TensorFlow学习记录:VGGNet卷积神经网络模型
1.VGGNet模型结构简介
VGGNet是由牛津大学计算机视觉几何组(Visual Geomety Group,VGG)和Google Deepmind公司的研究员合作研发的深度卷积神经网络,VGG的成员Karen Simonyan和Andrew Zisserman在2014年撰写的论文《Very Deep Convolutional Networks for Large-Scale Image Recongnition》中正式提出了该深度卷积神经网络的结构。
VGGNet对卷积神经网络的深度与其性能之间的关系进行了探索。网络的结构非常简洁,在整个网络中使用了大小相同的卷积核(3*3)和最大池化核(2*2)。通过重复堆叠的方式,使用这些卷积层和最大池化层成功地搭建了11~19层深地卷积神经网络。
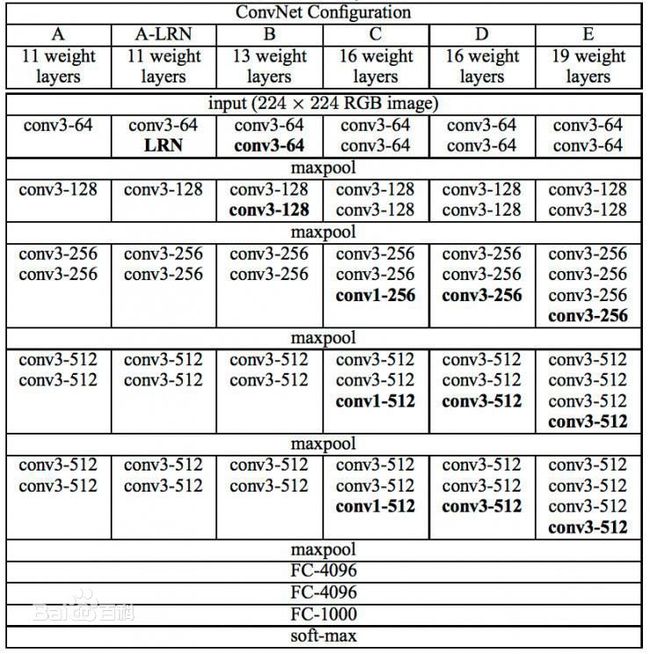
VGGNet通过不断地加深网络结构来提升性能,牛津大学计算机视觉几何组对11~19层地网络都进行了详尽的性能测试。根据网络深度的不同以及是否使用LRN,VGGNet可以分为A-E 6个级别。如下图所示为VGGNet各级别的网络结构表。
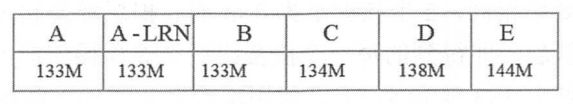
尽管从A级到E级对网络进行了逐步加深,但是网络的参数量并没有显著增加,这是因为最后3个全连层占据了大量的参数。在6个级别的VGGNet中,全连层都是相同的。卷积层的参数共享和局部连接对降低参数量做出了重大的贡献,但是由于卷积操作和池化操作的运算过程比较复杂,所以训练中比较耗时的依然是卷积层。下图展示了每一级别的参数量。
从第1张图可以看出,VGGNet共有5段卷积,每一段卷积内部有一定数量的卷积层(或1个或4个),所以是5阶段卷积特征提取。每一段卷积之后都有一个max-pool层,这些最大池化层被用来缩小图片的尺寸。
同一段内的卷积层拥有相同的卷积核数,之后每增加一段,该段内卷积层的卷积核数就增加1倍。接受input的第一段卷积中,每个卷积层拥有最少的64个卷积核,接着第二段卷积中每个卷积层的卷积核数量上升到128个;最后一段卷积拥有最多的卷积层数,每个卷积层拥有最多的512个卷积核。
C级的VGGNet有些例外,它的第一段和第二段卷积都与B级VGGNet相同,只是在第三段,第四段,第五段卷积中相比B级VGGNet各多了一个1*1大小卷积核的卷积层。这里核大小1*1的卷积运算主要用于在输入通道数和输出通道数不变(不发生数据降维)的情况下实现线性变换。
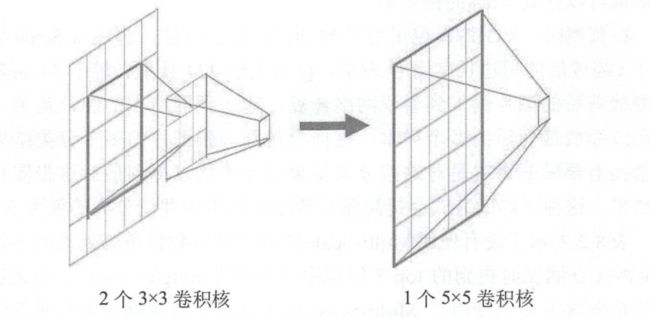
将多个3*3卷积核的卷积层堆叠在一起是一种非常有趣也非常有用的设计,这对降低卷积核的参数非常有帮助,同时也会加强CNN对特征的学习能力。下图展示了2个3*3卷积核的卷积层堆叠在一起的情况,我们将借助这幅图来进行一些说明。
如上图所示,左侧展示了2个核大小为3*3的卷积层堆叠起来的情况,右侧展示了只有1个核大小5*5的卷积层的情况。经过对比之后我们发现两者的效果相同,2个核大小为3*3的卷积层堆叠起来相当于一个核大小5*5的卷积层,即得到的每一个值会跟经过卷积操作前的5*5个像素产生关联(感受野由3*3变成5*5)。使用堆叠卷积层的方法能降低参数数量,左侧的情况下需要18(9+9)个参数,而右侧的情况下需要25个参数。
可以将这种2层相叠的情况扩展到3层或者4层或者更多的层,比如使用3个核大小3*3的卷积层堆叠起来的效果相当于1个核大小7*7的卷积层。当使用1个卷积层时,只能对卷积的结果使用一次激活函数(进行一次非线性变换),但是当堆叠在一起的卷积层达到3个或者4个之后,因为在每一次卷积结束之后都使用了一次激活函数,所以计算的过程中相当于进行了多次非线性变换,进而加强了CNN对特征的学习能力。
在网络训练时,VGGNet通过一个称为Multi-Scale的方法对图像进行数据增强处理。这个过程大致就是先将原始的图像缩放到不同的尺寸(缩放后的短边长度用S表示,在实践中,一般令S在[256,512]这个区间内取值),然后将得到的图像进行224*224的随机剪裁。数据增强处理能增加很多数据量,对于防止模型过拟合有很好的效果。因为卷积神经网络对于图像的的缩放有一定的不变性,所以将这种经过Multi-Scale多尺度缩放裁剪后的图片输入到卷积神经网络中训练可以增加网络的不变性。经过Multi-Scale多尺度缩放裁剪后可以获得多个版本的图像数据。下表所示为VGGNet使用Multi-Scale训练时得到的结果,可以看到D和E结构的网络都可以达到7.5%的错误率。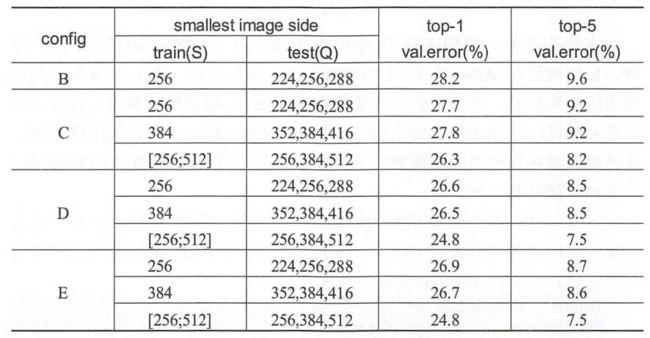
在预测时,VGGNet也采用了Multi-Scale的方法,将图像scale到一个尺寸(缩放后的短边长度用Q表示,Q会大于224且不必等于S)再剪裁,并将裁剪后的图片输入到卷积神经网络中计算。输入到网络中的图片是某一张图片经过缩放裁剪后的多个样本,这样会得到一张图片的多个分类结果,所以紧接着要做的就是对这些分类结果进行平均以得到最后这张图片的分类结果。这种平均的方式会提高图片数据的利用率并使分类的效果更好。
下表展示了没有使用Multi-Scale的方式进行数据增强处理时各级别的VGGNet在测试时得到的top-5错误率(也称为Single-Scale)。与之进行比较的的上表所示的使用了Multi-Scale的方式进行数据增强处理时各级别的VGGNet在测试时得到的top-5错误率。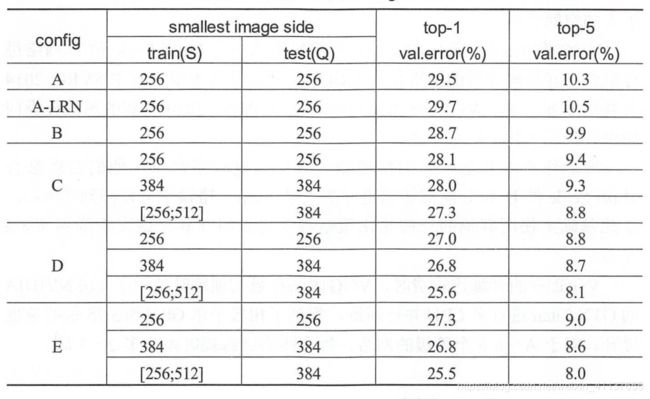
上两张表的数据均出自论文《Very Deep Convolutional Networks for Large-Scale Image Recongnition》。通过比较A与A-LRN的错位率,我们发现A-LRN的效果没有A的好,这说明LRN的作用不是很明显;将A与B,C,D,D进行比较,我们发现网络越深越好;将A与C进行比较,我们发现增加1*1的fillter对非线性的提升有很好的作用;将C与D进行比较,我们发现使用3*3的大fillter比使用1*1的小fillter能捕获更大的空间特征。
VGG将Single-Scale的6个不同等级的网络与Multi-Scale的D网络进行融合,并将融合后的网络作为VGGNet的最终版本提交到ILSVRC 2014大赛举办方。这个VGGNet的最终版本在ILSVRC 2014竞赛的图像分类问题中达到了7.3%的top-5错位误率。
2.使用TensorFlow搭建VGGNet并实现Cifar10数据集分类
在这里,我们选择D结构的VGGNet(又称为VGGNet-16。同理,E结构的VGGNet又称为VGGNet-19)进行说明。由于ImageNet数据集太庞大,所以我选择了对Cifar10数据集进行分类来了解VGGNet-16。
首先,编写Cifar10_data.py文件来实现对数据的读取和预处理
导入相关库和定义一些需要用到的变量
import os
import tensorflow as tf
os.environ['TF_CPP_MIN_LOG_LEVEL'] = '2'
import numpy as np
import time
import math
num_classes = 10 #一共有10个类别
num_examples_pre_epoch_for_train = 50000 #50000个样本用于训练
num_examples_pre_epoch_for_eval = 10000 #10000个样本用于测试
max_steps = 4000 #训练4000步
batch_size = 100 #每次训练100个样本
num_examples_for_eval = 10000
data_dir = "C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/Tensorflow/cifar-10-batches-bin" #下载的样本的路径
class CIFAR10Record(object): #定义一个空类,用于返回读取的Cifar-10数据
pass
接着定义一个read_cifar10()函数用于读取文件队列中的数据
def read_cifar10(file_queue): #file_queue为图片路径
result = CIFAR10Record() #创建一个CIFAR10Record对象
label_bytes = 1 #标签占一个字节
result.height = 32 #图像高为32像素
result.width = 32 #图像宽为32像素
result.depth = 3 #因为是RGB三通道,所以深度为3
image_bytes = result.height * result.width * result.depth #结果为3072,即一幅图像的大小为3072字节
record_bytes = label_bytes + image_bytes #加上标签,即一个样本一共有3073字节
reader = tf.FixedLengthRecordReader(record_bytes=record_bytes) #使用FixedLengthRecordReader类创建一个用于读取固定长度字节数信息的对象(针对bin文件而言)
result.key, value = reader.read(file_queue) #使用该类的read()方法读取指定路径下的文件
#这里得到的value就是record_bytes长度的包含多个label数据和image数据的字符串
record_bytes = tf.decode_raw(value, tf.uint8)
#decode_raw()可以将字符串解析成图像对应的像素数组
#strided_slice(input,begin,end)用于对输入的input截取[begin,end)区间的数据
result.label = tf.cast(tf.strided_slice(record_bytes, [0], [label_bytes]), tf.int32)
#这里把record_bytes的第一个元素截取下来然后转换成int32类型的数
#剪切label之后剩下的就是图片数据,我们将这些数据的格式从[depth*height*width]转换为[depth,height,width]
depth_major = tf.reshape(tf.strided_slice(record_bytes, [label_bytes], [label_bytes + image_bytes]),
[result.depth, result.height, result.width])
#将[depth,height,width]的格式转换为[height,width,depth]的格式
result.uint8image = tf.transpose(depth_major, [1, 2, 0])
return result
紧接着read_cifar10()函数的是inputs函数,这个函数用于构建文件路径,将构建的文件路径传给read_cifar10()函数读取样本,对读取到的样本进行数据增强处理。
def inputs(data_dir, batch_size, distorted): #data_dir为文件路径,batch_size为读取批量大小,distorted是否对样本进行增强处理
#拼接文件名路径列表
filenames = [os.path.join(data_dir, "data_batch_%d.bin" % i) for i in range(1, 6)]
#创建一个文件队列,并调用read_cifar10()函数读取队列中的文件,在后面还要调用一个tf.train.start_queue_runners()函数才开始读取图片
file_queue = tf.train.string_input_producer(filenames)
read_input = read_cifar10(file_queue)
#使用tf.cast()对图片数据进行转换
reshaped_image = tf.cast(read_input.uint8image, tf.float32)
num_examples_per_epoch = num_examples_pre_epoch_for_train
if distorted != None:
#将[32,32,3]大小的图片随机剪裁成[24,24,3]的大小
cropped_image = tf.random_crop(reshaped_image, [24, 24, 3])
#随机左右翻转图片
flipped_image = tf.image.random_flip_left_right(cropped_image)
#随机调整亮度
adjusted_brightness = tf.image.random_brightness(flipped_image, max_delta=0.8)
#随机调整对比度
adjusted_contrast = tf.image.random_contrast(adjusted_brightness, lower=0.2, upper=1.8)
#对图片每一像素减去平均值并除以像素方差
float_image = tf.image.per_image_standardization(adjusted_contrast)
#设置图片及标签的形状
float_image.set_shape([24, 24, 3])
read_input.label.set_shape([1])
min_queue_examples = int(num_examples_pre_epoch_for_eval * 0.4)
print("Filling queue with %d CIFAR image before starting to train.""This will take a few minutes." % min_queue_examples)
#shuffle_batch()函数通过随机打乱张量的顺序创建批次.
images_train, labels_train = tf.train.shuffle_batch([float_image, read_input.label], batch_size=batch_size,
num_threads=16,
capacity=min_queue_examples + 3 * batch_size,
min_after_dequeue=min_queue_examples)
return images_train, tf.reshape(labels_train, [batch_size])
#不对图像进行数据增强处理
else:
resized_image = tf.image.resize_image_with_crop_or_pad(reshaped_image, 24, 24)
float_image = tf.image.per_image_standardization(resized_image)
float_image.set_shape([24, 24, 3])
read_input.label.set_shape([1])
min_queue_examples = int(num_examples_per_epoch * 0.4)
images_test, labels_test = tf.train.batch([float_image, read_input.label], batch_size=batch_size,
num_threads=16, capacity=min_queue_examples + 3 * batch_size)
return images_test, tf.reshape(labels_test, [batch_size])
接下来编写VGGNet_Cifar-10.py文件,这个脚本文件用于搭建VGGNet-16结构,读取Cifar10_data.py中预处理过的数据来训练VGGNet-16。
导入相关库和定义一些变量
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
import time
import math
import Cifar10_data
max_steps=300000 #最大步数,其实到15万步的时候loss率就可以达到0了,可以自行调整
batch_size=32 #如果显存不足的话可以调小一点,12或者10以下也行
data_dir="/content/drive/My Drive/cifar-10-batches-bin/" #cifar-10数据保存路径
VGGNet-16包含了很多层的卷积,为了能够在前向传播的过程中不需要对每一个卷积操作都定义一个命名空间,这里先写一个函数conv_op(),用来创建卷积层并将本层的参数存入参数列表,这样做可以缩减代码长度。
首先看一下conv_op()函数的定义中需要传递进来的参数。input是输入的tensor,name是这一层的名称,kernel_height和kernel_width分别是卷积核的高和宽,num_out是输出通道数(也就是卷积核的数量),step_h和step_w分别是步长的高和宽,para代表传递进来的参数列表。
进入到函数的第一步,就是使用get_shape()[-1].value获取输入input 的通道数.注意,这里gei_shape()函数使用[-1]表示获取后一个维皮的 值,在这个维度上一般就是上一层网络输出或者图片输入的深度。例如. 如采输入的图片尺存为224*224*3.那么get_shape()[-1]会得到最后 的那个3。得到的数值3是元组的形式,所以还通过取value属性得到真实的值。
之后就是在name_scope()中用get_variable()函数创建卷积核的权重参数。 权重参数初始化的方法采用了 contrib.layers.xavicr_inhializcr_conv2d(), 该方法会根椐某一卷积层输入、输出单元的数自动调整为最合适的分布。这种变最初始化的方法属于Xavier初始化方法。Xavier初始化方法源于Xavier Glorot在一篇论文中提出的一个观点——如粜深度学习模型的权重初始化得太小,那么信号将在每层间传递时逐渐被缩小,从而导致难以产生作用;但如果权重初始化得太大,那么信号将在每层间传递时逐渐被放大,甚至有可能产生发散和失效.应用了 Xavier初始化方法的Xaivw初始化器要做的就是给权重一个不大不小的初始化器.从数学的角度来看,这个权里满足均值为0.同时方差为2/(n(in)+n(out)的分布(分布可以用均匀分布或者高斯分布)。
初始化权重參败后,会使用这个去权重参数和input进行卷积运算操作、使用Variable()函数创建偏置参数、添加偏置以及使用RcLU激活操作,并将经过激活后的值作为函数的结果返回,这部分和—般的卷积处理过程相同。最后还要将创建卷积层时用到的参数kernel和biases添加进参数列表para。函数代码如下:
def conv_op(input,name,kernel_h,kernel_w,num_out,step_h,step_w,para):
num_in=input.get_shape()[-1].value #num_in是输入深度,这个参数被用来确定卷积核的输入通道数
with tf.name_scope(name) as scope:
kernel=tf.get_variable(scope+"w",shape=[kernel_h,kernel_w,num_in,num_out],dtype=tf.float32,initializer=tf.contrib.layers.xavier_initializer_conv2d())
conv=tf.nn.conv2d(input,kernel,(1,step_h,step_w,1),padding="SAME")
biases=tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0,dtype=tf.float32,shape=[num_out]),trainable=True,name="b")
activation=tf.nn.relu(tf.nn.bias_add(conv,biases),name=scope)
para+=[kernel,biases]
return activation
VGGNet-16也包含了几个全连层,同样为了缩减代码的长度,我们还需要像定义卷积创建函数conv_op()那样定义全连层的创建函数—— fc_op()。
在fc_op()函数内还是一样要先获取输入input的通道数,然后在name_ scope内使用get_variable()创建全连接层的权重参数,权重参数的形状是二维的,由输入的通道数num_in和输出的通道数num_out确定。权重参数的初始化方法同样也使用Xavier初始化方法——contrib.iayers.xavier_initializer()。对于偏置参数biases,这里不再初始化为0,而是赋予一个较小的值 0.1。 TensorFlow 提供了 nn.relu_layer()函数,简化了使用 matmul()函数进行矩阵相乘、使用bias_add()函数添加偏置以及使用relu()函数进行非线性变换的过程。为了缩减代码,这里也采用了这个函数。
函数的最后同样是将这个全连层用到的参数weights和biases添加进参 数列表para,并将进行非线性处理之后得到的激活值activation作为函数的结果返回。函数代码如下:
def fc_op(input,name,num_out,para):
num_in=input.get_shape()[-1].value #num_in为输入单元的数量
with tf.name_scope(name) as scope:
weights=tf.get_variable(scope+"w",shape=[num_in,num_out],dtype=tf.float32,initializer=tf.contrib.layers.xavier_initializer())
biases=tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.1,dtype=tf.float32,shape=[num_out]),name="b")
activation=tf.nn.relu_layer(input,weights,biases) #tf.nn.relu_layer()函数会同时完成矩阵乘法和加偏置项并计算relu激活值
para+=[weights,biases]
return activation
完成了卷积层和全连层的创建函数,接下来就开始创建VGGNet-16的网络结构,这部分内容被放到了函数inference_op()内。
对于函数inference_op(),传入的参数有input和keep_prob。其中参数 keep_prob用于控制dropout的比率,在后续的定义计算图的代码中可以找 到keep_prob的定义。它就是一个placeholder,对于前向传播和反向传播的过程,keep_prob有着不同的取值。在函数的最前面是创建的一个参数列表 parameters[]。这个参数列表会被传递到conv_op()函数和fc_op()函数中,用于记录所用到的权重参数和偏置参数。
VGGNet-16在整体上可以划分为8个部分(8段),前5段为卷积网络,后3段为全连网络。首先来创建第一段卷积网络,这一段卷积网络由2个卷积层和1个最大池化层构成。对于卷积层,我们使用写好的函数conv_op()来创建。这两个卷积层的卷积核的大小都是3x3,同时卷积核数量(输出通道数)也均为64,步长为1*1。第一个卷积层的输入input的尺寸为32x32x3 (没有加入batch_size),输出尺寸为32x32x3;而第二个卷积层的输入、输出尺寸均为32x32x3 (接收来自第一个卷积层的输出)。两个卷积层之后是一个2x2的最大池化层,由于步长也是2,所以经过最大池化之后,输出结果尺寸变为了16x16x64。
第二段卷积网络和第一段的结构非常类似,两个卷积层的卷积核尺寸也是3x3,只是经由这两个卷积层之后输出的通道数都变为了 128。最大池化层和第一段卷积的最大池化层一致,所以得出这一段卷积网络的输出尺寸变为 8x8x128。
第三段卷积网络在结构上和前两段不同的是,这里的卷积层数变为了3个。每个卷积层的卷积核大小依然是3x3,但是每个卷积层的输出通道数则增长至256。最大池化层和前两段卷积的最大池化层一致,所以得出这一段卷积网络的输出尺寸变为4x4x256。
第四段卷积网络也是3个卷积层加1个最大池化层 。所有的配置和第三 段 卷 积 一 致 ,只 是 每 个 卷 积 层的输出通道数在上一段256的基础上又发生了翻倍,达到了512。所以得出这一段卷积网络的输出尺寸变为2x2x512。
最后一段卷积网络同样是3个卷积核尺寸为3x3的卷积层加1个最大池化层,只是不再増加卷积层的输出 通道数,将通道数继续维持在512。所以可以计算到这里输出的尺寸变为1x1x512。函数内创建5段卷积的代码 如下:
def inference_op_loss(input,keep_prob,y_):
parameters=[]
#第一段卷积,输出大小为16*16*64(省略了第一个batch_size参数)
conv1_1=conv_op(input,name="conv1_1",kernel_h=3,kernel_w=3,num_out=4,step_h=1,step_w=1,para=parameters)
conv1_2=conv_op(conv1_1,name="conv1_2",kernel_h=3,kernel_w=3,num_out=64,step_h=1,step_w=1,para=parameters)
pool1=tf.nn.max_pool(conv1_2,ksize=[1,2,2,1],strides=[1,2,2,1],padding="SAME",name="pool1")
print(pool1.op.name,' ',pool1.get_shape().as_list())
#第二段卷积,输出大小为8*8*128(省略了第一个batch_size参数)
conv2_1=conv_op(pool1,name="conv2_1",kernel_h=3,kernel_w=3,num_out=128,step_h=1,step_w=1,para=parameters)
conv2_2=conv_op(conv2_1,name="conv2_2",kernel_h=3,kernel_w=3,num_out=128,step_h=1, step_w=1,para=parameters)
pool2=tf.nn.max_pool(conv2_2,ksize=[1,2,2,1],strides=[1,2,2,1],padding="SAME",name="pool2")
print(pool2.op.name,' ',pool2.get_shape().as_list())
#第三段卷积,输出大小为4*4*256(省略了第一个batch_size参数)
conv3_1=conv_op(pool2,name="conv3_1",kernel_h=3,kernel_w=3,num_out=256,step_h=1,step_w=1,para=parameters)
conv3_2=conv_op(conv3_1,name="conv3_2",kernel_h=3,kernel_w=3,num_out=256,step_h=1,step_w=1,para=parameters)
conv3_3=conv_op(conv3_2,name="conv3_3",kernel_h=3,kernel_w=3,num_out=256,step_h=1,step_w=1,para=parameters)
pool3=tf.nn.max_pool(conv3_3,ksize=[1,2,2,1],strides=[1,2,2,1],padding="SAME",name="bool3")
print(pool3.op.name,' ',pool3.get_shape().as_list())
#第四段卷积,输出大小为2*2*512(省略了第一个batch_size参数)
conv4_1=conv_op(pool3,name="conv4_1",kernel_h=3,kernel_w=3,num_out=512,step_h=1,step_w=1,para=parameters)
conv4_2=conv_op(conv4_1,name="conv4_2",kernel_h=3,kernel_w=3,num_out=512,step_h=1,step_w=1,para=parameters)
conv4_3=conv_op(conv4_2,name="conv4_3",kernel_h=3,kernel_w=3,num_out=512,step_h=1,step_w=1,para=parameters)
pool4=tf.nn.max_pool(conv4_3,ksize=[1,2,2,1],strides=[1,2,2,1],padding="SAME",name="pool4")
print(pool4.op.name,' ',pool4.get_shape().as_list())
#第五段卷积,输出大小为1*1*512(省略了第一个batch_size参数)
conv5_1 = conv_op(pool4, name="conv5_1", kernel_h=3, kernel_w=3, num_out=512, step_h=1, step_w=1, para=parameters)
conv5_2 = conv_op(conv5_1, name="conv5_2", kernel_h=3, kernel_w=3, num_out=512, step_h=1, step_w=1, para=parameters)
conv5_3 = conv_op(conv5_2, name="conv5_3", kernel_h=3, kernel_w=3, num_out=512, step_h=1, step_w=1, para=parameters)
pool5 = tf.nn.max_pool(conv5_3, ksize=[1, 2, 2, 1], strides=[1, 2, 2, 1], padding="SAME", name="pool5")
print(pool5.op.name,' ',pool5.get_shape().as_list())
在函数inference_op()内完成了5段卷积的创建后,为了能和全连网络相连,同样还需要将输出的结果扁平化。和之前一样,这里需要使用get_Shape()函数获取Pool5的尺寸信息,然后得到全连层的输入单元数flattened_shape,然后使用 reshape()函数将 pool5 “拉直”。
创建的第一个全连层有4096个单元,使用激活函数ReLU。全连层后面有一个Dropout层,根据前向传播或反向传播时传递进来的keep_prob参数不同,Dropout层执行不同的操作。
第二个全连层与第一个全连层一致,同样有4096个隐藏单元。最后的—个全连层与前两个全连层一致,只是隐藏单元数降为1000个。在最后一层结束后,为了计算损失值,我们使用了tf.nn.sparse_softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits()函数。优化器选择了Adam算法的AdamOptimizer,并设置全局学习速率为0.001。以下是这半部分的代码:
pool_shape=pool5.get_shape().as_list()
flattened_shape=pool_shape[1]*pool_shape[2]*pool_shape[3]
reshaped=tf.reshape(pool5,shape=[-1,flattened_shape],name="reshaped")
print(reshaped.op.name,' ',reshaped.get_shape().as_list())
#第一个全连接层
fc_6=fc_op(reshaped,name="fc6",num_out=4096,para=parameters)
fc_6_drop=tf.nn.dropout(fc_6,keep_prob,name="fc6_drop")
#第二个全连接层
fc_7=fc_op(fc_6_drop,name="fc7",num_out=4096,para=parameters)
fc_7_drop=tf.nn.dropout(fc_7,keep_prob,name="fc7_drop")
#第三个全连层
fc_8_weights=tf.get_variable("fc8w",shape=[fc_7_drop.get_shape()[-1],10],dtype=tf.float32,initializer=tf.contrib.layers.xavier_initializer())
fc_8_biases=tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.1,dtype=tf.float32,shape=[10]),name="b")
fc_8=tf.add(tf.matmul(fc_7_drop,fc_8_weights),fc_8_biases)
parameters+=[fc_8_weights,fc_8_biases]
cross_entropy=tf.nn.sparse_softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=fc_8,labels=tf.cast(y_,tf.int64))
loss=tf.reduce_mean(cross_entropy,name="Train_cost")
train_op=tf.train.AdamOptimizer(0.001).minimize(loss)
top_k_op=tf.nn.in_top_k(fc_8,y_,1)
return train_op,loss,top_k_op,parameters
之后可以将进行计算图以及会话的设计。首先使用with.tf.Graph().as_defautl()定义默认的Graph,然后使用Cifar10_data.py文件中定义的inputs()方法分别读取用于训练和验证模型准确率的数据。
接下来,创建2个placeholder用来存放在运行会话时传递到inference_op()函数中的x和y_,然后调用inference_op()函数为计算图添加主要的计算结构。
完成这些后,就可以调用with tf.Session()创建新的Session,训练的过程被安排在for循环内,但在启动for循环之前要初始化所有变量并通过tf.train.start_queue_runners()函数来启动线程,这是因为在数据增强的处理过程中使用tf.train.shuffle_batch()函数时通过参数num_threads配置了将16个线程用于组织batch的操作。注意,如果在这里没有启动线程,那么后续的步骤是没办法进行的。
在每一step训练过程中,我们需要使用Session()的run()函数执行images_train和labels_train的计算来获得一个batch的训练数据,再将这个batch的数据通过feed的方式传入train_op和loss的计算过程。
在每轮训练结束后还会通过time.py中的time()函数记录这一轮训练的耗时。每隔100step会计算并展示当前的loss,每秒中能训练的样本数量,以及训练一个batch数据所花费的时间。每隔1000step会计算当前状态下的模型在测试集上的准确率。测试集一个有10000张图片,但是我们依然要像训练时那样一个batch一个batch地输入数据。为了最大限度地使用完验证数据,我们先计算评测全部测试样本一共要多少个batch,得到一个num_batch,这个变量就作为循环进行的次数。
每一step都会使用run()函数执行获取images_test, labels_test的batch的过程,然后通过top_k_op操作计算模型能在这个batch上得到正确预测结果的样本数量,最后汇总所有预测正确的样本数量,求得全部测试样本中预测正确的样本数量,并将正确率打印出来。以下是这一部分的代码:
with tf.Graph().as_default():
images_train,labels_train=Cifar10_data.inputs(data_dir=data_dir,batch_size=batch_size,distorted=True) #用于训练的数据
iamges_test,labels_test=Cifar10_data.inputs(data_dir=data_dir,batch_size=batch_size,distorted=None) #用于验证准确率的数据
x=tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[batch_size,32,32,3])
y_=tf.placeholder(tf.int32,[batch_size])
train_op, loss, top_k_op, parameters = inference_op_loss(x, keep_prob=1.0, y_=y_)
config = tf.ConfigProto()
config.gpu_options.allocator_type = "BFC"
init_op=tf.global_variables_initializer()
with tf.Session(config=config) as sess:
sess.run(init_op)
tf.train.start_queue_runners() #开启多线程
print(sess.run(tf.report_uninitialized_variables()))
for step in range(max_steps):
start_time=time.time()
image_batch,label_batch=sess.run([images_train,labels_train])
_,loss_value=sess.run([train_op,loss],feed_dict={x:image_batch,y_:label_batch})
duration=time.time()-start_time
if step % 100 == 0: #每100step打印loss,每秒钟能训练的数量,以及训练一个batch数据所花费的时间
examples_per_sec=batch_size/duration
sec_per_batch=float(duration)
print("Step %d ,loss=%.2f (%.1f examples/sec;%.3f sec/batch)"%(step,loss_value,examples_per_sec,sec_per_batch))
if step % 1000 ==0 and step > 0:#每1000step在测试集上评测模型的准确率
num_batch = int(math.ceil(num_examples_for_eval/batch_size))
true_count = 0
total_sample_count = num_batch * batch_size
#在一个for循环内统计所有预测正确的样例个数
for j in range (num_batch):
image_batch,label_batch = sess.run([iamges_test,labels_test])
predictions = sess.run([top_k_op],feed_dict={x:image_batch,y_:label_batch})
true_count += np.sum(predictions)
#打印准确率信息
print("accuracy = %.3f%%"%((true_count/total_sample_count)*100))
saver.save(sess,"/content/drive/My Drive/使用VGGNet跑Cifar10数据集/model_path_MovingAverage/model.ckpt",global_step=step)
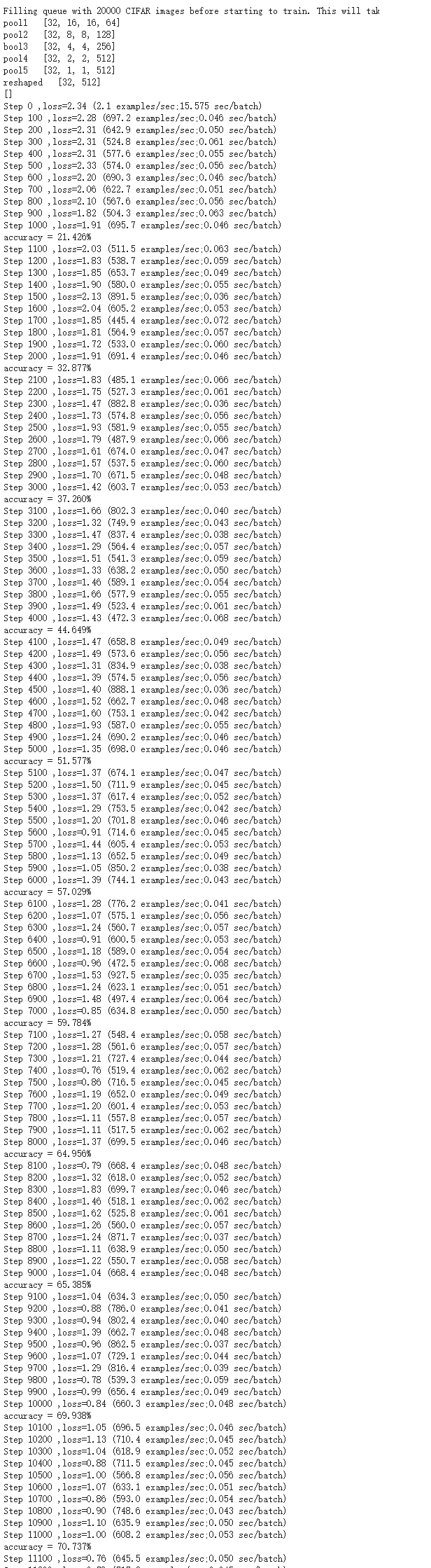
训练过程0-10000Step截图
100000-120000Step截图
参考书籍:《TensorFlow深度学习算法原理与编程实战》 蒋子阳 著