Mybatis-plus基础以及SpringBoot整合Mybatis-plus
目录
(一)环境搭建
1.快速引入spring boot项目相关依赖
2.引入mybatis-plus相关maven依赖
3.创建数据表
4. 创建java bean
5. 配置application.proprties
(二)基于mybatis-plus的入门helloworld---CRUD实验
1.mybatis与mybatis-plus实现方式对比
2.BaseMapper接口介绍
(1)如何理解核心接口BaseMapper?
(2)BaseMapper接口为我们定义了哪些方法?
(3) mybatis-plus中常用的注解
3.增删查改操作
(1)插入
(2)修改
(3)查询
(4)删除
(三)不得不提的条件构造器---Wrapper
1.wrapper及其子类介绍
2.带条件的crud实验
(1)带条件的查询
(2)带条件的更新
(3)带条件的删除
(一)环境搭建
1.快速引入spring boot项目相关依赖
将STS与eclipse集成,快速新建SpringBoot项目,勾选如下选项
![]()
![]()
一路next,pom.xml文件会帮我们配置好.
ps:由于我们使用的数据源使阿里巴巴的druid,在springboot项目构建模板并没有这一选项,我们还需要手动引入(同理,后面的mybatis-plus相关依赖也需要手动引入)
进入mvnrepository官网搜索相关依赖,添加到pom.xml文件中
https://mvnrepository.com/
com.alibaba
druid
1.1.21
2.引入mybatis-plus相关maven依赖
同理,进入mvnrepository官网搜索相关依赖,添加到pom.xml文件中
com.baomidou
mybatis-plus
3.3.1
引入mybatis-plus在spring boot中的场景启动器
com.baomidou
mybatis-plus-boot-starter
3.3.1
ps:切记不可再在pom.xml文件中引入mybatis与mybatis-spring的maven依赖,这一点,mybatis-plus的官方文档中已经说明的很清楚了.
3.创建数据表
(1)SQL语句
-- 创建表
CREATE TABLE tbl_employee(
id INT(11) PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT,
last_name VARCHAR(50),
email VARCHAR(50),
gender CHAR(1),
age INT
);
INSERT INTO tbl_employee(last_name,email,gender,age) VALUES('Tom','[email protected]',1,22);
INSERT INTO tbl_employee(last_name,email,gender,age) VALUES('Jerry','[email protected]',0,25);
INSERT INTO tbl_employee(last_name,email,gender,age) VALUES('Black','[email protected]',1,30);
INSERT INTO tbl_employee(last_name,email,gender,age) VALUES('White','[email protected]',0,35);(2) 数据表结构
![]()
4. 创建java bean
根据数据表新建相关实体类
package com.example.demo.pojo;
public class Employee {
private Integer id;
private String lastName;
private String email;
private Integer gender;
private Integer age;
public Employee() {
super();
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
public Employee(Integer id, String lastName, String email, Integer gender, Integer age) {
super();
this.id = id;
this.lastName = lastName;
this.email = email;
this.gender = gender;
this.age = age;
}
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getLastName() {
return lastName;
}
public void setLastName(String lastName) {
this.lastName = lastName;
}
public String getEmail() {
return email;
}
public void setEmail(String email) {
this.email = email;
}
public Integer getGender() {
return gender;
}
public void setGender(Integer gender) {
this.gender = gender;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Employee [id=" + id + ", lastName=" + lastName + ", email=" + email + ", gender=" + gender + ", age="
+ age + "]";
}
}
5. 配置application.proprties
数据源使用druid
spring.datasource.username=root
spring.datasource.password=20182022
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/my?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8&useSSL=false&serverTimezone=GMT%2B8
spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
spring.datasource.type=com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
(二)基于mybatis-plus的入门helloworld---CRUD实验
ps:在进行crud实验之前,简单对mybatis与mybatis-plus做一个简单的对比
1.mybatis与mybatis-plus实现方式对比
(1)提出问题: 假设我们已存在一张 tbl_employee 表,且已有对应的实体类 Employee,实现 tbl_employee 表的 CRUD 操作我们需要做什么呢?
(2)实现方式: 基于 Mybatis 需要编写 EmployeeMapper 接口,并手动编写 CRUD 方法 提供 EmployeeMapper.xml 映射文件,并手动编写每个方法对应的 SQL 语句. 基于 Mybatis-plus 只需要创建 EmployeeMapper 接口, 并继承 BaseMapper 接口.这就是使用 mybatis-plus 需要完成的所有操作,甚至不需要创建 SQL 映射文件。
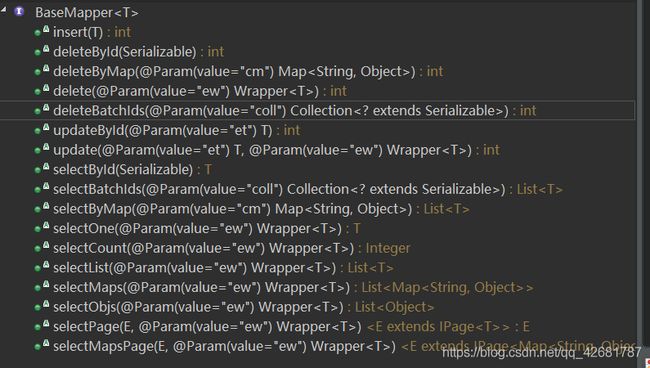
2.BaseMapper接口介绍
(1)如何理解核心接口BaseMapper?
在使用Mybatis-Plus是,核心操作类是BaseMapper接口,其最终也是利用的Mybatis接口编程的实现机制,其默认提供了一系列的增删改查的基础方法,并且开发人员对于这些基础操作不需要写SQL进行处理操作(Mybatis提供的机制就是需要开发人员在mapper.xml中提供sql语句),那样我们可以猜测肯定是Mybatis-Plus完成了BaseMapper接口提供的方法的SQL语句的生成操作。
(2)BaseMapper接口为我们定义了哪些方法?
BaseMapper接口源码:
/*
* Copyright (c) 2011-2020, baomidou ([email protected]).
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not
* use this file except in compliance with the License. You may obtain a copy of
* the License at
*
* https://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT
* WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the
* License for the specific language governing permissions and limitations under
* the License.
*/
package com.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.mapper;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.conditions.Wrapper;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.metadata.IPage;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.toolkit.Constants;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Param;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* Mapper 继承该接口后,无需编写 mapper.xml 文件,即可获得CRUD功能
*
这个 Mapper 支持 id 泛型
*
* @author hubin
* @since 2016-01-23
*/
public interface BaseMapper extends Mapper {
/**
* 插入一条记录
*
* @param entity 实体对象
*/
int insert(T entity);
/**
* 根据 ID 删除
*
* @param id 主键ID
*/
int deleteById(Serializable id);
/**
* 根据 columnMap 条件,删除记录
*
* @param columnMap 表字段 map 对象
*/
int deleteByMap(@Param(Constants.COLUMN_MAP) Map columnMap);
/**
* 根据 entity 条件,删除记录
*
* @param wrapper 实体对象封装操作类(可以为 null)
*/
int delete(@Param(Constants.WRAPPER) Wrapper wrapper);
/**
* 删除(根据ID 批量删除)
*
* @param idList 主键ID列表(不能为 null 以及 empty)
*/
int deleteBatchIds(@Param(Constants.COLLECTION) Collection idList);
/**
* 根据 ID 修改
*
* @param entity 实体对象
*/
int updateById(@Param(Constants.ENTITY) T entity);
/**
* 根据 whereEntity 条件,更新记录
*
* @param entity 实体对象 (set 条件值,可以为 null)
* @param updateWrapper 实体对象封装操作类(可以为 null,里面的 entity 用于生成 where 语句)
*/
int update(@Param(Constants.ENTITY) T entity, @Param(Constants.WRAPPER) Wrapper updateWrapper);
/**
* 根据 ID 查询
*
* @param id 主键ID
*/
T selectById(Serializable id);
/**
* 查询(根据ID 批量查询)
*
* @param idList 主键ID列表(不能为 null 以及 empty)
*/
List selectBatchIds(@Param(Constants.COLLECTION) Collection idList);
/**
* 查询(根据 columnMap 条件)
*
* @param columnMap 表字段 map 对象
*/
List selectByMap(@Param(Constants.COLUMN_MAP) Map columnMap);
/**
* 根据 entity 条件,查询一条记录
*
* @param queryWrapper 实体对象封装操作类(可以为 null)
*/
T selectOne(@Param(Constants.WRAPPER) Wrapper queryWrapper);
/**
* 根据 Wrapper 条件,查询总记录数
*
* @param queryWrapper 实体对象封装操作类(可以为 null)
*/
Integer selectCount(@Param(Constants.WRAPPER) Wrapper queryWrapper);
/**
* 根据 entity 条件,查询全部记录
*
* @param queryWrapper 实体对象封装操作类(可以为 null)
*/
List selectList(@Param(Constants.WRAPPER) Wrapper queryWrapper);
/**
* 根据 Wrapper 条件,查询全部记录
*
* @param queryWrapper 实体对象封装操作类(可以为 null)
*/
List> selectMaps(@Param(Constants.WRAPPER) Wrapper queryWrapper);
/**
* 根据 Wrapper 条件,查询全部记录
* 注意: 只返回第一个字段的值
*
* @param queryWrapper 实体对象封装操作类(可以为 null)
*/
List (3) mybatis-plus中常用的注解
@TableName:对数据表名注解
@TableId:表主键标识
@TableId(value = "id", type = IdType.AUTO):自增
@TableId(value = "id", type = IdType.ID_WORKER_STR):分布式全局唯一ID字符串类型
@TableId(value = "id", type = IdType.INPUT):自行输入
@TableId(value = "id", type = IdType.ID_WORKER):分布式全局唯一ID 长整型类型
@TableId(value = "id", type = IdType.UUID):32位UUID字符串
@TableId(value = "id", type = IdType.NONE):无状态
@TableField:表字段标识
@TableField(exist = false):表示该属性不为数据库表字段,但又是必须使用的。
@TableField(exist = true):表示该属性为数据库表字段。
@TableField(condition = SqlCondition.LIKE):表示该属性可以模糊搜索。
@TableField(fill = FieldFill.INSERT):注解填充字段 ,生成器策略部分也可以配置!
@FieldStrategy:
@FieldFill
@Version:乐观锁注解、标记
@EnumValue:通枚举类注解
@TableLogic:表字段逻辑处理注解(逻辑删除)
@SqlParser:租户注解
@KeySequence:序列主键策略
常用的就三个:@TableName @TableId @TableField
查看更多注解以及详解,请移步至官网:
https://mybatis.plus/guide/annotation.html#tablename由于我们的数据表名于实体类的类名不一致,并且实体类于数据表还存在字段名不对应的情况,因此我们需要引入mybatis-plus的注解.
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.annotation.IdType;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.annotation.TableField;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.annotation.TableId;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.annotation.TableName;
/*
* MybatisPlus会默认使用实体类的类名到数据中找对应的表.
*
*/
@Component
@TableName(value = "tbl_employee")
public class Employee {
/*
* @TableId:
* value: 指定表中的主键列的列名, 如果实体属性名与列名一致,可以省略不指定.
* type: 指定主键策略.
*/
@TableId(value="id" , type =IdType.AUTO)
private Integer id;
@TableField(value = "last_name")
private String lastName;
private String email;
private Integer gender;
private Integer age;
public Employee() {
super();
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
public Employee(Integer id, String lastName, String email, Integer gender, Integer age) {
super();
this.id = id;
this.lastName = lastName;
this.email = email;
this.gender = gender;
this.age = age;
}
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getLastName() {
return lastName;
}
public void setLastName(String lastName) {
this.lastName = lastName;
}
public String getEmail() {
return email;
}
public void setEmail(String email) {
this.email = email;
}
public Integer getGender() {
return gender;
}
public void setGender(Integer gender) {
this.gender = gender;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Employee [id=" + id + ", lastName=" + lastName + ", email=" + email + ", gender=" + gender + ", age="
+ age + "]";
}
}
3.增删查改操作
编写EmployeeMapper接口继承BaseMapper接口
package com.example.demo.mapper;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Mapper;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.mapper.BaseMapper;
import com.example.demo.pojo.Employee;
/**
*
* @author zhou'en'xian
*基于Mybatis-plus实现: 让XxxMapper接口继承 BaseMapper接口即可.
*BaseMapper : 泛型指定的就是当前Mapper接口所操作的实体类类型
*/
@Mapper
public interface EmpolyeeMapper extends BaseMapper {
}
准备测试环境:
package com.example.demo;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import com.example.demo.mapper.EmpolyeeMapper;
import com.example.demo.pojo.Employee;
@SpringBootTest
class MybatisplusApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private Employee employee;
@Autowired
private EmpolyeeMapper empolyeeMapper;
}
(1)插入
// 插入一条记录
int insert(T entity);
@Test
void insert() {
employee.setAge(20);
employee.setEmail("[email protected]");
employee.setGender(1);
employee.setLastName("张三");
empolyeeMapper.insert(employee);
//int id=employee.getId();此方法可以获取插入当前记录在数据库中的id
//在mybatis中如果立马获取插入数据的主键id,是不是需要配置呢?感受到mybatis-plus的强大了吗?
}(2)修改
// 根据 ID 修改
int updateById(@Param(Constants.ENTITY) T entity);
//T entity 实体对象 (set 条件值,可为 null)@Test
void update() {
employee.setId(1);
employee.setAge(18);
employee.setEmail("[email protected]");
employee.setGender(0);
employee.setLastName("lili");
empolyeeMapper.updateById(employee);
}控制台打印出的sql语句
如果我们不设置实体类的email与gender属性,结果是怎样的呢?
@Test
void update() {
employee.setId(2);
employee.setAge(21);
//employee.setEmail("[email protected]");
//employee.setGender(1);
employee.setLastName("lihua");
empolyeeMapper.updateById(employee);
}控制台sql语句:
显然,mybatis-plus为我们做了非空判断,空值的话,默认不更新对应的字段.想一想,这是不是类似于mybatis中的动态sql呢?这种处理效果又会带来什么好处呢?
(3)查询
// 根据 ID 查询
T selectById(Serializable id);
// 查询(根据ID 批量查询)
List selectBatchIds(@Param(Constants.COLLECTION) Collection idList);
// 查询(根据 columnMap 条件)
List selectByMap(@Param(Constants.COLUMN_MAP) Map columnMap);
selectById方法
@Test
void select() {
Employee employee=empolyeeMapper.selectById(4);
System.out.println(employee);
}selectBatchIds方法
@Test
void select() {
Listlist =new ArrayList();
list.add(1);
list.add(2);
list.add(3);
Listli=empolyeeMapper.selectBatchIds(list);
for(Employee employee:li) {
System.out.println(employee);
}
}
ps:发现该方法底层使用的竟然是sql的in关键字
selectByMap方法
@Test
void select() {
Mapmap=new HashMap();
map.put("age", 22);
map.put("id", 16);
Listli=empolyeeMapper.selectByMap(map);
for(Employee employee:li) {
System.out.println(employee);
}
}
(4)删除
// 删除(根据ID 批量删除)
int deleteBatchIds(@Param(Constants.COLLECTION) Collection idList);
// 根据 ID 删除
int deleteById(Serializable id);
// 根据 columnMap 条件,删除记录
int deleteByMap(@Param(Constants.COLUMN_MAP) Map columnMap); (三)不得不提的条件构造器---Wrapper
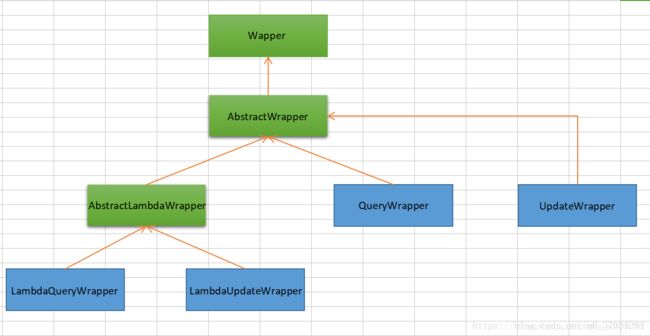
1.wrapper及其子类介绍
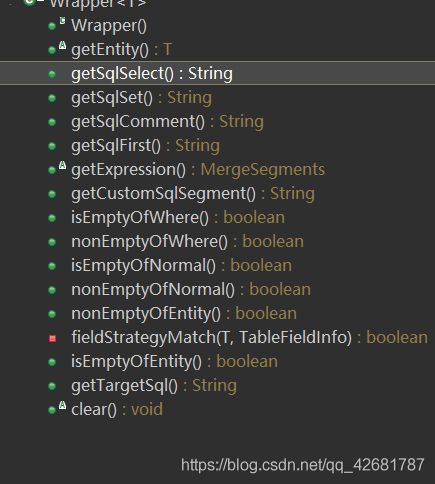
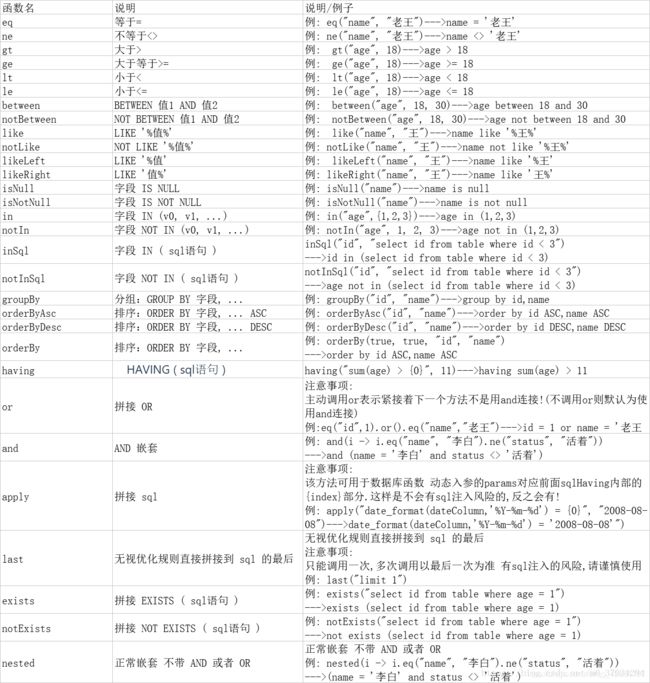
(1)Wrapper :条件构造抽象类,最顶端父类,抽象类中提供3个方法以及其他方法.
(2)AbstractWrapper : 用于查询条件封装,生成 sql 的 where 条件,QueryWrapper(LambdaQueryWrapper) 和 UpdateWrapper(LambdaUpdateWrapper) 的父类用于生成 sql 的 where 条件, entity 属性也用于生成 sql 的 where 条件
AbstractWrapper比较重要,里面的方法需要重点学习.
该抽象类提供的重要方法如下:
(3)AbstractLambdaWrapper : Lambda 语法使用 Wrapper统一处理解析 lambda 获取 column。
(4)LambdaQueryWrapper :看名称也能明白就是用于Lambda语法使用的查询Wrapper
(5)LambdaUpdateWrapper : Lambda 更新封装Wrapper
(6)QueryWrapper : Entity 对象封装操作类,不是用lambda语法,自身的内部属性 entity 也用于生成 where 条件
该类的重要方法:
select方法
select(String... sqlSelect)
select(Predicate predicate)
select(Class entityClass, Predicate predicate)
/*
例: select("id", "name", "age")
例: select(i -> i.getProperty().startsWith("test"))
*/
(7)UpdateWrapper : Update 条件封装,用于Entity对象更新操作.
该类主要有以下三个重要的方法:
set方法
set(String column, Object val)
set(boolean condition, String column, Object val)
/*
SQL SET 字段
例: set("name", "老李头")
例: set("name", "")--->数据库字段值变为空字符串
例: set("name", null)--->数据库字段值变为null
说明:boolean condition为控制该字段是否拼接到最终的sql语句中
*/setSql方法
setSql(String sql)
/*
设置 SET 部分 SQL
例: setSql("name = '老李头'")
*/2.带条件的crud实验
(1)带条件的查询
// 根据 entity 条件,查询一条记录
T selectOne(@Param(Constants.WRAPPER) Wrapper queryWrapper);
// 根据 entity 条件,查询全部记录
List selectList(@Param(Constants.WRAPPER) Wrapper queryWrapper);
// 根据 Wrapper 条件,查询全部记录
List> selectMaps(@Param(Constants.WRAPPER) Wrapper queryWrapper);
// 根据 Wrapper 条件,查询全部记录。注意: 只返回第一个字段的值
List (2)带条件的更新
@Test
void update() {
UpdateWrapper updateWrapper=new UpdateWrapper();
updateWrapper.eq("last_name", "lili").eq("age", 18).set("id", 100).set(false, "email", "[email protected]");
empolyeeMapper.update(employee, updateWrapper);
}
} 其中set("id", 100).set(false, "email", "[email protected]");中email属性设置为false,从执行的sql可以看出,设置为false不会拼接到最终的执行sql中
(3)带条件的删除
// 根据 entity 条件,删除记录
int delete(@Param(Constants.WRAPPER) Wrapper wrapper);
// 根据 columnMap 条件,删除记录
int deleteByMap(@Param(Constants.COLUMN_MAP) Map columnMap);