Lombok之@EqualsAndHashCode使用
一. 为什么要用@EqualsAndHashCode?
在java.lang.Object中有两个实例方法——equals和hashCode。这两个方法就像孪生兄弟一样,重写equals,就要重写hashCode。至于为什么?可以看这篇博客《java中==,equals,hashcode》补补课。现在,我们来看看如何手动重写equals和hashCode方法。可以,使用Intellij IDEA的快捷键生成equals和hashCode方法:
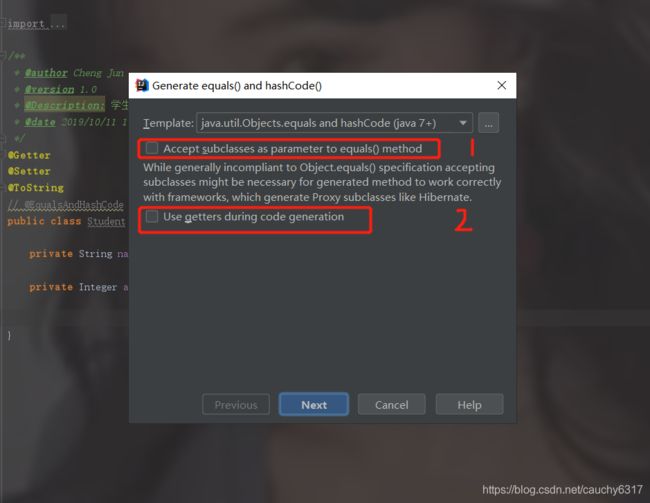
在Template的下拉框中有着不同的选项用于生成equals和hashCode方法,我们选择java.util.Objects.equals and hashCode (java 7+),利用jdk1.7 的Objects工具类。上图的可选项1是指是否将从父类继承的字段包含到生成的equals方法中,可选项2是指是否使用getter方法,如果不是getter方法(student.getName()),则使用对象.成员变量(student.name)的形式直接访问成员变量。
@Getter
@Setter
@ToString
// @EqualsAndHashCode
public class Student {
private String name;
private Integer age;
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
Student student = (Student) o;
return Objects.equals(name, student.name) &&
Objects.equals(age, student.age);
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(name, age);
}
}
可以看到生成的代码中使用Objects的类方法equals(Object o)和hash()。同样的问题,生成的方法占据了不小的篇幅。
二. @EqualsAndHashCode如何使用?
@EqualsAndHashCode的使用很简单,只需在Student类加上@EqualsAndHashCode后,编译,再查看编译后的文件。
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (o == this) {
return true;
} else if (!(o instanceof Student)) {
return false;
} else {
Student other = (Student)o;
if (!other.canEqual(this)) {
return false;
} else {
Object this$name = this.getName();
Object other$name = other.getName();
if (this$name == null) {
if (other$name != null) {
return false;
}
} else if (!this$name.equals(other$name)) {
return false;
}
Object this$age = this.getAge();
Object other$age = other.getAge();
if (this$age == null) {
if (other$age != null) {
return false;
}
} else if (!this$age.equals(other$age)) {
return false;
}
return true;
}
}
}
protected boolean canEqual(Object other) {
return other instanceof Student;
}
public int hashCode() {
int PRIME = true;
int result = 1;
Object $name = this.getName();
int result = result * 59 + ($name == null ? 43 : $name.hashCode());
Object $age = this.getAge();
result = result * 59 + ($age == null ? 43 : $age.hashCode());
return result;
}
出于文章篇幅的考虑,只贴出了由@EqualsAndHashCode注解生成的代码。可以看到生成访问控制符为protected的canEqual(Object other)方法。

可以看到,只要属性全部相等,student和student1的equals方法就返回true。但是 == 永远判断是内存地址,所以当某个类重写了equals方法后,就要使用equals方法去做判断。
三. @EqualsAndHashCode源码
package lombok;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
/**
* Generates implementations for the {@code equals} and {@code hashCode} methods inherited by all objects, based on relevant fields.
*
* Complete documentation is found at the project lombok features page for @EqualsAndHashCode.
*/
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.SOURCE)
public @interface EqualsAndHashCode {
/**
* Any fields listed here will not be taken into account in the generated {@code equals} and {@code hashCode} implementations.
* Mutually exclusive with {@link #of()}.
*
* Will soon be marked {@code @Deprecated}; use the {@code @EqualsAndHashCode.Exclude} annotation instead.
*
* @return A list of fields to exclude.
*/
String[] exclude() default {};
/**
* If present, explicitly lists the fields that are to be used for identity.
* Normally, all non-static, non-transient fields are used for identity.
*
* Mutually exclusive with {@link #exclude()}.
*
* Will soon be marked {@code @Deprecated}; use the {@code @EqualsAndHashCode.Include} annotation together with {@code @EqualsAndHashCode(onlyExplicitlyIncluded = true)}.
*
* @return A list of fields to use (default: all of them).
*/
String[] of() default {};
/**
* Call on the superclass's implementations of {@code equals} and {@code hashCode} before calculating for the fields in this class.
* default: false
*
* @return Whether to call the superclass's {@code equals} implementation as part of the generated equals algorithm.
*/
boolean callSuper() default false;
/**
* Normally, if getters are available, those are called. To suppress this and let the generated code use the fields directly, set this to {@code true}.
* default: false
*
* @return If {@code true}, always use direct field access instead of calling the getter method.
*/
boolean doNotUseGetters() default false;
/**
* Any annotations listed here are put on the generated parameter of {@code equals} and {@code canEqual}.
* This is useful to add for example a {@code Nullable} annotation.
* The syntax for this feature depends on JDK version (nothing we can do about that; it's to work around javac bugs).
* up to JDK7:
* {@code @EqualsAndHashCode(onParam=@__({@AnnotationsGoHere}))}
* from JDK8:
* {@code @EqualsAndHashCode(onParam_={@AnnotationsGohere})} // note the underscore after {@code onParam}.
*
* @return List of annotations to apply to the generated parameter in the {@code equals()} method.
*/
AnyAnnotation[] onParam() default {};
/**
* Placeholder annotation to enable the placement of annotations on the generated code.
* @deprecated Don't use this annotation, ever - Read the documentation.
*/
@Deprecated
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.SOURCE)
@Target({})
@interface AnyAnnotation {}
/**
* Only include fields and methods explicitly marked with {@code @EqualsAndHashCode.Include}.
* Normally, all (non-static, non-transient) fields are included by default.
*
* @return If {@code true}, don't include non-static non-transient fields automatically (default: {@code false}).
*/
boolean onlyExplicitlyIncluded() default false;
/**
* If present, do not include this field in the generated {@code equals} and {@code hashCode} methods.
*/
@Target(ElementType.FIELD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.SOURCE)
public @interface Exclude {}
/**
* Configure the behaviour of how this member is treated in the {@code equals} and {@code hashCode} implementation; if on a method, include the method's return value as part of calculating hashCode/equality.
*/
@Target({ElementType.FIELD, ElementType.METHOD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.SOURCE)
public @interface Include {
/**
* Defaults to the method name of the annotated member.
* If on a method and the name equals the name of a default-included field, this member takes its place.
*
* @return If present, this method serves as replacement for the named field.
* 是指当一个方法的名称和变量名相同时,包含方法进入equals,不包含字段。
*/
String replaces() default "";
}
}
- 元注解:@Target(ElementType.TYPE)只能在类上使用,@Retention(RetentionPolicy.SOURCE)只在代码里保留。
- 注解属性:
- exclude,of不用了解,准备弃用了,使用EqualsAndHashCode.Exclude和EqualsAndHashCode.Include代替;
- callSuper表示是否将父类的equals和hashCode方法加到该子类的equals和hashCode方法中;
- doNotUseGetters表示是否使用getter访问成员变量;
- onParam参考Lombok实验室之onX使用;
- onlyExplicitlyIncluded为false时,所有的非静态和非瞬态的字段都会被包含进equals和hashCode方法中;为true时,只有在字段上明确使用了EqualsAndHashCode.Include注解才会被包含进equals和hashCode方法中。
四. 特别说明
本文已经收录在Lombok注解系列文章总览中,并继承上文中所提的特别说明。
源码地址:gitee