LeetCode(84) Largest Rectangle in Histogram
题目
Given n non-negative integers representing the histogram’s bar height where the width of each bar is 1, find the area of largest rectangle in the histogram.
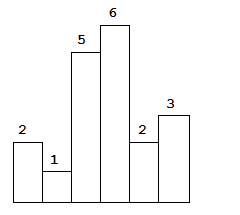
Above is a histogram where width of each bar is 1, given height = [2,1,5,6,2,3].

The largest rectangle is shown in the shaded area, which has area = 10 unit.
For example,
Given height = [2,1,5,6,2,3],
return 10.
分析
如木桶理论,题目给定一组矩形柱高度序列,求出其构成的直方图最大面积;
方法一:
依次遍历每个坐标位置,从该柱形左右延展,当高度降低时停止延展,求出其组成的矩形面积,实时更新最大面积;
但是大数据集会超时;
方法二:
查看资料看到一个经典的栈解决方法参考网址~~
给出详细解析:
1、如果已知height数组是升序的,应该怎么做?
比如1,2,5,7,8
那么就是(1*5) vs. (2*4) vs. (5*3) vs. (7*2) vs. (8*1)
也就是max(height[i]*(size-i))
2、使用栈的目的就是构造这样的升序序列,按照以上方法求解。
但是height本身不一定是升序的,应该怎样构建栈?
比如2,1,5,6,2,3
(1)2进栈。s={2}, result = 0
(2)1比2小,不满足升序条件,因此将2弹出,并记录当前结果为2*1=2。
将2替换为1重新进栈。s={1,1}, result = 2
(3)5比1大,满足升序条件,进栈。s={1,1,5},result = 2
(4)6比5大,满足升序条件,进栈。s={1,1,5,6},result = 2
(5)2比6小,不满足升序条件,因此将6弹出,并记录当前结果为6*1=6。s={1,1,5},result = 6
2比5小,不满足升序条件,因此将5弹出,并记录当前结果为5*2=10(因为已经弹出的5,6是升序的)。s={1,1},result = 10
2比1大,将弹出的5,6替换为2重新进栈。s={1,1,2,2,2},result = 10
(6)3比2大,满足升序条件,进栈。s={1,1,2,2,2,3},result = 10
栈构建完成,满足升序条件,因此按照升序处理办法得到上述的max(height[i]*(size-i))=max{3*1, 2*2, 2*3, 2*4, 1*5, 1*6}=8<10
综上所述,result=10
AC代码
class Solution {
public:
/*方法一:每个坐标点左右延伸(当高度降低停止延伸)构造矩形,但是大集合TLE*/
int largestRectangleArea1(vector<int> &height) {
if (height.empty())
return 0;
int maxArea = 0;
int len = height.size();
for (int i = 0; i < len; ++i)
{
/*记录包含第i个柱体的矩形面积*/
int tmpArea = height[i];
int left = i - 1, right = i + 1;
/*左侧扩展*/
while (left >= 0 && height[left] >= height[i])
{
tmpArea += height[i];
--left;
}//while
/*右侧扩展*/
while (right < len && height[right] >= height[i])
{
tmpArea += height[i];
++right;
}//while
if (maxArea < tmpArea)
maxArea = tmpArea;
}//for
return maxArea;
}
/*方法二:利用栈*/
int largestRectangleArea(vector<int> &height) {
if (height.empty())
return 0;
stack<int> stk;
int len = height.size();
int maxArea = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++)
{
if (stk.empty() || stk.top() <= height[i])
stk.push(height[i]);
else
{
int count = 0;
while (!stk.empty() && stk.top() > height[i])
{
count++;
maxArea = max(maxArea, stk.top()*count);
stk.pop();
}
while (count--)
stk.push(height[i]);
stk.push(height[i]);
}//else
}//for
int count = 1;
while (!stk.empty())
{
maxArea = max(maxArea, stk.top()*count);
stk.pop();
count++;
}//while
return maxArea;
}
};GitHub测试程序源码