【spring源码分析(二)】IOC容器初始化---AbstarctApplicationContext类的refresh方法
承接上篇文章,分析AbstarctApplicationContext类的refresh方法
首先看下refresh方法的源码
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
//重新设置容器启动时间和启动标志字段
prepareRefresh();
//创建DefaultListableBeanFactory(真正生产和管理bean的容器)
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
/**
* 为BeanFactory配置容器特性,例如类加载器、事件处理器等
* 1.addPropertyEditorRegistrar,设置用户定义的propertyEditor注册器
* 2.addBeanPostProcessor,设置ApplicationContextAwareProcessor,处理ApplicationContextAware实现接口的Bean。
* 3.ignoreDependencyInterface,设置不解析某些接口的依赖关系
* 4.registerResolvableDependency,设置特殊接口和bean的绑定关系
*/
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
//为容器的某些子类指定特殊的BeanPostProcessor事件处理器
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
//调用所有实现BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口的类,在spring的bean创建之前,然后按不同的优先级顺序,依次执行BeanFactoryPostProcessor的 postProcessBeanFactory 方法,修改bean的定义属性
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
//创建并注册实现BeanPostProcessor接口的类到BeanFactory中(Bean的后置处理器)
//BeanPostProcessor的执行时机,由配置文件中bean的定义决定。如果定义的bean是singleton并且不是抽象类,也不延迟初始化,则BeanPostProcessor是在refresh()方法的finishBeanFactoryInitialization方法中执行;而对于prototype的bean,BeanPostProcessor是在程序执行getBean时执行。
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
/**
* 为spring容器初始化MessageSource
* 如果spring配置文件没有定义messageSource,则使用默认的实现类DelegatingMessageSource
*/
initMessageSource();
/**
* 为spring容器初始化并注册ApplicationEventMulticaster
* 如果spring配置文件没有定义applicationEventMulticaster,则使用默认的
* 默认的ApplicationEventMulticaster实现类是SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster
*/
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
//调用子类的某些特殊Bean初始化方法
onRefresh();
//注册实现ApplicationListener接口的bean
registerListeners();
/**
* 注意:Bean的IoC、DI和AOP都是发生在此步骤
*
* 1.清除用于类型匹配的classLoader
* 2.冻结beanDefinitions中设置,不能再修改bean的配置
* 3.实例化非延迟加载的单例bean(未设置属性),包括由FactoryBean实例化的bean
* 4.设置属性(注入)
* 5.初始化bean(比如调用init-method方法)
* 6.调用BeanPostProcessor后置处理器,对单例bean进行处理
*
*/
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
//初始化容器的生命周期事件处理器,并发布容器的生命周期事件
finishRefresh();
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " +
"cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex);
}
//销毁以创建的单态Bean
destroyBeans();
//取消refresh操作,重置容器的同步标识
cancelRefresh(ex);
// Propagate exception to caller.
throw ex;
}
finally {
// Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we
// might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore...
resetCommonCaches();
}
}
}下面分析refresh方法的主要步骤
一、ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory()
总体步骤如下:
- 定位资源文件。定位外部资源,把xml的配置文件转换成resource。resource的转换是先通过ResourcePatternResolver来解析可识别格式的配置文件的路径(如"classpath*:"等),如果没有指定格式,则默认会按照类路径的资源来处理。
- 加载资源文件。通过BeanDefinitionReader 读取并解析 Resource 资源,生成IOC容器的内部数据结构BeanDefinition。
- 注册。将生成的BeanDefinition注册到BeanDefinitionRegistry,完成对BeanFactory的初始化。BeanFactory内部其实是维护了一个用来存储BeanDefinition的HashMap容器。
protected ConfigurableListableBeanFactory obtainFreshBeanFactory() {
//使用委派设计模式,父类定义抽象的refreshBeanFactory()方法,具体实现调用子类容器的refreshBeanFactory()方法
refreshBeanFactory();
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = getBeanFactory();
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Bean factory for " + getDisplayName() + ": " + beanFactory);
}
return beanFactory;
}分析第3行,实际调用了子类容器AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext的refreshBeanFactory()方法,源码如下:
protected final void refreshBeanFactory() throws BeansException {
if (hasBeanFactory()) {
//销毁已有容器
destroyBeans();
closeBeanFactory();
}
try {
//创建IoC容器
DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = createBeanFactory();
beanFactory.setSerializationId(getId());
//对IoC容器进行定制化,如设置启动参数,开启注解的自动装配等
customizeBeanFactory(beanFactory);
//加载BeanDefinition,使用委派模式,只定义抽象的loadBeanDefinitions方法,具体调用子类容器的方法
loadBeanDefinitions(beanFactory);
synchronized (this.beanFactoryMonitor) {
this.beanFactory = beanFactory;
}
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("I/O error parsing bean definition source for " + getDisplayName(), ex);
}
}主要分析第14行,AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext中仅仅定义了抽象的loadBeanDefinitions方法,容器真正调用的是其子类AbstractXmlApplicationContext对该方法的实现,AbstractXmlApplicationContext相关源码如下:
public abstract class AbstractXmlApplicationContext extends AbstractRefreshableConfigApplicationContext {
//实现父类抽象的载入Bean定义方法
protected void loadBeanDefinitions(DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException, IOException {
//创建Bean读取器,并通过回调设置到容器中去,容器使用该读取器读取Bean定义资源
XmlBeanDefinitionReader beanDefinitionReader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(beanFactory);
beanDefinitionReader.setEnvironment(this.getEnvironment());
//为Bean读取器设置Spring资源加载器,AbstractXmlApplicationContext的
//祖先父类AbstractApplicationContext继承DefaultResourceLoader,因此,容器本身也是一个资源加载器
beanDefinitionReader.setResourceLoader(this);
//为Bean读取器设置SAX xml解析器
beanDefinitionReader.setEntityResolver(new ResourceEntityResolver(this));
//当Bean读取器读取Bean定义的Xml资源文件时,启用Xml的校验机制
initBeanDefinitionReader(beanDefinitionReader);
//Bean读取器真正实现加载的方法
loadBeanDefinitions(beanDefinitionReader);
}
//Bean读取器加载Bean定义资源
protected void loadBeanDefinitions(XmlBeanDefinitionReader reader) throws BeansException, IOException {
//获取Bean定义资源的定位
Resource[] configResources = getConfigResources();
if (configResources != null) {
//Bean读取器调用其父类AbstractBeanDefinitionReader,读取定位的Bean定义资源
reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configResources);
}
//如果子类中获取的Bean定义资源定位为空,则获取FileSystemXmlApplicationContext构造方法中setConfigLocations方法设置的资源
String[] configLocations = getConfigLocations();
if (configLocations != null) {
//Bean读取器调用其父类AbstractBeanDefinitionReader读取定位的Bean定义资源
reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configLocations);
}
}
}主要分析第24行,从这里依次调用AbstractXmlApplicationContext—>AbstractBeanDefinitionReader—>XmlBeanDefinitionReader类中的loadBeanDefinitions方法,该方法调用到XmlBeanDefinitionReader 类的doLoadBeanDefinitions方法,部分源码如下:
protected int doLoadBeanDefinitions(InputSource inputSource, Resource resource)
throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
try {
//将XML文档中的信息保存到Document对象中,具体解析过程由documentLoader实现
Document doc = doLoadDocument(inputSource, resource);
//解析Document对象获取BeanDefinition信息,并进行注册
return registerBeanDefinitions(doc, resource);
}
catch (BeanDefinitionStoreException ex) {
throw ex;
}
}主要分析第7行,进入registerBeanDefinitions方法,源码如下:
//按照Spring的Bean语义要求将Bean定义资源解析并转换为容器内部数据结构
public int registerBeanDefinitions (Document doc, Resource resource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
//创建BeanDefinitionDocumentReader对象,用来解析Document对象
BeanDefinitionDocumentReader documentReader = createBeanDefinitionDocumentReader();
int countBefore = getRegistry().getBeanDefinitionCount();
//使用委派模式,BeanDefinitionDocumentReader只是个接口,具体由实现类DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader完成
documentReader.registerBeanDefinitions(doc, createReaderContext(resource));
return getRegistry().getBeanDefinitionCount() - countBefore;
}主要分析第 7行,关注createReaderContext方法和DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader类的registerBeanDefinitions方法。首先看下createReaderContext方法源码:
public XmlReaderContext createReaderContext(Resource resource) {
return new XmlReaderContext(resource, this.problemReporter, this.eventListener,
this.sourceExtractor, this, getNamespaceHandlerResolver());
}该方法主要是用来创建并获取namespaceHandlerResolver。
其次看下registerBeanDefinitions方法的源码:
public void registerBeanDefinitions(Document doc, XmlReaderContext readerContext) {
this.readerContext = readerContext;
logger.debug("Loading bean definitions");
Element root = doc.getDocumentElement();
doRegisterBeanDefinitions(root);
}
protected void doRegisterBeanDefinitions(Element root) {
BeanDefinitionParserDelegate parent = this.delegate;
//具体的解析过程由BeanDefinitionParserDelegate实现,
//BeanDefinitionParserDelegate中定义了Spring Bean定义XML文件的各种元素
this.delegate = createDelegate(getReaderContext(), root, parent);
if (this.delegate.isDefaultNamespace(root)) {
// 处理 profile
String profileSpec = root.getAttribute(PROFILE_ATTRIBUTE);
if (StringUtils.hasText(profileSpec)) {
String[] specifiedProfiles = StringUtils.tokenizeToStringArray(
profileSpec, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate.MULTI_VALUE_ATTRIBUTE_DELIMITERS);
if (!getReaderContext().getEnvironment().acceptsProfiles(specifiedProfiles)) {
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Skipped XML bean definition file due to specified profiles [" + profileSpec +
"] not matching: " + getReaderContext().getResource());
}
return;
}
}
}
//解析前处理
preProcessXml(root);
//解析出文档中的BeanDefinition
parseBeanDefinitions(root, this.delegate);
//解析后处理
postProcessXml(root);
this.delegate = parent;
}程序首先处理 profile属性(主要用于我们切换环境,比如切换开发、测试、生产环境),其次调用parseBeanDefinitions方法,parseBeanDefinitions方法源码如下:
//Spring在解析xml文件中的标签的时候会区分当前的标签是四种默认标签(import、alias、bean和beans)还是自定义标签(aop、mvc、tx),
//如果是自定义标签,则会按照自定义标签的逻辑解析当前的标签
protected void parseBeanDefinitions(Element root, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate) {
// 检查root节点的命名空间是否为默认命名空间
// spring配置文件中默认的命名空间为"http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
if (delegate.isDefaultNamespace(root)) {
//获取Bean定义的Document对象根元素的所有子节点
NodeList nl = root.getChildNodes();
for (int i = 0; i < nl.getLength(); i++) {
Node node = nl.item(i);
//获得Document节点是XML元素节点
if (node instanceof Element) {
Element ele = (Element) node;
// 检查子节点的命名空间是否为默认命名空间
if (delegate.isDefaultNamespace(ele)) {
// 解析默认命名空间的元素节点
parseDefaultElement(ele, delegate);
}
else {
//没有使用Spring默认的XML命名空间,则使用用户自定义的解析规则解析元素节点
delegate.parseCustomElement(ele);
}
}
}
}
else {
//Document的根节点没有使用Spring默认的命名空间,则使用用户自定义的解析规则解析Document根节点
delegate.parseCustomElement(root);
}
}分析parseDefaultElement方法,源码如下:
private void parseDefaultElement(Element ele, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate) {
//解析元素节点是的节点
if (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, IMPORT_ELEMENT)) {
importBeanDefinitionResource(ele);
}
//解析元素节点是的节点
else if (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, ALIAS_ELEMENT)) {
processAliasRegistration(ele);
}
//解析元素节点是的节点
else if (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, BEAN_ELEMENT)) {
processBeanDefinition(ele, delegate);
}
//解析元素节点是的节点
else if (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, NESTED_BEANS_ELEMENT)) {
// recurse
doRegisterBeanDefinitions(ele);
}
} 针对前3中方法,下面分别分析下,第4中方法其实是递归调用单个bean的处理方法,所以这里不做分析。
进入importBeanDefinitionResource方法,源码如下:
//解析导入元素,从给定的导入路径加载Bean定义资源到Spring IoC容器中
protected void importBeanDefinitionResource(Element ele) {
//获取给定的导入元素的location属性
String location = ele.getAttribute(RESOURCE_ATTRIBUTE);
//如果导入元素的location属性值为空,则没有导入任何资源,直接返回
if (!StringUtils.hasText(location)) {
getReaderContext().error("Resource location must not be empty", ele);
return;
}
//使用系统变量值解析location属性值
location = getReaderContext().getEnvironment().resolveRequiredPlaceholders(location);
Set actualResources = new LinkedHashSet(4);
//标识给定的导入元素的location是否是绝对路径
boolean absoluteLocation = false;
try {
absoluteLocation = ResourcePatternUtils.isUrl(location) || ResourceUtils.toURI(location).isAbsolute();
}
catch (URISyntaxException ex) {
}
//给定的导入元素的location是绝对路径
if (absoluteLocation) {
try {
//使用资源读入器加载给定路径的Bean定义资源
int importCount = getReaderContext().getReader().loadBeanDefinitions(location, actualResources);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Imported " + importCount + " bean definitions from URL location [" + location + "]");
}
}
catch (BeanDefinitionStoreException ex) {
getReaderContext().error(
"Failed to import bean definitions from URL location [" + location + "]", ele, ex);
}
}
else {
//给定的导入元素的location是相对路径
try {
int importCount;
//将给定导入元素的location封装为相对路径资源
Resource relativeResource = getReaderContext().getResource().createRelative(location);
//封装的相对路径资源存在
if (relativeResource.exists()) {
//使用资源读入器加载Bean定义资源
importCount = getReaderContext().getReader().loadBeanDefinitions(relativeResource);
actualResources.add(relativeResource);
}
//封装的相对路径资源不存在
else {
//获取Spring IoC容器资源读入器的基本路径
String baseLocation = getReaderContext().getResource().getURL().toString();
//根据Spring IoC容器资源读入器的基本路径加载给定导入
//路径的资源
importCount = getReaderContext().getReader().loadBeanDefinitions(
StringUtils.applyRelativePath(baseLocation, location), actualResources);
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Imported " + importCount + " bean definitions from relative location [" + location + "]");
}
}
catch (IOException ex) {
getReaderContext().error("Failed to resolve current resource location", ele, ex);
}
catch (BeanDefinitionStoreException ex) {
getReaderContext().error("Failed to import bean definitions from relative location [" + location + "]",
ele, ex);
}
}
Resource[] actResArray = actualResources.toArray(new Resource[actualResources.size()]);
//在解析完元素之后,发送容器导入其他资源处理完成事件
getReaderContext().fireImportProcessed(location, actResArray, extractSource(ele));
} 进入processAliasRegistration方法,源码如下:
//解析别名元素,为Bean向Spring IoC容器注册别名
protected void processAliasRegistration(Element ele) {
//获取别名元素中name的属性值
String name = ele.getAttribute(NAME_ATTRIBUTE);
//获取别名元素中alias的属性值
String alias = ele.getAttribute(ALIAS_ATTRIBUTE);
boolean valid = true;
//别名元素的name属性值为空
if (!StringUtils.hasText(name)) {
getReaderContext().error("Name must not be empty", ele);
valid = false;
}
//别名元素的alias属性值为空
if (!StringUtils.hasText(alias)) {
getReaderContext().error("Alias must not be empty", ele);
valid = false;
}
if (valid) {
try {
//向容器的资源读入器注册别名
getReaderContext().getRegistry().registerAlias(name, alias);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
getReaderContext().error("Failed to register alias '" + alias +
"' for bean with name '" + name + "'", ele, ex);
}
//在解析完元素之后,发送容器别名处理完成事件
getReaderContext().fireAliasRegistered(name, alias, extractSource(ele));
}
} 进入processBeanDefinition方法,源码如下:
//解析Bean定义资源Document对象的普通元素
protected void processBeanDefinition(Element ele, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate) {
// BeanDefinitionHolder是对BeanDefinition的封装,即Bean定义的封装类
//对Document对象中元素的解析由BeanDefinitionParserDelegate实现
BeanDefinitionHolder bdHolder = delegate.parseBeanDefinitionElement(ele);
if (bdHolder != null) {
bdHolder = delegate.decorateBeanDefinitionIfRequired(ele, bdHolder);
try {
//向Spring IoC容器注册解析得到的Bean定义,这是Bean定义向IoC容器注册的入口,本质是放到一个map里面
BeanDefinitionReaderUtils.registerBeanDefinition(bdHolder, getReaderContext().getRegistry());
}
catch (BeanDefinitionStoreException ex) {
getReaderContext().error("Failed to register bean definition with name '" +
bdHolder.getBeanName() + "'", ele, ex);
}
//在完成向Spring IoC容器注册解析得到的Bean定义之后,发送注册事件
getReaderContext().fireComponentRegistered(new BeanComponentDefinition(bdHolder));
}
} 分析第5行,进入parseBeanDefinitionElement方法,源码如下:
//解析Bean定义资源文件中的元素,该主要处理元素的id,name和别名属性
public BeanDefinitionHolder parseBeanDefinitionElement(Element ele, BeanDefinition containingBean) {
//获取元素中的id属性值
String id = ele.getAttribute(ID_ATTRIBUTE);
//获取元素中的name属性值
String nameAttr = ele.getAttribute(NAME_ATTRIBUTE);
获取元素中的alias属性值
List aliases = new ArrayList();
//将元素中的所有name属性值存放到别名中
if (StringUtils.hasLength(nameAttr)) {
String[] nameArr = StringUtils.tokenizeToStringArray(nameAttr, BEAN_NAME_DELIMITERS);
aliases.addAll(Arrays.asList(nameArr));
}
String beanName = id;
//如果元素中没有配置id属性时,将别名中的第一个值赋值给beanName
if (!StringUtils.hasText(beanName) && !aliases.isEmpty()) {
beanName = aliases.remove(0);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("No XML 'id' specified - using '" + beanName +
"' as bean name and " + aliases + " as aliases");
}
}
//检查元素所配置的id或者name的唯一性,containingBean标识元素中是否包含子元素
if (containingBean == null) {
//检查元素所配置的id、name或者别名是否重复
checkNameUniqueness(beanName, aliases, ele);
}
//详细对元素中配置的Bean定义进行解析的地方
AbstractBeanDefinition beanDefinition = parseBeanDefinitionElement(ele, beanName, containingBean);
if (beanDefinition != null) {
if (!StringUtils.hasText(beanName)) {
try {
if (containingBean != null) {
//如果元素中没有配置id、别名或者name,且没有包含子元素,为解析的Bean生成一个唯一beanName并注册
beanName = BeanDefinitionReaderUtils.generateBeanName(
beanDefinition, this.readerContext.getRegistry(), true);
}
else {
//如果元素中没有配置id、别名或者name,且包含了子元素,为解析的Bean使用别名向IoC容器注册
beanName = this.readerContext.generateBeanName(beanDefinition);
//为解析的Bean使用别名注册时,为了向后兼容 给别名添加类名后缀
String beanClassName = beanDefinition.getBeanClassName();
if (beanClassName != null &&
beanName.startsWith(beanClassName) && beanName.length() > beanClassName.length() &&
!this.readerContext.getRegistry().isBeanNameInUse(beanClassName)) {
aliases.add(beanClassName);
}
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Neither XML 'id' nor 'name' specified - " +
"using generated bean name [" + beanName + "]");
}
}
catch (Exception ex) {
error(ex.getMessage(), ele);
return null;
}
}
String[] aliasesArray = StringUtils.toStringArray(aliases);
return new BeanDefinitionHolder(beanDefinition, beanName, aliasesArray);
}
//当解析出错时,返回null
return null;
} 分析29行,进入parseBeanDefinitionElement方法,源码如下:
//详细对元素中配置的Bean定义其他属性进行解析,由于上面的方法中已经对
//Bean的id、name和别名等属性进行了处理,该方法中主要处理除这三个以外的其他属性数据
public AbstractBeanDefinition parseBeanDefinitionElement(
Element ele, String beanName, BeanDefinition containingBean) {
//记录解析的
this.parseState.push(new BeanEntry(beanName));
//这里只读取元素中配置的class名字,然后载入到BeanDefinition中去
//只是记录配置的class名字,不做实例化,对象的实例化在依赖注入时完成
String className = null;
if (ele.hasAttribute(CLASS_ATTRIBUTE)) {
className = ele.getAttribute(CLASS_ATTRIBUTE).trim();
}
try {
String parent = null;
//如果元素中配置了parent属性,则获取parent属性的值
if (ele.hasAttribute(PARENT_ATTRIBUTE)) {
parent = ele.getAttribute(PARENT_ATTRIBUTE);
}
//根据元素配置的class名称和parent属性值创建BeanDefinition
//为载入Bean定义信息做准备
AbstractBeanDefinition bd = createBeanDefinition(className, parent);
//对当前的元素中配置的一些属性进行解析和设置,如配置的单态(singleton)属性等
parseBeanDefinitionAttributes(ele, beanName, containingBean, bd);
//为元素解析的Bean设置description信息 bd.setDescription(DomUtils.getChildElementValueByTagName(ele, DESCRIPTION_ELEMENT));
//对元素的meta(元信息)属性解析
parseMetaElements(ele, bd);
//对元素的lookup-method属性解析
parseLookupOverrideSubElements(ele, bd.getMethodOverrides());
//对元素的replaced-method属性解析
parseReplacedMethodSubElements(ele, bd.getMethodOverrides());
//解析元素的构造方法设置
parseConstructorArgElements(ele, bd);
//解析元素的设置
parsePropertyElements(ele, bd);
//解析元素的qualifier属性
parseQualifierElements(ele, bd);
//为当前解析的Bean设置所需的资源和依赖对象
bd.setResource(this.readerContext.getResource());
bd.setSource(extractSource(ele));
return bd;
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
error("Bean class [" + className + "] not found", ele, ex);
}
catch (NoClassDefFoundError err) {
error("Class that bean class [" + className + "] depends on not found", ele, err);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
error("Unexpected failure during bean definition parsing", ele, ex);
}
finally {
this.parseState.pop();
}
//解析元素出错时,返回null
return null;
} 经过对xml转换成的Document对象中的元素解析,Spring IoC现在已经将XML形式定义的Bean定义资源文件,转换为IOC的数据结构BeanDefinition(存储的是一些静态信息),下面需要向容器注册Bean定义信息才算完成IoC容器的初始化过程(还没有开始实例化bean和依赖注入)。
回到上面分析的DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader类的parseDefaultElement方法中,进一步进入processBeanDefinition方法中,这里再看下源码:
protected void processBeanDefinition(Element ele, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate) {
BeanDefinitionHolder bdHolder = delegate.parseBeanDefinitionElement(ele);
if (bdHolder != null) {
bdHolder = delegate.decorateBeanDefinitionIfRequired(ele, bdHolder);
try {
// Register the final decorated instance.
BeanDefinitionReaderUtils.registerBeanDefinition(bdHolder, getReaderContext().getRegistry());
}
catch (BeanDefinitionStoreException ex) {
getReaderContext().error("Failed to register bean definition with name '" +
bdHolder.getBeanName() + "'", ele, ex);
}
// Send registration event.
getReaderContext().fireComponentRegistered(new BeanComponentDefinition(bdHolder));
}
}查看第7行,进入registerBeanDefinition方法,该方法实现了BeanDefinition注册到BeanDefinitionRegistry中的。源码如下:
//将解析的BeanDefinitionHold注册到容器中
public static void registerBeanDefinition(BeanDefinitionHolder definitionHolder, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry)throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
//获取解析的BeanDefinition的名称
String beanName = definitionHolder.getBeanName();
//向IoC容器注册BeanDefinition,实际调用的是DefaultListableBeanFactory类的registerBeanDefinition方法
registry.registerBeanDefinition(beanName, definitionHolder.getBeanDefinition());
//如果解析的BeanDefinition有别名,向容器为其注册别名
String[] aliases = definitionHolder.getAliases();
if (aliases != null) {
for (String aliase : aliases) {
registry.registerAlias(beanName, aliase);
}
}
}进入第6行方法,源码如下:
public void registerBeanDefinition(String beanName, BeanDefinition beanDefinition)
throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
Assert.hasText(beanName, "Bean name must not be empty");
Assert.notNull(beanDefinition, "BeanDefinition must not be null");
if (beanDefinition instanceof AbstractBeanDefinition) {
try {
((AbstractBeanDefinition) beanDefinition).validate();
}
catch (BeanDefinitionValidationException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(beanDefinition.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"Validation of bean definition failed", ex);
}
}
BeanDefinition oldBeanDefinition;
oldBeanDefinition = this.beanDefinitionMap.get(beanName);
if (oldBeanDefinition != null) {
if (!isAllowBeanDefinitionOverriding()) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(beanDefinition.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"Cannot register bean definition [" + beanDefinition + "] for bean '" + beanName +
"': There is already [" + oldBeanDefinition + "] bound.");
}
else if (oldBeanDefinition.getRole() < beanDefinition.getRole()) {
// e.g. was ROLE_APPLICATION, now overriding with ROLE_SUPPORT or ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE
if (this.logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
this.logger.warn("Overriding user-defined bean definition for bean '" + beanName +
"' with a framework-generated bean definition: replacing [" +
oldBeanDefinition + "] with [" + beanDefinition + "]");
}
}
else if (!beanDefinition.equals(oldBeanDefinition)) {
if (this.logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
this.logger.info("Overriding bean definition for bean '" + beanName +
"' with a different definition: replacing [" + oldBeanDefinition +
"] with [" + beanDefinition + "]");
}
}
else {
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug("Overriding bean definition for bean '" + beanName +
"' with an equivalent definition: replacing [" + oldBeanDefinition +
"] with [" + beanDefinition + "]");
}
}
//把beanDefinition放入到map中
this.beanDefinitionMap.put(beanName, beanDefinition);
}
else {
if (hasBeanCreationStarted()) {
//注册的过程中需要线程同步,以保证数据的一致性
synchronized (this.beanDefinitionMap) {
//把beanDefinition放入到map中
this.beanDefinitionMap.put(beanName, beanDefinition);
List updatedDefinitions = new ArrayList<>(this.beanDefinitionNames.size() + 1);
updatedDefinitions.addAll(this.beanDefinitionNames);
updatedDefinitions.add(beanName);
this.beanDefinitionNames = updatedDefinitions;
if (this.manualSingletonNames.contains(beanName)) {
Set updatedSingletons = new LinkedHashSet<>(this.manualSingletonNames);
updatedSingletons.remove(beanName);
this.manualSingletonNames = updatedSingletons;
}
}
}
else {
//把beanDefinition放入到map中
this.beanDefinitionMap.put(beanName, beanDefinition);
this.beanDefinitionNames.add(beanName);
this.manualSingletonNames.remove(beanName);
}
this.frozenBeanDefinitionNames = null;
}
if (oldBeanDefinition != null || containsSingleton(beanName)) {
//重置所有已经注册过的BeanDefinition的缓存
resetBeanDefinition(beanName);
}
}至此,整个IOC容器初始化过程全部完成(BeanDefinition的加载、解析、注册),IoC容器中已经拥有了整个Bean的配置信息。这些数据是IOC容器控制反转的基础,使用这些数据,容器可以进行依赖注入。
BeanDefinition的加载、解析、注册主要涉及类:
- XMLBeanDefinitionReader:加载xml并转换成Document对象。
- DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader:完成解析和处理。通过BeanDefinitionReaderUtils,将得到的BeanDefinitionHolder中的的BeanDefinition和BeanName等取出来,然后注册到Bean工厂中。
- DefaultListableBeanFactory(bean工厂):它有一个ConcurrentHashMap成员变量,以beanName为键,BeanDefinition为值保存注册的bean。
二、prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory)和postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory)
这两个步骤,其实是为beanFactory设置一些spring内置的BeanPostProcessor实现类等信息。BeanPostProcessor能在spring容器实例化bean之后,在执行bean的初始化方法前后,增加自己的处理逻辑。初始化方法指的是以下两种方法:
1)bean实现了InitializingBean接口,对应的方法为afterPropertiesSet
2)在bean定义的时候,通过init-method设置的方法
三、invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory)
此方法的源码如下:
protected void invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate.invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory, getBeanFactoryPostProcessors());
// Detect a LoadTimeWeaver and prepare for weaving, if found in the meantime
// (e.g. through an @Bean method registered by ConfigurationClassPostProcessor)
if (beanFactory.getTempClassLoader() == null && beanFactory.containsBean(LOAD_TIME_WEAVER_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new LoadTimeWeaverAwareProcessor(beanFactory));
beanFactory.setTempClassLoader(new ContextTypeMatchClassLoader(beanFactory.getBeanClassLoader()));
}
}
接着进入invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors方法,部分源码如下:
public static void invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory, List beanFactoryPostProcessors) {
// Invoke BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors first, if any.
Set processedBeans = new HashSet<>();
if (beanFactory instanceof BeanDefinitionRegistry) {
BeanDefinitionRegistry registry = (BeanDefinitionRegistry) beanFactory;
List regularPostProcessors = new LinkedList<>();
List registryProcessors = new LinkedList<>();
// 这里首先获取所有的beanFactoryPostProcessors,并遍历
for (BeanFactoryPostProcessor postProcessor : beanFactoryPostProcessors) {
if (postProcessor instanceof BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor) {
BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor registryProcessor =
(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor) postProcessor;
registryProcessor.postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(registry);
registryProcessors.add(registryProcessor);
}
else {
regularPostProcessors.add(postProcessor);
}
}
// Do not initialize FactoryBeans here: We need to leave all regular beans
// uninitialized to let the bean factory post-processors apply to them!
// Separate between BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors that implement
// PriorityOrdered, Ordered, and the rest.
List currentRegistryProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
// 获取spring配置文件中定义的所有实现BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口的bean
String[] postProcessorNames =
beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false);
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, PriorityOrdered.class)) {
currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class));
processedBeans.add(ppName);
}
}
sortPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, beanFactory);
registryProcessors.addAll(currentRegistryProcessors);
invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry);
currentRegistryProcessors.clear();查看方法中的invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors方法,该方法对于每个实现BeanFactoryPostProcessor的类(根据优先级进行排序,然后按顺序依次调用—》实现PriorityOrdered接口的bean,优先执行postProcessBeanFactory方法;实现Ordered接口的bean,第二优先级执行对应的方法;而对于没有实现排序接口的类,则在最后执行对应的方法),调用postProcessBeanFactory方法修改bean的定义信息
四、registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory)
该方法源码如下:
//注册所有实现BeanPostProcessor接口的bean
protected void registerBeanPostProcessors(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate.registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, this);
}
public static void registerBeanPostProcessors(
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory, AbstractApplicationContext applicationContext) {
String[] postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanPostProcessor.class, true, false);
// Register BeanPostProcessorChecker that logs an info message when
// a bean is created during BeanPostProcessor instantiation, i.e. when
// a bean is not eligible for getting processed by all BeanPostProcessors.
int beanProcessorTargetCount = beanFactory.getBeanPostProcessorCount() + 1 + postProcessorNames.length;
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new BeanPostProcessorChecker(beanFactory, beanProcessorTargetCount));
// Separate between BeanPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered,
// Ordered, and the rest.
List priorityOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
List internalPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
List orderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<>();
List nonOrderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<>();
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, PriorityOrdered.class)) {
BeanPostProcessor pp = beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanPostProcessor.class);
priorityOrderedPostProcessors.add(pp);
if (pp instanceof MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor) {
internalPostProcessors.add(pp);
}
}
else if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, Ordered.class)) {
orderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName);
}
else {
nonOrderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName);
}
}
// 向AbstractBeanFactory类注册实现了PriorityOrdered接口的BeanPostProcessors处理类,且BeanPostProcessors类通过sortPostProcessors排序(执行的顺序)
sortPostProcessors(priorityOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, priorityOrderedPostProcessors);
// 向AbstractBeanFactory类注册实现了Ordered接口的BeanPostProcessors处理类
List orderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
for (String ppName : orderedPostProcessorNames) {
BeanPostProcessor pp = beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanPostProcessor.class);
orderedPostProcessors.add(pp);
if (pp instanceof MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor) {
internalPostProcessors.add(pp);
}
}
sortPostProcessors(orderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, orderedPostProcessors);
// Now, register all regular BeanPostProcessors.
List nonOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
for (String ppName : nonOrderedPostProcessorNames) {
BeanPostProcessor pp = beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanPostProcessor.class);
nonOrderedPostProcessors.add(pp);
if (pp instanceof MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor) {
internalPostProcessors.add(pp);
}
}
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, nonOrderedPostProcessors);
// Finally, re-register all internal BeanPostProcessors.
sortPostProcessors(internalPostProcessors, beanFactory);
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, internalPostProcessors);
// Re-register post-processor for detecting inner beans as ApplicationListeners,
// moving it to the end of the processor chain (for picking up proxies etc).
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ApplicationListenerDetector(applicationContext));
}
再查看下上面方法中的registerBeanPostProcessors方法
private static void registerBeanPostProcessors(
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory, List postProcessors) {
for (BeanPostProcessor postProcessor : postProcessors) {
//向AbstractBeanFactory类中注册BeanPostProcessor类
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(postProcessor);
}
}五、registerListeners
该方法的主要功能是注册实现ApplicationListener接口的bean,源码如下:
protected void registerListeners() {
// Register statically specified listeners first.
for (ApplicationListener listener : getApplicationListeners()) {
getApplicationEventMulticaster().addApplicationListener(listener);
}
// Do not initialize FactoryBeans here: We need to leave all regular beans
// uninitialized to let post-processors apply to them!
String[] listenerBeanNames = getBeanNamesForType(ApplicationListener.class, true, false);
for (String listenerBeanName : listenerBeanNames) {
getApplicationEventMulticaster().addApplicationListenerBean(listenerBeanName);
}
// Publish early application events now that we finally have a multicaster...
Set earlyEventsToProcess = this.earlyApplicationEvents;
this.earlyApplicationEvents = null;
if (earlyEventsToProcess != null) {
for (ApplicationEvent earlyEvent : earlyEventsToProcess) {
getApplicationEventMulticaster().multicastEvent(earlyEvent);
}
}
}- 先注册静态特定的listener,不过默认是空的。
- 调用beanFactory.getBeansOfType(ApplicationListener.class, true, false),获取所有实现ApplicationListener接口的bean。该方法底层先调用getBeanNamesForType方法获取所有实现ApplicationListener接口的beanName,然后针对每个beanName,调用getBean方法获取对应的bean实例。
- 调用getApplicationEventMulticaster().addApplicationListener(listener),注册每个bean。
spring的ApplicationListener是一个典型的观察者模式,类图结构如下(链接:https://blog.csdn.net/caihaijiang/article/details/37727681)
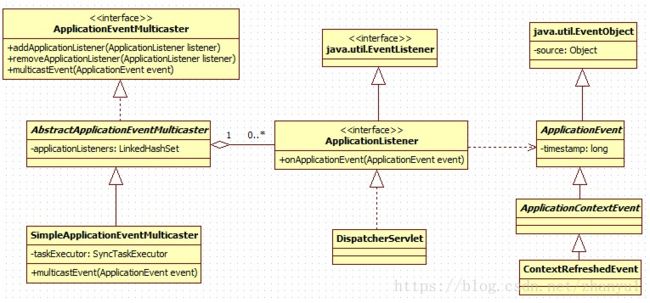
ApplicationEventMulticaster在接收到ApplicationEvent事件之后,通过multicastEvent方法,通知所有的观察者ApplicationListener。SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster类的multicastEvent源码如下:
public void multicastEvent(final ApplicationEvent event, @Nullable ResolvableType eventType) {
ResolvableType type = (eventType != null ? eventType : resolveDefaultEventType(event));
for (final ApplicationListener listener : getApplicationListeners(event, type)) {
Executor executor = getTaskExecutor();
if (executor != null) {
executor.execute(() -> invokeListener(listener, event));
}
else {
invokeListener(listener, event);
}
}
}分析以上代码可知,在for循环里面,通过同步的方式(SyncTaskExecutor),调用每一个listener的onApplicationEvent方法。
六、finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory)—创建非延迟初始化bean的方法
执行此方法之前,一直未实例化bean(创建bean对象),该方法会创建非延迟初始化的单例bean对象,并通过执行BeanPostProcesssors处理器对该bean对象进行处理。该方法源码如下:
protected void finishBeanFactoryInitialization(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
// Initialize conversion service for this context.
if (beanFactory.containsBean(CONVERSION_SERVICE_BEAN_NAME) &&
beanFactory.isTypeMatch(CONVERSION_SERVICE_BEAN_NAME, ConversionService.class)) {
beanFactory.setConversionService(
beanFactory.getBean(CONVERSION_SERVICE_BEAN_NAME, ConversionService.class));
}
// Register a default embedded value resolver if no bean post-processor
// (such as a PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer bean) registered any before:
// at this point, primarily for resolution in annotation attribute values.
if (!beanFactory.hasEmbeddedValueResolver()) {
beanFactory.addEmbeddedValueResolver(strVal -> getEnvironment().resolvePlaceholders(strVal));
}
// Initialize LoadTimeWeaverAware beans early to allow for registering their transformers early.
String[] weaverAwareNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(LoadTimeWeaverAware.class, false, false);
for (String weaverAwareName : weaverAwareNames) {
getBean(weaverAwareName);
}
// Stop using the temporary ClassLoader for type matching.
beanFactory.setTempClassLoader(null);
// Allow for caching all bean definition metadata, not expecting further changes.
beanFactory.freezeConfiguration();
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
beanFactory.preInstantiateSingletons();
}真正执行相关初始化工作的是方法preInstantiateSingletons,进入DefaultListableBeanFactory.preInstantiateSingletons(),部分源码如下:
public void preInstantiateSingletons() throws BeansException {
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug("Pre-instantiating singletons in " + this);
}
// Iterate over a copy to allow for init methods which in turn register new bean definitions.
// While this may not be part of the regular factory bootstrap, it does otherwise work fine.
List beanNames = new ArrayList<>(this.beanDefinitionNames);
// Trigger initialization of all non-lazy singleton beans...
for (String beanName : beanNames) {
RootBeanDefinition bd = getMergedLocalBeanDefinition(beanName);
//bean是非懒加载且单例
if (!bd.isAbstract() && bd.isSingleton() && !bd.isLazyInit()) {
//如果bean是FactoryBean类型,则通过在前面加“&”,调用getBean获取对应的FactoryBean
if (isFactoryBean(beanName)) {
Object bean = getBean(FACTORY_BEAN_PREFIX + beanName);
if (bean instanceof FactoryBean) {
final FactoryBean factory = (FactoryBean) bean;
boolean isEagerInit;
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null && factory instanceof SmartFactoryBean) {
isEagerInit = AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedAction)
((SmartFactoryBean) factory)::isEagerInit,
getAccessControlContext());
}
else {
isEagerInit = (factory instanceof SmartFactoryBean &&
((SmartFactoryBean) factory).isEagerInit());
}
if (isEagerInit) {
getBean(beanName);
}
}
}
else {
//真正创建bean对象的地方
getBean(beanName);
}
}
}进入到了AbstractBeanFactory类的doGetBean方法,核心部分为createBean方法,接着进入AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory类的createBean方法,核心部分为doCreateBean方法。doCreateBean方法源码如下:
protected Object doCreateBean(final String beanName, final RootBeanDefinition mbd, final @Nullable Object[] args)
throws BeanCreationException {
// Instantiate the bean.
BeanWrapper instanceWrapper = null;
if (mbd.isSingleton()) {
instanceWrapper = this.factoryBeanInstanceCache.remove(beanName);
}
if (instanceWrapper == null) {
//创建bean实例对象,但并未设置属性
instanceWrapper = createBeanInstance(beanName, mbd, args);
}
final Object bean = instanceWrapper.getWrappedInstance();
Class beanType = instanceWrapper.getWrappedClass();
if (beanType != NullBean.class) {
mbd.resolvedTargetType = beanType;
}
// Allow post-processors to modify the merged bean definition.
synchronized (mbd.postProcessingLock) {
if (!mbd.postProcessed) {
try {
applyMergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessors(mbd, beanType, beanName);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"Post-processing of merged bean definition failed", ex);
}
mbd.postProcessed = true;
}
}
// Eagerly cache singletons to be able to resolve circular references
// even when triggered by lifecycle interfaces like BeanFactoryAware.
boolean earlySingletonExposure = (mbd.isSingleton() && this.allowCircularReferences &&
isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName));
if (earlySingletonExposure) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Eagerly caching bean '" + beanName +
"' to allow for resolving potential circular references");
}
addSingletonFactory(beanName, () -> getEarlyBeanReference(beanName, mbd, bean));
}
// Initialize the bean instance.
Object exposedObject = bean;
try {
//填充属性(注入相关属性)
populateBean(beanName, mbd, instanceWrapper);
//初始化bean(在实例化之后进行)
exposedObject = initializeBean(beanName, exposedObject, mbd);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
if (ex instanceof BeanCreationException && beanName.equals(((BeanCreationException) ex).getBeanName())) {
throw (BeanCreationException) ex;
}
else {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Initialization of bean failed", ex);
}
}
if (earlySingletonExposure) {
Object earlySingletonReference = getSingleton(beanName, false);
if (earlySingletonReference != null) {
if (exposedObject == bean) {
exposedObject = earlySingletonReference;
}
else if (!this.allowRawInjectionDespiteWrapping && hasDependentBean(beanName)) {
String[] dependentBeans = getDependentBeans(beanName);
Set actualDependentBeans = new LinkedHashSet<>(dependentBeans.length);
for (String dependentBean : dependentBeans) {
if (!removeSingletonIfCreatedForTypeCheckOnly(dependentBean)) {
actualDependentBeans.add(dependentBean);
}
}
if (!actualDependentBeans.isEmpty()) {
throw new BeanCurrentlyInCreationException(beanName,
"Bean with name '" + beanName + "' has been injected into other beans [" +
StringUtils.collectionToCommaDelimitedString(actualDependentBeans) +
"] in its raw version as part of a circular reference, but has eventually been " +
"wrapped. This means that said other beans do not use the final version of the " +
"bean. This is often the result of over-eager type matching - consider using " +
"'getBeanNamesOfType' with the 'allowEagerInit' flag turned off, for example.");
}
}
}
}
// Register bean as disposable.
try {
registerDisposableBeanIfNecessary(beanName, bean, mbd);
}
catch (BeanDefinitionValidationException ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Invalid destruction signature", ex);
}
return exposedObject;
}该方法主要关注有注释的三部分。在该方法中,首先调用createBeanInstance方法,运用反射创建bean实例对象(这个时候执行bean的构造方法),接着调用populateBean方法,对bean进行填充,注入相关依赖,之后再调用方法initializeBean,进行相关初始化工作。initializeBean源码如下:
protected Object initializeBean(final String beanName, final Object bean, @Nullable RootBeanDefinition mbd) {
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedAction) () -> {
invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean);
return null;
}, getAccessControlContext());
}
else {
invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean);
}
Object wrappedBean = bean;
if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) {
//执行每个BeanPostProcessor的postProcessBeforeInitialization
wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName);
}
try {
//执行bean的初始化方法
invokeInitMethods(beanName, wrappedBean, mbd);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
(mbd != null ? mbd.getResourceDescription() : null),
beanName, "Invocation of init method failed", ex);
}
if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) {
//执行每个BeanPostProcessor的postProcessAfterInitialization
wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName);
}
return wrappedBean;
}分析以上代码可知,首先调用applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization方法,执行每个BeanPostProcessor的postProcessBeforeInitialization,然后调用invokeInitMethods方法,执行bean的初始化方法,最后调用applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization方法,执行每个BeanPostProcessor的postProcessAfterInitialization方法。
接下来看下invokeInitMethods方法的源码:
protected void invokeInitMethods(String beanName, final Object bean, @Nullable RootBeanDefinition mbd)
throws Throwable {
boolean isInitializingBean = (bean instanceof InitializingBean);
//如果bean是InitializingBean类型,则执行afterPropertiesSet方法
if (isInitializingBean && (mbd == null || !mbd.isExternallyManagedInitMethod("afterPropertiesSet"))) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Invoking afterPropertiesSet() on bean with name '" + beanName + "'");
}
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
try {
AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedExceptionAction) () -> {
((InitializingBean) bean).afterPropertiesSet();
return null;
}, getAccessControlContext());
}
catch (PrivilegedActionException pae) {
throw pae.getException();
}
}
else {
((InitializingBean) bean).afterPropertiesSet();
}
}
//如果bean不是InitializingBean类型,则执行init-method方法
if (mbd != null && bean.getClass() != NullBean.class) {
String initMethodName = mbd.getInitMethodName();
if (StringUtils.hasLength(initMethodName) &&
!(isInitializingBean && "afterPropertiesSet".equals(initMethodName)) &&
!mbd.isExternallyManagedInitMethod(initMethodName)) {
invokeCustomInitMethod(beanName, bean, mbd);
}
}
}分析以上代码可知,首先执行afterPropertiesSet方法(如果bean是InitializingBean类型),然后再通过反射,执行init-method指定的方法(如果bean不是InitializingBean类型)。