Volley源码解析 Request请求
Volley源码解析<三> Request请求
@[Volley, 请求接口, Request]
声明:转载请注明出处,知识有限,如有错误,请多多交流指正!
- Volley源码解析三 Request请求
-
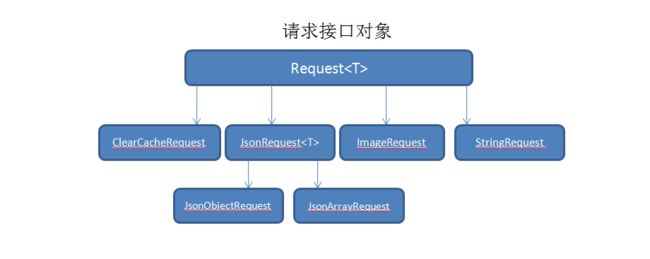
- Request请求接口结构
- 请求对象类解析
-
Request请求接口结构
- Request:用来构造一个请求对象
- ClearCacheRequest: 一个模拟的用来清理缓存的请求
- JsonRequest
:发送和接收JSON相关的接口 - JsonArrayRequest :发送和接收JSON数组
- JsonObjectRequest:发送和接收JSON对象
- ImageRequest :发送和接收Image
- StringRequest :响应的主体为字符串
请求对象类解析
- Request类包含
Method接口,用来支持 8 种 Http 请求方式 GET, POST, PUT, DELETE, HEAD, OPTIONS, TRACE, PATCH
public interface Method {
int DEPRECATED_GET_OR_POST = -1;
int GET = 0;
int POST = 1;
int PUT = 2;
int DELETE = 3;
int HEAD = 4;
int OPTIONS = 5;
int TRACE = 6;
int PATCH = 7;
}- Request类包含
Priority枚举,用来设置优先级,主要有4种
public enum Priority {
LOW,
NORMAL,
HIGH,
IMMEDIATE
}- 子类实现Request必须要实现2个抽象方法
abstract protected Response parseNetworkResponse(NetworkResponse response);
abstract protected void deliverResponse(T response); parseNetworkResponse:解析原始的响应信息,并返回一个特定的响应类型即Response中的T类型结果deliverResponse:分发响应解析的类容给调用监听者
常用方法
public Map
@Override
public int compareTo(Request other) {
Priority left = this.getPriority();
Priority right = other.getPriority();
// 优先级越高,在请求队列中排得越前,相同优先级的序号越低,排得越前。
// High-priority requests are "lesser" so they are sorted to the front.
// Equal priorities are sorted by sequence number to provide FIFO ordering.
return left == right ?
this.mSequence - other.mSequence :
right.ordinal() - left.ordinal();
} private Integer
mSequence: 请求的序号,相同优先级的请求在请求队列中根据序号来进行排序,序号低的排在队列前面。
- StringRequest:响应字符串数据,主要是实现
parseNetworkResponse方法
@Override
protected Response parseNetworkResponse(NetworkResponse response) {
String parsed;
try {
parsed = new String(response.data, HttpHeaderParser.parseCharset(response.headers));
} catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e) {
parsed = new String(response.data);
}
return Response.success(parsed, HttpHeaderParser.parseCacheHeaders(response));
} HttpHeaderParser.parseCharset(response.headers): 主要是获取编码格式如utf-8,默认编码是ISO-8859-1
String parsed:将data封装到String
Response.success:将数据封装到Response中返回
- JsonObjectRequest:JSONObject数据
@Override
protected Response parseNetworkResponse(NetworkResponse response) {
try {
String jsonString = new String(response.data, HttpHeaderParser.parseCharset(response.headers, PROTOCOL_CHARSET));
return Response.success(new JSONObject(jsonString), HttpHeaderParser.parseCacheHeaders(response));
} catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e) {
return Response.error(new ParseError(e));
} catch (JSONException je) {
return Response.error(new ParseError(je));
}
} 先将数据转换成String,再封装成JSONObject,返回数据
JsonArrayRequest:JSONArray数据,和JsonObjectRequest原理一样,只是封装成JSONArray数据
ImageRequest:请求一个位图Bitmap数据
构造方法
public ImageRequest(String url, Response.Listener listener, int maxWidth, int maxHeight,ScaleType scaleType, Config decodeConfig, Response.ErrorListener errorListener) 其中
- url:图片的URL地址
- listener:图片请求成功的回调
- maxWidth:用于指定允许图片最大的宽度
- maxHeight:用于指定允许图片最大的高度
- scaleType:就是ImageViews ScaleType,设置缩放方式
- decodeConfig:指定图片的颜色属性,Bitmap.Config其中ARGB_8888可以展示最好的颜色属性,每个图片像素占据4个字节的大小,而RGB_565则表示每个图片像素占据2个字节大小
- errorListener:图片请求失败的回调
说明:maxWidth和maxHeight,如果指定的网络图片的宽度或高度大于这里的最大值,则会对图片进行压缩,
指定成0的话就表示不管图片有多大,都不会进行压缩
请求的优先级最低
@Override
public Priority getPriority() {
return Priority.LOW;
}如何将数据转成Bitmap的呢?先看parseNetworkResponse方法
@Override
protected Response parseNetworkResponse(NetworkResponse response) {
// Serialize all decode on a global lock to reduce concurrent heap usage.
synchronized (sDecodeLock) {
try {
return doParse(response);
} catch (OutOfMemoryError e) {
VolleyLog.e("Caught OOM for %d byte image, url=%s", response.data.length, getUrl());
return Response.error(new ParseError(e));
}
}
} synchronized (sDecodeLock): 一次只能对一个图片进行编码,加载,避免OOM的发生
主要是调用了doParse(response)方法,对图片进行处理
private Response doParse(NetworkResponse response) {
byte[] data = response.data;
BitmapFactory.Options decodeOptions = new BitmapFactory.Options();
Bitmap bitmap = null;
// 如果mMaxWidth和mMaxHeight都为0,则按照bitmap实际大小进行decode
if (mMaxWidth == 0 && mMaxHeight == 0) {
decodeOptions.inPreferredConfig = mDecodeConfig;
bitmap = BitmapFactory.decodeByteArray(data, 0, data.length, decodeOptions);
} else {
// 如果其中一个不为0,则按照原始位图的宽高比进行解码,如果都不为0, 则将解码成最适合width x height区域并且保持原始位图宽高比的位图。
// If we have to resize this image, first get the natural bounds.
// 1. 先decode一次,求出图片的实际大小
decodeOptions.inJustDecodeBounds = true;
BitmapFactory.decodeByteArray(data, 0, data.length, decodeOptions);
int actualWidth = decodeOptions.outWidth;
int actualHeight = decodeOptions.outHeight;
// Then compute the dimensions we would ideally like to decode to.
// 2. 求出根据给定的参数的目标宽度和长度
int desiredWidth = getResizedDimension(mMaxWidth, mMaxHeight, actualWidth, actualHeight, mScaleType); //宽度缩放
int desiredHeight = getResizedDimension(mMaxHeight, mMaxWidth, actualHeight, actualWidth, mScaleType); //高度缩放
// Decode to the nearest power of two scaling factor.
decodeOptions.inJustDecodeBounds = false;
// TODO(ficus): Do we need this or is it okay since API 8 doesn't support it?
// decodeOptions.inPreferQualityOverSpeed = PREFER_QUALITY_OVER_SPEED;
// 3. 根据实际大小和所需大小去找到一个最合适的大小
decodeOptions.inSampleSize = findBestSampleSize(actualWidth, actualHeight, desiredWidth, desiredHeight);
Bitmap tempBitmap = BitmapFactory.decodeByteArray(data, 0, data.length, decodeOptions);
// If necessary, scale down to the maximal acceptable size.
// 如果通过上述缩放后图片的大小仍然比所需大小要大,那么按照所需大小进一步进行缩放
if (tempBitmap != null && (tempBitmap.getWidth() > desiredWidth || tempBitmap.getHeight() > desiredHeight)) {
bitmap = Bitmap.createScaledBitmap(tempBitmap, desiredWidth, desiredHeight, true);
tempBitmap.recycle();
} else {
bitmap = tempBitmap;
}
}
if (bitmap == null) {
return Response.error(new ParseError(response));
} else {
// 最后将结果包装成Response返回给Delivery
return Response.success(bitmap, HttpHeaderParser.parseCacheHeaders(response));
}
}