如何用Python编写一个Lisp解释器

作者 | Peter Norvig 译者 | Tianyu 编辑 | Freesia
出品 | Python大本营(ID: pythonnews)
本文有两个目的:一是展示如何实现一个计算机语言的解释器,二是演示如何使用 Python 3 构造 Lisp 的一种方言 Schema,我把我的语言解释器称作 Lispy。几年前,作者曾展示过如何用 Java 和 Common Lisp 写 Schema 解释器。而本次的目的很纯粹,作者会尽可能简明扼要,就像 Alan Kay 所谓的 “软件中的麦克斯韦方程组”。
Schema 程序的语法和语义
语言的语法是指组成正确的语句或表达式的顺序;语义指那些表达式或语句的内在含义。例如,在数学表达式语言中(以及诸多编程语言中),一加二的语法是 “1 + 2”,而语义是指对两个数字执行相加操作,得到的结果为 3 。当我们计算一个数值时,也可以说我们在评估一种表达形式;我们可以说 “1+2” 估值为 3,并写成 “1 + 2” ⇒ 3. Schema 的语法不同于其他大多数编程语言。考虑如下情况:

Java 的语法规范十分繁杂(关键词、中缀运算符、三种括号、运算符优先级、点语法、引号、逗号、分号),但 Schema 的语法要简单得多:
- Schema 程序仅由表达式组成。没有表达式和语句之分。
- 数字(比如:1)和符号(比如:A)都可以称为原子表达式;它们无法再细分了。这和 Java 中的 counterpart 类似,但 Schema 不同,一些运算符号,如 + 和 > 也是标识符,和 A 及 fn 的地位是平等的。
- 还有列表表达式:一个 "(" ,后面接零或多个表达式,后面再接一个 ")"。列表的第一个元素决定了其含义是什么:
- 以关键词作为开头的列表,如 (if ...),是一种特殊形式,含义取决于关键词是什么。
- 以非关键词开头的列表,如 (fn ...),是函数的调用。
Schema 的妙处在于整个语言体系仅需 5 个关键词和 8 种语法形式。对比之下,Python 有 33 个关键词和 110 种语法形式,Java 有 50 个关键词和 133 种语法形式。那些括号也许看起来有些吓人,但 Schema 的语法具备着简单性与一致性。(有人开玩笑说 Lisp 就是“大量把人搞疯的括号”;而我认为 Lisp 象征着语法的纯粹性。) 在本文中,我们会介绍 Schema 语言及其解释器的所有特点,但中间要经过两个步骤,先定义一个简单的语言,再定义 Schema 语言的全部内容。
语言1:Lispy Calculator
Lispy Calculator 是 Schema 的一部分,仅使用了五种语法方式。因其基于 Lispy Calculator,只要你熟练使用前缀表示法,就可以做任何典型计算机可以做的运算。你可以做两件典型计算机语言所不能做的两件事:"if" 表达式和定义新变量。下面是一个示例程序,基于公式 π r2,计算半径为10的圆形面积:
(define r 10)
(* pi (* r r))| Expression(表达式) | Syntax(语法) | Semantics and Example(语义和例子) |
| variable reference | symbol | 一个标识符被解释为变量名;它的值是变量的值。例子:r ⇒ 10 (假设 r 已被定义为10) |
| constant literal | number | 计算结果为数字本身。例子:12 ⇒ 12 or -3.45e+6 ⇒ -3.45e+6 |
| conditional | (if test conseq alt) | 执行 test;如果结果为 true,计算返回 conseq;否则返回 alt。例子:(if (> 10 20) (+ 1 1) (+ 3 3)) ⇒ 6 |
| definition | (define symbol exp) | 定义一个新变量,并计算表达式 exp 赋值给它。例子:(define r 10) |
| procedure call | (proc arg...) | 如果表达式不是这些标识符 if, define 或 quote,那它就是一个过程。执行表达式及全部参数,那么该过程就会被调用,而参数值列表也被调用。例子:(sqrt (* 2 8)) ⇒ 4.0 |
在该表的语法一栏,标识符必须为符号,数字必须为整数或小数,而其它斜体 字可以为任何表达式,arg... 则表示零或多个 arg 的重复。
语言解释器到底是做什么的?
语言解释器包括两个部分:
- Parsing:parsing 组件获得字符串形式的输入,并根据语言的语法规则进行验证,然后将程序翻译成内部的表示形式。在一个简单的解释器中,内部的表示形式是一个树形结构(一般被称为抽象语法树),反应了程序语句和表达式的嵌套结构。在被称为编译器的语言翻译器中,常常有一系列内部的表示形式,以抽象语法树开头,然后紧接着一系列指令,可以直接被计算机执行。
- Execution:内部的表示形式是根据语言的语义规则进行处理的,因此才能执行计算。Lispy 的 execution 函数叫作 eval(注意这和 Python 的内置函数同名)。
下面是解释器工作过程的图片:
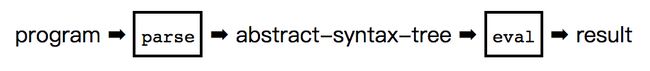 这里举一个简单的小例子,看看 parse 和 eval 能做些什么:
这里举一个简单的小例子,看看 parse 和 eval 能做些什么:
>> program = "(begin (define r 10) (* pi (* r r)))"
>>> parse(program)
['begin', ['define', 'r', 10], ['*', 'pi', ['*', 'r', 'r']]]
>>> eval(parse(program))
314.1592653589793类型定义
我们来明确一下 Scheme 对象的表示方法:
Symbol = str # A Scheme Symbol is implemented as a Python str
Number = (int, float) # A Scheme Number is implemented as a Python int or float
Atom = (Symbol, Number) # A Scheme Atom is a Symbol or Number
List = list # A Scheme List is implemented as a Python list
Exp = (Atom, List) # A Scheme expression is an Atom or List
Env = dict # A Scheme environment (defined below)
# is a mapping of {variable: valueParsing:parse, tokenize, read_from_tokens
传统上来看,parsing 一般分成两部分:词法分析(lexical analysis),也就是将输入字符串分成一系列 token,以及语义分析(syntactic analysis),也就是将 tokens 组装成后向抽象语法树。Lispy 的 tokens 是括号、标识符和数字。有许多用于词法分析的工具(如 Mike Lesk 和 Eric Schmidt 的 lex),但现在我们选择使用一个非常简单的工具:Python 的 str.split 函数。tokenize 函数以字符串作为输入,在每个括号两边加空格,然后调用 str.split 获取 tokens 列表:
def tokenize(chars: str) -> list:
"Convert a string of characters into a list of tokens."
return chars.replace('(', ' ( ').replace(')', ' ) ').split()下面我们在程序示例中使用 tokenize:
>>> program = "(begin (define r 10) (* pi (* r r)))"
>>> tokenize(program)
['(', 'begin', '(', 'define', 'r', '10', ')', '(', '*', 'pi', '(', '*', 'r', 'r', ')', ')', ')']函数 parse 以字符串的表达形式作为程序输入,调用 tokenize 获取 tokens 列表,然后调用 read_from_tokens 来组装抽象语法树。read_from_tokens 会关注第一个 token,如果第一个是 ')',那么是一个语法错误。如果第一个是 '(',那么我们就开始建立子表达式的列表,直到我们遇到匹配的 ')'。任何没有括号的 token 一定是标识符或数字。我们可以让 Python 对此做判断:对于每个不含括号的 token,首先尝试将其解释为整数,然后是小数,如果哪个都不符合,那么它一定是个标识符。下面来看一下 parse 实例:
def parse(program: str) -> Exp:
"Read a Scheme expression from a string."
return read_from_tokens(tokenize(program))
def read_from_tokens(tokens: list) -> Exp:
"Read an expression from a sequence of tokens."
if len(tokens) == 0:
raise SyntaxError('unexpected EOF')
token = tokens.pop(0)
if token == '(':
L = []
while tokens[0] != ')':
L.append(read_from_tokens(tokens))
tokens.pop(0) # pop off ')'
return L
elif token == ')':
raise SyntaxError('unexpected )')
else:
return atom(token)
def atom(token: str) -> Atom:
"Numbers become numbers; every other token is a symbol."
try: return int(token)
except ValueError:
try: return float(token)
except ValueError:
return Symbol(token)
>>> program = "(begin (define r 10) (* pi (* r r)))"
>>> parse(program)
['begin', ['define', 'r', 10], ['*', 'pi', ['*', 'r', 'r']]]环境
环境是指变量名与值之间的映射。eval 默认使用全局环境,包括一组标准函数的名称(如 sqrt 和 max,以及操作符 *)。环境也可以由用户进行变量自定义:
import math
import operator as op
def standard_env() -> Env:
"An environment with some Scheme standard procedures."
env = Env()
env.update(vars(math)) # sin, cos, sqrt, pi, ...
env.update({
'+':op.add, '-':op.sub, '*':op.mul, '/':op.truediv,
'>':op.gt, '<':op.lt, '>=':op.ge, '<=':op.le, '=':op.eq,
'abs': abs,
'append': op.add,
'apply': lambda proc, args: proc(*args),
'begin': lambda *x: x[-1],
'car': lambda x: x[0],
'cdr': lambda x: x[1:],
'cons': lambda x,y: [x] + y,
'eq?': op.is_,
'expt': pow,
'equal?': op.eq,
'length': len,
'list': lambda *x: List(x),
'list?': lambda x: isinstance(x, List),
'map': map,
'max': max,
'min': min,
'not': op.not_,
'null?': lambda x: x == [],
'number?': lambda x: isinstance(x, Number),
'print': print,
'procedure?': callable,
'round': round,
'symbol?': lambda x: isinstance(x, Symbol),
})
return env
global_env = standard_env()Evaluation: eval
我们已经做好实现 eval 的准备了。作为初学者,来回顾一下之前的 Lispy Calculator 表:
Expression(表达式) |
Syntax(语法) |
Semantics and Example (语义和例子) |
variable reference |
symbol |
一个标识符被解释为变量名;它的值是变量的值。 例子:r ⇒ 10 (假设 r 已被定义为10) |
constant literal |
number |
计算结果为数字本身。 例子:12 ⇒ 12 or -3.45e+6 ⇒ -3.45e+6 |
conditional |
(if test conseq alt) |
执行 test;如果结果为 true,计算返回 conseq;否则返回 alt。 例子:(if (> 10 20) (+ 1 1) (+ 3 3)) ⇒ 6 |
definition |
(define symbol exp) |
定义一个新变量,并计算表达式 exp 赋值给它。 例子:(define r 10) |
procedure call |
(proc arg...) |
如果表达式不是这些标识符 if, define 或 quote,那它就是一个过程。执行表达式及全部参数,那么该过程就会被调用,而参数值列表也被调用。 例子:(sqrt (* 2 8)) ⇒ 4.0 |
下面是实现 eval 的代码,完全遵循上面的表格:
def eval(x: Exp, env=global_env) -> Exp:
"Evaluate an expression in an environment."
if isinstance(x, Symbol): # variable reference
return env[x]
elif not isinstance(x, Number): # constant number
return x
elif x[0] == 'if': # conditional
(_, test, conseq, alt) = x
exp = (conseq if eval(test, env) else alt)
return eval(exp, env)
elif x[0] == 'define': # definition
(_, symbol, exp) = x
env[symbol] = eval(exp, env)
else: # procedure call
proc = eval(x[0], env)
args = [eval(arg, env) for arg in x[1:]]
return proc(*args)>>> eval(parse("(begin (define r 10) (* pi (* r r)))"))
314.1592653589793
Interaction: A REPL
一直输入 eval 固然很枯燥。Lisp 的一个伟大之处就在于交互式 read-eval-print 循环:为编程者提供了输入表达式,并立即读取,计算,然后输出的途径,而非冗长的构建/编译/运行过程。那么,我们来定义一下 repl 函数,函数 schemestr 返回了一个代表 Schema 对象的字符串:
def repl(prompt='lis.py> '):
"A prompt-read-eval-print loop."
while True:
val = eval(parse(raw_input(prompt)))
if val is not None:
print(schemestr(val))
def schemestr(exp):
"Convert a Python object back into a Scheme-readable string."
if isinstance(exp, List):
return '(' + ' '.join(map(schemestr, exp)) + ')'
else:
return str(exp)>>> repl()
lis.py> (define r 10)
lis.py> (* pi (* r r))
314.159265359
lis.py> (if (> (* 11 11) 120) (* 7 6) oops)
42
lis.py> (list (+ 1 1) (+ 2 2) (* 2 3) (expt 2 3))
lis.py>
语言2:Full Lispy
现在我们来拓展一下,下面的表格展示了一个更加完整的 Schema 子集:
| Expression(表达式) | Syntax(语法) | Semantics and Example(语义和例子) |
| quotation | (quote exp) | 返回表达式 exp 的值,但不进行计算。例子:(quote (+ 1 2)) ⇒ (+ 1 2) |
| assignment | (set! symbol exp) | 执行 exp 并把值赋给 symbol,symbol 必须被预先定义好。例子:(set! r2 (* r r)) |
| procedure | (lambda (symbol...)exp) | 创造一个带参数 (symbol...) 的过程,exp 为其主体。例子:(lambda (r) (* pi (* r r))) |
lambda 这种特殊形式可以进行 procedure(过程)的创建。我们希望 procedure 能这样运行:
lis.py> (define circle-area (lambda (r) (* pi (* r r)))
lis.py> (circle-area (+ 5 5))
314.159265359将 Env 重定义为 Class
为了方便操作局部变量,我们将 Env 重定义为 dict 的子类。当我们计算 (circle-area (+ 5 5)) 时,我们会先获取 procedure 的主体 (* pi (* r r)),然后在 r 作为单独局部变量的环境下进行计算,但同时也存在全局环境作为“外部”环境;这样我们就得到了 * 和 pi 的值。换句话说,我们需要这样一个环境,将局部(蓝色框标注的)环境嵌在外部(红色框标注的)环境内:
当我们在这样一个嵌套环境中查看变量时,我们首先看到的是最内层,如果没有找到变量名,再转移到外面一层。过程和环境是耦合的,接下来试着来一起定义它们:
class Env(dict):
"An environment: a dict of {'var': val} pairs, with an outer Env."
def __init__(self, parms=(), args=(), outer=None):
self.update(zip(parms, args))
self.outer = outer
def find(self, var):
"Find the innermost Env where var appears."
return self if (var in self) else self.outer.find(var)
class Procedure(object):
"A user-defined Scheme procedure."
def __init__(self, parms, body, env):
self.parms, self.body, self.env = parms, body, env
def __call__(self, *args):
return eval(self.body, Env(self.parms, args, self.env))
global_env = standard_env()def eval(x, env=global_env):
"Evaluate an expression in an environment."
if isinstance(x, Symbol): # variable reference
return env.find(x)[x]
elif not isinstance(x, List):# constant
return x
op, *args = x
if op == 'quote': # quotation
return args[0]
elif op == 'if': # conditional
(test, conseq, alt) = args
exp = (conseq if eval(test, env) else alt)
return eval(exp, env)
elif op == 'define': # definition
(symbol, exp) = args
env[symbol] = eval(exp, env)
elif op == 'set!': # assignment
(symbol, exp) = args
env.find(symbol)[symbol] = eval(exp, env)
elif op == 'lambda': # procedure
(parms, body) = args
return Procedure(parms, body, env)
else: # procedure call
proc = eval(op, env)
vals = [eval(arg, env) for arg in args]
return proc(*vals)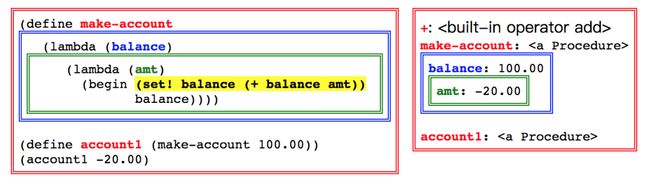 每个矩形框代表一个环境,框的颜色与环境中所定义的变量的颜色相对应。在程序的后两行,我们定义了 account1,并调用了 (account1 -20.00);这表示创建了一个期初余额为100刀的银行账户,被取出了20刀。在计算 (account1 -20.00) 的过程中,我们对 eval 表达式做了高亮处理。该表达式含三个变量,amt 在最内层(绿色)里。但 balance 不在这一层,我们需要看绿色环境外面的 env,即蓝色层。最后,变量 + 不在这三层中,我们需要找更外面的层,来到全局(红色)环境。这个先看内环境再看外环境的过程叫作 lexical scoping。
下面来看看我们可以做哪些事。
每个矩形框代表一个环境,框的颜色与环境中所定义的变量的颜色相对应。在程序的后两行,我们定义了 account1,并调用了 (account1 -20.00);这表示创建了一个期初余额为100刀的银行账户,被取出了20刀。在计算 (account1 -20.00) 的过程中,我们对 eval 表达式做了高亮处理。该表达式含三个变量,amt 在最内层(绿色)里。但 balance 不在这一层,我们需要看绿色环境外面的 env,即蓝色层。最后,变量 + 不在这三层中,我们需要找更外面的层,来到全局(红色)环境。这个先看内环境再看外环境的过程叫作 lexical scoping。
下面来看看我们可以做哪些事。
>>> repl()
lis.py> (define circle-area (lambda (r) (* pi (* r r))))
lis.py> (circle-area 3)
28.274333877
lis.py> (define fact (lambda (n) (if (<= n 1) 1 (* n (fact (- n 1))))))
lis.py> (fact 10)
3628800
lis.py> (fact 100)
9332621544394415268169923885626670049071596826438162146859296389521759999322991
5608941463976156518286253697920827223758251185210916864000000000000000000000000
lis.py> (circle-area (fact 10))
4.1369087198e+13
lis.py> (define first car)
lis.py> (define rest cdr)
lis.py> (define count (lambda (item L) (if L (+ (equal? item (first L)) (count item (rest L))) 0)))
lis.py> (count 0 (list 0 1 2 3 0 0))
3
lis.py> (count (quote the) (quote (the more the merrier the bigger the better)))
4
lis.py> (define twice (lambda (x) (* 2 x)))
lis.py> (twice 5)
10
lis.py> (define repeat (lambda (f) (lambda (x) (f (f x)))))
lis.py> ((repeat twice) 10)
40
lis.py> ((repeat (repeat twice)) 10)
160
lis.py> ((repeat (repeat (repeat twice))) 10)
2560
lis.py> ((repeat (repeat (repeat (repeat twice)))) 10)
655360
lis.py> (pow 2 16)
65536.0
lis.py> (define fib (lambda (n) (if (< n 2) 1 (+ (fib (- n 1)) (fib (- n 2))))))
lis.py> (define range (lambda (a b) (if (= a b) (quote ()) (cons a (range (+ a 1) b)))))
lis.py> (range 0 10)
(0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9)
lis.py> (map fib (range 0 10))
(1 1 2 3 5 8 13 21 34 55)
lis.py> (map fib (range 0 20))
(1 1 2 3 5 8 13 21 34 55 89 144 233 377 610 987 1597 2584 4181 6765)
Lispy 评估
我们从下面几个角度来评估 Lispy:
- 轻量:Lispy 非常小:去掉注释和空格,共117行;源码大小为4K。我用 Java 写的 Schema 最小版本有1664行,源码大小为57K。Jscheme 最初名为 SILK (Scheme in Fifty Kilobytes),但我仅通过计算字节码来保证不超限,而非通过改变源码。Lispy 在这方面做得好多了;我认为它符合 Alan Kay 在1972年提出的,你可以通过一页代码来创造世界上最棒的语言。
- 快速:Lispy 计算 (fact 100) 用时0.003秒。这对我来说,速度足够快了。
- 完整:和标准版 Schema 相比,Lispy 不是很完整。主要包括以下几个缺陷:
- 语法:缺少注释、quote/quasiquote 声明、# literals、派生表达式类型(如源自 if 的 cond,源自 lambda 的 let)和点表示法列表。
- 语义:缺少 call/cc 和 tail recursion。
- 数据类型:缺少字符串、字符、布尔、向量等。
- 过程:缺少100个原始 procedure。
- 错误恢复:Lispy 无法检测和报告错误,也无法对其进行恢复。Lispy 需要编程者操作无失误。
- 性能:这就要由读者来判断了。在我看来,它可以达到我的目的,即充当 Lisp 的解释器。
真实的故事
追溯这个想法的来源有助于理解解释器的工作原理,我下面讲一个真实的故事。让我们将时间推回到1984年,当时我正在写博士论文。那时还没有 LateX,也没有 Microsoft Word,我用的是 troff。不幸的是,troff 没有向前引用符号标签:我想写出 "As we will see on page @theorem-x",然后在合适的地方写类似 "@(set theorem-x \n%)" 的东西。我的研究生伙伴 Tony DeRose 也有同样的需求,于是我们一起勾勒出了一个简单的 Lisp 程序,可用作预处理器。然而,我们当时造出的 Lisp 虽然善于读取 Lisp 表达式,但读取非 Lisp 表达式时,慢得令人发指。
于是,我和 Tony 分道扬镳了。他认为最难的部分是表达式的解释器;他需要的是 Lisp,他知道如何编写 C 程序来处理非 Lisp 字符,并将其链接到 Lisp 程序。我不知道如何将其连在一起,但我认为,为这个语言写一个解释器更容易,所以我用 C 写了个解释器。有趣的是,Tony 用 C 写了个 Lisp 程序,因为他是个 C 程序员。而我写了个 C 程序,因为我是个 Lisp 程序员。
最后,我们都把工作搞定了。
原文链接: https://norvig.com/lispy.html
(*本文为Python大本营编译文章,转载请联系微信 1092722531)
社群福利
扫码添加小助手,回复:大会,加入2019 AI开发者大会福利群,每周一、三、五更新技术福利,还有不定期的抽奖活动~
![]()
◆
精彩推荐
◆

60+技术大咖与你相约 2019 AI ProCon!3.5折优惠票,倒计时4天速抢进行中......2019 AI开发者大会将于9月6日-7日在北京举行,这一届AI开发者大会有哪些亮点?一线公司的大牛们都在关注什么?AI行业的风向是什么?2019 AI开发者大会,倾听大牛分享,聚焦技术实践,和万千开发者共成长。
用Python给女友准备个绝对甜蜜的七夕礼物
谁偷偷删了你的微信?别慌!Python帮你都揪出来了
干货 | 20个Python教程,掌握时间序列的特征分析(附代码)
吐血整理!140种Python标准库、第三方库和外部工具都有了
如何用爬虫技术帮助孩子秒到心仪的幼儿园(基础篇)
Python传奇:30年崛起之路
干货 | Python后台开发的高并发场景优化解决方案
2019年最新华为、BAT、美团、头条、滴滴面试题目及答案汇总