begin());
s.erase(20);
printSet(s);
}
- set查找操作
find(key);//查找键key是否存在,若存在,返回该键的元素的迭代器;若不存在,返回set.end();
count(key);//查找键key的元素个数
lower_bound(keyElem);//返回第一个key>=keyElem元素的迭代器。
upper_bound(keyElem);//返回第一个key>keyElem元素的迭代器。
equal_range(keyElem);//返回容器中key与keyElem相等的上下限的两个迭代器。
void test02()
{
set s;
s.insert(10);
s.insert(30);
s.insert(20);
s.insert(50);
s.insert(40);
set::iterator it = s.find(20);
if (it == s.end())
{
cout << "未找到该元素" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "找到了元素:" << *it << endl;
}
//lower_bound(keyElem);//返回第一个key>=keyElem元素的迭代器。
set::iterator it2 = s.lower_bound(30);
if (it2 == s.end())
{
cout << "未找到该元素" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "找到了元素:" << *it2 << endl;
}
//upper_bound(keyElem);//返回第一个key>keyElem元素的迭代器。
set::iterator it3 = s.upper_bound(30);
if (it3 == s.end())
{
cout << "未找到该元素" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "找到了元素:" << *it3 << endl;
}
//equal_range(keyElem);//返回容器中key与keyElem相等的上下限的两个迭代器。
//它的返回值是
//使用对组去接收该函数的返回值
pair::iterator, set::iterator>p = s.equal_range(30);
if (p.first == s.end())
{
cout << "未找到该元素" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "找到了元素:" << *(p.first) << endl;
}
if (p.second == s.end())
{
cout << "未找到该元素" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "找到了元素:" << *(p.second) << endl;
}
}
- pair的使用
//pair的使用
void test03()
{
pairp("TOM", 18);
cout << "姓名:" << p.first << endl;
cout << "年龄:" << p.second << endl;
pairp2 = make_pair("Jerry", 20);
cout << "姓名:" << p2.first << endl;
cout << "年龄:" << p2.second << endl;
}
- set插入成功或失败可以通过inset的返回值来判断,inset返回pair
void test04()
{
set s;
s.insert(10);
s.insert(30);
s.insert(20);
s.insert(50);
s.insert(40);
pair::iterator, bool> p;
p = s.insert(60);
if (p.second)
{
cout << "第一次插入成功" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "第一次插入失败" << endl;
}
p = s.insert(60);
if (p.second)
{
cout << "第二次插入成功" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "第二次插入失败" << endl;
}
}
- multiset可以插入重复的数据
void test05()
{
multiset ms;
ms.insert(10);
ms.insert(10);
ms.insert(10);
for (multiset::iterator it = ms.begin(); it != ms.end(); ++it)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
- set指定排序规则:在定义set时写一个仿函数放入模板参数列表
class myCompare
{
public:
bool operator()(int v1, int v2) const
{
return v1 > v2;
}
};
void test06()
{
//插入时指定插入的规则,要在定义set的时候增加一个仿函数写进模板参数列表
set s;
s.insert(10);
s.insert(30);
s.insert(20);
s.insert(50);
s.insert(40);
for (set::iterator it = s.begin(); it != s.end(); ++it)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
class Person
{
public:
Person(string name, int age)
{
this->m_Name = name;
this->m_Age = age;
}
string m_Name;
int m_Age;
};
class comparePerson
{
public:
bool operator()(const Person& p1, const Person& p2) const
{
return p1.m_Age < p2.m_Age;
}
};
void test07()
{
sets;
Person p1("刘备", 30);
Person p2("关羽", 29);
Person p3("张飞", 28);
Person p4("赵云", 31);
Person p5("吕布", 32);
Person p6("曹操", 35);
Person p7("孙权", 34);
s.insert(p1);
s.insert(p2);
s.insert(p3);
s.insert(p4);
s.insert(p5);
s.insert(p6);
s.insert(p7);
for (set::iterator it = s.begin(); it != s.end(); ++it)
{
cout << "姓名:" << it->m_Name << " 年龄:" << it->m_Age << endl;
}
}
5.map容器
- map中的每一个元素都以键值对的形式存在,并且会根据key的值进行排序,底层用红黑树实现
void test01()
{
map m;
//方法1
m.insert(pair(1, 10));
//方法2
m.insert(make_pair(2, 20));
//方法3
m.insert(map::value_type(3, 30));
//方法4
m[4] = 40; //[]的使用是 如果确保key值存在,可以对指定的key读写对应的value
//m[5]; //这样会误插一个key为5,value为0 的键值对
//cout << m[5] << endl; //这样也会误插
for (map::iterator it = m.begin(); it != m.end(); ++it)
{
cout << "key = " << it->first << " value = " << it->second << endl;
}
}
- map删除操作
clear();//删除所有元素
erase(pos);//删除pos迭代器所指的元素,返回下一个元素的迭代器。
erase(beg,end);//删除区间[beg,end)的所有元素 ,返回下一个元素的迭代器。
erase(keyElem);//删除容器中key为keyElem的对组。
void test02()
{
map m;
m.insert(pair(1, 10));
m.insert(make_pair(2, 20));
m.insert(map::value_type(3, 30));
m[4] = 40;
m.erase(3);
for (map::iterator it = m.begin(); it != m.end(); ++it)
{
cout << "key = " << it->first << " value = " << it->second << endl;
}
}
- map查找操作
find(key);//查找键key是否存在,若存在,返回该键的元素的迭代器;/若不存在,返回map.end();
count(keyElem);//返回容器中key为keyElem的对组个数。对map来说,要么是0,要么是1。对multimap来说,值可能大于1。
lower_bound(keyElem);//返回第一个key>=keyElem元素的迭代器。
upper_bound(keyElem);//返回第一个key>keyElem元素的迭代器。
equal_range(keyElem);//返回容器中key与keyElem相等的上下限的两个迭代器。
void test03()
{
map m;
m.insert(pair(1, 10));
m.insert(make_pair(2, 20));
m.insert(map::value_type(3, 30));
m[4] = 40;
map::iterator it = m.find(3);
if (it == m.end())
{
cout << "没有找到" << endl;
}
else {
cout << "找到了元素:key = " << it->first << " value = " << it->second << endl;
}
map::iterator it2 = m.lower_bound(3);
if (it2 == m.end())
{
cout << "没有找到" << endl;
}
else {
cout << "找到了元素:key = " << it2->first << " value = " << it2->second << endl;
}
map::iterator it3 = m.upper_bound(3);
if (it3 == m.end())
{
cout << "没有找到" << endl;
}
else {
cout << "找到了元素:key = " << it3->first << " value = " << it3->second << endl;
}
pair::iterator, map::iterator> p = m.equal_range(3);
if (p.first == m.end())
{
cout << "没有找到" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "找到了元素:key = " << p.first->first<< " value = " << p.first->second << endl;
}
if (p.second == m.end())
{
cout << "没有找到" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "找到了元素:key = " << p.second->first << " value = " << p.second->second << endl;
}
}
- map指定排序规则
class myCompare
{
public:
bool operator()(int v1, int v2) const
{
return v1 > v2;
}
};
void test04()
{
map m;
m.insert(pair(1, 10));
m.insert(make_pair(2, 20));
m.insert(map::value_type(3, 30));
m[4] = 40;
for (map::iterator it = m.begin(); it != m.end(); ++it)
{
cout << "key = " << it->first << " value = " << it->second << endl;
}
}