【muduo】base篇---ThreadPool
一、线程池简介
1. 线程池的概念:
线程池就是首先创建一些线程,它们的集合称为线程池。使用线程池可以很好地提高性能,线程池在系统启动时即创建大量空闲的线程,程序将一个任务传给线程池,线程池就会启动一条线程来执行这个任务,执行结束以后,该线程并不会死亡,而是再次返回线程池中成为空闲状态,等待执行下一个任务。
2. 线程池的工作机制
2.1 在线程池的编程模式下,任务是提交给整个线程池,而不是直接提交给某个线程,线程池在拿到任务后,就在内部寻找是否有空闲的线程,如果有,则将任务交给某个空闲的线程。
2.1 一个线程同时只能执行一个任务,但可以同时向一个线程池提交多个任务。
3. 使用线程池的原因:
多线程运行时间,系统不断的启动和关闭新线程,成本非常高,会过渡消耗系统资源,以及过渡切换线程的危险,从而可能导致系统资源的崩溃。这时,线程池就是最好的选择了。
线程池本质上也是生产者消费者问题:生产者线程向任务队列添加任务,消费者线程(在线程队列中)从任务队列取出任务去执行。
![]()
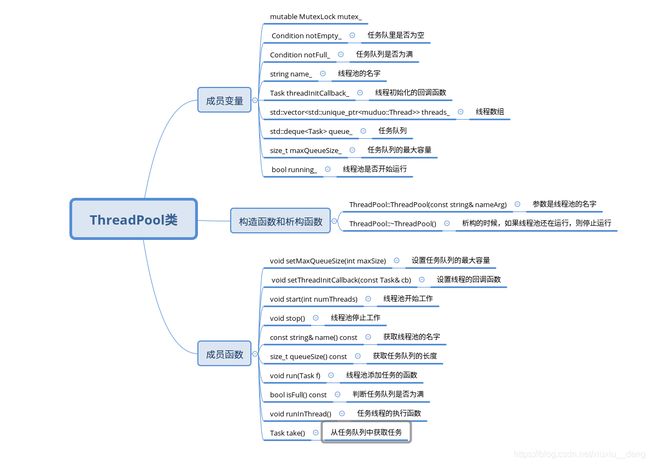
二、ThreadPool
线程池ThreadPool用到了前面分析的Thread、MutexLock、Condition。ThreadPool可以设置工作线程的数量,并向任务队列放入任务。放入到任务队列中的任务将由某个工作线程执行。
muduo库的线程数目属于启动时配置,当线程池启动时,线程数目就已经固定下来。
客端通过Thread::run()函数向任务队列push任务,线程池等待处理任务。task(任务)是客端要执行的函数,通过boost::bind注册成为回调函数,放进任务队列当中。
三、源代码
Thread.h
// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style license
// that can be found in the License file.
//
// Author: Shuo Chen (chenshuo at chenshuo dot com)
#ifndef MUDUO_BASE_THREADPOOL_H
#define MUDUO_BASE_THREADPOOL_H
#include "muduo/base/Condition.h"
#include "muduo/base/Mutex.h"
#include "muduo/base/Thread.h"
#include "muduo/base/Types.h"
#include
#include
//
namespace muduo
{
class ThreadPool : noncopyable
{
public:
typedef std::function Task;
explicit ThreadPool(const string& nameArg = string("ThreadPool"));
~ThreadPool();
// Must be called before start().
void setMaxQueueSize(int maxSize) { maxQueueSize_ = maxSize; } //设置线程池线程的最大数目
void setThreadInitCallback(const Task& cb) //设置线程执行前的回调函数
{ threadInitCallback_ = cb; }
void start(int numThreads); //启动线程池,numThreads是线程池的容量
void stop(); //终止线程池
const string& name() const从法
{ return name_; }
size_t queueSize() const;
// Could block if maxQueueSize > 0
// There is no move-only version of std::function in C++ as of C++14.
// So we don't need to overload a const& and an && versions
// as we do in (Bounded)BlockingQueue.
// https://stackoverflow.com/a/25408989
void run(Task f);
private:
bool isFull() const REQUIRES(mutex_); //判满
void runInThread(); //线程池的线程运行函数;循环调用take获取任务,并执行任务
Task take(); //从队列中取任务
mutable MutexLock mutex_; //mutable表示在const函数里也可以改变它
Condition notEmpty_ GUARDED_BY(mutex_); //任务队列非空,有任务可以执行了,唤醒等待的线程
Condition notFull_ GUARDED_BY(mutex_); //任务队列非满,有空间可以用了,
string name_;
Task threadInitCallback_; //线程初始化回调函数
std::vector> threads_; //工作线程容器(线程数组)
std::deque queue_ GUARDED_BY(mutex_); //任务队列,声明一个任务列表
size_t maxQueueSize_; //队列最大大小
bool running_; //线程池运行标志
};
} // namespace muduo
#endif // MUDUO_BASE_THREADPOOL_H
Thread.cc
// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style license
// that can be found in the License file.
//
// Author: Shuo Chen (chenshuo at chenshuo dot com)
#include "muduo/base/ThreadPool.h"
#include "muduo/base/Exception.h"
#include
#include
using namespace muduo;
ThreadPool::ThreadPool(const string& nameArg)
: mutex_(),
notEmpty_(mutex_), //初始化的时候需要把condition和mutex 关联起来
notFull_(mutex_),
name_(nameArg),
maxQueueSize_(0),
running_(false)
{
}
ThreadPool::~ThreadPool()
{
if (running_)
{
stop(); //析构函数会调用stop,唤醒所有休眠的线程,然后等待所有线程处理完
}
}
/********************************************************************
Description : 启动线程池。
*********************************************************************/
void ThreadPool::start(int numThreads) //参数为线程数量,会创建相应数量的线程,线程函数为ThreadPool::runInThread
{
assert(threads_.empty());
running_ = true; //启动标志
threads_.reserve(numThreads); //保证threads_容量至少为numThreads,预留空间,避免多次自动增长
for (int i = 0; i < numThreads; ++i)
{
char id[32];
snprintf(id, sizeof id, "%d", i+1);
//创建工作线程并加入线程数组,绑定的函数为runInThread
threads_.emplace_back(new muduo::Thread(
std::bind(&ThreadPool::runInThread, this), name_+id));
//启动线程,即runInThread函数执行
threads_[i]->start();
}
//如果线程池线程数为0,且设置了回调函数
if (numThreads == 0 && threadInitCallback_)
{
threadInitCallback_(); //本线程自己执行init回调函数
}
}
/********************************************************************
Description : 终止线程池。
*********************************************************************/
void ThreadPool::stop()
{
{
MutexLockGuard lock(mutex_);
running_ = false;
//不管当前线程在执行什么任务,通知所有线程去notEmpty_.wait()处等待
//因为running_为false,所有线程不会再执行任何任务了。
notEmpty_.notifyAll();
}
//回收所有线程
for (auto& thr : threads_)
{
thr->join();
}
}
//获取任务队列的大小
size_t ThreadPool::queueSize() const
{
MutexLockGuard lock(mutex_);
return queue_.size();
}
/********************************************************************
Description : 向任务队列中添加任务。
*********************************************************************/
void ThreadPool::run(Task task)
{
if (threads_.empty())
{
task(); //如果没有子线程,就在主线程中直接执行该task
}
else
{
MutexLockGuard lock(mutex_);
while (isFull())
{
notFull_.wait(); //等待任务队列不为满的条件
}
assert(!isFull());
//如果任务队列不满,则可以向任务队列中添加任务
queue_.push_back(std::move(task));
notEmpty_.notify(); //唤醒等待任务队列不为空的线程来取任务
}
}
ThreadPool::Task ThreadPool::take()
{
MutexLockGuard lock(mutex_);
// always use a while-loop, due to spurious wakeup
while (queue_.empty() && running_)
{
notEmpty_.wait(); //条件变量的wait操作使用while包裹,预防“虚假唤醒”(如被其它线程抢占了)。
}
Task task;
if (!queue_.empty())
{
task = queue_.front();
queue_.pop_front();
if (maxQueueSize_ > 0)
{
notFull_.notify();
}
}
return task;
}
//判断任务队列是否满
bool ThreadPool::isFull() const
{
mutex_.assertLocked();
return maxQueueSize_ > 0 && queue_.size() >= maxQueueSize_;
}
/********************************************************************
Description : 取任务并执行。
*********************************************************************/
void ThreadPool::runInThread()
{
try
{
if (threadInitCallback_)
{
threadInitCallback_();
}
while (running_) //当线程池启动之后,就在while1循环中不停地取任务执行
{
Task task(take()); //取任务并初始化task,无任务会阻塞
if (task) //如果任务非空
{
task(); //执行该任务
}
}
}
catch (const Exception& ex)
{
fprintf(stderr, "exception caught in ThreadPool %s\n", name_.c_str());
fprintf(stderr, "reason: %s\n", ex.what());
fprintf(stderr, "stack trace: %s\n", ex.stackTrace());
abort();
}
catch (const std::exception& ex)
{
fprintf(stderr, "exception caught in ThreadPool %s\n", name_.c_str());
fprintf(stderr, "reason: %s\n", ex.what());
abort();
}
catch (...)
{
fprintf(stderr, "unknown exception caught in ThreadPool %s\n", name_.c_str());
throw; // rethrow
}
}
使用示例:
#include "muduo/base/ThreadPool.h"
#include "muduo/base/CountDownLatch.h"
#include "muduo/base/CurrentThread.h"
#include "muduo/base/Logging.h"
#include
#include // usleep
void print()
{
printf("tid=%d\n", muduo::CurrentThread::tid());
}
void printString(const std::string& str)
{
LOG_INFO << str;
usleep(100*1000);
}
void test(int maxSize)
{
LOG_WARN << "Test ThreadPool with max queue size = " << maxSize;
muduo::ThreadPool pool("MainThreadPool");
pool.setMaxQueueSize(maxSize);
pool.start(5);
LOG_WARN << "Adding";
pool.run(print);
pool.run(print);
for (int i = 0; i < 100; ++i)
{
char buf[32];
snprintf(buf, sizeof buf, "task %d", i);
pool.run(std::bind(printString, std::string(buf)));
}
LOG_WARN << "Done";
muduo::CountDownLatch latch(1);
pool.run(std::bind(&muduo::CountDownLatch::countDown, &latch));
latch.wait();
pool.stop();
}
int main()
{
test(0);
test(1);
test(5);
test(10);
test(50);
}