基于FPGA的HDMI输出接口设计
基于FPGA的HDMI输出接口设计
- HDMI接口简述
- HDMI协议简述
- HDMI接口设计
- HDMI代码
- 总结
HDMI接口简述
HDMI接口是现在特别常用的音视频接口,另一个常用的视频流接口是VGA接口,他们主要的区别如下:
HDMI接口:是数字信号接口,可传输音频和视频,硬件接口较小
VGA接口:是模拟信号接口,只可传输视频流数据,硬件接口较大
现在的电脑一般都带有HDMI接口,其中HDMI接口也分为三种大小,但是他们三者之间的协议是完全相同的,所以只需要购买相应的连接线即可。而且HDMI与VGA之间也有相互转换的转接线,通过这种转接线也可实现两者协议的相互转换。通过本次实验我们也可以发现,HDMI接口就是在VGA接口的基础上发展而来的,至于HDMI接口为什么可以做到那么小,主要是数据与VGA不同,是串行传输的。
HDMI的实现方法有两种,一种是使用HDMI芯片,另一种因为HDMI协议本身就是数字协议,所以我们来使用IO模拟,本次实验使用的是第二种方法。
项目描述,本次实验是通过HDMI在显示屏上显示三个彩条,本次的实验也是在VGA协议的基础上改来的。
软件环境:vivado2019.1 软件
硬件环境:米联客MA7035(100T)开发板
HDMI协议简述
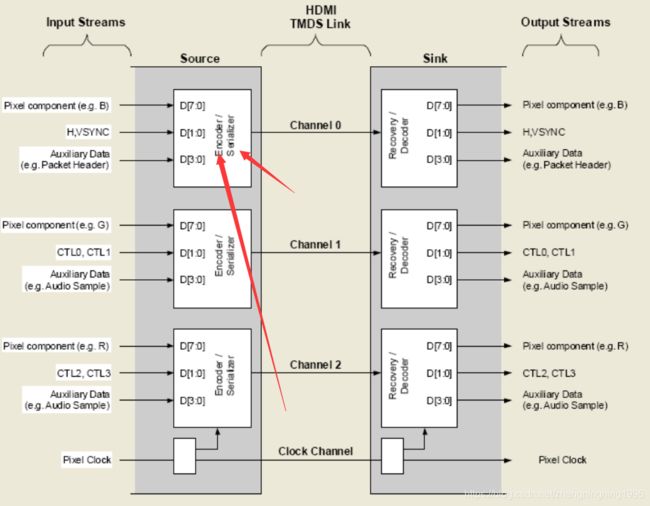
一个 HDMI 连接包括三个 TMDS 数据通道,一个 TMDS 时钟通道。 TMDS 时钟通道以某种定常的速率运行,该速率和视频的像素率成比例。在每个 TMDS 时钟通道周期中,三个 TMDS 数据通道每个都发送 10 比特数据。这个 10 位的字被编码,采用某种不同的编码技术。输入到信源端的输入流,包含视频像素,数据包,和控制数据。数据包包括音频数据和辅助以及相关的纠错码。
对上面进一步解释得,HDMI一共存在三条数据通道和一条时钟通道,上面传来的数据通过编码与串行化传输到外面去。其中channel0是连接到blue数据,它的两个控制端是连接场同步信号和行同步信号,其余两个通道分别连接green与red信号,通道的控制端连接音频信号,一般我们设置成0即可。
HDMI接口设计
这里给出HDMI输出接口得设计框图:
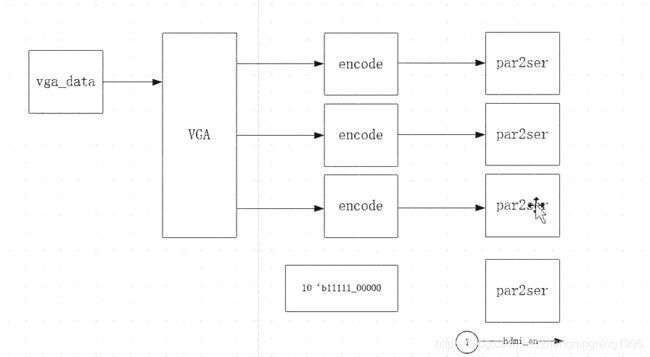
从上面得图形中我们也可以发现,HDMI设计主要包括三个模块,VGA模块,encode模块,par2ser模块,关于par2ser模块我们上一篇文章已经进行了讲解,encode模块也就是著名得8bit转10bit编码(xilinx官网下载即可)。其中上面最后一个par2ser模块是时钟模块,输入得数据10‘b11111_00000经过串行转换之后正好作为HDMI得随路时钟,这里这样做而不是直接输出一个时钟得原因是为了让时钟和数据对齐。
HDMI代码
经过上面得框图与上一篇论文关于串行化的设计,相信大家对HDMI协议已经有了初步的了解,接下来我们将给出该项目的代码,因为在家中没有硬件实验条件,所以代码没有下板验证,代码中有可能存在一些小错误无法发现。
hdmi_top模块:
`timescale 1ns / 1ps
// *********************************************************************************
// Project Name : OSXXXX
// Author : zhangningning
// Email : [email protected]
// Website :
// Module Name : hdmi_top.v
// Create Time : 2020-02-24 09:18:16
// Editor : sublime text3, tab size (4)
// CopyRight(c) : All Rights Reserved
//
// *********************************************************************************
// Modification History:
// Date By Version Change Description
// -----------------------------------------------------------------------
// XXXX zhangningning 1.0 Original
//
// *********************************************************************************
module hdmi_top(
//System Interfaces
input sclk ,
input rst_n ,
//HDMI Interfaces
output wire [ 2:0] hdmi_data_p ,
output wire [ 2:0] hdmi_data_n ,
output wire hdmi_clk_p ,
output wire hdmi_clk_n ,
output wire hdmi_oen
);
//========================================================================================\
//**************Define Parameter and Internal Signals**********************************
//========================================================================================/
wire clk_65mhz ;
wire clk_325mhz ;
wire locked ;
wire hsync ;
wire vsync ;
wire [ 7:0] vga_data_r ;
wire [ 7:0] vga_data_g ;
wire [ 7:0] vga_data_b ;
wire vga_de ;
wire [ 9:0] vga_data_r_10bit;
wire [ 9:0] vga_data_g_10bit;
wire [ 9:0] vga_data_b_10bit;
//========================================================================================\
//************** Main Code **********************************
//========================================================================================/
assign hdmi_oen = 1'b1;
clk_wiz_0 clk_wiz_0_inst(
// Clock out ports
.clk_out1 (clk_65mhz ), // output clk_out1
.clk_out2 (clk_325mhz ), // output clk_out2
// Status and control signals
.resetn (rst_n ), // input resetn
.locked (locked ), // output locked
// Clock in ports
.clk_in1 (sclk )
);
vga_drive vga_drive_inst(
.vga_clk (clk_65mhz ),
.rst_n (~locked ),
.hsync (hsync ),
.vsync (vsync ),
.vga_data_r (vga_data_r ),
.vga_data_g (vga_data_g ),
.vga_data_b (vga_data_b ),
.vga_de (vga_de )
);
encode encode_blue(
.clkin (clk_65mhz ), // pixel clock input
.rstin (~locked ), // async. reset input (active high)
.din (vga_data_b ), // data inputs: expect registered
.c0 (hsync ), // c0 input
.c1 (vsync ), // c1 input
.de (vga_de ), // de input
.dout (vga_data_b_10bit ) // data outputs
);
encode encode_green(
.clkin (clk_65mhz ), // pixel clock input
.rstin (~locked ), // async. reset input (active high)
.din (vga_data_g ), // data inputs: expect registered
.c0 (1'b0 ), // c0 input
.c1 (1'b0 ), // c1 input
.de (vga_de ), // de input
.dout (vga_data_g_10bit ) // data outputs
);
encode encode_red(
.clkin (clk_65mhz ), // pixel clock input
.rstin (~locked ), // async. reset input (active high)
.din (vga_data_r ), // data inputs: expect registered
.c0 (1'b0 ), // c0 input
.c1 (1'b0 ), // c1 input
.de (vga_de ), // de input
.dout (vga_data_r_10bit ) // data outputs
);
par2ser par2ser_blue(
.clk_1x (clk_65mhz ),
.clk_5x (clk_325mhz ),
.rst_n (locked ),
.par_data (vga_data_b_10bit ),
.ser_data_p (hdmi_data_p[0] ),
.ser_data_n (hdmi_data_n[0] )
);
par2ser par2ser_green(
.clk_1x (clk_65mhz ),
.clk_5x (clk_325mhz ),
.rst_n (locked ),
.par_data (vga_data_g_10bit ),
.ser_data_p (hdmi_data_p[1] ),
.ser_data_n (hdmi_data_n[1] )
);
par2ser par2ser_red(
.clk_1x (clk_65mhz ),
.clk_5x (clk_325mhz ),
.rst_n (locked ),
.par_data (vga_data_r_10bit ),
.ser_data_p (hdmi_data_p[2] ),
.ser_data_n (hdmi_data_n[2] )
);
par2ser par2ser_clk(
.clk_1x (clk_65mhz ),
.clk_5x (clk_325mhz ),
.rst_n (locked ),
.par_data (10'b11111_00000 ),
.ser_data_p (hdmi_clk_p ),
.ser_data_n (hdmi_clk_n )
);
endmodule
encode模块:
//
//
// Xilinx, Inc. 2008 www.xilinx.com
//
//
//
// File name : encode.v
//
// Description : TMDS encoder
//
// Date - revision : Jan. 2008 - v 1.0
//
// Author : Bob Feng
//
// Disclaimer: LIMITED WARRANTY AND DISCLAMER. These designs are
// provided to you "as is". Xilinx and its licensors make and you
// receive no warranties or conditions, express, implied,
// statutory or otherwise, and Xilinx specifically disclaims any
// implied warranties of merchantability, non-infringement,or
// fitness for a particular purpose. Xilinx does not warrant that
// the functions contained in these designs will meet your
// requirements, or that the operation of these designs will be
// uninterrupted or error free, or that defects in the Designs
// will be corrected. Furthermore, Xilinx does not warrantor
// make any representations regarding use or the results of the
// use of the designs in terms of correctness, accuracy,
// reliability, or otherwise.
//
// LIMITATION OF LIABILITY. In no event will Xilinx or its
// licensors be liable for any loss of data, lost profits,cost
// or procurement of substitute goods or services, or for any
// special, incidental, consequential, or indirect damages
// arising from the use or operation of the designs or
// accompanying documentation, however caused and on any theory
// of liability. This limitation will apply even if Xilinx
// has been advised of the possibility of such damage. This
// limitation shall apply not-withstanding the failure of the
// essential purpose of any limited remedies herein.
//
// Copyright © 2006 Xilinx, Inc.
// All rights reserved
//
//
`timescale 1 ps / 1ps
module encode (
input clkin, // pixel clock input
input rstin, // async. reset input (active high)
input [7:0] din, // data inputs: expect registered
input c0, // c0 input
input c1, // c1 input
input de, // de input
output reg [9:0] dout // data outputs
);
// Counting number of 1s and 0s for each incoming pixel
// component. Pipe line the result.
// Register Data Input so it matches the pipe lined adder
// output
reg [3:0] n1d; //number of 1s in din
reg [7:0] din_q;
always @ (posedge clkin) begin
n1d <= din[0] + din[1] + din[2] + din[3] + din[4] + din[5] + din[6] + din[7];
din_q <= din;
end
///
// Stage 1: 8 bit -> 9 bit
// Refer to DVI 1.0 Specification, page 29, Figure 3-5
///
wire decision1;
assign decision1 = (n1d > 4'h4) | ((n1d == 4'h4) & (din_q[0] == 1'b0));
/*
reg [8:0] q_m;
always @ (posedge clkin) begin
q_m[0] <=#1 din_q[0];
q_m[1] <=#1 (decision1) ? (q_m[0] ^~ din_q[1]) : (q_m[0] ^ din_q[1]);
q_m[2] <=#1 (decision1) ? (q_m[1] ^~ din_q[2]) : (q_m[1] ^ din_q[2]);
q_m[3] <=#1 (decision1) ? (q_m[2] ^~ din_q[3]) : (q_m[2] ^ din_q[3]);
q_m[4] <=#1 (decision1) ? (q_m[3] ^~ din_q[4]) : (q_m[3] ^ din_q[4]);
q_m[5] <=#1 (decision1) ? (q_m[4] ^~ din_q[5]) : (q_m[4] ^ din_q[5]);
q_m[6] <=#1 (decision1) ? (q_m[5] ^~ din_q[6]) : (q_m[5] ^ din_q[6]);
q_m[7] <=#1 (decision1) ? (q_m[6] ^~ din_q[7]) : (q_m[6] ^ din_q[7]);
q_m[8] <=#1 (decision1) ? 1'b0 : 1'b1;
end
*/
wire [8:0] q_m;
assign q_m[0] = din_q[0];
assign q_m[1] = (decision1) ? (q_m[0] ^~ din_q[1]) : (q_m[0] ^ din_q[1]);
assign q_m[2] = (decision1) ? (q_m[1] ^~ din_q[2]) : (q_m[1] ^ din_q[2]);
assign q_m[3] = (decision1) ? (q_m[2] ^~ din_q[3]) : (q_m[2] ^ din_q[3]);
assign q_m[4] = (decision1) ? (q_m[3] ^~ din_q[4]) : (q_m[3] ^ din_q[4]);
assign q_m[5] = (decision1) ? (q_m[4] ^~ din_q[5]) : (q_m[4] ^ din_q[5]);
assign q_m[6] = (decision1) ? (q_m[5] ^~ din_q[6]) : (q_m[5] ^ din_q[6]);
assign q_m[7] = (decision1) ? (q_m[6] ^~ din_q[7]) : (q_m[6] ^ din_q[7]);
assign q_m[8] = (decision1) ? 1'b0 : 1'b1;
/
// Stage 2: 9 bit -> 10 bit
// Refer to DVI 1.0 Specification, page 29, Figure 3-5
/
reg [3:0] n1q_m, n0q_m; // number of 1s and 0s for q_m
always @ (posedge clkin) begin
n1q_m <= q_m[0] + q_m[1] + q_m[2] + q_m[3] + q_m[4] + q_m[5] + q_m[6] + q_m[7];
n0q_m <= 4'h8 - (q_m[0] + q_m[1] + q_m[2] + q_m[3] + q_m[4] + q_m[5] + q_m[6] + q_m[7]);
end
parameter CTRLTOKEN0 = 10'b1101010100;
parameter CTRLTOKEN1 = 10'b0010101011;
parameter CTRLTOKEN2 = 10'b0101010100;
parameter CTRLTOKEN3 = 10'b1010101011;
reg [4:0] cnt; //disparity counter, MSB is the sign bit
wire decision2, decision3;
assign decision2 = (cnt == 5'h0) | (n1q_m == n0q_m);
/
// [(cnt > 0) and (N1q_m > N0q_m)] or [(cnt < 0) and (N0q_m > N1q_m)]
/
assign decision3 = (~cnt[4] & (n1q_m > n0q_m)) | (cnt[4] & (n0q_m > n1q_m));
// pipe line alignment
reg de_q, de_reg;
reg c0_q, c1_q;
reg c0_reg, c1_reg;
reg [8:0] q_m_reg;
always @ (posedge clkin) begin
de_q <= de;
de_reg <= de_q;
c0_q <= c0;
c0_reg <= c0_q;
c1_q <= c1;
c1_reg <= c1_q;
q_m_reg <= q_m;
end
///
// 10-bit out
// disparity counter
///
always @ (posedge clkin or posedge rstin) begin
if(rstin) begin
dout <= 10'h0;
cnt <= 5'h0;
end else begin
if (de_reg) begin
if(decision2) begin
dout[9] <= ~q_m_reg[8];
dout[8] <= q_m_reg[8];
dout[7:0] <= (q_m_reg[8]) ? q_m_reg[7:0] : ~q_m_reg[7:0];
cnt <=#1 (~q_m_reg[8]) ? (cnt + n0q_m - n1q_m) : (cnt + n1q_m - n0q_m);
end else begin
if(decision3) begin
dout[9] <= 1'b1;
dout[8] <= q_m_reg[8];
dout[7:0] <= ~q_m_reg[7:0];
cnt <=#1 cnt + {q_m_reg[8], 1'b0} + (n0q_m - n1q_m);
end else begin
dout[9] <= 1'b0;
dout[8] <= q_m_reg[8];
dout[7:0] <= q_m_reg[7:0];
cnt <= cnt - {~q_m_reg[8], 1'b0} + (n1q_m - n0q_m);
end
end
end else begin
case ({c1_reg, c0_reg})
2'b00: dout <= CTRLTOKEN0;
2'b01: dout <= CTRLTOKEN1;
2'b10: dout <= CTRLTOKEN2;
default: dout <= CTRLTOKEN3;
endcase
cnt <= 5'h0;
end
end
end
endmodule
par2ser模块:
`timescale 1ns / 1ps
// *********************************************************************************
// Project Name : OSXXXX
// Author : zhangningning
// Email : [email protected]
// Website :
// Module Name : par2ser.v
// Create Time : 2020-02-23 14:20:43
// Editor : sublime text3, tab size (4)
// CopyRight(c) : All Rights Reserved
//
// *********************************************************************************
// Modification History:
// Date By Version Change Description
// -----------------------------------------------------------------------
// XXXX zhangningning 1.0 Original
//
// *********************************************************************************
module par2ser(
input clk_1x ,
input clk_5x ,
input rst_n ,
input [ 9:0] par_data ,
output wire ser_data_p ,
output wire ser_data_n
);
//========================================================================================\
//**************Define Parameter and Internal Signals**********************************
//========================================================================================/
wire shiftout1 ;
wire shiftout2 ;
wire ser_data ;
//========================================================================================\
//************** Main Code **********************************
//========================================================================================/
OBUFDS #(
.IOSTANDARD ("DEFAULT" ), // Specify the output I/O standard
.SLEW ("SLOW" ) // Specify the output slew rate
) OBUFDS_inst (
.O (ser_data_p ), // Diff_p output (connect directly to top-level port)
.OB (ser_data_n ), // Diff_n output (connect directly to top-level port)
.I (ser_data ) // Buffer input
);
OSERDESE2 #(
.DATA_RATE_OQ ("DDR" ), // DDR, SDR
.DATA_RATE_TQ ("DDR" ), // DDR, BUF, SDR
.DATA_WIDTH (10 ), // Parallel data width (2-8,10,14)
.INIT_OQ (1'b0 ), // Initial value of OQ output (1'b0,1'b1)
.INIT_TQ (1'b0 ), // Initial value of TQ output (1'b0,1'b1)
.SERDES_MODE ("MASTER" ), // MASTER, SLAVE
.SRVAL_OQ (1'b0 ), // OQ output value when SR is used (1'b0,1'b1)
.SRVAL_TQ (1'b0 ), // TQ output value when SR is used (1'b0,1'b1)
.TBYTE_CTL ("FALSE" ), // Enable tristate byte operation (FALSE, TRUE)
.TBYTE_SRC ("FALSE" ), // Tristate byte source (FALSE, TRUE)
.TRISTATE_WIDTH (1 ) // 3-state converter width (1,4)
) OSERDESE2_inst_master (
.OFB ( ), // 1-bit output: Feedback path for data
.OQ (ser_data ), // 1-bit output: Data path output
// SHIFTOUT1 / SHIFTOUT2: 1-bit (each) output: Data output expansion (1-bit each)
.SHIFTOUT1 ( ),
.SHIFTOUT2 ( ),
.TBYTEOUT ( ), // 1-bit output: Byte group tristate
.TFB ( ), // 1-bit output: 3-state control
.TQ ( ), // 1-bit output: 3-state control
.CLK (clk_5x ), // 1-bit input: High speed clock
.CLKDIV (clk_1x ), // 1-bit input: Divided clock
// D1 - D8: 1-bit (each) input: Parallel data inputs (1-bit each)
.D1 (par_data[0] ),
.D2 (par_data[1] ),
.D3 (par_data[2] ),
.D4 (par_data[3] ),
.D5 (par_data[4] ),
.D6 (par_data[5] ),
.D7 (par_data[6] ),
.D8 (par_data[7] ),
.OCE (1'b1 ), // 1-bit input: Output data clock enable
.RST (~rst_n ), // 1-bit input: Reset
// SHIFTIN1 / SHIFTIN2: 1-bit (each) input: Data input expansion (1-bit each)
.SHIFTIN1 (shiftout1 ),
.SHIFTIN2 (shiftout2 ),
// T1 - T4: 1-bit (each) input: Parallel 3-state inputs
.T1 (1'b0 ),
.T2 (1'b0 ),
.T3 (1'b0 ),
.T4 (1'b0 ),
.TBYTEIN (1'b0 ), // 1-bit input: Byte group tristate
.TCE (1'b0 ) // 1-bit input: 3-state clock enable
);
// End of OSERDESE2_inst instantiation
OSERDESE2 #(
.DATA_RATE_OQ ("DDR" ), // DDR, SDR
.DATA_RATE_TQ ("DDR" ), // DDR, BUF, SDR
.DATA_WIDTH (10 ), // Parallel data width (2-8,10,14)
.INIT_OQ (1'b0 ), // Initial value of OQ output (1'b0,1'b1)
.INIT_TQ (1'b0 ), // Initial value of TQ output (1'b0,1'b1)
.SERDES_MODE ("SLAVE" ), // MASTER, SLAVE
.SRVAL_OQ (1'b0 ), // OQ output value when SR is used (1'b0,1'b1)
.SRVAL_TQ (1'b0 ), // TQ output value when SR is used (1'b0,1'b1)
.TBYTE_CTL ("FALSE" ), // Enable tristate byte operation (FALSE, TRUE)
.TBYTE_SRC ("FALSE" ), // Tristate byte source (FALSE, TRUE)
.TRISTATE_WIDTH (1 ) // 3-state converter width (1,4)
) OSERDESE2_inst_slave (
.OFB ( ), // 1-bit output: Feedback path for data
.OQ ( ), // 1-bit output: Data path output
// SHIFTOUT1 / SHIFTOUT2: 1-bit (each) output: Data output expansion (1-bit each)
.SHIFTOUT1 (shiftout1 ),
.SHIFTOUT2 (shiftout2 ),
.TBYTEOUT ( ), // 1-bit output: Byte group tristate
.TFB ( ), // 1-bit output: 3-state control
.TQ ( ), // 1-bit output: 3-state control
.CLK (clk_5x ), // 1-bit input: High speed clock
.CLKDIV (clk_1x ), // 1-bit input: Divided clock
// D1 - D8: 1-bit (each) input: Parallel data inputs (1-bit each)
.D1 ( ),
.D2 ( ),
.D3 (par_data[8] ),
.D4 (par_data[9] ),
.D5 ( ),
.D6 ( ),
.D7 ( ),
.D8 ( ),
.OCE (1'b1 ), // 1-bit input: Output data clock enable
.RST (~rst_n ), // 1-bit input: Reset
// SHIFTIN1 / SHIFTIN2: 1-bit (each) input: Data input expansion (1-bit each)
.SHIFTIN1 ( ),
.SHIFTIN2 ( ),
// T1 - T4: 1-bit (each) input: Parallel 3-state inputs
.T1 (1'b0 ),
.T2 (1'b0 ),
.T3 (1'b0 ),
.T4 (1'b0 ),
.TBYTEIN (1'b0 ), // 1-bit input: Byte group tristate
.TCE (1'b0 ) // 1-bit input: 3-state clock enable
);
endmodule
上面便是HDMI的设计模块,相信同学们从上面的代码结合程序框图可以学会HDMI的接口设计。
总结
创作不易,认为文章有帮助的同学们可以关注点赞支持。(工程也都在群中)对文章有什么看法或者需要更近一步交流的同学,可以加入下面的群:
![]()