Android Glide学习笔记
Glide是比较常用的图片加载库,因为我在项目里使用到了,所以会跟EventBus一样参考网上前辈的文章做一个学习笔记。
开源库的比较
图片加载是 Android 项目中必备的需求,而图片加载的开源库也有很多:有 UniversalImageLoader、Picasso、Fresco、Glide等。
- UniversalImageLoader是老牌的图片加载库(我在最初的两个项目里使用的都是它)。但是作者已经不再维护项目了,所以 UniversalImageLoader不推荐在项目中使用了。
- Picasso 是图片开源库,是Glide的基础。
- Glide 是基于 Picasso 的,做了大量优化与改进。Glide 默认的 Bitmap 格式是 RGB_565 格式,而 Picasso 默认的是 ARGB_8888 格式,这个内存开销要小一半。在磁盘缓存方面,Picasso 只会缓存原始尺寸的图片,而 Glide 缓存的是多种规格。最重要的一个特性是 Glide 支持加载 Gif 动态图,而 Picasso 不支持该特性。总体来说,Glide 是在 Picasso 基础之上进行的二次开发,各个方面做了不少改进,不过这也导致他的包比 Picasso 大不少。
- Fresco 是新一代的图片加载库, Android 应用程序可用的内存有限,经常会因为图片加载导致 OOM。而 Fresco就在更底层的 Native 堆处理图片。于是 Fresco 将图片放到一个特别的内存区域叫 Ashmem 区,就是属于 Native 堆,图片将不再占用 App 的内存,Java 层对此无能为力,这里是属于 C++ 的地盘,所以能大大的减少 OOM。所以此库包也比较大,底层涉及到的 C++ 领域。
- 大部分情况 Glide 都能满足需求,但是如果 App 中大量使用图片,那么用 Fresco是更好的选择。
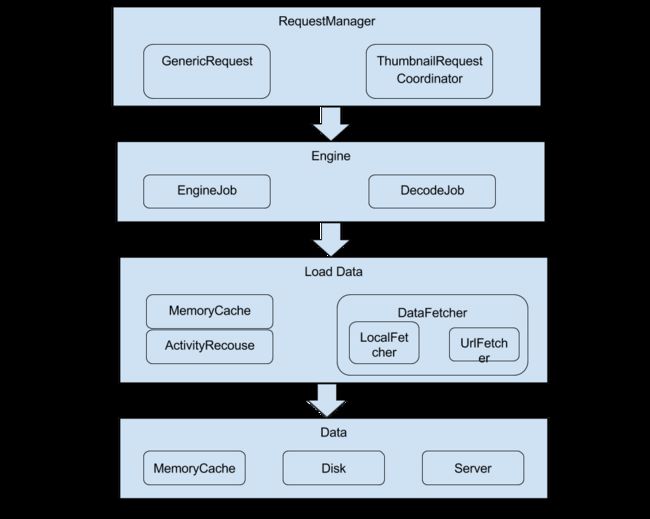
设计图
流程图
使用与简介
Glide.with(imageView.getContext())
.load(url)
.placeholder(defaultImage)
.error(failImage)
.into(imageView);如上,Glide 库使用流接口(fluent interface)。流接口(fluent Interface)是指实现一种实现面向对象的能提高代码可读性的API的方法。Glide可以从资源,文件目录和网络上加载图片资源。当加载图片时,Glide 使用3个来源:内存,磁盘和网络(从最快到最慢排序)。Glide 建造者要求最少有三个参数:
with(Context context) ;load(String imageUrl) - 这里你可以指定哪个图片应该被加载,同上它会是一个字符串的形式表示一个网络图片的 URL;into(ImageView targetImageView) 你的图片会显示到对应的 ImageView 中。
Glide.with方法
如上一段的代码可以看出,调用了Glide类的with方法(例子里使用的是第一个)。
////获取RequestManager对象,该类实现了LifeCycleListener接口,绑定Activity/Fragment生命周期,对请求进行暂停,恢复,清除操作。
public static RequestManager with(Context context) {//获取RequestManager对象
//得到RequestManagerRetriever实例,该类将RequestManager和自定义Fragment(如RequestManagerFragment,SupportRequestManagerFragment)绑定,从而实现在生命周期管理回调。这里自定义Fragment值得注意。
RequestManagerRetriever retriever = RequestManagerRetriever.get();//新建一个handler,handler = new Handler(Looper.getMainLooper(), this /* Callback */);RequestManagerRetriever实现了Handler.Callback。
return retriever.get(context);
}
public static RequestManager with(Activity activity) {
RequestManagerRetriever retriever = RequestManagerRetriever.get();
return retriever.get(activity);
}
public static RequestManager with(FragmentActivity activity) {
RequestManagerRetriever retriever = RequestManagerRetriever.get();
return retriever.get(activity);
}
@TargetApi(Build.VERSION_CODES.HONEYCOMB)
public static RequestManager with(android.app.Fragment fragment) {
RequestManagerRetriever retriever = RequestManagerRetriever.get();
return retriever.get(fragment);
}
public static RequestManager with(Fragment fragment) {
RequestManagerRetriever retriever = RequestManagerRetriever.get();
return retriever.get(fragment);
}可以看出,5个函数都是起先调用了RequestManagerRetriever retriever = RequestManagerRetriever.get()。他们最后都创建了RequestManager对象。
RequestManagerRetriever
public RequestManager get(Context context) {
if (context == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("You cannot start a load on a null Context");
} else if (Util.isOnMainThread() && !(context instanceof Application)) {//判断是不是主线程,并且context不是Application的实例
if (context instanceof FragmentActivity) {
return get((FragmentActivity) context);
} else if (context instanceof Activity) {
return get((Activity) context);
} else if (context instanceof ContextWrapper) {
return get(((ContextWrapper) context).getBaseContext());
}
}
return getApplicationManager(context);
}在这里,特别提到ContextWrapper,它与context的关系如下图:
如果我调用了Glide.with(imageView.getContext())的话,那么应该调用return get((FragmentActivity) context);步骤。
public RequestManager get(FragmentActivity activity) {
if (Util.isOnBackgroundThread()) {//判断是否在主线程
return get(activity.getApplicationContext());
} else {
assertNotDestroyed(activity);//判断界面是否已经销毁了
FragmentManager fm = activity.getSupportFragmentManager();//获取FragmentManager 对象(android.support.v4.app包带的)
return supportFragmentGet(activity, fm);//创建Fragment,RequestManager并将其绑定
}
}RequestManager/supportFragmentGet
RequestManager supportFragmentGet(Context context, FragmentManager fm) {
//获取RequestManagerFragment,主要利用Frament进行请求生命周期管理
SupportRequestManagerFragment current = getSupportRequestManagerFragment(fm);
RequestManager requestManager = current.getRequestManager();
//requestManager 为空,即首次加载初始化requestManager ,并调用setRequestManager设置到RequestManagerFragment
if (requestManager == null) {
requestManager = new RequestManager(context, current.getLifecycle(), current.getRequestManagerTreeNode());
current.setRequestManager(requestManager);//复用
}
return requestManager;
}SupportRequestManagerFragment 是一个无界面的Fragment类,起到把请求和Activity生命周期同步的作用。上面代码主要的部分就是getSupportRequestManagerFragment函数,获取到了一个fragment。
getSupportRequestManagerFragment
RequestManagerFragment getRequestManagerFragment(FragmentManager fm) {
RequestManagerFragment current = (RequestManagerFragment)fm.findFragmentByTag("com.bumptech.glide.manager");//强转,看看有没有以当前tag命名的fragment,不为空的话直接返回,为空的话需要创建。
if(current == null) {
current = (RequestManagerFragment)this.pendingRequestManagerFragments.get(fm);//pendingRequestManagerFragments是一个hashmap,创建的RequestManagerFragment 对象会存放在其中,复用。
if(current == null) {
current = new RequestManagerFragment();
this.pendingRequestManagerFragments.put(fm, current);//存放在hashmap里。
fm.beginTransaction().add(current, "com.bumptech.glide.manager").commitAllowingStateLoss();
this.handler.obtainMessage(1, fm).sendToTarget();//发送消息,同时会把hashmap中的fragment移除(代码不贴了)
}
}
return current;
}上面的代码中,创建RequestManagerFragment是比较关键的一步。
com.bumptech.glide.manager/RequestManagerFragment
public class RequestManagerFragment extends Fragment {
private final ActivityFragmentLifecycle lifecycle;
private final RequestManagerTreeNode requestManagerTreeNode;
private RequestManager requestManager;
private final HashSet childRequestManagerFragments;
private RequestManagerFragment rootRequestManagerFragment;
public RequestManagerFragment() {
this(new ActivityFragmentLifecycle());
}
@SuppressLint({"ValidFragment"})
RequestManagerFragment(ActivityFragmentLifecycle lifecycle) {
this.requestManagerTreeNode = new RequestManagerFragment.FragmentRequestManagerTreeNode();
this.childRequestManagerFragments = new HashSet();
this.lifecycle = lifecycle;
}
//中间省略一些方法
public void onStart() {
super.onStart();
this.lifecycle.onStart();//调用lifecycle相应onStart方法
}
public void onStop() {
super.onStop();
this.lifecycle.onStop();//调用lifecycle相应onStop方法
}
public void onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy();
this.lifecycle.onDestroy();//调用lifecycle相应onDestroy方法
}
} RequestManagerFragment 继承了Fragment。并且在其生命周期onStart(),onStop(),onDestory()中调用了ActivityFragmentLifecycle 中相应的方法。ActivityFragmentLifecycle实现了Lifecycle 接口,其中定义了onStart()等函数的具体实现。
经过上面这么多步骤,得到的RequestManagerFragment将作为参数创建RequestManager对象。load函数位于RequestManager类中。
com.bumptech.glide/RequestManager
RequestManager(Context context, final Lifecycle lifecycle, RequestManagerTreeNode treeNode, RequestTracker requestTracker, ConnectivityMonitorFactory factory) {
this.context = context.getApplicationContext();
this.lifecycle = lifecycle;
this.treeNode = treeNode;
this.requestTracker = requestTracker;
this.glide = Glide.get(context);//获取Glide实例,不同于一般的单例
this.optionsApplier = new RequestManager.OptionsApplier();
ConnectivityMonitor connectivityMonitor = factory.build(context, new RequestManager.RequestManagerConnectivityListener(requestTracker));//通过工厂类ConnectivityMonitorFactory的build方法获取ConnectivityMonitor (一个用于监控网络连接事件的接口)
if(Util.isOnBackgroundThread()) {
(new Handler(Looper.getMainLooper())).post(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
lifecycle.addListener(RequestManager.this);
}
});
} else {
lifecycle.addListener(this);
}
lifecycle.addListener(connectivityMonitor);
}构造函数将刚创建的fragment的lifeCycle传入,并将RequestManager这个listener添加到lifeCycle中,从而实现绑定。在RequestManager的构造方法里看到了requestTracker,该对象就是跟踪请求取消,重启,完成,失败;requestTracker在生命周期函数中都执行了。RequestManagerFragment 主要是用来连接生命周期方法,RequestManager用来实现生命周期中请求方法,而RequestManagerRetriever绑定了RequestManager。
Glide初始化
public static Glide get(Context context) {
if(glide == null) {
Class var1 = Glide.class;
synchronized(Glide.class) {
if(glide == null) {//首先这是一个基本的单例
Context applicationContext = context.getApplicationContext();//获取ApplicationContext
//解析清单文件配置的自定义GlideModule的metadata标签,返回一个GlideModule集合
List modules = (new ManifestParser(applicationContext)).parse();//parse函数见下一个模块
GlideBuilder builder = new GlideBuilder(applicationContext);
Iterator i$ = modules.iterator();
GlideModule module;
//循环集合,执行GlideModule 实现类中的方法
while(i$.hasNext()) {
module = (GlideModule)i$.next();
module.applyOptions(applicationContext, builder);
}
glide = builder.createGlide();//初始化了很多变量,如Engine对象等。
i$ = modules.iterator();
while(i$.hasNext()) {
module = (GlideModule)i$.next();
//注册组件
module.registerComponents(applicationContext, glide);
}
}
}
}
return glide;
}parse
com.bumptech.glide.module/ManifestParser
public List parse() {
ArrayList modules = new ArrayList();
try {
ApplicationInfo e = this.context.getPackageManager().getApplicationInfo(this.context.getPackageName(), 128);//128在github上的最新代码里替换为了PackageManager.GET_META_DATA,通过PackageManager获取metadata所有信息。
if(e.metaData != null) {//清单文件含有metadata
Iterator i$ = e.metaData.keySet().iterator();
//遍历metadata
while(i$.hasNext()) {
String key = (String)i$.next();
if("GlideModule".equals(e.metaData.get(key))) {找到匹配字符串“GlideModule”
modules.add(parseModule(key));
}
}
}
return modules;
} catch (NameNotFoundException var5) {
throw new RuntimeException("Unable to find metadata to parse GlideModules", var5);
}
} 上面函数中parseModule(key)返回的结果最后add在了ArrayList里。
parseModule
private static GlideModule parseModule(String className) {//通过反射获取GlideModule实例,className是类的路径
Class clazz;
try {
clazz = Class.forName(className);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException var6) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unable to find GlideModule implementation", var6);
}
Object module;
try {
module = clazz.newInstance();//反射获取对象
} catch (InstantiationException var4) {
throw new RuntimeException("Unable to instantiate GlideModule implementation for " + clazz, var4);
} catch (IllegalAccessException var5) {
throw new RuntimeException("Unable to instantiate GlideModule implementation for " + clazz, var5);
}
if(!(module instanceof GlideModule)) {
throw new RuntimeException("Expected instanceof GlideModule, but found: " + module);
} else {
return (GlideModule)module;
}
}createGlide
com.bumptech.glide/GlideBuilder.java
Glide createGlide() {
if(this.sourceService == null) {
int calculator = Math.max(1, Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors());
this.sourceService = new FifoPriorityThreadPoolExecutor(calculator);//初始化线程池
}
if(this.diskCacheService == null) {
this.diskCacheService = new FifoPriorityThreadPoolExecutor(1);
}
MemorySizeCalculator calculator1 = new MemorySizeCalculator(this.context);
if(this.bitmapPool == null) { //设置Bitmap池
if(VERSION.SDK_INT >= 11) {
int size = calculator1.getBitmapPoolSize();
this.bitmapPool = new LruBitmapPool(size);
} else {
this.bitmapPool = new BitmapPoolAdapter();
}
}
if(this.memoryCache == null) {
this.memoryCache = new LruResourceCache(calculator1.getMemoryCacheSize());
}
if(this.diskCacheFactory == null) {//内部磁盘缓存
this.diskCacheFactory = new InternalCacheDiskCacheFactory(this.context);
}
if(this.engine == null) { //初始化引擎类
this.engine = new Engine(this.memoryCache, this.diskCacheFactory, this.diskCacheService, this.sourceService);
}
if(this.decodeFormat == null) {
this.decodeFormat = DecodeFormat.DEFAULT;//默认解码格式PREFER_RGB_565
}
return new Glide(this.engine, this.memoryCache, this.bitmapPool, this.context, this.decodeFormat);
}上面的分析,主要是下面的用法准备的:
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="com.bumptech.glide.integration.volley">
<application>
<meta-data
android:name="com.bumptech.glide.integration.volley.VolleyGlideModule"
android:value="GlideModule"/>//GlideModule去寻找name也就是key
application>
manifest>关于GlideModule,我也不太懂。。。
load
RequestManager创建完毕后,我们调用了load方法。以我上面的例子来看,我传入的是string(url),也就是调用了下面的函数:
RequestManager.java
public DrawableTypeRequest load(String string) {
return (DrawableTypeRequest)this.fromString().load(string);
}
public DrawableTypeRequest fromString() {
return this.loadGeneric(String.class);
}
private DrawableTypeRequest loadGeneric(Class modelClass) {
ModelLoader streamModelLoader = Glide.buildStreamModelLoader(modelClass, this.context);
ModelLoader fileDescriptorModelLoader = Glide.buildFileDescriptorModelLoader(modelClass, this.context);
if(modelClass != null && streamModelLoader == null && fileDescriptorModelLoader == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unknown type " + modelClass + ". You must provide a Model of a type for" + " which there is a registered ModelLoader, if you are using a custom model, you must first call" + " Glide#register with a ModelLoaderFactory for your custom model class");
} else {
return (DrawableTypeRequest)this.optionsApplier.apply(new DrawableTypeRequest(modelClass, streamModelLoader, fileDescriptorModelLoader, this.context, this.glide, this.requestTracker, this.lifecycle, this.optionsApplier));
}// 创建DrawableTypeRequest,它是GenericRequestBuilder的子类
} DrawableRequestBuilder.java
public DrawableRequestBuilder load(ModelType model) {
super.load(model);//调用父类方法,如下
return this;
} DrawableRequestBuilder.java
public GenericRequestBuilder load(ModelType model) {
this.model = model;
this.isModelSet = true;
return this;//GenericRequestBuilder返回自身对象
} placeholder,error和into等函数在DrawableRequestBuilder中都定义了,但是它们最终都调用的是DrawableRequestBuilder中的函数,这里其实就是一个建造者模式了,可以链式书写代码,初始化其中的属性,并且最终调用了into函数来进行请求。
into
public Target into(ImageView view) {
Util.assertMainThread();
if(view == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("You must pass in a non null View");
} else {
if(!this.isTransformationSet && view.getScaleType() != null) {
switch(GenericRequestBuilder.SyntheticClass_1.$SwitchMap$android$widget$ImageView$ScaleType[view.getScaleType().ordinal()]) {
case 1:
this.applyCenterCrop();
break;
case 2:
case 3:
case 4:
this.applyFitCenter();
}
}
return this.into(this.glide.buildImageViewTarget(view, this.transcodeClass));//跟代码最后发现函数最终执行到了当前类的obtainRequest函数,发起了请求。
}
} 上面的函数调用到了下面的函数:
public > Y into(Y target) {
Util.assertMainThread();
if(target == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("You must pass in a non null Target");
} else if(!this.isModelSet) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("You must first set a model (try #load())");
} else {
//获取Request 对象
Request previous = target.getRequest();
if(previous != null) {//复用
previous.clear();
this.requestTracker.removeRequest(previous);//requestTracker是请求跟踪类对象,主要管理请求的发起,暂停,清除
previous.recycle();
}
Request request = this.buildRequest(target);//创建请求对象,如下
target.setRequest(request);
this.lifecycle.addListener(target);//将target加入lifecycle
this.requestTracker.runRequest(request);//执行请求
return target;
}
} buildRequest
buildRequestRecursive实则调用了buildRequestRecursive函数。
private Request buildRequestRecursive(Target target, ThumbnailRequestCoordinator parentCoordinator) {
ThumbnailRequestCoordinator coordinator;
Request fullRequest;
Request thumbnailRequest;
if(this.thumbnailRequestBuilder != null) {//如果配置了thumbnail(缩略图)请求,则构建一个ThumbnailRequestCoordinator(包含了FullRequest和ThumbnailRequest)请求,否则简单的构建一个Request
if(this.isThumbnailBuilt) {
throw new IllegalStateException("You cannot use a request as both the main request and a thumbnail, consider using clone() on the request(s) passed to thumbnail()");
} else {
if(this.thumbnailRequestBuilder.animationFactory.equals(NoAnimation.getFactory())) {
this.thumbnailRequestBuilder.animationFactory = this.animationFactory;
}
if(this.thumbnailRequestBuilder.priority == null) {
this.thumbnailRequestBuilder.priority = this.getThumbnailPriority();
}
if(Util.isValidDimensions(this.overrideWidth, this.overrideHeight) && !Util.isValidDimensions(this.thumbnailRequestBuilder.overrideWidth, this.thumbnailRequestBuilder.overrideHeight)) {
this.thumbnailRequestBuilder.override(this.overrideWidth, this.overrideHeight);
}
coordinator = new ThumbnailRequestCoordinator(parentCoordinator);
fullRequest = this.obtainRequest(target, this.sizeMultiplier.floatValue(), this.priority, coordinator);
this.isThumbnailBuilt = true;
thumbnailRequest = this.thumbnailRequestBuilder.buildRequestRecursive(target, coordinator);
this.isThumbnailBuilt = false;
coordinator.setRequests(fullRequest, thumbnailRequest);
return coordinator;
}
} else if(this.thumbSizeMultiplier != null) {
coordinator = new ThumbnailRequestCoordinator(parentCoordinator);
fullRequest = this.obtainRequest(target, this.sizeMultiplier.floatValue(), this.priority, coordinator);
thumbnailRequest = this.obtainRequest(target, this.thumbSizeMultiplier.floatValue(), this.getThumbnailPriority(), coordinator);
coordinator.setRequests(fullRequest, thumbnailRequest);
return coordinator;
} else {
return this.obtainRequest(target, this.sizeMultiplier.floatValue(), this.priority, parentCoordinator);
}
} 最终调用了obtainRequest函数。至此请求对象创建成功。
runRequest(发送请求)
public void runRequest(Request request) {
this.requests.add(request);//添加request对象到集合中,requests是一个set,Set是一个不包含重复元素的 collection,在这里是无序的。
if(!this.isPaused) {
request.begin();//如果当前状态是非暂停的,调用begin方法发送请求
} else {
this.pendingRequests.add(request);//将请求加入到挂起的请求集合,RequestTracker在RequestManager类中初始化,并且跟踪着生命周期
}
}begin函数
GenericRequest.java,通过request的实现类GenericRequest查看begin方法执行的内容。
public void begin() {
this.startTime = LogTime.getLogTime();
if(this.model == null) {/加载错误占位图设置
this.onException((Exception)null);
} else {
this.status = GenericRequest.Status.WAITING_FOR_SIZE;
//验证宽高是否合法
//发送请求
this.onSizeReady(this.overrideWidth, this.overrideHeight);
} else {
this.target.getSize(this);
}
if(!this.isComplete() && !this.isFailed() && this.canNotifyStatusChanged()) {//加载前默认占位图设置回调,应该会在 this.onSizeReady(this.overrideWidth, this.overrideHeight);前面执行完。
this.target.onLoadStarted(this.getPlaceholderDrawable());
}
if(Log.isLoggable("GenericRequest", 2)) {
this.logV("finished run method in " + LogTime.getElapsedMillis(this.startTime));
}
}
}onSizeReady
public void onSizeReady(int width, int height) {
if(Log.isLoggable("GenericRequest", 2)) {
this.logV("Got onSizeReady in " + LogTime.getElapsedMillis(this.startTime));
}
if(this.status == GenericRequest.Status.WAITING_FOR_SIZE) {
this.status = GenericRequest.Status.RUNNING;//将请求状态更新为运行状态
width = Math.round(this.sizeMultiplier * (float)width);
height = Math.round(this.sizeMultiplier * (float)height);
ModelLoader modelLoader = this.loadProvider.getModelLoader();
DataFetcher dataFetcher = modelLoader.getResourceFetcher(this.model, width, height);
if(dataFetcher == null) {
this.onException(new Exception("Failed to load model: \'" + this.model + "\'"));
} else {
ResourceTranscoder transcoder = this.loadProvider.getTranscoder();
if(Log.isLoggable("GenericRequest", 2)) {
this.logV("finished setup for calling load in " + LogTime.getElapsedMillis(this.startTime));
}
this.loadedFromMemoryCache = true;
this.loadStatus = this.engine.load(this.signature, width, height, dataFetcher, this.loadProvider, this.transformation, transcoder, this.priority, this.isMemoryCacheable, this.diskCacheStrategy, this);//进入Engine逻辑
this.loadedFromMemoryCache = this.resource != null;
if(Log.isLoggable("GenericRequest", 2)) {
this.logV("finished onSizeReady in " + LogTime.getElapsedMillis(this.startTime));
}
}
}
}Engine类封装了数据获取的重要入口方法,向request层提供如load(), release()等方法,Engine主要负责图片加载。
Engine/load方法
public Engine.LoadStatus load(Key signature, int width, int height, DataFetcher fetcher, DataLoadProvider loadProvider, Transformation transformation, ResourceTranscoder transcoder, Priority priority, boolean isMemoryCacheable, DiskCacheStrategy diskCacheStrategy, ResourceCallback cb) {
Util.assertMainThread();//判断是否在主线程
long startTime = LogTime.getLogTime();
String id = fetcher.getId();
//创建Enginekey,这是给每次加载资源的唯一标示。
EngineKey key = this.keyFactory.buildKey(id, signature, width, height, loadProvider.getCacheDecoder(), loadProvider.getSourceDecoder(), transformation, loadProvider.getEncoder(), transcoder, loadProvider.getSourceEncoder());
//从缓存加载图片, 从内存缓存中获取资源,获取成功后会放入到activeResources中
EngineResource cached = this.loadFromCache(key, isMemoryCacheable);
if(cached != null) {
// 获取数据成功,会回调onResourceReady方法。
cb.onResourceReady(cached);
if(Log.isLoggable("Engine", 2)) {
logWithTimeAndKey("Loaded resource from cache", startTime, key);
}
return null;
} else {
// 尝试从活动Resources 中获取,它表示的是当前正在使用的Resources,与内存缓存不同之处是clear缓存时不会clear它。
EngineResource active = this.loadFromActiveResources(key, isMemoryCacheable);
if(active != null) {
cb.onResourceReady(active);//回调
if(Log.isLoggable("Engine", 2)) {
logWithTimeAndKey("Loaded resource from active resources", startTime, key);
}
return null;
} else {
EngineJob current = (EngineJob)this.jobs.get(key);
if(current != null) {//判断jobs中是否已经存在任务,如果存在说明任务之前已经提交了
current.addCallback(cb);
if(Log.isLoggable("Engine", 2)) {
logWithTimeAndKey("Added to existing load", startTime, key);
}
return new Engine.LoadStatus(cb, current);
} else {//缓存没有获取到,创建EngineJob 对象
EngineJob engineJob = this.engineJobFactory.build(key, isMemoryCacheable);
DecodeJob decodeJob = new DecodeJob(key, width, height, fetcher, loadProvider, transformation, transcoder, this.diskCacheProvider, diskCacheStrategy, priority); //EngineRunnable 是任务执行阶段的入口
EngineRunnable runnable = new EngineRunnable(engineJob, decodeJob, priority);
this.jobs.put(key, engineJob);
engineJob.addCallback(cb);
// 开始提交job,线程池执行函数
engineJob.start(runnable);
if(Log.isLoggable("Engine", 2)) {
logWithTimeAndKey("Started new load", startTime, key);
}
return new Engine.LoadStatus(cb, engineJob);
}
}
}
} 先根据调用loadFromCache从内存加载,若返回值为空再次从活动的资源中加载,若再次为空查看jobs是否提交过任务,若没有提交则创建EngineRunnable,并将任务提交到engineJob中。
Transformation类负责处理资源,这里面出现BitmapPool类,达到Bitmap复用。
先从cache中寻找资源,如果找到则将其从cache中移除并放入activeResources中,否则从activeResources中寻找。cache是LruResourceCache对象,作为资源的LRU缓存;activeResources是以弱引用为值的Map,用于缓存使用中的资源。比一般内存缓存额外多一级缓存的意义在于,当内存不足时清理cache中的资源时,不会对使用中的Bitmap造成影响。
DecodeJob是整个任务的核心部分,它的流程图如下:
转自:Glide源码分析
![]()
这里主要是内存缓存。
EngineRunnable/run
EngineRunnable实现了Runnable接口。
public void run() {
if(!this.isCancelled) {
Exception exception = null;
Resource resource = null;
try {
resource = this.decode();//数据的获取,编解码
} catch (Exception var4) {
if(Log.isLoggable("EngineRunnable", 2)) {
Log.v("EngineRunnable", "Exception decoding", var4);
}
exception = var4;
}
if(this.isCancelled) {//如果当前状态是取消,则回收各种资源防止内存泄露
if(resource != null) {
resource.recycle();
}
} else {
if(resource == null) {//加载失败回调
this.onLoadFailed(exception);
} else {
this.onLoadComplete(resource);//加载成功回调
}
}
}
}
private Resource decode() throws Exception {
return this.isDecodingFromCache()?this.decodeFromCache():this.decodeFromSource();//如果图片是本地缓存里的,那么就执行decodeFromCache;否则执行decodeFromSource。
}decodeFromCache
private Resource decodeFromCache() throws Exception {
Resource result = null;
try {
result = this.decodeJob.decodeResultFromCache();//取到Resource
} catch (Exception var3) {
if(Log.isLoggable("EngineRunnable", 3)) {
Log.d("EngineRunnable", "Exception decoding result from cache: " + var3);
}
}
if(result == null) {
result = this.decodeJob.decodeSourceFromCache();//为空的话创建一个,否则直接返回Resource对象。
}
return result;
}decodeResultFromCache
DecodeJob.java
DecodeJob.java实现了Runnable接口,调度任务的核心类,整个请求的繁重工作都在这里完成:处理来自缓存或者原始的资源,应用转换动画以及transcode。
public Resource decodeResultFromCache() throws Exception {
if(!this.diskCacheStrategy.cacheResult()) {
return null;
} else {
long startTime = LogTime.getLogTime();
Resource transformed = this.loadFromCache(this.resultKey);//从DiskCache中获取资源
if(Log.isLoggable("DecodeJob", 2)) {
this.logWithTimeAndKey("Decoded transformed from cache", startTime);
}
startTime = LogTime.getLogTime();
Resource result = this.transcode(transformed);
if(Log.isLoggable("DecodeJob", 2)) {
this.logWithTimeAndKey("Transcoded transformed from cache", startTime);
}
return result;
}
} decodeResultFromCache方法从磁盘缓存中获取对应Bitmap并将其转码。
decodeSourceFromCache方法从磁盘缓存中获取对应Bitmap并将其转换。
decodeFromSource函数
另一条逻辑是执行decodeFromSource(对应decodeFromCache函数)。
public Resource decodeFromSource() throws Exception {
Resource decoded = this.decodeSource();
return this.transformEncodeAndTranscode(decoded);//编码之后通过transformEncodeAndTranscode方法进行转换处理。
} // 调用decodeJob来完成数据获取和编解码
private Resource decodeSource() throws Exception {
Resource decoded = null;
Object var5;
try {
long startTime = LogTime.getLogTime();
//数据拉取
Object data = this.fetcher.loadData(this.priority);//获取数据
if(Log.isLoggable("DecodeJob", 2)) {
this.logWithTimeAndKey("Fetched data", startTime);
}
if(!this.isCancelled) {
decoded = this.decodeFromSourceData(data);//编码
return decoded;
}
var5 = null;
} finally {
this.fetcher.cleanup();
}
return (Resource)var5;
} 最后调用transformEncodeAndTranscode函数保存DiskLruCache函数。后半部分的源码我自己看的也是晕乎乎的,如果有更好的方法,麻烦告知一下~
总结
Glide优点在于其生命周期的管理,资源类型的支持多,内存也较为友好。Glide的架构扩展性高,但是难以理解,各种接口、泛型,需要一定的学习才能熟练运用(源码对于我来说难度很高~)。它支持对处理后的资源Disk缓存;能通过BitmapPool对Bitmap复用,还能使用activityResources缓存正在使用的resource,对于BitmapPool饱和移除的Bitmap直接调用recycle加速内存回收。本文主要是个人学习做的一个笔记,中间借鉴了详谈高大上的图片加载框架Glide -源码篇这个前辈的文章。主要是走了一遍流程,感觉Glide的源码相对于开源的一些UI控件,还是更为复杂,所以很多步骤没有写完,并不是很完整。里面夹杂了一些自己的理解,如果有错误,希望您能指出,共同进步~
Glide - 开始!
ANDROID开源项目推荐之「图片加载到底哪家强」
Glide - 回调:SimpleTarget 和 ViewTarget 用于自定义视图类
Glide源码分析
详谈高大上的图片加载框架Glide -源码篇
Glide 源码解析
Glide源码分析