本文总结的是我们大家在python中常见的数据预处理方法,以下通过sklearn的preprocessing模块来介绍;
1. 标准化(Standardization or Mean Removal and Variance Scaling)
变换后各维特征有0均值,单位方差。也叫z-score规范化(零均值规范化)。计算方式是将特征值减去均值,除以标准差。
sklearn.preprocessing.scale(X)
一般会把train和test集放在一起做标准化,或者在train集上做标准化后,用同样的标准化器去标准化test集,此时可以用scaler
scaler = sklearn.preprocessing.StandardScaler().fit(train)
scaler.transform(train)
scaler.transform(test)
实际应用中,需要做特征标准化的常见情景:SVM
2. 最小-最大规范化
最小-最大规范化对原始数据进行线性变换,变换到[0,1]区间(也可以是其他固定最小最大值的区间)
min_max_scaler = sklearn.preprocessing.MinMaxScaler()
min_max_scaler.fit_transform(X_train)
3.规范化(Normalization)
规范化是将不同变化范围的值映射到相同的固定范围,常见的是[0,1],此时也称为归一化。
将每个样本变换成unit norm。
X = [[ 1, -1, 2],[ 2, 0, 0], [ 0, 1, -1]]
sklearn.preprocessing.normalize(X, norm='l2')
得到:
array([[ 0.40, -0.40, 0.81], [ 1, 0, 0], [ 0, 0.70, -0.70]])
可以发现对于每一个样本都有,0.4^2+0.4^2+0.81^2=1,这就是L2 norm,变换后每个样本的各维特征的平方和为1。类似地,L1 norm则是变换后每个样本的各维特征的绝对值和为1。还有max norm,则是将每个样本的各维特征除以该样本各维特征的最大值。
在度量样本之间相似性时,如果使用的是二次型kernel,需要做Normalization
4. 特征二值化(Binarization)
给定阈值,将特征转换为0/1
binarizer = sklearn.preprocessing.Binarizer(threshold=1.1)
binarizer.transform(X)
5. 标签二值化(Label binarization)
lb = sklearn.preprocessing.LabelBinarizer()
6. 类别特征编码
有时候特征是类别型的,而一些算法的输入必须是数值型,此时需要对其编码。
enc = preprocessing.OneHotEncoder()
enc.fit([[0, 0, 3], [1, 1, 0], [0, 2, 1], [1, 0, 2]])
enc.transform([[0, 1, 3]]).toarray() #array([[ 1., 0., 0., 1., 0., 0., 0., 0., 1.]])
上面这个例子,第一维特征有两种值0和1,用两位去编码。第二维用三位,第三维用四位。
另一种编码方式
newdf=pd.get_dummies(df,columns=["gender","title"],dummy_na=True)
7.标签编码(Label encoding)
le = sklearn.preprocessing.LabelEncoder()
le.fit([1, 2, 2, 6])
le.transform([1, 1, 2, 6]) #array([0, 0, 1, 2])
#非数值型转化为数值型
le.fit(["paris", "paris", "tokyo", "amsterdam"])
le.transform(["tokyo", "tokyo", "paris"]) #array([2, 2, 1])
8.特征中含异常值时
sklearn.preprocessing.robust_scale
9.生成多项式特征
这个其实涉及到特征工程了,多项式特征/交叉特征。
poly = sklearn.preprocessing.PolynomialFeatures(2)
poly.fit_transform(X)
原始特征: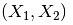
转化后: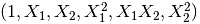
总结
以上就是为大家总结的python中常用的九种预处理方法分享,希望这篇文章对大家学习或者使用python能有一定的帮助,如果有疑问大家可以留言交流
。
|
|
I have data of the form:
X Y
3.53 0
4.93 50
5.53 60
6.21 70
7.37 80
9.98 90
16.56 100
And I want to find out n so that this can be fit to a function of the form:
I am trying to determine n by Box-Cox transformation. How can this be done in Python?
python numpy scipy curve-fitting
|
|
asked
May 3 '15 at 20:14
Tom Kurushingal
1,217
3
17
48
|
|
| |
|
|
up vote
5 down vote
|
I think you want scipy.stats.boxcox.
from scipy import stats
import numpy as np
data = np.fromstring('3.53 0 4.93 50 5.53 60 6.21 70 7.37 80 9.98 90 16.56 100', sep=' ').reshape(7, 2)
stats.boxcox(data[0,])
(array([ 0.91024309, 1.06300488, 1.10938333, 1.15334193, 1.213348 ,
1.30668122, 1.43178909]), -0.54874593147877893)
|