(数据结构)1.图的邻接矩阵和邻接表应用。 2.求连通图的深度优先生成树和广度优先生成树。 3.采用普里姆算法求最小生成树。 4.采用克鲁斯卡尔算法求最小生成树。
实验内容
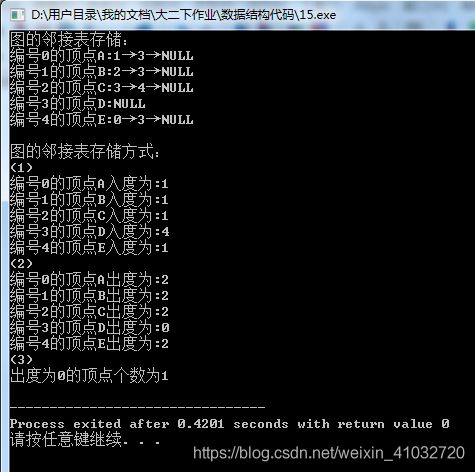
1、假设不带权有向图采用邻接矩阵g存储,设计实现以下功能的算法:
(1)求出图中每个顶点的入度。
(2)求出图中每个顶点的出度。
(3)求出图中出度为0的顶点数。
2、假设不带权有向图采用邻接表G存储,设计实现以下功能的算法:
(1)求出图中每个顶点的入度。
(2)求出图中每个顶点的出度。
(3)求出图中出度为0的顶点数。
3、假设一个连通图采用邻接表作为存储结构,试设计一个算法,判断其中是否存在经过顶点v的回路。
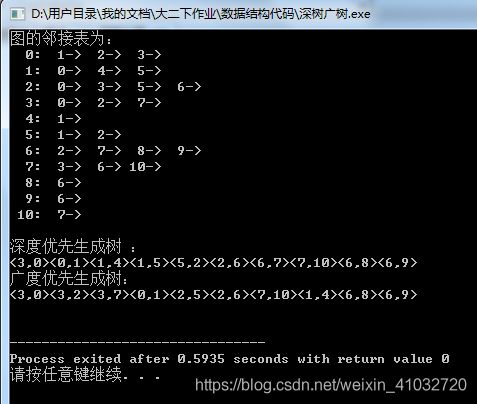
4、编写一个程序exp8-4.cpp,输出一个连通图的深度优先生成树和广度优先生成树,并对图8.24求从顶点3出发的一棵深度优先生成树和一棵广度优先生成树。
5、编写一个程序exp8-5.cpp,实现求带权连通图最小生成树的普里姆算法。对于如图8.55所示的带权连通图G,输出从顶点0出发的一棵最小生成树。
6、6.编写一个程序exp8-6.cpp,实现求带权连通图最小生成树的克鲁斯卡尔算法。对于如图8.55所示的带权连通图G,输出从顶点0出发的一棵最小生成树。
代码实现
1、
#include
#include
#define MAX_V 5
#define INF 2147483647
//图的邻接矩阵结构
typedef struct
{
int No; //顶点编号
char info; //顶点信息,这里用作顶点名
} Ver;
typedef struct //图的邻接矩阵结构
{
int adjMat[MAX_V][MAX_V]; //邻接矩阵
int v; //点的个数
int e; //边的个数
Ver ver[MAX_V]; //顶点数组用于盛放顶点信息
} MatGraph;
//创建图的邻接矩阵
void CreateMat(MatGraph *&G,int A[MAX_V][MAX_V],int v,int e) {
int i,j;
G=(MatGraph*)malloc(sizeof(MatGraph));
for(i=0;iver[i].No=i; //给节点编号
G->ver[i].info='A'+i; //这里节点信息域作为节点名,赋上A,B,C...字母
}
for(i=0;i=0;j--)
G->adjMat[i][j]=A[i][j];
G->e=e;
G->v=v;
}
//图的邻接矩阵存储方式求各顶点入度
void MatInDegree(MatGraph *G) {
int i,j,count; //count为顶点的人度
for(i=0;i < G->v;i++)
{
count=0;
printf("编号%d的顶点%c的入度为:",G->ver[i].No,G->ver[i].info);
for(j=0;j < G->v;j++)
if(G->adjMat[j][i]==1)
count++;
printf("%d\n",count);
}
}
//图的邻接矩阵存储方式求各顶点出度
void MatOutDegree(MatGraph *G) {
int i,j,count; //count为顶点的出度
for(i=0;i < G->v;i++)
{
count=0;
printf("编号%d的顶点%c的出度为:",G->ver[i].No,G->ver[i].info);
for(j=0;j < G->v;j++)
if(G->adjMat[i][j]==1)
count++;
printf("%d\n",count);
}
}
//图的邻接矩阵存储方式求出度为0的顶点个数
void MatZeroOutDegree(MatGraph *G) {
int i,j,count=0; //count为出度顶点的个数
for(i=0;i < G->v;i++)
{
for(j=0;j < G->v;j++)
if(G->adjMat[i][j]==1)
break;
if(j==G->v) //j==G->v说明邻接矩阵该行没有为1的值,既出度为0
count++;
}
printf("出度为0的顶点个数为%d\n",count);
}
//图的邻接矩阵存储方式输出
void DispMat(MatGraph *G) {
int i,j;
printf("\n图的邻接矩阵存储:\n");
for(i=0;i < G->v;i++)
{
printf("编号%d的顶点%c:",G->ver[i].No,G->ver[i].info);
for(j=0;j < G->v;j++)
printf("%d ",G->adjMat[i][j]); //没有权,这里的链表只输出邻接顶点编号
printf("\n");
}
}
int main()
{
int mat[MAX_V][MAX_V]=
{ //图的形状:
{0,1,0,1,0}, // 1
{0,0,1,1,0}, // ↙↓↖
{0,0,0,1,1}, // 2 →3← 0
{0,0,0,0,0}, // ↘↑↗
{1,0,0,1,0} // 4
};
int v=5,e=8;
MatGraph* MG=NULL;
CreateMat(MG,mat,v,e);
DispMat(MG);
printf("\n图的邻接矩阵存储方式:\n");
printf("(1)\n");
MatInDegree(MG);
printf("(2)\n");
MatOutDegree(MG);
printf("(3)\n");
MatZeroOutDegree(MG);
return 0;
}
#include
#include
#define MAX_V 5
#define INF 2147483647
//图的邻接表结构
typedef struct edgeNode //邻接表边节点
{
int adjVNo; //邻接点编号∵题目规定为不带权图∴不设权值的空间
struct edgeNode *next; //下一条边的指针
} ENode;
typedef struct
{
char info; //顶点信息,这里用作顶点名
ENode * first; //邻接表中边节点链表的头指针,指向第一个边节点
} VNode; //邻接表头结点,也是顶点类型
typedef struct
{
VNode Ver[MAX_V]; //邻接表头结点数组,也是顶点数组
int v; //点的个数
int e; //边的个数
} AdjGraph;
//创建图的邻接表
void CreateAdj(AdjGraph *&G,int A[MAX_V][MAX_V],int v,int e)
{
int i,j;
ENode* p=NULL;
G=(AdjGraph*)malloc(sizeof(AdjGraph));
for(i=0;iVer[i].first=NULL;
G->Ver[i].info='A'+i; //这里节点信息域作为节点名,赋上A,B,C...字母
}
for(i=0;i=0;j--)
if(A[i][j]!=0 && A[i][j]!=INF)
{
p=(ENode*)malloc(sizeof(ENode));
p->adjVNo=j;
p->next=G->Ver[i].first; //头插法
G->Ver[i].first=p;
}
G->e=e;
G->v=v;
}
//图的邻接表存储方式输出
void DispAdj(AdjGraph *G)
{
int i;
ENode *p;
printf("图的邻接表存储:\n");
for(i=0;i < G->v;i++)
{
p=G->Ver[i].first;
printf("编号%d的顶点%c:",i,G->Ver[i].info);
while(p!=NULL)
{
printf("%d→",p->adjVNo); //没有权,这里的链表只输出邻接顶点编号
p=p->next;
}
printf("NULL\n");
}
}
//图的邻接表存储方式求各顶点入度
void AdjInDegree(AdjGraph *G) {
int i,j,count; //count为顶点的人度
ENode *p;
for(i=0;i < G->v;i++) //共G->v个节点
{
count=0;
printf("编号%d的顶点%c入度为:",i,G->Ver[i].info);
for(j=0;j < G->v;j++) //对每个节点都要遍历图的所有边
{
p=G->Ver[j].first;
while(p!=NULL)
{
if(p->adjVNo==i) //如果边节点的邻接顶点为现在要找的顶点,既当前正在遍历的顶点为该边终点时
count++; //则入度+1
p=p->next;
}
}
printf("%d\n",count);
}
}
//图的邻接表存储方式求各顶点出度
void AdjOutDegree(AdjGraph *G)
{
int i,count; //count为顶点的出度
ENode *p;
for(i=0;i < G->v;i++)
{
p=G->Ver[i].first;
count=0;
printf("编号%d的顶点%c出度为:",i,G->Ver[i].info);
while(p!=NULL)
{
count++;
p=p->next;
}
printf("%d\n",count);
}
}
//图的邻接表存储方法,求出度为0的顶点个数
void AdjZeroOutDegree(AdjGraph *G)
{
int i,count=0; //count为出度顶点的个数
ENode *p;
for(i=0;i < G->v;i++)
{
if(G->Ver[i].first==NULL)
count++;
}
printf("出度为0的顶点个数为%d\n",count);
}
int main()
{
int adj[MAX_V][MAX_V]=
{ //图的形状:
{0,1,0,1,0}, // 1
{0,0,1,1,0}, // ↙↓↖
{0,0,0,1,1}, // 2→ 3←0
{0,0,0,0,0}, // ↘↑↗
{1,0,0,1,0} // 4
};
int v=5,e=8;
AdjGraph* AG=NULL;
CreateAdj(AG,adj,v,e);
DispAdj(AG);
printf("\n图的邻接表存储方式:\n");
printf("(1)\n");
AdjInDegree(AG);
printf("(2)\n");
AdjOutDegree(AG);
printf("(3)\n");
AdjZeroOutDegree(AG);
return 0;
}
#include
#include
#define INF 32767 //定义无穷大
#define MAXV 100 //最大顶点个数
typedef char InfoType;
//定义邻接表类型
typedef struct ANode
{
int adjvex;
struct ANode *nextarc;
int weight;
} ArcNode;
typedef struct Vnode
{
InfoType info;
int count;
ArcNode *firstarc;
}VNode;
typedef struct
{
VNode adjlist[MAXV];
int n,e;
}AdjGraph;
//创建邻接表
void CreateAdj(AdjGraph *&G,int A[MAXV][MAXV],int n,int e)
{
int i,j;
ArcNode *p;
G=(AdjGraph *)malloc(sizeof(AdjGraph));
for(i=0;iadjlist[i].firstarc=NULL;
for(i=0;i=0;j--)
{
if(A[i][j]!=0&&A[i][j]!=INF)
{
p=(ArcNode *)malloc(sizeof(ArcNode));
p->adjvex=j;
p->weight=A[i][j];
p->nextarc=G->adjlist[i].firstarc;
G->adjlist[i].firstarc=p;
}
}
}
G->n=n;G->e=n;
}
//输出邻接表
void DispAdj(AdjGraph *G)
{
int i;
ArcNode *p;
for(i=0;in;i++)
{
p=G->adjlist[i].firstarc;
printf("%3d:",i);
while(p!=NULL)
{
printf("%3d[%d]->",p->adjvex,p->weight);
p=p->nextarc ;
}
printf("^\n");
}
}
//销毁邻接表
void DestroyAdj(AdjGraph *&G)
{
int i;
ArcNode *pre,*p;
for(i=0;in;i++)
{
pre=G->adjlist[i].firstarc;
if(pre!=NULL)
{
p=pre->nextarc ;
while(p!=NULL)
{
free(pre);
pre=p;p=p->nextarc ;
}
free(pre);
}
}
free(G);
}
//判断有无经过顶点v的回路
int visited[MAXV]; //全局变量数组
void Cycle(AdjGraph *G,int u,int v,int d,bool &has)
{
ArcNode *p;
int w;
visited[u]=1;d++;
p=G->adjlist[u].firstarc;
while(p!=NULL)
{
w=p->adjvex ;
if(visited[w]==0)
Cycle(G,w,v,d,has);
else if(w==v&&d>1)
{
has=true;
return;
}
p=p->nextarc ;
}
}
bool hasCycle(AdjGraph *G,int m)
{
bool has=false;
Cycle(G,m,m,-1,has);
return has;
}
int main()
{
int adj[MAXV][MAXV]=
{ //图的形状:
{0,1,0,1,0}, // 1
{0,0,1,1,0}, // ↙↓↖
{0,0,0,1,1}, // 2→ 3←0
{0,0,0,0,0}, // ↘↑↗
{1,0,0,1,0} // 4
};
int v=5,e=8;
int m=3;
AdjGraph* AG=NULL;
printf("图的邻接表存储:\n");
CreateAdj(AG,adj,v,e);
DispAdj(AG);
printf("v=3\n");
if(hasCycle(AG,v))
{
printf("有经过顶点%d的回路!",m);
}
else
{
printf("没有经过顶点%d的回路!",m);
}
return 0;
}
#include
#include
#define MAXV 100
//以下定义邻接矩阵类型
typedef struct
{
int no; //顶点编号
int info; //顶点其余的信息
}VertexType;
typedef struct
{
int edges[MAXV][MAXV]; //邻接矩阵
int n,e; //顶点数,弧数
VertexType vexs[MAXV]; //存放顶点信息
}MGraph;
//定义邻接表类型
typedef struct ANode //弧的节点结构类型
{
int adjvex; //该弧的终点位置
struct ANode *nextarc;
int info; //弧的相关信息
} ArcNode;
typedef struct Vnode //邻接表头结点类型
{
int data; //顶点信息
ArcNode *firstarc; //指向第一条弧
}VNode;
typedef VNode AdjList[MAXV];
typedef struct
{
AdjList adjlist;
int n,e;
}ALGraph;
int visited[MAXV];
//深度优先遍历
void DFS(ALGraph *G,int v)
{
ArcNode *p;
visited[v]=1;
p=G->adjlist[v].firstarc;
while(p!=NULL)
{
if(visited[p->adjvex]==0)
{
printf("<%d,%d>",v,p->adjvex);
DFS(G,p->adjvex);
}
p=p->nextarc;
}
}
//广度优先遍历
void BFS(ALGraph *G,int v)
{
ArcNode *p;
int queue[MAXV],front=0,rear=0;
int w,i;
for(i=0;in;i++)
visited[i]=0;
visited[v]=1;
rear=(rear+1)%MAXV;
queue[rear]=v;
while(front!=rear)
{
front=(front+1)%MAXV;
w=queue[front];
p=G->adjlist[w].firstarc;
while(p!=NULL)
{
if(visited[p->adjvex]==0)
{
printf("<%d,%d>",w,p->adjvex);
visited[p->adjvex]=1;
rear=(rear+1)%MAXV;
queue[rear]=p->adjvex;
}
p=p->nextarc;
}
}
printf("\n");
}
void DispAdj(ALGraph *G) //输出邻接表
{
int i;
ArcNode *p;
for(i=0;in;i++)
{
p=G->adjlist[i].firstarc;
if(p) printf("%3d:",i);
while(p)
{
printf("%3d->",p->adjvex);
p=p->nextarc;
}
printf("\n");
}
}
void MatToList(MGraph g,ALGraph *&G) //将邻接矩阵 g 转换为邻接表 G
{
int i,j,n=g.n;
ArcNode *p;
G=(ALGraph *)malloc(sizeof(ALGraph));
for(i=0;iadjlist[i].firstarc=NULL;
for(i=0;i=0;j--)
if(g.edges[i][j])
{
p=(ArcNode *)malloc(sizeof(ArcNode));
p->adjvex=j;
p->info=g.edges[i][j];
p->nextarc=G->adjlist[i].firstarc;
G->adjlist[i].firstarc=p;
}
G->n=n;
G->e=g.e;
}
int main()
{
int i,j;
MGraph g;
ALGraph *G;
int A[MAXV][11]={
{0,1,1,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0},
{1,0,0,0,1,1,0,0,0,0,0},
{1,0,0,1,0,1,1,0,0,0,0},
{1,0,1,0,0,0,0,1,0,0,0},
{0,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0},
{0,1,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0},
{0,0,1,0,0,0,0,1,1,1,0},
{0,0,0,1,0,0,1,0,0,0,1},
{0,0,0,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,0},
{0,0,0,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,0},
{0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,0,0,0}};
g.n=11;g.e=13;
for(i=0;i #include
#include
#define INF 32767 //定义无穷大
#define MAXV 100 //最大顶点个数
typedef char InfoType;
//定义邻接矩阵类型
typedef struct
{
int no;
InfoType info;
}VertexType;
typedef struct
{
int edges[MAXV][MAXV];
int n,e;
VertexType vexs[MAXV];
}MatGraph;
//输出邻接矩阵
void DispMat(MatGraph g)
{
int i,j;
for(i=0;i #include
#include
#define INF 32767 //定义无穷大
#define MAXV 100 //最大顶点个数
#define MAXE 100
typedef char InfoType;
//定义邻接矩阵类型
typedef struct
{
int no;
InfoType info;
}VertexType;
typedef struct
{
int edges[MAXV][MAXV];
int n,e;
VertexType vexs[MAXV];
}MatGraph;
typedef struct
{
int u;
int v;
int w;
}Edge;
//输出邻接矩阵
void DispMat(MatGraph g)
{
int i,j;
for(i=0;i=0&&temp.w